A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed. In some cases, this operation is complemented by removal of the ovaries and cervix. Indications for hysterectomy vary, most often for cancer.
Our expert in this field:
Otkhozoria Marika Davidovna
Gynecologist, doctor of the highest qualification category, candidate of medical sciences, gynecologist, endocrinologist, reproductive specialist
Call the doctor
Removing the uterus is a major surgical procedure. The recovery period after such an operation is quite long, but currently there are minimally invasive techniques that help shorten it and reduce the risk of complications.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic employs highly qualified gynecological surgeons. They perform hysterectomies and other gynecological procedures in an operating room equipped with the latest equipment. Our doctors are fluent in modern surgical techniques, which ensure minimal surgical trauma and the fastest possible recovery.
Types and methods of hysterectomy
Surgeons use different techniques to remove the body of the uterus and nearby organs of the reproductive system:
- Abdominal.
- Vaginal.
- Laparoscopic.
- Combined.
Abdominal access method
The technique is outdated, but is still used by many hospitals. Its disadvantages are:
- severe trauma;
- long stay in hospital;
- long-term rehabilitation;
- large blood loss;
- cosmetic defects on the body;
- adhesions often form;
- the patient experiences severe pain;
- there are high risks of infection, etc.
Vaginal removal
This technique is often used during planned hysterectomy. Its advantages include:
- low morbidity;
- minimal blood loss;
- fast rehabilitation;
- absence of cosmetic defects;
- rapid return to normal lifestyle.
Laparoscopic access
Today, this technique is most often used by doctors during gynecological operations, in particular, removal of the uterus. Its advantages are:
- low morbidity;
- visual monitoring of the progress of the operation;
- dissection of adhesions;
- short rehabilitation period.
Attention! When performing laparoscopy, an inexperienced surgeon can injure neighboring organs. It is not used in patients with cancer.
Combined method or assisted vaginal hysterectomy
The technique involves the simultaneous use of laparoscopic and vaginal techniques. Operation using this method is indicated for patients with the following abnormal conditions:
- fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- adhesions;
- pathologies in the ovaries, fallopian tubes;
- previously performed operations on the organs of the peritoneum and pelvis.
Important! This method is used by surgeons when operating on nulliparous patients or women whose anatomical features make it difficult to reduce the uterus.
How is a hysterectomy performed?
How the hysterectomy operation goes is of interest to all patients, without exception. To dispel doubts and clarify any questions that have arisen, you should communicate with the surgeon on the eve of the intervention.
After the woman has been transported to the operating room, she is placed on the operating table and her limbs are fixed.
- In the case of vaginal hysterectomy, the patient's legs are bent at the knees and hip joints (as on a gynecological chair) and spread apart.
- During laparotomy or laparoscopic access, the anterior abdominal wall is treated with antiseptic solutions, while the patient is under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia.
A layer-by-layer incision is made in the abdominal wall, then the situation of the organs in the pelvis is assessed (the size of the uterus, the location of nodes, the condition of the appendages; if a malignant process is suspected, the periuterine tissue and neighboring organs are examined for metastases).
The final decision on the extent of the operation is made by surgeons after opening the abdomen. The uterus and/or appendages are cut off, hemostasis is performed and the abdominal wall is sutured in layers. If necessary, the abdominal cavity is drained (risk of bleeding, peritonitis and other circumstances). If hysterectomy was planned in advance, then on the operating table the vagina is sanitized with antiseptic solutions and tamponed with a sterile napkin.
During laparoscopic removal of the uterus, after treating the anterior abdominal wall with antiseptics, 3 (on average) small incisions, 1.5–2 cm long, are made in it. Through one, a laparoscope with a microvideo camera is inserted, which feeds an image of the internal organs onto a large monitor (the operating surgeon is guided by it), and through the remaining 2, air is pumped into the abdominal cavity and special laparoscopic surgical instruments are inserted. The course of the operation in the future is no different from abdominal hysterectomy.
A vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus through the vagina. After aseptic treatment of the vagina, a speculum and a lift are inserted into it, and an incision is made in the upper third. Technically, this operation is more complex and requires a certain skill of the surgeon.
Example from practice: When I first did a supravaginal (laparotomy) amputation of the uterus, I experienced my first shock when I cut open the stomach and saw the uterus, all in knots. I just wanted to give up everything and leave, as in the joke: “nothing works out anyway.” In principle, amputation of the uterus is a simple operation, but pitfalls lurk in the capture of the uterine arteries (they run along the ribs - the sides of the uterus, but of course they are not visible to the eye). 2 clamps are applied to the uterine arteries at the place of their intended course on each side (at a distance from each other). After which the uterus is cut off, the arterial stumps are ligated, the uterine stump is sutured with suturing of the appendages, it is peritonized and the anterior abdominal wall is sutured tightly. And so, after the uterus was cut off, blood gushed out from one side and instantly flooded the entire stomach. This means that the artery was not intercepted. But the surgeon (very experienced) was not at a loss and blindly intercepted the pulsating vessel (it happened on his part). This was my second shock during the operation. The further course of the operation was without complications, the postoperative period was smooth. The patient was discharged with gratitude for the operation and for the fact that she did not have to go to the regional hospital.
Consequences depending on the type of intervention
- Subtotal hysterectomy. The neck is preserved. The uterus is removed with or without appendages.
- Total hysterectomy. The cervix and body of the uterus are amputated, without or with appendages.
- Hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy. The uterus, tubes, and ovaries are removed.
- Radical hysterectomy. The uterus, regional lymph nodes, pelvic tissue, part of the omentum are amputated, and a third of the vagina is resected.
Who gets their fallopian tubes removed?
The main indications for fallopian tube resection are:
- ectopic pregnancy with localization of the fertilized egg in the tube;
- pyosalpinx - accumulation of pus;
- hydrosalpinx is an accumulation of serous fluid.
Additionally, the appendages are removed along with the uterus if a hysterectomy is performed. This approach allows you to avoid subsequent inflammatory and other changes in the fallopian tubes. If a hysterectomy is performed because of cancer, expanding the scope of the operation reduces the risk of recurrence.
Complications
The severity of complications after surgery directly depends on the following factors:
- age group of the patient;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies;
- severity of the disease;
- general well-being;
- the doctor's chosen method for removing the uterus.
Pain
Women who have had a hysterectomy will experience pain in the lower and central part of the abdomen for several months. Discomfort may radiate to the lumbar region and back.
The cause of the pain syndrome lies in a slight deformation of the spinal column and a change in the natural location of the bladder.
Urinary dysfunction
Due to the fact that before the operation the patient is inserted into the bladder, which remains in place for 1-2 days, this organ is injured.
You may experience discomfort during urination for several months. The bladder will work differently after a hysterectomy for the following reasons:
- inflammatory process;
- weakening of muscle tissue;
- the anterior wall of the vagina is lowered;
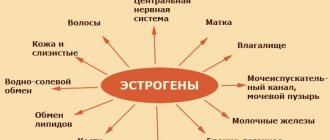
- estrogen is generated in the body in insufficient quantities;
- weakened sphinctral muscles;
- the patient suffered psychological trauma.
Hematomas
This complication is extremely rare. Usually, after the operation, the patient is left with a neat suture, the size and location of which depends on the type of operation. Hematomas can form due to local hemorrhages after unsuccessfully administered drugs.
Thrombosis on the legs
Any operation carries a risk of blood clots in the lower extremities. To prevent thromboembolism, patients have their legs wrapped with elastic bandages up to the knees or hips before surgery.
The lower limbs should remain in this state for several days. But they are also prescribed blood thinners.
Attention! In the future, a woman should lead a physically active lifestyle in order to prevent the development of varicose veins and subsequent thrombosis.
Vaginal dryness
In this category of patients after surgery, problems with the generation of vaginal lubrication are observed as a complication. You can protect dry mucous membranes with the help of special lubricants.
Bleeding
Patients may experience spotting for two weeks after hysterectomy. To prevent the development of infection or inflammation, they are prescribed antibiotics. If you experience intense bleeding, you should immediately go to a hospital.
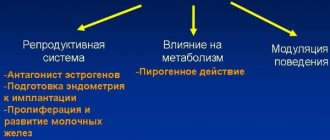
Early menopause
After 40 years, the female body gradually prepares for menopause. During menopause, unpleasant symptoms arise, which are very difficult for many patients to tolerate. If the uterus was removed before this point, they will be able to avoid pain, hot flashes, and decreased/increased libido.
Mood swings
After removal of the uterus, a hormonal imbalance occurs in the body of women. As a result, many patients become depressed and experience frequent mood swings.
The removal of the uterus is especially difficult for girls who have not been able to experience the joy of motherhood. Experienced psychologists should work with them, and they will also need the support of loved ones.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of vaginal wall prolapse consists of performing a standard gynecological examination, which determines the part of the vagina involved in the pathological process and the degree of prolapse. In total, there are 4 degrees of vaginal wall prolapse:
- 1st degree – Characterizes a condition when the walls of the vagina have shifted from their natural position, but do not yet reach the entrance to the vagina by 2 cm or more
- 2nd degree - At this stage of prolapse, the vaginal walls are at the level of the entrance to the vagina.
- 3rd degree - In this case, there is prolapse of the vaginal walls beyond the genital slit, but not more than 2/3 of its length
- Stage 4 – Complete prolapse of the vaginal walls
With the first two degrees, the patient may not feel the prolapse and it is often asymptomatic and requires only observation. 3-4 degree prolapse is an advanced stage of the disease, which requires treatment.
Life after hysterectomy
Women should not regard surgical intervention as an irreversible process that puts an end to their future life. With proper rehabilitation, it will be possible to adapt to the changes that have occurred in the body:
- abstaining from sex for 8 weeks;
- taking hormone-containing drugs;
- regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist;
- routine ultrasound;
- transition to dietary nutrition;
- physical activity;
- help from a psychologist.
Moderate exercise and Kegel exercises
After removal of the uterus, women can begin moderate physical activity a few months later. In such a situation, doctors recommend performing Kegel exercises, which will strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and increase their tone.
Hormone replacement therapy
After removal of the uterus, the amount of testosterone in the female body, which is responsible for the normal level of muscle mass, rapidly decreases. Due to the lack of this element the patient:
- rapidly gain weight;
- lose sexual desire;
- lose libido.
To replenish the concentration of testosterone, doctors prescribe hormone-containing drugs: “Divigel”, “Estroferm”, “Estrimax”, “Feminal”.
Diet
Against the background of hormonal changes, women begin to rapidly gain weight. Hormone-containing drugs that they will have to drink on an ongoing basis until menopause also contribute to weight gain.
These unpleasant consequences can be prevented through a diet that excludes all harmful foods and provides for fractional meals.
The effect of hysterectomy on sex life
Many doctors advise women to hide from their husbands the fact that their uterus was removed during surgery. Their ability to enjoy sex will not disappear; they will also be able to lead an active sex life as before. But, after surgery to remove the uterus, they need to abstain from sexual intercourse for 2 months.
Attention! After removal of the organ, women will begin to have problems with lubrication in the vagina. Special medications will help solve this issue.
Preparing for surgery
Hysterectomy is a planned intervention. The woman is given a hospitalization date in advance: the operation will be performed on the same or the next day. It is imperative to tell the doctor about any allergic reactions to medications and latex, chronic diseases, and the medications the patient is taking. Medicines that reduce blood clotting may need to be stopped for a while, as otherwise the operation will be accompanied by the risk of large blood loss.
Before a hysterectomy, a woman undergoes a preoperative examination, which includes:
- General and biochemical blood test.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood clotting study, coagulogram.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Tests for infections: HIV, syphilis, viral hepatitis, smear for flora, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, PCR for chlamydia.
- Cytological smear from the cervix.
- ECG.
- Consultation with a therapist and, if necessary, other specialists.
The list of studies and analyzes can be expanded if a woman suffers from cardiovascular pathologies, respiratory diseases, or diabetes. If you plan to remove the uterus through vaginal access, it is first important to identify and eliminate foci of infection in the vagina.
The day before, you need to shave the hair in the pubic area and perineum. Hysterectomy is performed under general anesthesia, so you should not eat or drink anything for 8–10 hours before surgery. In addition to the surgeon, the patient is first consulted by an anesthesiologist. In some cases, spinal anesthesia can be used. The anesthetic is injected into the spinal canal under the membranes of the spinal cord in the lumbar region, while the lower half of the body loses sensitivity, and the woman remains conscious.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Reviews
Tatyana, 35 years old:
At about 21 years old, I was diagnosed with a fibroid node. For many years they treated him with various medications, but only managed to slow down his growth. After 30, the tumor began to gradually increase in size. I listened to my parents and was in no hurry to have the operation, but in vain. As a result, the uterus with tubes and ovaries was removed, as the fibroids had grown to enormous sizes. I immediately fell into depression because I dreamed of children, whose birth I had to give up on. My husband was very supportive and offered to adopt the child himself. Now our family has a son who will go to school this year. As for health, the removal of the uterus and ovaries had a negative impact on the body as a whole. I started having problems with my thyroid gland, I noticed age-related changes on my skin, my mood often fluctuated, I became more nervous and hysterical.