Among the group of skin diseases, dermatitis of various etiologies is most common. The epidermis in individual patients may be highly susceptible to endogenous and exogenous factors, provoking the development of inflammation and rashes. This leads to a deterioration in the appearance of the skin and the general condition of the body.
Almost every third person has encountered this pathology after contact with any allergen or other irritant. Many suffer from this disorder on a chronic basis. The course of the skin disease is replaced by phases of exacerbation of symptoms and their subsidence. Dermatitis combines a large group of autoimmune disorders and infectious diseases that have their own distinctive characteristics. The article talks about dermatitis photo symptoms and treatment in adults.
Causes
The main types/forms of the skin disease in question can develop for distant and close reasons. The first category of reasons includes predisposition:
| Acquired | We are talking about those patients who suffered atopic dermatitis in childhood - they develop a predisposition to the occurrence of various types and forms of the skin disease in question. Moreover, the parents never had a history of dermatitis. |
| Genetic | according to statistics, parents diagnosed with dermatitis of any form give birth to children with the same disease in 96% of cases, but if only one parent has this skin disease, then this probability is only 58% |
Related causes of dermatitis (they are also classified as provoked):
- the entry into the blood of irritants that can cause dermatitis - chemicals, pollen, food, medications, etc.
- stressful condition. Many are sure that stress is a simple ailment that quickly goes away after proper rest. In fact, a stressful state is a complex protective reaction of the body, which occurs under the influence of hormones.
Even if irritants enter the blood, this does not mean the immediate development of dermatitis - it is necessary that favorable factors be present:
- high air temperature;
- severely weakened immunity - for example, against the background of a long-term illness;
- receiving radiation - for example, from the sun or quartz lamps;
- prolonged exposure to cold on the skin - for example, dermatitis may appear after not wearing gloves during a cold winter.
[adsen]
Prevention
To prevent or minimize the occurrence of dermatitis, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- giving up bad habits - alcohol, smoking;
- normalize your rest/sleep schedule;
- try to eat right, especially eat foods enriched with vitamins;
- lead an active lifestyle, do exercises, walk more, ride a bike;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoid stress;
- follow all safety rules when working with aggressive chemicals and in unfavorable environments;
- use sunscreen;
- Do not leave untreated illnesses to chance.
Classification
Depending on the cause of development, the following types of dermatitis are distinguished.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic pathology of the skin rich in sebaceous glands, resulting from the activation of the opportunistic lipophilic yeast fungus Malassezia furfur.
- Photodermatitis is a skin rash that occurs due to increased sensitivity to sunlight (visible light rays and UV radiation).
- Allergic contact dermatitis is a classic delayed-type reaction that develops due to the body's increased sensitivity to the allergen and the involvement of T-lymphocytes in the immune process.
- Simple contact dermatitis is an immediate skin reaction that occurs when directly exposed to an irritating agent.
- Toxic-allergic dermatitis (toxidermia) is an acute inflammation of the skin that occurs under the influence of a toxic allergenic agent that enters the body through the digestive, respiratory tract or by injection.
- Atopic dermatitis is a chronic polyetiological skin pathology that is inherited.
People who are in a constant state of stress are more susceptible to the disease. Those with dry skin are also at risk, especially in windy and cold weather.
What it is?
In simple words, dermatitis is a skin disease caused by external or internal (physical, chemical, biological) agents, often due to hereditary predisposition and stress. Dermatitis is manifested by local and general reactions. Depending on the nature and severity of the pathogenesis, the disease is accompanied by a decrease in skin functions and disruption of the body’s homeostasis.
Factors of pathogenic influence in dermatitis:
- Stress. In the stage of exhaustion of adaptive reactions, stress can be the only factor against the background of unstable health (hereditary predisposition, weak immunity) or combined with other factors of pathogenic influence;
- Contact. Burns (thermal, chemical, solar, allergic), frostbite - all this provokes contact dermatitis;
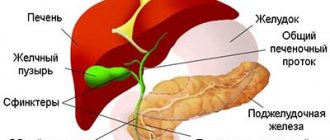
- Penetration. The pathogen enters the blood through the digestive tract, respiratory system or parenterally (subcutaneously, intramuscularly, intravenously) - then atopic dermatitis develops.
Dermatitis is a term that unites a wide variety of skin diseases into a common nosological group. In textbooks on medical dermatology, skin diseases are designated as predominantly local (dermatitis) or systemic (toxidermia, dermatoses). However, there is almost always a relationship between local and general diseases.
Symptoms of dermatitis
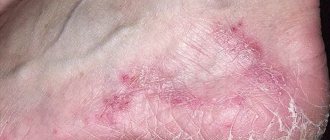
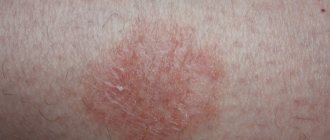
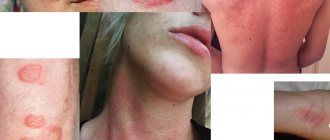
For each of the above types of dermatitis in adults, characteristic symptoms have been identified (see photo). But doctors also identify several common signs that will be characteristic of each of the existing types of disease:
- Redness (erythema). Erythema is increased blood filling of the dermal capillaries. In the acute form, redness with unclear edges and swelling is observed. For chronic dermatitis, erythema is not necessary. When pressed, the area of hyperemic skin turns pale for a while. Erythema should not be confused with hemorrhage (bleeding under the skin). Hemorrhage is considered as a separate manifestation of skin pathologies - hemorrhagic diathesis;
- Itching (prurigo). Its intensity depends on the strength of irritation of the skin nerve endings. The discrepancy between the strength of prurigo and skin manifestations (severe itching with minor rashes) is a sign of allergy in atopic dermatitis. With contact dermatitis, itching at the site of application of the pathogen is adequate to the damage;
- Exudation. In acute forms of dermatitis, exudative inflammation with copious discharge is possible. In chronic forms - lichenification (thickening of skin areas with a rough pattern), cracks in the skin and excoriation (self-scratching);
- Peeling of the skin (desquamation). Pathological desquamation is caused by increased dryness (xerosis) of the skin due to dehydration and insufficiency of the sebaceous glands. Desquamation and xerosis are observed in chronic dermatitis with allergic and inflammatory processes.
- Rash (eczema). The morphology of the rash and its localization are typical for specific dermatitis. The most common localization of rashes is moving parts of the body (skin over joints), face, scalp, sides of the body, groin area.
Additional symptoms are important in the differential diagnosis of specific dermatitis; they are identified during questioning, examination, laboratory tests and functional tests.
Drying ointments
At the stage of the weeping process, ointments and creams for dermatitis with a drying effect are used. Products containing zinc, sulfur, tar, ichthyol, acetylsalicylic acid and other substances have this effect. These include:
- Tsindol;
- Zinc ointment;
- Naftaderm;
- Coloidin;
- Desitin et al.
These drugs also have an antiseptic, antifungal effect, reduce itching, and normalize the processes of keratinization of the skin.
Atopic dermatitis
The pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis is based on genetically determined features of the immune response. Most often, the disease develops in children with a hereditary predisposition between the ages of 1 and 5 years.
The development of the pathological process is provoked by food products (proteins of animal and plant origin), stress and other unfavorable exogenous factors, UV radiation, as well as aggressive meteorological influences.
Atopic dermatitis occurs with periods of exacerbations and remissions and is characterized by the development of skin inflammatory reactions, increased reactivity to various irritants, itching and rashes. The disease begins in early childhood, but over time its clinical manifestations weaken, and by the age of 30-40 a spontaneous cure occurs, or symptoms regress.
Forecast
It is impossible to say definitively how the disease will develop. This depends on many factors: the age and lifestyle of the patient, the duration and stage of the disease, and the spread of the process. The type of dermatitis plays an extremely important role. There are diseases that almost never recur (for example, simple contact dermatitis), and there are those that often become chronic (for example, allergic and atopic dermatitis).
The prognosis of the disease is favorable if the patient consults a qualified specialist in time, who makes the correct diagnosis, finds the cause of dermatitis and prescribes treatment. The patient must follow all instructions and lead a healthy lifestyle. In this case, dermatitis may go away without a trace.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis, which can be seen in the photo on the Internet:
- red plaques with clear boundaries (with dry dermatitis);
- high blood supply to the dermal capillaries (erythema);
- weeping in the groin, behind the ears;
- the appearance of cracks, serous crusts;
- exudative inflammation;
- itchy dermatitis;
- uneven peeling on the head, dandruff, alopecia;
- damage to large areas of skin in severe cases;
- the occurrence of other types of eczema (ear dermatitis and others).
Inflammation of the skin as a result of high secretion of altered sebum or after exposure to microbes is called seborrheic or fungal dermatitis. It is not a contagious disease and therefore cannot be transmitted from person to person. The activity of opportunistic fungi manifests itself under stress, endocrine or immune disorders, and various forms of damage to the nervous system. They concentrate on areas of the skin inhabited by sebaceous glands: face, chest, back, ears, head.
Emollient ointments
Emollient ointment for skin dermatitis will not only help reduce itching, but also promote rapid healing of the skin, relieve inflammation, and eliminate dryness and cracks. Such means include:
- Bepanten;
- Panthenol;
- Eplan;
- Radevit;
- We see;
- Topicrem;
- Emolium.
These drugs contain different substances, but the effects of their use are similar. If you need to choose an ointment for dermatitis for children, then it is better to opt for a product from this group.
Allergic dermatitis
Inflammation occurs as a result of the body's reaction to a specific pathogen. The causative agents can be dust, plant pollen, animal hair, odors of perfumes or chemicals, medications, food, liquids, etc. It is often associated with seasonal manifestations of allergies. Intoxication can occur as a result of the production of certain substances in diseases of the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland, helminthic infestations, and the development of tumors.
How it manifests itself:
- the skin becomes covered with large red spots;
- small bubbles form on their surface;
- then they burst, forming weeping wounds;
- the rash is very itchy;
- accompanied by sneezing, coughing, lacrimation, and increased sensitivity to light.
An allergen can enter the bloodstream with food, through the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, or through injections. Located on any area of the skin or mucous membrane.
Hyposensitizing agents: names, instructions for use
If the doctor decides that tablets are needed for treatment, these can be prednisolone, calcium gluconate and sodium thiosulfate.
Calcium gluconate
When calcium is present in the body in sufficient quantities, the permeability of the vascular walls decreases, which prevents the penetration of allergens. Calcium thus shortens the healing process for dermatitis. It is taken in the form of gluconate, orally, in a course, but in special cases it is prescribed intravenously.
Calcium gluconate
However, calcium supplements have contraindications:
- increase blood clotting;
- promote the development of atherosclerosis;
- cause bleeding;
- contribute to hypercalcemia.
Sodium thiosulfate
A drug that helps remove toxins from the body. Used intravenously, in the form of a 30% solution, 1 time per day. After administration, the itching stops. Can be used topically by rubbing a 60% solution into the affected areas of the skin. Normalizes skin condition, increases resistance to infections, strengthens nails and hair.
Prednisolone
Available in various dosages, intended for the treatment of both adults and children. It is an anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, anti-allergic substance. Available in the form of tablets, injections, ointments.
| Daily dose | ||
| Pills | Injection | Ointment |
| 20–30 mg taken after meals | 100–200 mg until symptoms disappear completely | Apply a thin layer to the affected areas 3 times a day, course 1–2 weeks |
Contact dermatitis
These are inflammatory processes on the skin caused by contact with a certain irritant. These are friction, pressure, exposure to temperature, radiation, burns and other strong irritants. With this type, direct damage to the skin occurs, symptoms appear immediately, and contact with the irritant must be eliminated as soon as possible.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis:
- swelling;
- hemorrhages, microhematomas;
- pronounced hyperemia;
- small papules, vesicles;
- weeping, scales, crusts;
- large bubbles;
- zones of necrosis.
Like food dermatitis, this is a type of allergic form of the disease. Occurs after contact with substances that cause an inflammatory response in the body. These may be chemical reagents, UV rays (photocontact or photodermatitis), x-rays, high/low temperature or mechanical factors. Stinging cells, pollen, plant sap, and caterpillar larvae can provoke a skin reaction. The main difference between this type of eczema is that it has no incubation period.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of dermatitis consists of an initial blood test. To exclude the possibility of mycotic skin lesions joining the current processes, seeding and microscopic examination of scales from the area that has been affected is also carried out.
Allergic dermatitis requires various types of allergy tests, mainly skin tests are used for this. In frequent cases, the allergic nature of the factor acting as an irritant is determined through a blood test (increased lg E level). Based on the results of the studies, an appropriate assessment of the patient’s condition is made.
Diagnosis of the disease
To know how to treat allergic dermatitis, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist or therapist. The specialist will examine and interview the patient, then prescribe laboratory tests. They are necessary to exclude infectious pathologies and confirm the preliminary diagnosis. The patient must undergo:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- scraping from affected areas;
- bacteriological culture of the liquid, if any;
- stool analysis to identify parasites and dysbacteriosis.
Additionally, skin tests may be prescribed to determine the irritant, as well as an immunogram. In cases where allergic dermatosis is caused by diseases of internal organs, consultation with specialized specialists will be required.
Treatment of dermatitis
In the case of dermatitis, the effectiveness of treatment depends on its form and is always selected individually.
Treatment of dermatitis in adults should begin by determining the cause. It is necessary to identify the irritant (allergen, toxic substance, microbial pathogen) and eliminate it. If the irritant is not identified, as is often the case with allergic and especially neuroallergic dermatitis, treatment will be only symptomatic, i.e. aimed at eliminating symptoms and maintaining remission.
Treatment of dermatitis is conservative, consisting of local and general therapy. Acute dermatitis and dermatitis in children, as a rule, are treated only with local remedies, while chronic forms require a combination of general and local therapy. Local therapy for dermatitis consists of treating the affected areas of the skin. Skin rashes are treated with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs in the form of mash, powders, ointments, solutions - depending on the form of the inflammatory element and its stage. Dermatitis on the face (seborrheic) is treated with antifungal ointments. Chronic dermatitis is treated with corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs, acute dermatitis is treated with aniline dyes. Deep ulcerative lesions are treated in a hospital setting.
General treatment of dermatitis consists of taking immunomodulatory, antihistamine, and sedatives, depending on the cause of the disease. It is also necessary to eliminate all sources of chronic infection, such as teeth destroyed by caries, chronic sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc.
Fighting the disease
Diseases can be chronic. Some are considered incurable. In any case, it is necessary to undergo courses of treatment and be observed by a doctor.
Treatment of dermatitis includes the use of external preparations (ointments, creams, lotions), vitamin and mineral complexes.
Physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed. Diet therapy and drugs that restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are added to drug treatment. In some cases, your doctor will prescribe systemic corticosteroids.
If the skin is affected, regardless of the size of the affected area, avoid prolonged exposure to the sun. Sometimes the rash is a reaction to ultraviolet radiation.
Diet for dermatitis
For allergic dermatitis, a special diet and balanced nutrition are included in the patient’s health system. Properly organized nutrition and hypoallergenic foods in the patient’s diet are the key to preventing new doses of allergens from entering the body. Before visiting a doctor, you must independently determine the minimum list of products that can be consumed without the risk of exacerbating allergic reactions.
Products that often cause allergies:
- Protein - pork, fatty beef, milk, chicken egg, fish, seafood, caviar, smoked meats, delicacies, stewed meat;
- Vegetable - legumes, sauerkraut, pickled vegetables, all red berries, all tropical fruits, mushrooms, dried fruits (dried apricots, raisins, dates, figs);
- Drinks – sweet carbonated water, filled yoghurts, cocoa, coffee;
- Desserts – caramel, marmalade, chocolate, honey;
- Seasonings, sauces (ketchup, mayonnaise, soy sauce), canned soups, and any finished products containing dyes, emulsifiers, preservatives and other food additives
Moderately allergenic products:
- Drinks – black tea, green apple juices, herbal infusions;
- Protein – lamb, horse meat, rabbit;
- Vegetables - rye, buckwheat, corn, green fruits, potatoes;
- Desserts - yoghurts, mousses, curds.
Low allergenic products:
- Protein - some types of fish (cod and sea bass), lean veal, offal (liver, tongue), low-fat cottage cheese, butter;
- Vegetable - cereals (rice, pearl barley), green salad, cucumbers, zucchini, rutabaga, fresh cabbage, spinach, vegetable oil, pears, gooseberries, white cherries and white currants;
- Desserts – dried fruits from dried pears and apples, prunes.
- Drinks – fermented milk without added dyes, pear and apple compotes, rhubarb decoctions, low concentration green tea, still mineral water;
For dermatitis without an allergic load, proper nutrition is more important. The main principle is to include low-calorie, easily digestible foods in the diet. There are no universal recommendations. You can learn more about the products recommended for you personally from your doctor or nutritionist.
Diet therapy
The diet should be rich in foods that can support the immune system in a healthy state:
- Green leafy vegetables: broccoli, spinach, cabbage.
- Spices: rosemary, turmeric, oregano, marjoram, sage and thyme.
- Berries rich in antioxidants: cherries, cherries, strawberries, blueberries.
- Vegetables and fruits containing vitamin A: chard, watercress, pumpkin, apples, bananas.
- Vegetables containing vitamin B, biotin, B7: cabbage, green peas, potatoes.
- Vitamin C: tomatoes, sweet peppers, cauliflower.
- Vitamin E: almonds, avocado, wheat germ.
- Fermented foods: kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi.
- Spices: garlic, chili pepper, flaxseed oil and flaxseed.