IOP, or intraocular pressure, is a very important diagnostic indicator that determines the health of the visual organ.
It may increase or decrease.
Every person should have their intraocular pressure checked during their annual medical examination. This will help detect the presence of dangerous eye diseases at a very early stage of development. If you do not follow this advice and do not treat eye diseases, you may lose your sight.
Hypotension
It is also low pressure inside the eye. Causes:
- If your blood pressure has dropped. Studies have shown that blood pressure is closely related to blood pressure.
- Unsuccessful surgery.
- Inflammation of the eyeball. For example, iritis is an inflammation of the iris.
- Injury or something getting into the eye. May contribute to eyeball atrophy.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Kidney problems and others.
Speaking of symptoms, with dehydration and an infectious nature - this is dryness in the eye, loss of pupil luster, in rare cases the main apple sinks. But it is still difficult to determine incorrect ophthalmontus, because these symptoms manifest themselves mildly and imperceptibly. The only true symptom is a feeling of blurred vision.
Maintaining eye pressure of sixty is a really important point. Check your vision regularly, and if you notice the slightest symptoms, contact a specialist.
What complications may arise?
Problems with blood pressure in older age entail a number of serious complications and consequences. High blood pressure in women over 50 years of age can lead to heart attack or stroke, and kidney failure. The disease can also cause eye problems.
Complications of a high rate may include shortness of breath, lameness, coughing up blood, and atherosclerosis. Complications of low blood pressure: loss of consciousness, collapse, cardiac tamponade, or brain damage.
Traditional medicine
Sometimes drug therapy doesn't help control the signs of high or low IOP, and people don't know what to do during treatment. In this case, you can use traditional medicine methods that will eliminate problems with ophthalmotonus.
Alcohol tincture of golden mustache
To stabilize blood pressure, some doctors recommend using an alcohol tincture made from golden mustache. To do this, about 2-3 shoots of the plant are cut off. Then the cut shoots are thoroughly ground to a thick paste, after which the mixture is mixed with 500 ml of alcohol or vodka. The prepared solution is covered with a lid and infused for about 15 days in a room with a temperature of no more than 20 degrees.
The prepared tincture is drunk every day, one tablespoon before meals. Regular use of the tincture will eliminate all symptoms of high IOP.
Red clover infusion
An infusion of meadow clover is often used in folk medicine. It is used for varicose veins, thrombosis and gynecological diseases. Also, a medicinal infusion is used to cope with impaired ophthalmotonus. To prepare a medicinal mixture, add 100 grams of finely chopped plant to 300 ml of hot water. Then the mixture is covered with a lid for 5-6 hours.
Healing lotions
Sometimes, instead of tinctures, special eye lotions are used that will help eliminate the symptoms of unstable pressure. Often, lotions made from chamomile are used for this. To make them, pour boiling water over 100 grams of dry grass and leave for 20 minutes. Then all the herb is taken out of the hot water and placed in a small fabric bag. After this, the bag of chamomile is placed on the eye and left there until it cools completely. Then the procedure is repeated, but for the other eye.
You will have to make chamomile lotions every day for two weeks.
Nettle and lily of the valley lotions
Another remedy that will help quickly remove high IOP is made from lily of the valley and nettle leaves. It is very simple to prepare a medicinal lotion, so anyone can handle this work. To do this, 35 grams of lily of the valley and 120 grams of nettle are finely chopped and poured into 100 ml of hot water. The mixture is thoroughly stirred and left to infuse for about 7-8 hours. Then add a little salt to the liquid and mix again.
Dandelion and honey
People who are treated with folk remedies often use a medicinal mixture of honey and dandelions to reduce IOP. To prepare the medicine, you will need to mix 85 grams of honey with 70 grams of dried dandelion. Then the ingredients are poured with a small amount of water. The result should be a creamy, thick liquid that is spread on the eyelids in the evening. This mixture is used daily for about 10-15 days.
Motherwort decoction
A decoction made from motherwort helps cope with unstable eye pressure. To create the medicine, 20 grams of the dried plant is poured into one glass of very hot water. The container with the liquid is covered with a lid and infused for 20 minutes, after which it is placed on the gas stove. The mixture is boiled for about 10 minutes and removed from the stove. The boiled broth is filtered, cleared of leaves and mixed with 70 grams of honey. The medicine is taken three times a day, one tablespoon.
Mint drops
Mint drops are used not only to get rid of high IOP. They also help eliminate nausea, vomiting and headaches. The plant contains many essential oils, which improve blood circulation and slightly increase the size of blood vessels.
To prepare mint drops yourself to normalize ophthalmotonus, you will need to mix 150 ml of distilled water with two drops of mint oil. The prepared product will have to be instilled into the eyes daily, three times a day.
Aloe decoction for washing eyes
Intraocular pressure is sometimes lowered by rinsing the eyes. To do this, use a special decoction made from aloe leaves. To create the remedy, five leaves are plucked from the plant. Then they are thoroughly washed with water and cut into small pieces. The leaves are placed in a container with cold water and placed on a gas stove. The broth is boiled for at least 10 minutes, after which it is removed from the stove and infused. Aloe vera remedy is applied four times a day every two hours.
Potato compresses
Potato compress is popular among lovers of self-medication with folk remedies. To prepare this medicine, you will need three potatoes, completely peel them, chop them finely or pass them through a meat grinder. Then the chopped potatoes are mixed with table vinegar and water. The mixture is infused for half an hour, after which it is placed in a small piece of cloth. After this, a cloth bag with the potato mixture is placed on the eyelids.
Dill infusion
It's no secret that dill has a considerable number of beneficial properties. It is thanks to this that this plant helps to cope with glaucoma and other vision problems.
When treating, use dill decoction, during the preparation of which 80 grams of dill seeds are mixed with 450 ml of water. Place the container with dill on the gas stove and cook for about five minutes. Dill liquid is drunk every day, 80 ml.
Does eye pressure change with age?
Eye pressure depends on age. The highest value is in newborns, then gradually decreases until the age of 10.
From the age of 20 there is a tendency for pressure to slowly increase, and after 70 there is a slight decrease. This all applies to healthy eyes, in which these fluctuations are 1.5–2 mm.
Compare normal eye pressure in men and women. Pay attention to the table of normal eye pressure for men and women. Women normally have slightly higher eye pressure than men.
On average, this difference is 0.5 mm Hg. Art.
6/10
Algorithm for tonometry according to Maklakov
- Before starting the procedure, the holder and glass plates are disinfected with hydrogen peroxide or ethyl alcohol.
- Next, the prepared plates are covered with a thin, even layer of paint. Collargol or Bismarck-brown is usually used as a coloring agent.
- Since there is direct contact of the plate with the eye, anesthesia is used. The person lies down on the couch and a couple of minutes before the test, lidocaine, dicaine or proximetacaine is dripped into his eyes. When the anesthesia begins to take effect, the patient raises his hand and looks at his finger.
- The specialist carefully spreads the patient’s eyelids, tightly fixing his fingers on the periosteum. Then he lowers the tonometer onto the eye, which is fixed in the holder. The pressure of the metal cylinder causes the cornea to shrink. After the glass plates are removed, a certain amount of paint remains on the eye, which is washed off with saline solution.
- The doctor then performs the procedure on the other eye and then administers antibacterial disinfectant drops to the patient. Usually this is furatsilin, an aqueous solution of which has a detrimental effect on bacteria.
After the procedure itself, measurements and calculations are made. To do this, the paper must be moistened with alcohol and used metal cylinders placed on it. Circles of paint will be printed on the sheet. Using a ruler, the doctor must measure the diameter, which corresponds to millimeters of mercury. The normal pressure for this type of tonometry is 10-20 mm Hg.
These numbers may change during the day, because eye pressure is usually higher in the morning. Therefore, for a more accurate result, ophthalmologists advise carrying out the procedure several times a day and monitoring daily changes.
Preparing the paint is another necessary step for this procedure. Typically, the paint is collargol, which is mixed in a mortar with glycerin and distilled water. An analogue of collargol can be Bismarck-brown or methylene blue.
To cover the plates with prepared paint, you need a plug pad. But there is a safer treatment method in terms of possible infections - transfer the dye with a glass rod and rub it with a cotton swab.
When using anesthetic drops, the procedure is absolutely painless and easily tolerated by patients. Reviews from people who have completed it are only positive.
This is interesting: Coxarthrosis of the hip joint. Symptoms and treatment. Chondroprotectors, exercise therapy, diet, massage
The pressure in the right and left eyes is different - is this normal?
The pressure of the right and left eyes may differ, the so-called asymmetry. Normally, this difference should not be more than 4 mm Hg. Art.
8/10
Preventive actions
The following preventive measures are recommended to maintain health:
- Eliminate fatty and fried foods from the diet.
- Sports activities.
- Taking vitamins.
- Regular eye exercises.
- It is recommended to undergo treatment at a sanatorium once every six months.
- Complete rest.
- Limit consumption of caffeine-containing drinks.
Via
Women's health after 50 years gynecologyFashion for 50 year oldsWhat to wear after 50 years for a woman
When blood pressure is high, what kind of disease is it?
High eye pressure is the main problem with glaucoma. More than 90% of glaucoma treatments are aimed at reducing it. It has been proven that a decrease in IOP by 25% from the initial level provides a twofold reduction in the risk of blindness in glaucoma.
The insidiousness of glaucoma is that eye pressure within the normal range can also be combined with glaucoma, then they speak of low-pressure glaucoma. The paradox is that high blood pressure may not cause any processes or symptoms in the optic nerve, and the person will have good vision.
Expert opinion “All about vision” Many serious eye diseases occur with increased intraocular pressure. Doctors call this symptom ocular hypertension. The cause can only be determined by undergoing a full examination.
Expert
9/10
Characteristic symptoms
Increased IOP is classified into several types: stable, labile and transient. Stable is when the indicator is always above the norm. This indicates possible glaucoma. Labile – when indicators periodically change from high to normal. Transient is characterized by rare pressure surges.
Signs of high blood pressure include the following symptoms:
- Severe reduction in field of view.
- Rapid eye fatigue and redness.
- When looking at the light, rainbow arcs are formed.
- Twilight vision is impaired.
- Pain in the temples and brow ridges.
- Discomfort when reading or watching TV.
- The viewing angle is reduced.
Causes of eyeball hypertension
Glaucoma concept
Glaucoma is a multifactorial pathology. There are many reasons, the one-time or single impact of which contributes to the appearance of pathology.
Causes of the disease
- Hereditary predisposition is the leading factor leading to the development of the disease. The probability of developing glaucoma in people aged 35-45 years, born from sick parents, is close to 25%.
- Systematic stress loads.
- Eye injuries.
- Surgical interventions. The most dangerous operation is to replace the lens.
- Anatomical defects of the vascular apparatus of the eyeball. In the presence of atherosclerosis or a change in the coagulation properties of blood towards hypercoagulation, the incidence of glaucoma increases several times.
- Diseases of the heart and vascular bed (hypertension, arrhythmias of any nature).
- Metabolic disorders – diabetes mellitus, thyroiditis.
Symptoms of diabetes
Why is increased intraocular pressure dangerous?
A change in ophthalmotonus in one direction or another is a dangerous symptom that can cause vision loss.
As the pressure increases, the capillaries are compressed, which leads to injury to some areas of the eyeball. Compression of the optic nerves causes a deterioration in metabolic processes, as a result, the organ of vision does not receive enough necessary nutrients. This leads to permanent and sometimes irreversible vision loss due to ocular atrophy. Often, high IOP causes glaucoma.
No less dangerous is a decrease in ophthalmotonus. If at high pressure there is compression of blood vessels, then at low pressure the functioning of the vitreous body is disrupted. This leads to reduction and deformation of the eyeball, loss of vision. If signs of atrophy are detected, it is difficult to restore vision.
Sometimes a change in eye pressure is a symptom of other pathological changes in the body. For example, increased IOP indicates problems with the cardiovascular system, and low IOP indicates problems with the liver.
Monitoring eye pressure allows you to detect deviations from the norm in time. Timely and competent treatment helps prevent the onset of negative consequences.
IOP during the development of glaucoma
The key stages of progression of this pathology in ocular hypertension can be presented as follows.
The main cause of vision loss in glaucoma
- Violation of excretion. The deviation is due to many reasons: from an increase in the muscle tone of the trabecular tubules in the presence of stress to anatomical defects.
- Pressure rise above standard values.
- Reduced blood supply to the tissues of the ocular apparatus due to compression of the supply arteries.
- Hypoxia (decreased nutrition) of the components of the optic nerve, gradually turning into ischemia (lack of nutrition).
- Ischemia in the stage of decompensation. An additional negative factor is compression of the optic nerve head by intraocular formations, the volume of which tends to increase.
- Irreversible dystrophic and destructive processes in nervous tissue.
- The occurrence of neuropathy (manifested by a complex of visual abnormalities) and complete loss of the optic nerve (leads to an absolute absence of vision).
Glaucoma is a multifactorial multifactorial disease
Taking into account the above-described features, we can conclude that treatment of the disease should be aimed exclusively at achieving target pressure levels, which helps prevent the development of pathology and create conditions for the restoration of nerve cells that are in parabiosis (temporary death).
Glaucoma of the eye is an ophthalmological disease accompanied by increased eye pressure. IOP indicators may differ depending on the stage of the pathological process:
- Initial stage. There are no symptoms, IOP is 22-26 mm Hg. Art.
- Second degree. Visual functions are impaired, the viewing angle decreases, IOP is 27-33 mm Hg. Art.
- Advanced stage. Fluid stagnation occurs, causing severe visual impairment. IOP indicators are no more than 35 mm Hg. Art.
- Final stage. At this stage, immediate surgical intervention is necessary. IOP exceeds 35 mmHg. Art.
Fluctuations in intraocular pressure are acceptable, but only by 3 units.
Treatment
Treatment of the underlying cause is required to normalize eye pressure. Consultation with other specialists may be required. The ophthalmologist will advise what to drop into the eyes to reduce intraocular pressure.
Drug treatment
Therapy for elevated IOP includes several groups of drugs. It is recommended to start with one. If necessary, add drops from another group, or replace the drug with a combined one. Popular drugs that lower IOP:
- Beta-blockers reduce the production of aqueous humor: Timolol, Betoptik, Okumed.
- Cholinomimetics improve the outflow of moisture by constricting the pupil: Pilocarpine.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors reduce the synthesis of intraocular fluid: Trusopt, Azopt.
- Prostaglandins improve the outflow of ocular fluid: “Xalatan”, “Glaumax”, “Glauprost”, “Travatan”.
- Combined drugs: “Xalacom”, “Fotil”, “Cosopt”.
For low IOP, Atropine eye drops are prescribed. Vascular strengthening tablets “Ascorutin” and B vitamins “Neuromultivit” will improve the effect.
Surgical intervention
If there is no effect from drug treatment, the symptoms persist and progress, then the doctor decides that surgery is necessary. Surgical treatment is aimed at creating improved drainage of aqueous humor.
There are 3 common types of operations:
- Iridotomy is the creation of a hole in the iris.
- Iridectomy – removal of a section of the iris.
- Trabeculoplasty is the creation of outflow pathways for eye fluid.
The operations are performed using a laser machine. The recovery period is short, the risk of complications is minimal.
Folk remedies
At home, you can use folk remedies. Changes in intraocular pressure are a serious symptom that can lead to vision loss. Therefore, alternative treatment is permissible with the permission of a doctor in combination with medications.
Strong tea, coffee, exercise, and drinking plenty of fluids will briefly increase IOP. There are several recipes with herbal ingredients to reduce IOP.
- Golden mustache helps relieve high eye pressure plant. It is used in the form of an alcohol tincture. Method of preparation: infuse the crushed golden mustache in 0.5 liters of vodka for 2 weeks. Shake the container periodically. It is recommended to take 2 tsp orally. in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Meadow clover. To prepare the meadow clover infusion, pour 1 tsp. herbs with a glass of boiling water. Leave to infuse. After cooling, strain the infusion and drink every day before bed for 1 month.
- Motherwort. Recipe for preparing motherwort decoction: add 1 tbsp to half a liter of water. l. motherwort. Boil for at least 7 minutes over low heat. Cool and strain. Take the finished decoction 1 tbsp orally. l. three times a day.
- Mint. To reduce IOP, the use of mint drops is effective. Method of preparation: stir 1 drop of mint oil in half a glass of boiled water. It is enough to instill drops 1 time per day
- Aloe. To wash your eyes, you can prepare a decoction of aloe. To do this, pour boiling water over 5 medium-sized aloe leaves. Then simmer over low heat for 5 minutes. Cool the broth, then use it for rinsing every 6 hours.
- Potato. You can use raw potatoes as a compress. Grate 2 pieces on a fine grater, mix with 10 ml of 9% table vinegar. After half an hour of infusion, the mixture is ready for use. Wrap the pulp in a gauze napkin and apply to closed eyelids for 20 minutes.
Prevention measures
It is always easier to prevent diseases, so experts recommend adhering to the following rules in everyday life.
- Time for work and rest should be balanced. The body (including the visual system) needs at least 8 hours a day to rest.
- You need to take breaks throughout the day. At this time, you can allocate 3-5 minutes to perform eye exercises or massage.
- Before going to bed, it is recommended to massage the eyeballs with your fingertips, making circular movements clockwise and counterclockwise.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Stick to a balanced diet. Include more fresh fruits, berries and vegetables, and foods containing Omega-3 acids in the menu.
- Use vitamin complexes, which include microelements beneficial for eye health.
- When performing exercises, you should not put too much pressure on your eyeballs. Heavy physical exercises involving heavy lifting and other overexertion are also not recommended. This automatically increases the IOP.
- Spend more time outdoors on weekends. Active games and hikes are the best cure for all diseases.
Periodically you need to visit an ophthalmologist for a preventive examination. This will help identify the problem at an early stage, which will simplify treatment.
About other measurement methods
There are several basic ways to determine eye pressure. The first is palpation, that is, the doctor determines the IOP with his fingers through the patient’s eyelid. It is usually used after surgery, when it is impossible to use special instruments for examination.
Measuring intraocular pressure by palpation
Non-contact method. Obviously, the tonometer in this case does not contact the eye. Indicators of corneal deformation are determined using air pressure. The fastest results can be achieved with computer processing. Local anesthesia is not required and there may be no side effects.
Pneumotonometry
With the contact method, the measuring instrument is in contact with the eye, and therefore, to avoid pain, anesthesia is used. This type of tonometry can be:
applanation. Maklakov weights or a Goldman tonometer are used, very accurate results;
Goldmann applanation tonometer
impressive. Here measurements are made with an Icare or Scholz tonometer. The procedure itself is based on the use of a special rod, which is gently pressed into the cornea. Everything happens quickly and painlessly;
Icare tonometer
contour dynamic. It implies strict adherence to the measurement rules; the results are not as accurate as in the first case. But it has one advantage - it is the individuality of the blood supply.
Dynamic contour tonometer
Features of tonometry according to Maklakov
Despite its age, the maklak method is very accurate, fast and inexpensive. One of the features of its implementation is that it is still a contact method, which means there is a risk of infection.
In addition, many people do not like the touch of a foreign object to the eye. But is this too high a price for an accurate result?
A good alternative to measuring intraocular pressure according to Maklakov is electronography. But since it is done using expensive equipment, which is not available in all clinics, measuring intraocular pressure according to Maklakov is still the most popular.
It should also be remembered that the intraocular pressure measured by Maklakov will be higher than the result in other methods, so they cannot be compared with each other.
Restrictions
- Recent eye surgery
- Allergy to anesthesia
- Inflammatory eye diseases
Evaluation of ophthalmotonometry results
The flatter the patient's cornea, the larger the diameter of the cylinder imprint. And the smaller the diameter of the light circle, the higher the pressure. The diameter of the print is measured with a transparent ruler, and the specialist places it with the scale down to avoid distortion. The ruler has already marked divisions in millimeters of mercury and there is no need to convert anything further.
Equipment and structure of the device
- Two 10 gram cylinders with flat ends made of frosted glass;
- Holder for carrying out the procedure,
- Ruler for measuring the diameter of the print. The Polyak ruler can also be used;
- Case for storing the tonometer.
Treatment of intraocular pressure
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to avoid various complications of increased and decreased eye pressure - atrophy of eye tissue, glaucoma, etc. Doctors strongly recommend measuring eye pressure at least once every three years (for patients over 40 years old).
Treatment of ophthalmotonus depends on the causes that provoked it. If the cause is a certain disease, then only if it is completely cured can the eye pressure be brought back to normal. If the cause is any eye pathology, then an ophthalmologist will deal with the treatment, prescribing the necessary eye drops.
For glaucoma, the doctor prescribes medications designed to reduce eye pressure (pilocarpine, travaprost, Fotil, etc.). Often, during treatment, the ophthalmologist changes the medications used.
When diagnosing inflammatory eye diseases, antibacterial drops are prescribed.
If the cause of the increase in ophthalmotonus was the computer, the so-called. computer vision syndrome, then the doctor prescribes drops that moisturize the eyes (Visine, Ophtolic, etc.). They relieve dryness and fatigue from the eyes. Independent use of such drugs is allowed.
Additionally, eye gymnastics and vitamins necessary for vision are prescribed (blueberry forte, complivit, okuvait, ophthalmo, etc.).
If treatment with medications does not give positive dynamics, then they resort to laser pressure correction or microsurgery.
Drops for eye pressure
Such drugs quite effectively normalize intraocular pressure. They nourish the tissues of the entire eye and remove excess fluid from the eyeball.
In this article you will find out the causes and methods of treatment for pain in the eyes.
Here you will find out what symptoms appear with stye of the eye.
Are you worried about nervous eye tics? Find out the main reasons - https://moezrenie.com/simptomy/dergaetsya-glaz.html
In general, IOP drops are divided into several types:
Prostaglandins – increase the discharge of intraocular fluid (Tafluprost, Xalatan, Travatan). They are quite effective: after instillation, blood pressure noticeably decreases within a couple of hours. Unfortunately, they also have side effects: the color of the iris changes, redness of the eyes, and rapid growth of eyelashes are observed.
Cholinomimetics – contract the eye muscles and constrict the pupil, which significantly increases the amount of outflow of intraocular fluid (Carbocholine, Pilokartin, etc.). They also have side effects: the pupil becomes narrow, which significantly limits the visual field, and also provokes pain in the temples, eyebrows and forehead.
Beta blockers are designed to reduce the amount of fluid produced in the eyeball. The action begins half an hour after instillation (okumed, okumol, timolol, okupress, arutimol, etc.). Side effects of these drugs manifest themselves in the form of: bronchospasm, decreased heart contractions. But there are beta blockers such as Betoptik-s and Betoptik, which have a much less pronounced effect on the heart and respiratory organs.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - designed to reduce the amount of intraocular fluid produced (Trusopt, Azopt, etc.)
Such medications do not have a negative effect on the functioning of the heart and respiratory system, but patients with kidney diseases should use them with extreme caution and only as prescribed by a doctor.
Drug treatment of intraocular pressure can be supplemented with traditional medicine. She offers many different decoctions, compresses, lotions and infusions. The main thing is not to forget about eye hygiene and the treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Problems with eye pressure can lead to serious vision problems or even blindness. Therefore, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist in a timely manner at the slightest deviation in the functioning of the visual organs. Timely treatment and modern diagnostic methods will help return vision to normal.
Video: how to check eye pressure
Measuring intraocular pressure (IOP) Watch video
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials of the article do not encourage self-treatment
Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient. Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
Article updated: 02/07/2020
How is the measurement carried out?
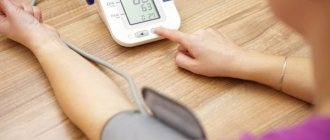
It should be noted that not all people referred for annual preventive examinations to an ophthalmologist are enthusiastic about the upcoming measurement of intraocular pressure. Women may be afraid of ruining carefully applied makeup; men will refer to the absence of any complaints about their own organs of vision. Meanwhile, measuring intraocular pressure is a mandatory procedure for people who have turned 40 or older, even if they assure the doctor that they are in perfect health.
Measuring intraocular pressure is carried out using special equipment and instruments, and in general, modern ophthalmology uses 3 main types of measuring intraocular pressure:
- The above-mentioned method according to Maklakov - many patients remember it, know it and most of all dislike it, since drops are dropped into the eyes, providing local anesthesia, and “weights” are installed (for a very short time), which are quickly removed and lowered onto a clean sheet of paper so that leave imprints indicating the value of IOP. This method is more than 100 years old, but it still has not lost its relevance;
- Pneumotonometry, very similar to Maklakov tonometry, but different in that it uses an air jet. Unfortunately, this study is not particularly accurate;
- Electron diffraction is the most modern method, successfully replacing the previous two. It is used mainly in specialized institutions (not all clinics can yet afford expensive ophthalmological equipment). The method is classified as non-contact, highly accurate and safe research.
Most often in the Russian Federation and neighboring countries, Maklakov tonometry or non-contact tonometry using an electronograph are used.