What is herpes?
But in fact, there are many more varieties of it. The cause of herpes is an extremely contagious virus that is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. Scientists identify 8 types of herpes viruses, of which two can cause “colds” on the lips: herpes virus type 1 (more often) and type 2 (less often). A distinctive feature of all herpes viruses is the ability to remain hidden inside cells until a decrease in immunity allows the herpes to move into the next stage of the disease, in which it begins to multiply.
Classification
Based on the mechanism of infection, a distinction is made between primary and recurrent ortholabiltic herpes . According to clinical manifestation and area of damage:
- Limited damage - single vesicles on the surface of the lips.
- Multiple lesions - multiple vesicles on the lips, which can merge and involve the red border of the lips.
- Extensive damage - vesicles extend beyond the lips, the process involves the skin of the perioral area, nasolabial triangle, and less often - the skin on the cheeks.
Why is herpes dangerous?
Herpes viruses are extremely widespread in nature and among people. This is largely due to the highly contagious and easy transmission of the virus. At room temperature, the virus can remain active for up to a day.
Infection occurs when virus particles enter the mucous membranes (mouth, nose, eyes, genitals) from a sick person. In children, contact with intact skin is sufficient.
Having penetrated the body, the virus migrates along nerve endings to nerve cells (neurons), where it lurks until favorable conditions. Once the immune defense is reduced, it begins to multiply and causes the characteristic symptoms of herpes.
Possible complications
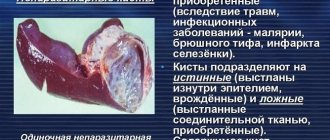
Herpes on internal organs is a very dangerous disease. Ignoring medication intake leads to unpleasant consequences. When hepatitis is advanced, the patient is diagnosed with liver failure. The mortality rate reaches 30%. Neglect of pneumonia ends in death in 80% of cases.
In newborns, herpes type 5 affects the formation of pathologies of internal organs and nervous tissue. Herpetic encephalitis may develop, which will cause the death of the baby (in 65% of cases). Only 10% of surviving children develop in accordance with age norms.
If you ignore treatment for herpetic encephalitis, 80% of patients fall into a coma. The mortality rate from brain inflammation reaches 30%. Surviving patients suffer from seizures, dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
Symptoms of internal herpes can be confused with other pathologies of organs and their systems. A complete diagnostic complex and competent therapy will help prevent the development of life-threatening consequences.
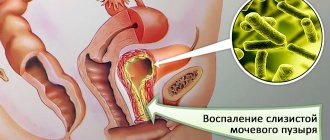
Genital herpes (genital)
The cause of genital herpes in most cases is the herpes virus type 2, which causes rashes on the genitals of men and women. It is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through protected sexual contact. The symptoms of genital herpes are almost identical to those on the lips, except for the location of the blisters. The first and second types of viruses are combined under the general name “herpes simplex virus”, since they can cross-infect areas characteristic of each other: the face and genitals, if they accidentally enter the corresponding places. In addition to the lips, herpes simplex can spread further and cause inflammation of the oral mucosa - stomatitis, which very often manifests herpes in children. Herpetic stomatitis can develop into herpetic sore throat. In newborns, the virus can cause damage to the eyes and even the brain (herpetic meningitis).
Type 4 - Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-IV)
Quite a dangerous type for people of any age category. If it falls into a child's body with air through the nose, throat, through the mouth with saliva, and even as a result of a handshake, it can provoke the development of serious diseases, or may not cause harm at all. This species is included in the group of contagious infections and a person who has received a primary infection may not notice the disease, spreading it to healthy people.
The disease can be detected based on test results and the following symptoms:
- Increase in liver size;
- Swelling of the tonsils;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- A sore throat;
- Increased sweating;
- Temperature 40C;
- Chills.
Stage 4 herpes can cause the development of cancer, hepatitis, mononucleosis, and herpetic sore throat.
Herpes on the body (shingles)
It is caused by a type 3 virus - the same as chickenpox in children. Chickenpox is the primary reaction to the penetration of the virus. After the acute stage of herpes, the disease develops into chronic herpes, with the virus hiding in nerve cells for several decades, after which, for as yet unknown reasons, herpes becomes more active and causes shingles in some people. Signs of herpes zoster are rashes on the chest, on one side, along the rib, and in rare cases on the neck. They are accompanied by severe pain, which in some cases remains for a long time (herpetic neuralgia). Less commonly, the virus affects the optic nerves, and then signs of herpes rashes appear in the eye area. This is one of the most serious forms of the disease. Other types of herpes viruses can cause lymphoma (type 4), infectious mononucleosis (type 5), roseola infantile (type 6), Kaposi's sarcoma (type 8). Chronic fatigue syndrome is associated with herpes virus type 7.
Symptoms of postherpetic neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is an echo of the disease after recovery from type 3 herpes. After a relapse of the Zoster virus, the patient remains with a feeling of discomfort and symptoms of infection, although the disease has already “subsided.” Acute symptoms also disappear completely. So, with such neuralgia there are:
- residual drying and flaking crusts in places where there was shingles;
- throbbing pain or tingling in this area, sometimes extremely strong;
- itching between painful attacks, causing irritation, which only intensifies subsequent pain;
- numbness of the skin areas at the site of the former lichen or an extremely strong reaction to external irritants;
- muscle weakness and paralytic conditions (more often in old age).
Typically, postherpetic neuralgia lasts 2-3 weeks, but sometimes it remains for 2 months or even a year. Some symptoms last even longer, such as muscle weakness or extreme skin reactions. All this interferes with the normal lifestyle of people who have experienced reactivation of the chickenpox virus.
Treatment of herpes
It is currently impossible to completely cure the body of the herpes virus, since most of the time it remains in an inactive state in the cell nucleus. But the unpleasant symptoms of herpes can and should be treated. Medications can reduce the duration and frequency of chronic herpes. They may also help reduce the risk of passing herpes type 2 to susceptible partners.
How to cure herpes symptoms?
How can you treat the symptoms of herpes? There are only a few medications for the treatment of herpes that have proven effectiveness. The main ones are: acyclovir, valacyclovir (converted in the body to acyclovir) and famciclovir. The acyclovir molecule is integrated into the DNA of the virus and “deceives” it, disrupting the reproduction process. Treatment of herpes with acyclovir is relatively safe for humans if the herpes is treated in short courses. It can be used even in newborns. Famciclovir is somewhat stronger, but much more expensive and is only used orally.
How to treat herpes on the face and genitals?
In order to cure herpes on the face or genitals, in most cases it is enough to use an ointment with acyclovir or its analogues. If you do this in time, even before large bubbles appear, you can cope with the disease at home.
How to treat severe rashes?
If the rash is very severe, spread over a large area, and is accompanied by fever, then it is better to call a doctor. After examining you, he will tell you how to treat herpes, for example, he will prescribe acyclovir tablets. In some particularly severe cases (for example, herpetic meningitis), acyclovir can be used intravenously to treat herpes. However, remember that long-term oral use of these drugs (more than 10 days) can negatively affect the liver and should only be done under the supervision of a doctor.
How to prevent secondary bacterial infection?
With profuse rashes, there is sometimes a risk of secondary bacterial infection entering the ulcers. To prevent this, you need to treat the skin in the area of the rash with any antiseptic solution: brilliant green, chlorhexidine, miramistin, etc.
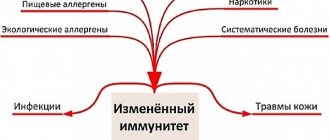
Why is it important to strengthen your immune system?
Strengthening the immune system is the second way to get rid of herpes. It is appropriate during the period when there are no acute manifestations (bubbles) and will help reduce the number of exacerbations of chronic herpes, but not eliminate the virus completely.
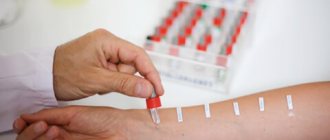
Diagnostics
The patient's examination is ordered directly by the doctor. It determines the presence of a herpes infection visually. Laboratory tests are carried out to identify the virus that caused the development of the disease, which is necessary for adequate treatment. To do this, laboratory research methods are prescribed to determine:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Determines the elements of the virus in human blood;
- Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF).
Other metas include:
- HSV test - immunodot G-specific glycoprotein. 98% guaranteed to correctly identify the virus and type of herpes;
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a method by which viruses, macromolecules and other compounds are detected. This method is based on the antigen-antibody reaction. Using a special enzyme, the resulting complex (antigen-antibody) is isolated.
After infection with the herpes virus, the body reacts by forming antibodies to it, which are called immunoglobulins. They come in IgG class and IgM class.
- IgG
- are formed in the blood during the course of herpes in a chronic form. If the virus is activated, the composition of immunoglobulins increases sharply. There are also: IgG to early early proteins, which appear a little later than IgM. They also indicate the activation of the chronic period or already the acute period of the disease; - IgM
- is formed in the blood within 1 or 2 weeks from the moment of infection with the virus. Experts call IgM an indicator of a primary infection, but in 20% of patients, viruses of this class are detected during the activation of an old infection.
There are 2 ELISA methods that help determine the herpes virus:
- Qualitative – it is used to determine the type of virus, the presence of antibodies, and the possibility of developing previous relapses;
- Quantitative - makes it possible to identify the antibody titer, and most importantly, the state of the immune system against the virus. An elevated antibody titer generally indicates a recent relapse of the disease.
Interpretation of a blood test for herpes:
| IgM indicators, where + the result is positive, – negative | IgG indicators, where + the result is positive, – negative | Conclusion |
| IgM - | to early proteins IgG +, late + | Acute primary infection or relapse |
| IgM - | to early proteins IgG -, late + | The body has immunity to the herpes virus (carriage) |
| IgM+ | to early proteins IgG +, late - | Primary acute infection |
| IgM+ | to early proteins IgG + late + | Primary acute infection |
| IgM - | to early proteins IgG – late – | There is no viral infection |
Using this table, you can compare test results and get a complete picture of their meaning.
In most cases, diagnosing simple and genital herpes in an intimate place is not particularly difficult only on the basis of visible signs and the nature of the development of the disease.
Herpes in children
Herpes in infants necessarily requires calling a pediatrician, since only a doctor knows how to treat herpes in each specific case. For a small child this is a fairly serious disease. A child can become infected from his parents. Therefore, if you have an exacerbation of herpes and rashes appear on your lips, do everything possible to avoid infecting your baby (see prevention of herpes). Genital herpes can be transmitted to the child from the mother during childbirth, if at that time she has rashes on the genitals. Herpes simplex can cause not only rashes on the face in children, but also stomatitis (up to 80% of all stomatitis in children are caused by this virus), sore throat, pneumonia and meningitis. All these are dangerous diseases for the baby. In addition to the first and second types of the virus, children can be affected by the third type (chickenpox) and the sixth type (infantile roseola).
Precautionary measures
In order for the disease to pass in a mild form and its complications to appear, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Rule #1. Avoid touching your face with your hands, especially in the area of blisters. Otherwise, you risk spreading the infection to a larger area of skin.
- Rule #2. During illness, be especially careful about your personal hygiene.
- Rule #3. Isolate yourself and try to avoid close contact with people, especially the elderly and children.
Genital herpes during pregnancy
Genital herpes during pregnancy If the primary infection with genital herpes occurs during pregnancy, then the risk of harmful effects on the fetus is quite high. In many cases, a miscarriage or developmental defects may occur in the child, since the mother’s body does not yet have anti-herpes antibodies, the virus penetrates the placenta to the fetus and damages it. If the infection occurred earlier, before pregnancy, then the antibodies produced by the mother’s body prevent the herpes virus from actively multiplying, protecting the fetus. In this case, only childbirth in the presence of herpetic eruptions on the genitals poses a danger.
Provoking factors
Most often, herpes inside the body is localized in the cavity of the lungs, liver and esophagus. Accordingly, there are three main forms of it:
- herpetic hepatitis;
- herpetic pneumonia;
- herpetic esophagitis.
The virus spreads through contact with the biological fluids of its carrier (blood, saliva, tears, breast milk). You can also become infected through sexual intercourse. Once it enters the body, herpes remains there forever. Signs of the disease appear when:
- decreased immunity is the main reason;
- regular hypothermia/overheating;
- development of infectious diseases;
- stress and fatigue;
- presence of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs).
Also, possible future carriers of herpes include children, pregnant women with weakened immune systems, and people who have undergone a blood transfusion. This also includes people with diabetes, malignant tumors and HIV infection.
Prevention of herpes
Prevention of herpes should be aimed at not infecting other people (mainly children, since most adults are already infected). If you have a rash on your lips, wear a gauze bandage, do not kiss your child, do not touch the sores, and wash your hands as often as possible. A sick person and a healthy person should not share utensils. Genital herpes is transmitted through sexual contact, usually if the patient has a rash. But we must remember that some people shed the virus even in the absence of rashes, so the risk of infection cannot be completely excluded. To prevent herpes infection in this case, condoms are quite effective; you can also use suppositories with benzalkonium chloride and miramistin. However, the most reliable way is to have one sexual partner.
Causes of the disease
Herpes simplex viral infections are easily transmitted through direct contact with lesions or body fluids of someone with herpes. Transmission can also occur through skin-to-skin contact during asymptomatic illness.
Other reasons include the following:
- Kissing an infected patient;
- Use of public toilets (when toilets are not sanitized);
- Frequent change of sexual partners, as well as oral sex with a carrier of the infection;
- Overheating or hypothermia of the body;
- Poor hygiene.
Risk factors for HSV-1 infections in children include poor hygiene practices, birth in poorly developed countries, low social status, and overcrowding.
Attention! The herpes simplex virus persists for 24 hours at normal air humidity and t +50 C. Its vital activity (at low temperatures) can persist for 5 days, and on a metal surface it survives for 2 hours. It is active even on sterile damp gauze and cotton wool until it dries completely (about 6 hours).
Diet
During treatment, to reduce symptoms, follow a diet that is high in lysine. This is milk and fermented milk products: cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, kefir, yogurt (preferably unsweetened). Eat seaweed salad, it is rich in iodine. Give preference to dishes made from poultry, potatoes, and eggs. Don't forget about fresh vegetables and fruits. Consume legumes in moderation. Additionally, take vitamins A, E and C, this will help fight the disease.
Avoid fatty foods, chocolate, cocoa, nuts and seeds for a while. Replace coffee in the morning with green tea. Exclude tomatoes from vegetables.
How to prevent disease and relapses
There is no clear scheme for preventing herpes rash on the body. There is a vaccine used against herpes zoster, but there are a number of contraindications for its administration: allergies, pregnancy, acute respiratory disease.
Special medications - immunomodulators, which are prescribed by an immunologist after the results of an examination and special tests, will help improve the functioning of the immune system.
Based on the fact that the virus manifests itself in a weakened body, great attention should be paid to health. To strengthen your immune system, make it a habit to eat right and on time. Exercising in the fitness center and gym will improve your health. A sauna and steam bath will also not be superfluous and will play a positive role in the prevention of herpes. No miracle drug can compete with a healthy lifestyle.
Hygiene rules
It is worth noting that herpes is a contagious disease. Most often, infection occurs when pimples form that contain serous fluid and resemble pustules. The disease is considered safe for others after dry crusts appear in areas of the rash on the body. Still, you should be careful and stay in bed until complete recovery. Do not wash in a hot bath.
- To avoid the spread of the disease, all patients should have personal belongings separate from their family members. Also, until recovery, tactile contact with relatives, children and strangers should be avoided.
- During the progression of the disease, you should not use cosmetics (including shampoos, scrubs and gels) due to possible allergic rashes and worsening of the condition after the rash spreads to the body. You can take a shower no more than 3 times a week. If possible, it is better to avoid frequent contact with water, since the habit of washing frequently contributes to the “spreading” of acne throughout the body.
Until crusts form on the sores, it is recommended to use only cotton underwear. When the pimples burst, the serous fluid flowing out of them in contact with clothing will not cause allergic reactions, irritation or pain. The natural fabric of the underwear will absorb all the liquid without causing infection.