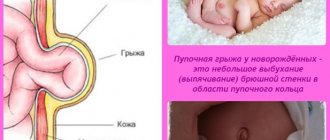
It is no coincidence that the inguinal space is the most common place for protruding hernias. The reason lies in its complex structure and natural “weakness”. It is especially weakened in men, although hernias also occur in women of different ages.
In the groin area there are several layers of fascia, between which lies the inguinal canal. In women, it contains the round ligament of the uterus, an artery and a nerve bundle. Like any channel, it has an outer and an inner ring (outlet and inlet).
Normally, all layers of the groin area successfully resist pressure from the organs from the inside. But with a combination of certain factors, they slip through the “weak” spots, forming a hernia.
Reasons for appearance
The development of a hernia is more likely in women who are at risk due to the presence of a predisposing factor in their lives:
- Physical inactivity. This disease manifests itself as a result of disorders of the musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, digestive system, and respiratory system.
- Tendency to inguinal hernia due to genetics.
- Weak body constitution of a woman.
But even these factors are not a reason to say that the disease will definitely manifest itself. Other provocateurs increase the likelihood of developing pathology.
| Factors | Causes |
| High pressure inside the abdominal cavity. |
|
| Weakness of the muscular system of the anterior abdominal wall. |
|
The risk group includes women aged 12-24 months and women over 40 years of age. In children, the appearance of the disease is explained either by a defect in the ligamentous apparatus or by anatomical weakness.
Hernia during pregnancy
During pregnancy, women experience several factors that contribute to the development of a hernia. An enlarged uterus leads to a shift in the center of gravity and improper redistribution of the load between the vertebrae. Also, a gradual increase in body weight leads to increased load on the spine. Changes in a woman's hormonal levels affect the condition of the spine. There is an increase in the amount of the hormone progesterone almost 100 times. This hormone has a relaxing effect on the walls of blood vessels and causes swelling of the nerve roots, which are subject to severe compression by the hernia. Increased production of the hormone relaxin leads to relaxation of the paravertebral muscles, which stimulates increased pressure directly on the spinal column. There is also an active consumption of calcium, which is necessary for fetal growth. If there is not enough calcium in the diet, then there is a deficiency in a woman’s bones, which increases the risk of destruction of the fibrous ring and the appearance of a hernia.
Classification
When determining the type of inguinal hernia, the following are taken into account:
- degree of damage to the posterior part of the canal;
- possibility of relapse;
- changes in the internal groin ring.
There are 7 types of this disease in total.
Direct hernia
This type of disease refers to acquired types of hernias. With it, the peritoneum protrudes through the gap in the groin, and the hernial sac is located separately from the spermatic cord.
Combined hernias
This is a rather severe form of the disease, when the hernia consists of several bags. They are not interconnected and go through separate holes. In the combined form of the disease, combinations of different types of hernias can be found.
Sliding hernias
The following organs may be present in sliding hernias:
- intestine;
- uterus;
- ovaries;
- bladder wall.
This type of disease is characterized by the presence of a hernial sac, consisting of 2 parts - the visceral layer and the parietal peritoneum.
Indirect hernias
This disease can be congenital or acquired.
Indirect hernias come in several forms:
- Inguinoscrotal hernia. Inside the scrotum is the lower part of the hernial sac. This condition leads to its growth.
- Canal hernia. The lower part of the bag is flush with the opening located in the groin canal.
- Cord hernia. The lower part of the sac is level with the spermatic cord.
Also, the pathology can be uncomplicated and complicated (it all depends on the course of the disease). Recurrent hernia is less common, postoperative hernia is more common. Recurrent hernias caused by poorly performed medical intervention are extremely rare.
Medical educational literature
Anatomical data.
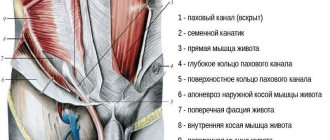
an acholar hernia forms within the inguinal triangle (Fig. 8). The lower side of this triangle is the Poupartian ligament (lig. Pouparti), the upper side is a horizontal line connecting the point located on the border of the upper and middle third of the Poupartian ligament with the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle.
The third side of the triangle is represented by a line running from the pubic tubercle (tuberculum pubicum) perpendicular to the upper line of the triangle. Within this triangle, the following tissues are detected during surgery (Fig. 9):
- Skin with subcutaneous tissue in which a.epigastrica supcrficialis occurs.
- The superficial fascia, tightly connected to the subcutaneous fat layer, and its deep layer (Thomson's fascia), adjacent to the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle.
- The aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle, which is a direct continuation of the oblique abdominal muscle. The lower edge of the aponeurosis is tucked downwards and inwards, lies on the bony arch of the anterior pelvic ring and forms an aponeurotic groove, attached to the anterosuperior iliac spine and to the pubic bone. This groove creates the Poupartian ligament. Above the pubic bone, closer to the midline of the abdomen, the aponeurosis forms two legs, between which is the external opening of the inguinal canal. The spermatic cord passes through it in men, and the round ligament of the uterus in women.
- The internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles are closely adjacent to each other. The lower edge of these muscles in the groove of the Poupart ligament approaches the spermatic cord, intimately adjacent to it, and then, crossing the cord, goes under the rectus abdominis muscle.
- The transversalis fascia, which is part of the intra-abdominal fascia, comes in varying densities.
- Preperitoneal tissue, which looks like adipose tissue.
- Peritoneum. If you look at the abdominal wall from the abdominal cavity, you can see five folds and depressions (pits), which are the places where hernias appear. The external inguinal fossa is the internal opening of the inguinal canal.
The inguinal canal has four walls. The anterior wall of the inguinal canal is formed by the aponeurosis of the external oblique abdominal muscle, the posterior wall by the transversus abdominis fascia, the upper by the free edge of the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles, and the lower by the Poupart ligament. This canal has an oblique direction and two openings: the subcutaneous (external) - external inguinal ring and the abdominal (internal) - internal inguinal ring.
Rice. 10, Descent of the testicle and vas deferens by the testicular cord into the scrotum
The formation of the inguinal canal is due to the process of descent of the testicle from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum (Fig. 10). The resulting vaginal process of the peritoneum gradually grows over its entire length, which delimits the scrotal cavity from the abdominal cavity. If the vaginal process of the peritoneum does not heal, conditions are created for the formation of a congenital inguinal hernia (Fig. 11). In this case, the spermatic cord will be located inside the hernial sac.
Rice. 11. Congenital (left) and acquired (right) indirect inguinal hernia (diagram): 1 - peritoneum: 2 - transverse fascia: 3 - small intestine; 4 - hernial sac: 5 - testicle: 6 - tunica vaginalis of the testicle; 7 - fleshy membrane: 8 - skin: 9 - hernial sac (tunica vaginalis of the testicle); 10 - internal fascia of the vas deferens
Diagnosis of inguinal hernias.
It is quite easy to recognize an inguinal hernia. Patients complain of pain in the corresponding groin area, which is associated with the appearance of a tumor-like formation in this area. The latter usually occurs with the patient in an upright position and disappears in the supine position. It appears during straining and physical activity. When examining a patient with an inguinal hernia in a vertical position, a tumor-like formation is detected in the groin area, which increases with coughing or straining the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. In the supine position, this formation disappears and is reduced into the abdominal cavity.
Rice. 12. Examination of the external opening of the inguinal canal
When examining the external opening of the inguinal canal using the index finger inserted into the inguinal canal through the scrotum (Fig. 12), it is possible to determine the symptom of a “cough push” - when the patient coughs, a push into the nail phalanx of the finger is noted by a hernial formation.
If the hernia exits the abdominal cavity through the external inguinal fossa and is located along the inguinal canal (an inguinal hernia), then the push is felt with the tip of the finger. If the hernia exits the abdominal cavity through the internal inguinal fossa and does not go through the inguinal canal (direct inguinal hernia), then the push is felt by the lateral surface of the nail phalanx. You can distinguish an oblique inguinal hernia from a direct one by the appearance of the hernia. An oblique hernia often has an oblong shape, and a straight hernia has a spherical shape. Often, a direct inguinal hernia is bilateral.
With an irreducible inguinal hernia, the tumor-like formation in the groin area does not change its size, regardless of the position of the patient. However, by studying the patient's medical history, it is possible to establish that this formation used to appear after physical activity and was reduced into the abdominal cavity in the supine position, but at a certain point it stopped disappearing. When examining a patient with an inguinal hernia, it is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the scrotum (palpate both testicles) and examine the inguinal canal from the opposite side.
If the hernial protrusion descends into the scrotal cavity and it appeared in the patient in childhood, one should think about a congenital inguinal hernia. At the same time, when the hernia is located in the scrotal cavity, it is not possible to palpate the testicle and the loop of intestine located in the hernial sac separately, since the testicle is also located in the hernial sac. In cases where there is a large acquired inguinal-scrotal hernia, the testicle can be palpated separately from the hernial formation. An irreducible inguinoscrotal hernia should be differentiated from hydrocele of the testicular membranes. In this case, it is necessary to use diaphanoscopy (examine the scrotal cavity using a beam of light). With hydrocele of the testicular membranes, an accumulation of fluid is detected in the scrotal cavity; with an inguinal scrotal hernia, there is no fluid in the scrotal cavity, but the contents of the hernial sac are detected.
When examining a patient with an inguinal hernia, it is necessary to pay attention to the function of urination. If there is difficulty urinating, which often happens with hypertrophy of prostate tissue, it is necessary to examine the prostate gland and determine the amount of residual urine in the bladder after the natural act of urination. An ultrasound examination of the bladder, performed before and after urination, can be used for this purpose. If a large (more than 50 ml) amount of residual urine is detected, one should think about the advisability of surgical treatment for the patient. If, when a hernial protrusion appears in the groin area, the patient experiences discomfort in the bladder area and (or) he notes the urge to urinate, one should think about the presence of a sliding inguinal hernia (the wall of the bladder slides) and be careful during surgery.
Treatment of inguinal hernias is only surgical. The purpose of the operation is to remove the hernial sac and perform plastic surgery of the inguinal canal. In young patients with small indirect inguinal hernias, plastic surgery can be limited to strengthening the anterior wall of the inguinal canal, with mandatory suturing of the deep inguinal ring. To strengthen the anterior wall of the inguinal canal, the methods of Girard (Fig. 13, a), A.V. Martynov (Fig. 13, b), and S.I. Spasokukotsky (Fig. 13, c, d) can be used.
Rice. 13. Options for plastic surgery of the inguinal canal: a - Girard method; b — A.U.Martynov’s method: c — S.I. Spasokukotsky’s method: d — S.I. Spasokukotsky’s method using M.A. Kimbarovsky’s seam; d - Bassini method; e - A.P. Krymov’s method: 1 - transverse fascia: 2 - internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles: 3 - spermatic cord; 4 - Poupart's ligament; 5 - aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle of the abdomen
With direct inguinal hernias, with inguinal hernias that occur in elderly patients, with recurrent inguinal hernias, the main cause of hernia formation is weakness of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. Therefore, strengthening of the inguinal canal in these cases should be performed through plastic surgery of its posterior wall. Among the methods that strengthen the posterior wall of the inguinal canal, the methods of Bassini (Fig. 13, e) and A.P. Krymov (Fig. 13, f) are most often used.
For complex forms of inguinal hernias, the methods of N.I. Kukudzhanov, P. Postempski, Sholdice are used. The surgical technique for each of these methods is described in detail in special manuals on operative surgery.
Since 1990, JDCorbitt, R.Ger, KAZucker first reported on laparoscopic intraperitoneal hernioplasty for inguinal hernia. In 1992, the first laparoscopic hernioplasty in Russia was performed by V.M. Sedov.
According to R.Gcr, laparoscopic hernioplasty has a number of advantages over traditional methods of hernia repair. He lists these benefits as:
- the possibility of survey laparoscopy of the abdominal organs before surgery;
- the maximum length of surgical wounds is 12 mm;
- atraumatic and tension-free operation technology;
- reducing the risk of damage to the spermatic cord and bladder:
- the possibility of simultaneous hernioplasty on both sides without an additional skin incision;
- reduction in the number of postoperative complications from the surgical wound;
- minimal pain after surgery;
- rapid recovery of the patient.
Rice. 14. Laparoscopic hernioplasty: a — trocar insertion points; 6 — separate implantation and fixation of polypropylene mesh for bilateral inguinal hernia
Indications for laparoscopic intraperitoneal hernioplasty do not differ from those for traditional hernia repair. Laparoscopic hernioplasty aims to strengthen the posterior wall of the groin area (Fig. 14). Laparoscopic hernioplasty cannot be performed, and therefore it is contraindicated during pregnancy, severe adhesions in the lower abdominal cavity, and giant inguinal-scrotal hernias. Laparoscopic hernioplasty should not be performed if laparoscopic hernioplasty relapses.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Symptoms
An inguinal hernia in women, the symptoms of which can be mild, has the main symptom - a protrusion of the lower abdominal wall in the groin area. If the hernia is small, it is not easy to notice. When lying down, it goes back and is not felt, but even with slight straining it appears again.
At first, the hernia does not manifest itself in any way. The girl does not experience any pain. The disease is also difficult to detect by touch. Only in rare cases, during physical work, girls may experience slight discomfort or heaviness in the side.
When the hernia becomes fully formed, the symptoms begin to fully manifest themselves.
The protrusion may appear in the area of the labia majora or in the crease of the groin. The pain begins to intensify. At first it will go away after a short rest, but then it will become constant and strong. This will significantly affect a woman’s ability to work. With large protrusions, inconvenience appears when moving.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the organ that passes through the groin canal. As an example, if it is an ovary, then pain occurs in the lower abdomen. It gives a lot of pain to the lower back. Such pain will intensify during menstruation. There are cases when the hernia is strangulated due to compression of the hernial sac in the area of the hernial orifice.
Symptoms of complications include:
- Constipation.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Difficulty in passing gases.
- Abdominal muscle tension.
- Nausea, which is accompanied by vomiting.
The disease in girls can occur without symptoms. Then it is possible to detect the disease only during a routine examination.
Pain in the inguinal rings
Many professional doctors accurately claim that the inguinal rings themselves cannot hurt, because the ring is only an opening. Also, pain in that area does not guarantee the presence of a hernia. Its appearance has nothing to do with inguinal rings.
The two most common problems that can be accompanied by pain around the rings are inguinal lymphadenitis and inguinal sprain. But still, instead of drawing conclusions on your own, you should contact a specialist.
Why is an inguinal hernia dangerous?
An inguinal hernia in women, the symptoms of which are just beginning to appear, does not pose any danger. But during the time the hernia manifests itself, complications may develop. The most serious of them is infringement, when it is urgently necessary to contact an ambulance.
In addition to pinching, an inflammatory process may begin to develop. As a rule, it occurs along with malaise and a slight increase in temperature. Another danger of the disease is stool blockage, when part of the intestine gets into the inside of the hernial sac. This complication directly affects the functioning of all gastrointestinal organs.
Typically, blockage occurs in older people. This kind of problem can only be solved through surgery. An inguinal hernia during pregnancy does not affect the development of the fetus. Doctors remove the hernia only after the patient gives birth. The patient is operated on 3 or 6 months after birth.
Complications of groin hernias in women
Naturally, a formed inguinal hernia causes a woman some discomfort and also represents a cosmetic defect. However, these are far from the most serious complications that protrusion can provoke.
- Inflammatory process. The development of inflammation inside the hernial sac occurs infrequently, but can significantly affect a woman’s health. Within the hernia, appendicitis may begin to develop, inflammation of the genital organs, and colitis may develop. Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process, body temperature will rise and general well-being will be disrupted. However, even minor inflammation can provoke the formation of adhesions, which, in turn, lead to the hernia becoming irreducible. In addition, emergency surgery may be required if acute inflammation develops. Its signs: a significant increase in body temperature, the appearance of vomiting and nausea, severe pain.
- Fecal impaction. When a section of the colon gets into the hernial sac, it can cause intestinal obstruction. This process develops gradually as feces accumulate in the sunken area. As a result, the woman suffers from digestive disorders. If this pathology is left untreated, it can lead to intestinal death. This occurs due to insufficient blood supply. Most often, this process affects older people with excess body weight. As for treatment, massage or taking laxatives can temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition. However, to fully eliminate the stagnant process, surgical intervention is necessary.
- Strangulated hernia. This is one of the most dangerous complications, as it occurs unexpectedly and abruptly for the patient. The entire contents of the hernial sac are compressed in the area of the excretory opening. There is a sharp disruption of blood circulation and compression of nerve fibers. According to statistics, up to 15% of patients are susceptible to a similar process.
The following symptoms indicate infringement:
- Inability to reduce a protrusion that was previously freely adjustable.
- The occurrence of severe pain in the groin area. The pain spreads to the entire abdominal cavity.
- The bag itself becomes dense, and tension is felt in it.
- The patient experiences vomiting and nausea.
- In some cases, a rise in body temperature is observed.
Diagnostics
The patient is examined by a surgeon. First, the doctor examines the groin area. He then asks several questions regarding the severity of the pain, level of physical activity, and how long ago the bulge was discovered. Based on the medical opinion, a decision is made on further treatment of the patient. In addition to the surgeon, the woman may have to undergo an examination by a gastroenterologist.
The article discusses in detail the symptoms of inguinal hernia in women.
There are other ways to examine a hernia:
- Ultrasound. During the examination, the specialist examines the scrotum, as well as the groin canals. The doctor may also order an examination of the abdomen or pelvis. This type of research is effective only if the hernial sac is completely filled.
- Herniography. The study is the most popular in diagnosing the disease. Its essence lies in the introduction of a special substance into the patient’s stomach using a prepared needle. When performing herniography, photographs are taken at the same time, which display the hernial sac with all its contents.
- Irrigoscopy. This method is used to identify an inguinal growth. The study is carried out if the patient is suspected of having a sliding hernia. During irrigoscopy, the large intestine is examined. For a more qualitative study, vegetables and fruits are excluded from the patient’s diet a few days before irrigoscopy. More attention should be paid to meat dishes. Before the procedure, food is completely stopped, you can only drink still water. During the procedure, a special substance is injected into the intestine, followed by an X-ray machine.
If a sliding hernia is detected in a patient, the doctor prescribes the following tests:
- Cystoscopy.
- Ultrasound of the bladder.
- Cystography.
Treatment without surgery
As such, girls currently do not have any means to cure an inguinal hernia. You can stop the process of its development (when it is small) by strengthening the abdominal muscles. Doctors allow me to do light physical activity.
These include:
- Walking.
- Swimming.
- Run.
- Aerobics.
If you completely refuse light physical activity, this will only worsen the situation.
Another way to treat a hernia is gymnastics. Exercises developed specifically for those suffering from an inguinal hernia will strengthen the abdominal muscles. They are done 3 times a day. In the morning and during the day, exercises should be done 30 minutes before meals. In the evening this time increases to an hour. In addition to gymnastics, patients are often prescribed physical therapy.
When treating an inguinal hernia without resorting to surgery, the following recommendations are used:
- Strict adherence to diet.
- Avoiding serious physical activity.
- Symptomatic medications are prescribed.
Folk remedies
An inguinal hernia in women, the symptoms of which are clearly expressed, cannot be completely cured using traditional methods, especially if the hernia has complications.
Medicines made according to folk recipes can:
- relieve inflammation;
- soothe pain;
- slightly slow down the development of the disease.
They are also used during the postoperative period.
For a higher effect, it is necessary to choose products that provide:
- Muscle recovery.
- Improving blood circulation in the perineum and pelvis.
- Restoring good functioning of the entire digestive system.
- Pain relief.
Most often, preference is given to herbal medicine. During treatment, herbs affect the disease itself and other internal organs. Inguinal hernia in women is treated using herbal teas that effectively affect the symptoms of the disease.
| Anti-inflammatory. |
|
| To improve digestion. |
|
| Astringents. |
|
| Painkillers. |
|
| From dropsy, as well as edema. |
|
| Herbs that eliminate congestion. |
|
During illness, constipation may occur.
You should take infusions of plants:
- glacium;
- castor bean;
- alyssum;
- Colchicum autumn columbine;
- European euonymus.
Ointments made from animal fat are widely used in treatment. The course of treatment with them is 1 month. The ointment is applied in the morning and evening. Camphor oil helps relieve inflammation and soothe pain. It is applied with light movements to the site of the hernia. This procedure is carried out once a day. The course of treatment is 1 month.
Apple cider vinegar is often used instead of camphor oil. Before use, it must be diluted in water. The ratio of ingredients should be 1:10. Rub this product once a day. Compresses are also used to improve overall well-being. Gooseberry herb helps with inflammation.
- Prepare the medicine in a double boiler for 10 minutes.
- Then the product is crushed and applied to the area where the hernia is located.
- The compress is fixed with a bandage and adhesive tape for more comfortable wearing.
- The procedure takes 40 minutes. 1 time per day, 2 weeks.
Shepherd's purse herb is used to relieve pain. For one procedure, 2 leaves of the plant are needed.
- The herb is steamed for 10 minutes.
- The sheets are wrapped in a bandage and carefully applied to the sore spot.
- It is necessary for the compress to remain on the hernia for 2 hours.
The duration of treatment is 2 weeks.
Do you need a bandage?
A bandage is a medical device for holding a muscle corset. This product is used during the recovery period after surgery. The bandage holds the muscles in the groin area under slight tension. This prevents the hernial sac from protruding. When the bag is large, the bandage prevents its further growth.
The device has several varieties: waist and in the form of swimming trunks. There are single-sided and double-sided bandages. The first type ensures that the bag is fixed on only one side. Double-sided bandages are suitable for women who lead an active lifestyle.
For a large hernia, it is necessary to use a bandage in the form of swimming trunks. Belt bands are necessary for girls to prevent the appearance of a hernia. The belt is comfortable to use. It is attached with adhesive tape, which allows you to adjust the pressure.
For pregnant girls, a corset in the form of a ribbon is best suited. This device can be adjusted.
The attending physician determines which bandage should be used. It is necessary to give preference to devices made from natural fabrics. The size of the bandage should correspond to the circumference of the hips. The small size greatly compresses the tissues and leads to poor circulation. A large bandage simply will not perform its functions.
What is a herniated disc?
A herniation in the spinal column is a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus from the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc.
If you are interested in learning about the structure of the spine in more detail, then you can refer to the article about its functions and sections, or to another one that talks about how many bones there are in the spine. They are posted on our website.
The basis of the spine is the vertebrae and the intervertebral discs located between them. The vertebrae consist of hard bone tissue, and by themselves they are immobile - their function is only to create support and hold the entire skeleton. They have special openings through which nerve endings and the spinal cord pass, which control the functioning of the entire body. And intervertebral discs consist of collagen fibers, a kind of mass that has a consistency somewhere between a gel and a dense jelly. The discs are covered with cartilage tissue on top for better adhesion to the vertebrae and giving this “hinge” the necessary strength. Thanks to the intervertebral discs, the spine is mobile, and a person can turn, bend, etc.
Diagram of the structure of the spine
Sometimes, due to certain factors, the nucleus leaves its normal limits because the annulus fibrosus is destroyed. The fibers of the tissues from which it consists become thinner. Since the nucleus pulposus is mobile, it falls out and remains protruded. This is what a hernia looks like.
Cross-sectional diagram of an intervertebral disc, which shows what a herniation looks like from the inside
Violation of the annulus fibrosus membrane does not cause pain. But the vertebrae between which the intervertebral disc is located have openings for the passage of nerve endings. A bulging nucleus pulposus puts pressure on these nerves, causing them to lose normal functionality and causing the person to experience severe pain.
Video - About spinal hernia in detail
When is surgery necessary?
Surgery to eliminate an inguinal hernia is performed not only routinely, but also urgently. The very occurrence of the disease in the patient is the reason for the operation. An inguinal hernia in women, the symptoms of which are difficulty urinating, pain and indigestion, is also removed routinely.
Emergency operations are performed in the following cases:
- intestinal obstruction;
- exacerbation of appendicitis;
- tissue disorders;
- strangulated hernia.
Before emergency surgery, a quick diagnosis is made. During a planned operation, the patient is prepared more carefully.
Questions frequently asked by a doctor during an appointment
- Is there pain in the area of the hernia? Its nature, intensity and distribution?
- Features of a hernia noted by a woman
- How long ago did the first symptoms appear?
- Was there any mention of a hernia in childhood?
- If hernia strangulation has occurred before, how often and with what outcome?
- Have any operations been performed for this hernia?
- What are the working conditions and features of the profession?
- How often do you play sports? What types of physical activity do you use?
- What diseases and surgeries have you had in the past?
- How were the pregnancies and births, if any?
- What other health complaints have you noticed lately?
Author:
Evtushenko Anna Aleksandrovna obstetrician-gynecologist
How is the operation performed?
Hernia removal begins with preparing the patient for surgery. Over the course of several weeks, the patient undergoes the necessary tests. The diet during preparation should be rich in vitamins and minerals. This will improve the woman’s immunity and the body will be better prepared for the upcoming stress.
Patients are strictly prohibited from taking medications that affect blood clotting. Contraceptives should be stopped one week before surgery. Smoking and alcohol are also excluded. The patient is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air. The choice of anesthesia is made taking into account the characteristics of the body.
The operation can be performed under:
- general anesthesia;
- local;
- regional anesthesia.
For severe anxiety attacks, the doctor prescribes a sedative. The operation itself is divided into 2 types: open surgery and laparoscopy. When performing an open operation, the surgeon makes an incision at the site of the protrusion, which allows you to get closer to the diseased area.
When the operation is simple, the hernial contents are repaired. If the operation is emergency, the surgeon makes a decision on the spot. If absolutely necessary, damaged tissue is removed.
During laparoscopy, small punctures are made in the abdominal cavity. The necessary equipment is carried through them. This method reduces the number of tissue injuries, and the patient goes through the rehabilitation period faster.
Recovery after surgery
Basically, within 6 hours after laparoscopy, the patient is able to move around on her own. The woman must spend the first day in a hospital under the supervision of doctors.
Foods excluded from the diet:
- fat;
- salty;
- tea and coffee;
- baking.
Mainly food consists of:
- porridge;
- natural juices;
- soups;
- fermented milk products with low fat content;
- steam omelettes.
A woman should:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- walk more;
- rest;
- Avoid strenuous physical activity as much as possible.
Complications after surgery
The most common complications include:
- Seams coming apart.
- Damage to the joint in the hip.
- Dyspeptic phenomena.
- Vein thrombosis in the lower leg area.
- Abdominal hernia due to surgery.
To eliminate these complications as much as possible, you must:
- follow all doctor’s recommendations;
- Avoid physical activity for a month;
- strictly follow a diet;
- wear a bandage.
Sprain
Normal sprains, which also involve the groin rings, occur quite often and for a variety of reasons. This injury is not the most painless, so it can be very difficult to survive.
Athletes most often encounter this problem after violating certain rules when working out in the gym, for example, lifting heavy weights. But despite this, many men have a natural tendency to frequent dislocations in the area of the hip joint, which subsequently leads to sprains. Inflammatory processes often create problems with tendons, disrupting their functioning, and then leading to serious consequences.