Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the force with which the brain fluid inside the skull presses on its walls. Its change significantly affects the state of human health. With pronounced deviations of the level of intracranial pressure from the norm, characteristic manifestations of the nervous system are observed. Low or high levels of intracranial pressure can even lead to death. Therefore, if this pathology is suspected, it is extremely necessary to measure intracranial pressure.
Increased intracranial pressure is a dangerous condition that every person has encountered. Pathology occurs both in children, including newborns, and in adults. It was noted that females are more susceptible to the disease than males.
In some cases, the symptoms of increased ICP do not cause any concern. This is what, in most cases, causes sad consequences. Because of this, you need to be aware of this issue, know the symptoms of the pathology, how you can measure intracranial pressure and ways to normalize it.
A little anatomy
This disease is associated with the cerebrospinal fluid that washes the brain and the brain itself. Liquor is an important intracranial fluid, the entire volume of which regulates pressure on the human brain.
If the volume of fluid is much higher than normal, this may cause an increase in pressure. That is, it can be noted that an increase in intracranial pressure is a set of symptoms, but not a disease as such. Read more about the symptoms and treatment of intracranial pressure below.
Causes of increased ICP
It is worth mentioning what causes intracranial pressure:
- skull injuries;
- the presence of a hematoma, a specific foreign body or a space-occupying tumor;
- inflammation of the brain (meningitis, ventriculitis, encephalitis);
- intoxication of the body;
- obesity;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- abnormal brain development;
- liver pathologies;
- excess cerebrospinal fluid;
- abscess;
- stroke;
- helminthiasis
High pressure inside the skull can also be triggered by: otitis media, severe migraines, bronchitis, excess amounts of vitamin A, malaria and mastoiditis. An important reason is long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids and hormonal contraceptives. All of the above reasons can increase the generation of cerebrospinal fluid, disrupt its circulation, and also interfere with normal absorption. Next, you should determine the signs of pathology and how to measure intracranial pressure at home.
Why does it happen?
The causes of this condition may be:
- inflammation of the brain and its membranes;
- received head injuries;
- hypertonic disease;
- endocrinological disorders;
- pathologies of the skeletal system (for example, the presence of osteochondrosis of the neck);
- neoplasms in the head;
- helminthiases.
Much less often, the characteristic clinical picture is caused by diseases that do not directly affect the head.
Certain medications can increase pressure in the skull. For example, glucocorticosteroids, some drugs from the group of antibiotics, hormonal contraception.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure
In medicine, high blood pressure is called intracranial hypertension, which without timely and proper treatment can lead to dangerous complications, including death. A person needs to know the main signs of increased benign intracranial pressure in order to contact a doctor who will examine the patient and take the necessary measures.
The danger of high blood pressure is that the signs may indicate some serious illnesses. Initially, a person may be bothered by frequent migraines, and a persistent feeling of fullness or compression appears in the temporal region. Those suffering from this disease should know how to measure intracranial pressure at home.
Manifestations in babies
The baby is not able to communicate the unpleasant sensations that he experiences, so parents and medical personnel have to navigate by indirect symptoms. The presence of pathology can be indicated by:
- cry;
- sleep disorders;
- lethargy;
- baby's refusal to eat;
- presence of vomiting;
- the appearance of seizures;
- involuntary eye movements;
- the presence of a swollen and pulsating fontanel;
- enlargement of the head (in medicine called hydrocephalus);
- violation of muscle tone (some muscle groups may be relaxed, while others are tense);
- the appearance or strengthening of the subcutaneous vascular network on the head.
Contrary to popular belief, nosebleeds, stuttering, and startling during sleep are usually not signs of this pathological condition.
Understanding the cause of such phenomena can be difficult, so you have to resort to instrumental examination methods.
Main features
Let's look at the signs of high intracranial pressure. It could be:
- nausea and possible vomiting;
- excessive sleepiness;
- fainting state;
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
- frequently recurring dizziness;
- memory loss;
- depression;
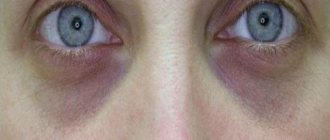
- bruises in the eye area (when the skin is pulled under the “bruises”, dilated veins can be seen);
- pressure surges;
- pain in the spine;
- thinking disorder;
- muscle paresis;
- decreased potency and sexual desire;
- absentmindedness;
- bradycardia;
- increased sweating;
- skin sensitivity;
- hearing and vision problems;
- pulsation in the eye sockets.
Decreased
Symptoms occur when the intracranial pressure drops to less than 10 mmHg (normal intracranial pressure). A person is bothered by a strong, squeezing and rather sharp headache. When the pressure decreases, “floaters” and flashes may appear before the eyes, discomfort is felt in the stomach, and a tingling sensation begins in the heart. Signs of decreased intracranial pressure also include motion sickness, loss of strength, and increased irritability. When bending down, the pain in the head may ease.
A severe and regularly recurring headache that surrounds the entire head may indicate increased ICP. Particularly painful sensations intensify at night and in the morning.
If the body is in a horizontal position, cerebrospinal fluid flows out of the skull. It continues to be actively secreted, but is absorbed more slowly, so ICP, as well as the accompanying symptoms, may intensify in the morning.
If the above symptoms of high pressure inside the skull are accompanied by a temperature of more than 38 degrees, uncoordinated movements and hallucinations, the patient may have meningitis. If the symptoms include decreased memory, increased sweating, and high fatigue, it is possible that increased blood pressure has developed due to a tumor in the brain.
Symptoms resulting from a fall or head injury may be associated with impaired consciousness and may also indicate possible brain damage. A person in this situation should immediately consult a doctor and undergo a thorough examination.
Measurement techniques
There are 3 known ways to measure intracranial pressure:
- Epidemic measurement.
- Subdural measurement.
- Measurement through the use of an intraverticular catheter.
The most progressive and modern method is the use of an intraverticular catheter by a specialist. It is inserted into a trepanation hole drilled in the skull to the ventricle of the brain. The ventricle inside has cerebrospinal fluid, which helps measure pressure and reduce it quite quickly by pumping out some fluid from the resulting cavity. But if the pressure is too high, the use of this technique will be unjustified, since inserting the catheter will be quite difficult.
If urgent pressure measurement is necessary, the subdural technique is mainly used: a subdural screw is installed in the finished burr hole.
Another way to measure intracranial pressure in an adult is an epidural. With this method, an ultra-precise epidural sensor is inserted into the skull. It is introduced between the skull and the dura mater of the brain also through a burr hole. This sensor is not suitable for reducing ICP, since it is impossible to completely pump out all the excess fluid.
Rules for measuring pressure
Many parents are interested in how to measure intracranial pressure in a child. Measuring a person’s ICP must be performed according to certain rules, under sterile conditions, since this is a very important and responsible procedure. A trepanation hole should be made in the skull, into which anesthetics are injected, then it is shaved and thoroughly treated with antiseptic solutions.
Blood pressure is measured using local or general anesthesia; doctors prescribe mild painkillers to eliminate some of the symptoms of the disease. They try to avoid the use of potent drugs, since during the procedure they additionally check indicators of brain functioning.
Increased pressure inside the skull is a quantitative indicator that accurately reflects the degree of influence of cerebrospinal fluid on the state of brain tissue, so it is impossible to establish this yourself, without the use of appropriate equipment.
But the patient can independently detect an increase in pressure based on certain clinical symptoms. Dizziness, heat in the temples, increased weakness, loss of consciousness, headache, attacks of suffocation, and blurred vision should alert you. These signs may indicate histological damage to the neural tissues of the brain.
The doctor needs not only to perform a thorough examination of the patient, but also to correctly interpret all the data and finally make a diagnosis in order to prescribe appropriate therapy. Experts believe that an increase in pressure can be objectively assessed and identified after intracranial surgery is performed on a patient by assessing the average pressure readings.
Consequences
If measures are not taken to normalize blood pressure, the disease will take a chronic form. This is fraught with the occurrence of many diseases, the most dangerous of which is stroke. Therefore, it is better to take the problem seriously and treat it immediately after the diagnosis is confirmed.
Treatment with folk remedies
- Alternative treatment should be used only for chronic disease or as an addition to already prescribed therapy.
Lemon juice with honey
Take one lemon. Cut it. Squeeze out the juice thoroughly. Add 2 tablespoons of honey and one hundred milliliters of water. Mix all ingredients thoroughly and drink. The treatment period is twenty days. After ten days there is a break.
Pollen with honey
Used for head massage. Take 2 parts of flower pollen, add honey. Mix the ingredients and leave for 72 hours in a place where sunlight does not penetrate. Then rub the mixture in small portions into the back of your head, the back of your neck and the bridge of your nose. Then wrap your head with a towel. Carry out the procedure every day for a month.
Methods for reducing pressure
If ICP increases due to an existing secondary process, the primary disease must initially be eradicated, for example, hormonal imbalance, atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis or hypertension. But symptomatic treatment of this disease is also very important.
The patient can independently determine the symptoms, and treatment for intracranial pressure is prescribed by a specialist. It will be as follows:
- Conservative: taking medications to enhance the outflow of excess blood from the brain, reducing the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid as much as possible. Doctors mostly prescribe diuretics. If a tumor or meningitis is detected, steroid-type anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce swelling. Doctors also recommend using potassium supplements and agents to improve venous blood flow. Nootropic drugs will be ineffective for this disease.
- Surgical. The most commonly used type of surgery is bypass surgery. A special tube is inserted through which excess fluid is pumped from the ventricles of the brain into the peritoneum. But there are also some disadvantages - the catheter can unexpectedly break, bend or become clogged. There are also a number of specific complications of this procedure.
To reduce intracranial pressure, tinctures of mint, hawthorn, medicinal valerian, eucalyptus or motherwort are used. These herbs eliminate vascular spasms, providing a mild calming effect on the patient.
Therapy
Before starting any treatment, you must undergo all examinations necessary to make a diagnosis.
Therapy for the described condition, first of all, comes down to eliminating the primary pathology. However, symptomatic treatment is also very important. It is represented by surgical and conservative methods.
Conservative ones mainly come down to taking medications to lower blood pressure and enhance the processes of blood outflow from brain structures.
First of all, diuretics are used (the effect of intravenous administration of Furosemide quickly appears). In the presence of edema, in addition to the medications listed, medications from the group of steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help to remove it. Drugs are prescribed to eliminate vasospasm, nootropics, and drugs that stimulate metabolism.
Physical therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures, massages are indicated.
If the disease, even after treatment, progresses, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment methods.
You should not self-medicate or resort to traditional medicine. This can significantly harm your health in this case.
Physiotherapy
After it has become clear that it is impossible to measure intracranial pressure at home, we should talk about how to normalize it and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. During the treatment process, you can use physiotherapeutic methods (electrophoresis with medicinal substances, applying a magnet to the collar area on the neck), physical therapy, massage of the spine, back of the head, base of the skull, circular shower and acupuncture. Basically, these techniques are used in uncomplicated cases of increased ICP, in the absence of a threat to normal life.
Treatment approach
The treatment regimen for intracranial hypertension depends on its cause, the severity of clinical signs and individual indications. Based on these parameters, treatment can be conservative, surgical or combined.
Drug therapy consists of the use of diuretics, sedatives, antispasmodics, and analgesics.
Surgical treatment involves removal of a neoplasm (tumor, cyst, hematoma) and/or shunting, i.e. creating an artificial outflow for cerebrospinal fluid.
In addition to the main treatment, physiotherapy methods, massage, and folk remedies can be used (after consultation with a doctor).
With idiopathic intracranial hypertension, lifestyle correction is required: proper nutrition, normalization of work and rest, regular but moderate physical activity, daily exposure to fresh air.