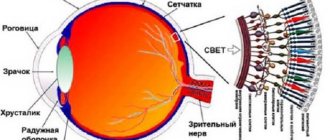
Fluid circulates inside the eye, which puts pressure on the outer shell of the organ of vision.
This phenomenon is called intraocular pressure (abbreviated IOP) and normally ranges from 12-22 mmHg.
When this indicator increases or decreases, it is customary to speak of increased or decreased IOP. Changes may be temporary or permanent.
The causes of deviations can be stress, strong efforts during childbirth, operations, injuries, and taking certain medications. If you suspect a change in IOP or experience symptoms of these conditions, you must promptly consult an ophthalmologist for an accurate diagnosis and prescription of comprehensive treatment. You should also not neglect measures to prevent increased or decreased IOP.
What is eye pressure?
What is eye pressure?
Source: Mon-mari.ru The eye is a hydrodynamic system. This means that intraocular fluid is constantly produced and excreted inside the eye. Intraocular pressure is the pressure that the inside of the eye exerts on the outer layer of the eye.
Eye pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). The normal range of eye pressure is from 12-22 mm Hg. Intraocular pressure is greater than 22 mm Hg. considered above normal.
When IOP is higher than normal but a person has no other signs of glaucoma, the condition is called ocular hypertension. If the intraocular pressure is less than 8 mmHg, then this condition is called ocular hypotony.
Doctors advise measuring eye pressure regularly, because it can reliably indicate the normal functioning of your visual system or warn of visual impairment. Moreover, both an increase and a decrease in pressure inside the eyeball is a bad sign.
Since it is the normal value of this indicator that contributes to the correct distribution of nutrients throughout the tissues and parts of the eye.
Symptom of "pressure in the eyes"
Often, patient complaints of distension in the eyeball, pain and discomfort are not associated with increased intraocular pressure. This condition is often observed with neurological diseases, increased blood pressure or, conversely, decreased blood pressure, general inflammatory diseases or other eye diseases.
Office workers who spend all day in front of the computer are frequent patients of the ophthalmologist who complain of a feeling of pressure in the eyes. This is due to visual fatigue and dry eyes (the so-called “Computer Vision Syndrome”).
The insidiousness of the disease is that at the initial stage it does not manifest itself in any way. The patient does not experience discomfort for a long time until the pathology causes serious changes.
Many people who experience burning, redness, or dry eyes mistake this as a symptom of fatigue. That's why they are in no hurry to see a doctor.
Quite often, the pathology is accompanied by headache and discomfort in the eyes. However, they get tired quickly. A person experiences unpleasant sensations when working at a computer or reading for a long time.
In addition, symptoms of high eye pressure include blurred vision. It decreases especially strongly in the evenings. Many people experience spots and spots before their eyes. Sometimes peripheral vision decreases.
The listed symptoms may indicate the occurrence of glaucoma. When blood pressure rises, acute attacks often occur. They are characterized by such manifestations as severe discomfort in the eyes, headaches, and nausea.
The pressure level increases significantly, and the quality of vision suffers. If these symptoms of high eye pressure appear, you should call an ambulance.
Heaviness in the eyes is the main sign of high intraocular pressure. And this is especially felt when a person presses his fingers on closed eyelids. Then you just feel fullness in your eyes. Patients feel the problem very acutely against the background of other diseases. We are talking about runny nose, colds, headaches.
It is worth knowing that normal intraocular pressure ranges from 16 to 26 millimeters of mercury. The norms vary slightly depending on age. If malfunctions occur in the human body, their result may be an increase in the secretion of ocular fluid and the pressure inside the eyes.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
An increase in intraocular pressure occurs due to the influence of such pathogenic factors:
- increased stress on the organ of vision (for example, prolonged viewing of TV shows or reading in poor lighting conditions);
- unfavorable family predisposition;
- pathological changes in the organ of vision;
- diseases of internal organs;
- chemical intoxication;
- imbalance of hormones;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- using certain eye drops;
- violation of the integrity of the eye membranes;
- prolonged stress;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- in women – menstrual irregularities, menopause;
- smoking;
- drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages;
- insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals into the body.
Reasons for decreased IOP:
- hypotension;
- retinal disinsertion;
- inflammation of the iris;
- dehydration;
- keratitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- blepharitis.
If low pressure inside the eye persists for more than a month, the nutrition of the eye may be disrupted, retinal detachment, optic nerve dystrophy and, as a result, complete blindness. The patient needs to urgently come to see a doctor if a halo appears when looking at a bright light.
Reasons for change
Slight changes in eye pressure from one season to the next, or even within one day, are normal.
Intraocular pressure changes with changes in heart rate or breathing, and may also be affected by exercise and fluid intake.
Intraocular pressure may be affected by exercise and fluid intake. Temporary changes in intraocular pressure may be caused by excessive alcohol consumption and caffeine use, coughing, vomiting, or straining from heavy lifting.
Persistent changes in IOP are caused by other reasons. There are several main reasons for persistent changes in IOP:
- Excessive or insufficient production of intraocular fluid.
- Excessive or insufficient drainage of intraocular fluid.
- Some medications may have a side effect that results in increased IOP. For example, steroid medications used to treat asthma and other conditions increase the risk of developing ocular hypertension.
- Eye injuries.
- Other eye diseases (pseudoexfoliation syndrome, chronic inflammatory diseases of the eye, retinal detachment, etc.).
- Eye surgeries.
Consequences of increased and decreased intraocular pressure
With increased intraocular pressure, the production and circulation of intraocular fluid is disrupted. This provokes the development of glaucoma. If the condition is not diagnosed in a timely manner, consequences occur - death of the optic nerve, loss of vision, disability.
With reduced intraocular pressure, the eyeball shrinks and atrophies. As a result, the functionality and processes in the vitreous body are disrupted, and blindness occurs.
Any change in IOP that is permanent and persistent is dangerous and can lead to a sharp deterioration of vision and blindness.
Kinds
There are several types of increased pressure inside the eyes:
- The transient type is caused by a short-term change in the indicator and its subsequent return to normal.
- Labile pressure also changes temporarily with subsequent normalization, but such changes occur regularly.
- Stable high blood pressure is constant, making it the greatest danger to humans.
- The reasons for such phenomena can be a lot from hypertension or excessive load on the eyeball, to stress or nervous strain.
- Also, the root cause of increased eye pressure may well be the presence of heart failure or dysfunction of the genitourinary system in the patient.
A disorder of the endocrine system or age-related changes in the body (mainly menopause in women) can also provoke such a pathology. And sometimes the cause of a sharp increase in pressure inside the eyeball can even be poisoning with certain types of chemicals.
Increased
This indicator changes under the influence of various factors. The main causes of high eye pressure include the following:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the body of various types. These problems lead to increased production of natural fluids in the organ of vision.
- Violations of the functions of the heart and blood vessels. In this case, not only blood pressure increases, but also eye pressure.
- Stress, physical or intellectual tension.
- Consequences of complex pathologies.
- Anatomical eye lesions.
People who have atherosclerosis or farsightedness should pay special attention to the health of their vision. The same applies to those whose immediate relatives had such disorders.
Many people are interested in whether eye pressure can affect blood pressure. Usually the opposite situation is observed, when transient intraocular pressure becomes the result of a jump in arterial pressure.
The cause of this condition may be ordinary fatigue associated with prolonged work at the computer or watching TV.
People with obesity and cardiovascular diseases who have a genetic predisposition to the disease are always at risk. Its symptoms depend on the intensity of the increase in pressure. If the excess of the norm is insignificant, then the condition may not manifest itself in any way.
Persistently increased pressure inside the eye is called “Glaucoma” (a disease in which, without treatment, there is a persistent decrease in vision, up to blindness). With a slight increase in indicators, the patient practically does not notice the disease until the eye becomes visually impaired or blind.
Glaucoma most often develops in people over 40 years of age (especially with unfavorable heredity - when there are relatives with such a diagnosis in the family).
Therefore, all people over 40 years of age are recommended to visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year for an examination and measurement of eye pressure.
In addition, the pressure inside the eye may not increase steadily, but under the influence of any internal or external factors (taking medications, against the background of increased blood pressure, endocrine diseases).
In this case, they speak of “ophthalmic hypertension.” As a rule, intensive eye treatment is not carried out in this case, limited to observation by an ophthalmologist and elimination of the cause that caused this condition.
Main symptoms of elevated IOP:
- headaches and eye pain; decreased field of vision
- blurred vision;
- cloudy picture before the eyes;
- poor vision at dusk and in the dark;
- decreased lateral vision, decreased field of vision.
Increased ophthalmotonus is divided into three types:
- transient, in which the pressure rises for a short period of time, and then returns to normal on its own;
- labile, in which the pressure rises briefly and then becomes normal, but this happens periodically;
- stable ophthalmotonus, in which high blood pressure becomes chronic and progresses.
In this case, treatment comes down primarily to rest and a change of environment.
Increased eye pressure is very insidious: it can be either short-term in nature and in this case does not pose a serious threat to human health, or permanent, when it can cause complete loss of vision.
That is why it is very important to carefully monitor your sensations and at the first signs of increased eye pressure, contact a specialist who will help determine the cause of the development of the pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Important
In order not to miss precious time and seek help in a timely manner, you need to know at least about the main symptoms of high eye pressure.
Increased eye pressure is difficult to detect at first; it is asymptomatic, but gradually the person begins to complain of fatigue, heaviness in the eyes, redness of the eyelids, throbbing pain in the temples, and so on.
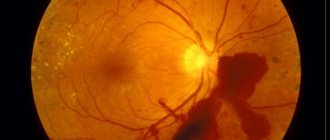
Quite often, an increase in pressure in the eye leads to the destruction of the cells that make up the retina and negatively affects the metabolic processes of the eyeball.
This condition is extremely dangerous for the patient, as it gradually changes the normal functioning of the visual apparatus and can provoke the development of various diseases.
Sometimes an increase in this indicator accompanies the development of glaucoma. Considering the fact that with such a disease, the filtration angle of the visual apparatus changes, a gradual increase in eye pressure within the departments of the visual system is understandable.
Initially, the angle of vision narrows, and then can close completely. By the way, such signs of pressure are accompanied by a drop in visual acuity and pain inside the eye.
Decreased
Hypotension is characterized by the fact that the level of pressure on the eye decreases to 10 mmHg. column and below. This is a dangerous phenomenon and can lead to complete loss of vision. Its first sign is a sharp deterioration in vision.
In case of decreased ophthalmotonus, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will identify the cause of the disease and prescribe treatment.
The reasons for low IOP are:
- retinal detachment;
- eye injuries, foreign bodies entering the eye;
- low blood pressure;
- Eyes hurt
- eye inflammation;
- liver problems;
- infectious diseases such as cholera, dysentery;
- hereditary predisposition, poorly developed eyeball;
- consequences of surgery;
- diabetes.
If a person suffers from low blood pressure, then he should constantly measure his blood pressure, regulate it, and treat it, since the IOP immediately decreases, and this can ultimately lead to loss of vision.
Patients with diabetes are also at risk. Since the level of sugar in the blood regulates all metabolic processes in the body, if there is a sharp jump in sugar levels, the patient can fall into a diabetic coma, while all body functions fail, including blood pressure.
When a foreign body enters the eyeball, vision deteriorates sharply, low intraocular pressure occurs, and atrophy of the eyeball often occurs, so you should immediately consult a doctor and take care of your eyes.
Often, reduced IOP does not manifest itself in any way, so people begin to see a doctor when their vision sharply decreases, which complicates treatment. But there are several signs by which one can guess the presence of this disease in the body.
For example, the eye becomes dry, loses its shine, blinking causes some inconvenience, and all these symptoms appear suddenly and unexpectedly. But the most dangerous factor is diabetes, so people should have their eyes checked regularly by an ophthalmologist.
Prevention of IOP
Prevention is aimed at:
- improvement of aqueous humor circulation;
- preventing fluctuations in intraocular pressure;
- preventing the occurrence of glaucoma and vision loss.
It is helpful to follow these guidelines.
- Do gymnastics and warm-up for the eyes, especially when working at the computer for a long time, excessive strain on the visual system. The simplest exercises are to look without turning your head, up and down, left and right, and blink. You can look at objects in the distance, then switch to nearby objects.
- Take multivitamin complexes designed to improve the functioning of the organ of vision. Enrich your daily diet with healthy vitamins and minerals, include carrots, fatty fish, and blueberries.
- Be outdoors every day and do exercises or choose any other physical activity you like.
- At least twice a year, undergo preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist, have your vision checked and measure intraocular pressure.
- After any operations on the organ of vision, adhere to the recommendations and restrictions of the specialist, instill the prescribed drops, take multivitamin complexes.
- Monitor blood sugar and pressure levels, heart and kidney function.
- When the first alarming symptoms appear, contact the clinic to diagnose the condition, determine the cause and prescribe comprehensive treatment.
- If you work at the computer for a long time, choose special glasses and moisturizing drops. Farsightedness and astigmatism also require correction.
Symptoms
Source: serdcedoc.com Symptoms of eye pressure will depend on the intensity of the increase in this indicator.
If the changes are minor, then external signs may be absent altogether. When the deviation from the norm grows, the patient may notice the presence of headaches, often in the temporal region, pain when moving the eyeball and increased fatigue in general.
Often, discomfort becomes especially noticeable when working in front of a computer monitor or when reading printed materials written in small print.
In especially severe cases, all of the above symptoms may be accompanied by visual disturbances or redness of the eyes. Although redness may indicate other diseases of the visual system.
With labile and stable ophthalmotonus, the cause may be impaired renal function, failure of the genitourinary system, cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
It can be difficult to fully understand the cause of IOP; women during menopause are also vulnerable to any disease, including this one. Often people suffer from this disease when poisoned by various poisons, when working with toxic substances, with eye and head injuries, and so on.
With low blood pressure, without proper treatment, the eyeball changes, it shrinks, the activity of the vitreous body is disrupted, and this also leads to blindness. As with any other disease, it is better to prevent it.
To do this, you need to consult with an ophthalmologist, and in case of pathology, the doctor will prescribe complex treatment, which must be strictly followed.
How dangerous is the problem?
The reasons for pressure deviations from the norm are most often associated with various diseases of the visual organ. The most dangerous is glaucoma, complete loss of vision. Therefore, it is not a harmless vision defect.
With a stable increase in pressure, changes occur in the cells and vessels of the fundus of the eye, and metabolic processes change. This poses a great danger to human health. This hides the causes of various diseases that can lead to serious complications: complete loss of vision, irreversible changes in the structure of the visual system.
Eye pressure standards
Source: lechusdoma.ru It is worth mentioning the norms of eye pressure - its value is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and depends on the method by which a specialist determines this value (the study is called “tonometry”).
The most widely used method today is “pneumotonometry” - measuring intraocular pressure using special equipment that acts on the human eye with a stream of air. In this case, there is no contact with the surface of the eye, there is no likelihood of infection and no discomfort on the part of the patient.
The value of eye pressure obtained in this way ranges from 10 to 21 mmHg. (depending on the measuring instrument manufacturer).
Another common way to measure eye pressure is using weights (according to Maklakov). The method is more accurate, but requires the use of anesthetics (an allergic reaction may develop) and contact of loads with the surface of the eye (there is a possibility of infection).
Normal values of eye pressure with this measurement method are from 15 to 26 mmHg. There are also other methods, but they are not so common.
The reason for the balance change may be:
- Application of various measurement techniques;
- Age;
- Measurement time;
- Hypertonic disease;
- High strain on the eyes.
Sometimes increased eye pressure is normal. In such a situation, an increase is observed in the morning, and by lunchtime the indicators become normal. The lowest pressure is observed at night.
It is also worth remembering that this indicator differs from person to person. But if the error exceeds 5 mmHg, this is an alarming symptom.
Complications
Intraocular pressure allows the eyes to function normally while maintaining their natural appearance and clarity of vision. In adults after 40 years of age, the likelihood of developing pathology increases. If deviations from the norm develop, symptoms and treatment are ignored, the following complications may develop (discussed in the table).
Table:
| List of complications | Characteristic |
| Malnutrition of eye tissues | When IOP changes, vascular constriction is possible, as a result, the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the tissues will be limited. |
| Deformation of eye tissue | When IOP increases/decreases, tissue stretches or contracts. If left untreated, the tissue may not return to its natural position. |
| Optic nerve clamp | Occurs when elevated IOP is advanced. Complete blindness may develop. |
| Headache | Occurs due to a violation of the condition of blood vessels. The symptom can be temporarily eliminated with tablets. |
The main and most dangerous complication is irreversible visual impairment or complete blindness due to tissue disruption.
Diagnostic methods
Source: 169562-ua.all.biz To identify symptoms of high eye pressure in adults, a number of procedures are performed:
- Maklakov tonometer. Palpation.
An experienced ophthalmologist can detect increased pressure by palpating through the eyelids.
Maklakov tonometer. Using this method, the specialist applies a droplet of anesthetic, after which he applies a metal weight weighing 5-10 g to the cornea. Then an imprint appears on the weight. It is transferred to special paper with a scale. Depending on the size of this imprint, the pressure is estimated.
- Non-contact tonometry.
This method does not involve contact with the eye cornea. Measuring eye pressure is called tonometry. There are two types of tonometry:
- Contact tonometry
- Non-contact tonometry
If, as a result of tonometry, you have a decreased or increased IOP, you may need additional eye examination to identify the causes of these changes.
Normal IOP in children
The normal intraocular pressure in children is the same in both sexes. For young patients, it is allowed to use tonometry to determine the indicator of eye functioning in question.
Parents need to pay attention to their child's behavior. When intraocular pressure changes, the child may experience heaviness in the eyes, pain in the head, and feel tired. Fatigue is especially noticeable in the evening.
At the first symptoms of increased ophthalmic tone in a child, he should be urgently shown to a pediatrician or ophthalmologist. After measuring the IOP value, he will develop further measures. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that glaucoma develops extremely rarely in children. An increase in IOP in young children often indicates a malfunction of the thyroid gland.
We recommend reading: Eye pressure in children
Treatment of the symptom of “eye pressure”
To eliminate pathology, various methods are used - it depends on the stage of the pathology. Exercises for the eyes When the function of the organ of vision is preserved, available means are used. The patient must systematically perform the following actions:
- Do eye exercises;
- Use special moisturizing drops;
- Avoid traumatic sports;
- Wear safety glasses;
- Reduce time spent working at the computer and watching TV;
- Avoid activities that require eye strain.
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause of the patient's complaints. If the pathology is in the eyes, then it is dealt with by an ophthalmologist (glaucoma, inflammatory diseases, etc.) - and, as a rule, appropriate eye drops are prescribed.
For glaucoma - drugs that reduce intraocular pressure, for inflammatory diseases - antibacterial eye drops. If we are talking about computer vision syndrome - moisturizing eye drops, vitamins for vision, gymnastics.
Physiotherapeutic effects on the eyes are just as good at relieving the sensation of eye pressure and helping to preserve visual function in case of a true increase in pressure (glaucoma).
The most advanced portable eye devices at the moment are “Sidorenko Glasses” - a device that can be used at home and combines 4 methods of influence at once - color pulse therapy, phonophoresis, vacuum massage and infrasound.
Only a specialist can determine the cause that caused the sensation of “eye pressure”. He also prescribes treatment. Therefore, if you have these complaints, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist.
Important
When choosing an eye clinic, it is a good idea to pay attention to the level of specialists and equipment, which will allow you to identify the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment. This allows you to avoid complications and quickly solve the problem.
It is important to choose an eye clinic where they will really help you, and not “brush off” or “pull” money without solving the problem.
Fluctuations in intraocular pressure that do not affect vision do not require drug treatment. Anti-pressure eye drops are used in cases of ocular hypertension or hypotension. Topical treatment in the form of eye pressure drops is often the first resort to normalize eye pressure.
Anti-pressure eye drops are often the first choice to normalize the pressure inside the eye.
Patients with severe and persistent changes in intraocular pressure require surgical treatment options. This can be either laser surgery or intraocular surgery. Basically, the choice of treatment depends on the cause that led to the change in eye pressure.
Eye hypertension should be treated first of all by finding out the cause of its occurrence. So if the patient’s main disease is the cardiovascular system and so on, then it must be brought back to normal.
If the cause of increased ophthalmotonia is an eye disease, the doctor will prescribe treatment. For glaucoma, the doctor prescribes drugs such as pilocarpine, travoprost and others. For eye inflammation, the ophthalmologist prescribes antibacterial drops.
If you constantly sit in front of the computer, that is, computer syndrome manifests itself, the doctor prescribes moisturizing drops, such as Visine, Ophtolic and others. They relieve eye fatigue, moisturize them, and can also be used independently.
Eye gymnastics and vitamins are used as aids. In case of advanced disease, the patient is prescribed a microsurgical operation or treated with a laser.
Treatment of eye pressure directly depends on the causes that provoked it. Often, drops come to the rescue that can increase the outflow of fluid and provide the eye tissue with additional nutrition.
If drug therapy cannot solve this problem and shows its complete failure, then the patient may be prescribed laser pressure correction. Sometimes microsurgical intervention is quite effective.
Useful video
5 interesting facts about intraocular pressure. The doctor talks about the importance of measuring and early diagnosing deviations in IOP indicators and the possible serious consequences.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 7 ratings, average: 4.43 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Drug therapy
Source: gipertenziya.info In addition to the listed methods, medications and lifestyle correction are used.
Doctors prescribe special drops for high eye pressure. Such substances improve the outflow of fluid and fill the eyes with nutrients. This allows you to cope with the problem at the initial stage of its development. Today there are many different drugs. However, doctors do not advise self-medication. That is why it is so important to contact an ophthalmologist in time, who will select the medicine.
Eye drops to reduce high blood pressure are divided into several groups:
- Carbanhydrase inhibitors (Azopt, Trusopt, etc.) Reduce the production of intraocular fluid. Possible side effects of these pressure eye drops: burning after instillation, redness of the eyes, bitter taste in the mouth.
- Prostaglandins (travatan, xalatan, taflotan, etc.) Increase the outflow of intraocular fluid. Side effects: darkening of the iris, lengthening of eyelashes.
- Beta blockers (Timolol, Betaxolol) Reduce the production of intraocular fluid. As a rule, they are prescribed together with prostaglandins. These pressure eye drops may affect your heart rate. May cause unwanted side effects in people with diabetes.
- Miotics are drugs that reduce the diameter of the pupil and thereby improve the outflow of intraocular fluid. One of the most prescribed drugs in this group by ophthalmologists is pilocarpine.
- Combined drugs that reduce the production of ocular fluid and increase the outflow - proxofeline.
All drops that reduce intraocular pressure (especially beta blockers) can cause complications. Therefore, these drops (antiglaucoma) should only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
A qualified specialist will not only prescribe drops taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, but will also monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
With increased eye pressure, drops are intended to drain excess fluid from the eye, and they also nourish the eye with useful substances.
These include prostaglandins such as:
- Travatan
- Tafluprost;
- Xalatan;
- Travatan.
These drops are quite popular as they are effective on the eye, but have side effects. With prolonged use of drops, the patient's pupil narrows, therefore the field of vision decreases, and pain in the temples and frontal parts may occur.
There are also a number of drugs aimed at improving vision, these include carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Trusop, Azop. They do not cause adverse reactions, but can negatively affect the functioning of the kidneys, so these drops should only be used as prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Symptoms of high and low IOP
In the initial form of development of the pathology, symptoms may be mild. Therefore, after 40 years and if there is a predisposition, it is recommended to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist at least once every 6 months.
A change in intraocular pressure may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
| Increased IOP | Reduced IOP |
| Severe headache in the temporal region | Increased dryness in the eyes, expressed by a lack of shine |
| Pain with eye movements (up, down, sides) | Feeling of sand in the eyes |
| Feeling of squeezing and heaviness in the eyes | When rubbing the eyelids, the eyeball feels softer to the touch |
| Increased tear production | Eyes look sunken |
| Bulging of the iris or cornea | The pupil reacts sluggishly to bright light |
General symptoms:
- rapid eye fatigue is felt even with light load;
- decreased quality of vision, deterioration can progress quickly;
- feeling of an invisible film before the eyes;
- at night, the eyes do not distinguish the contours of objects;
- the appearance of spots or circles before the eyes;
- impaired lateral vision;
- in advanced form there is nausea and vomiting for no reason.
Due to the disruption of the blood vessels, redness of the whites of the eyes may occur.
Surgery
If the disease has led to serious eye damage, radical treatment methods are needed. If eye pressure increases, surgical intervention is prescribed. Today, several types of operations are known:
- Excision of the iris using a laser;
- Laser stretching of trabeculae.
Thanks to such interventions, it is possible to normalize the outflow of fluid, which normalizes blood pressure.
In advanced cases, glaucoma develops. However, thanks to modern methods, it is possible to provide the patient with a normal lifestyle. If a person does not take any measures for a long time, there is a risk of developing dangerous pathologies of the organ of vision.
One of these disorders is optic nerve atrophy. This phenomenon is characterized by deterioration of vision, which subsequently leads to complete blindness. Dangerous complications include detachment or complete rupture of the retina, which requires surgical intervention.
A little about ocular hypertension and glaucoma
Increased eye pressure not caused by glaucoma is called ocular hypertension. The exact cause of the development of this syndrome cannot be determined at the moment. However, it has been proven that the main reasons for changes in pressure fluctuations inside the eye are: nervous and physical stress, hereditary and age factors, diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The condition of ocular hypertension is conventionally divided into symptomatic and pseudohypertension. The first develops when various eye diseases are not treated in a timely manner, when high blood pressure becomes the norm. Pseudohypertension is a rare phenomenon. Caused by incorrect patient behavior during measurement or any technical errors.
The development of persistent glaucoma is accompanied by prolonged high eye pressure. Treating the disease is long and difficult. Accompanied by a narrowing of the angle of vision, a decrease in acuity, and pain in the visual system.
- Angle-closure glaucoma - compresses the tubules that provide fluid removal in the drainage system of the eye.
- Open-angle glaucoma - there is a violation of the drainage system of the eye due to deterioration in functioning. The course of the disease may not bother a person and may be detected in the later stages.
With glaucoma, IOP is constantly elevated, which negatively affects eye function and leads to irreversible processes: optic nerve atrophy, retinal detachment, and complete loss of vision.
Traditional methods
Source: Linza.Guru Not all people accept traditional methods of treating intraocular pressure. There is a category of patients who agree to be treated much longer, but without the use of any type of intervention. They prefer traditional medicine. There are several techniques in the arsenal of traditional medicine that help normalize blood pressure:
- Pour boiling water over the meadow clover and leave to infuse. Take every day at night.
- Mix crushed purple flowers of the golden mustache with vodka. Infuse the medicine for a couple of weeks, shaking the mixture regularly. Take 1 dessert spoon on an empty stomach.
- It is useful to use kefir with the addition of cinnamon. This simple remedy can help reduce high eye pressure.
- Golden mustache. It is necessary to pour 500 milliliters of vodka into 20 crushed tendrils and leave for 12 days. The tincture must be shaken daily. Take the strained medicine every day on an empty stomach, one dessert spoon.
- Blueberry. When working at the computer for a long time, take a 5-minute break every hour. At this time, you can do eye exercises or massage your eyelids.
- Regularly eat blueberries, carrots, and fish.
- Exercise.
- Take eye vitamins regularly.
- Visit an ophthalmologist once a year.
Increased eye pressure leads to dangerous complications. With the development of glaucoma, a person can completely lose vision. Therefore, the very first symptoms of discomfort in the eyes should be the basis for a visit to an ophthalmologist, who will tell you what to do if you have high eye pressure.
To prevent eye disease, a person needs to avoid visual fatigue. This is especially true for people who spend most of their time in front of a computer. For good vision, exercise your eyes for at least one hour a day.
Then check your diet. The food should contain vitamins and minerals, and exclude foods with high amounts of cholesterol. A number of healthy foods include carrots, blueberries, sea fish, watermelon, and so on.
Risk group
High IOP most often worries the following categories of people with certain pathologies and diseases:
- atherosclerosis, hypertension, increased blood pressure, various heart and vascular diseases;
- farsightedness, astigmatism;
- complicated heredity or predisposition;
- severe stress and emotional outbursts, instability;
- eye strain, long periods of work at the computer;
- chemical poisoning;
- chronic kidney disease.
In adults over 60 years of age, increased IOP is a sign of glaucoma.
A decrease in IOP occurs for other reasons:
- dehydration, infectious processes;
- eye injuries;
- getting foreign objects into the eyes;
- retinal detachment caused by various factors;
- inflammatory process occurring in the eyeball;
- diabetes mellitus in the acute stage;
- low blood pressure and development of hypertension.
Measurement techniques
Intraocular pressure can be determined using several methods, which differ in the use of different devices or substances.
For example:
- according to Maklakov. To carry out the procedure, anesthetic drops are instilled into the eyes. When the anesthetic composition begins to take effect, cylindrical weights are placed on the eyes (for a short time). Next, they are placed on a clean sheet of paper, the diameter of the resulting prints indicates the IOP indicator;
- visual inspection and palpation . The doctor evaluates the visual condition of the eye tissues. After this, the patient closes his eyes, and the specialist lightly presses the index fingers of both hands on the eyeball from different sides. By the compliance of pressure, the ophthalmologist can determine whether there are deviations from the norm (it is impossible to obtain exact values). If the manipulation process requires effort, then the indicator is increased; if the fingers easily press through the sclera (the outer protective membrane of the eye), then the indicator is lowered. With a normal value, the specialist feels small impulses when pressing;
- fundus ophthalmoscopy . To measure pressure, special devices are used that allow you to assess the condition of the fundus, retina and blood vessels. Depending on the type of device used, diagnostics can be carried out in different ways (direct, using a Goldmann lens or laser);
- pneumotonometry. Refers to hardware methods. The patient sits in front of the device and focuses his gaze on the target designated by the doctor. After this, a small stream of air is supplied from the device to the eye, which puts pressure on the eye tissues and allows you to determine the IOP value;
- perimetry . The ophthalmologist determines the increase/decrease in intraocular pressure by assessing the patient’s ability to perform perimetric vision. To do this, during the examination you need to concentrate your gaze on one point, which the ophthalmologist then gradually moves to the right/left and up/down. The procedure is carried out alternately on both eyes.;
- impressive _ Intraocular pressure is measured using a special rod that penetrates the eye tissue through the pupil. This method is the most accurate.
The choice of IOP measurement method is determined by the ophthalmologist after a visual examination of the ocular tissues. To obtain accurate readings, it is recommended to take several measurements at different hours.