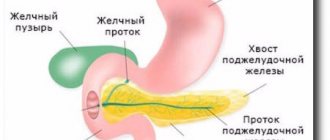
Lacunar tonsillitis is also called lacunar tonsillitis or diphthera-like tonsillitis. With lacunar tonsillitis, the palatine tonsils are affected. Only these tonsils have special depressions - lacunae (hence the name). One palatine tonsil can have up to 20 lacunae, but usually there are 12-14 of them. Lacunae are normally reservoirs for the accumulation of bacterial or viral pathogens that have entered the body. With the condition that the “gates” of infection are the nose, mouth or ear openings, and the pathogen itself can infect their mucous membranes.
Pathogenic bacteria trapped in the gaps are captured by macrophages, but are not completely destroyed, but are “unpacked.” Those. a pathogenic antigen is represented so that T lymphocytes “understand” how to destroy this particular pathogen. This happens normally.
The pathological condition is caused by:
- excessive accumulation of the pathogen in the gaps (worse when there are several types of pathogenic bacteria) - the immune system may simply not have time to “study” the “guests” and prepare T-lymphocytes for attack;
- if the immune system is already fighting something else, then typical pathogens of lacunar tonsillitis can trigger the inflammatory process (therefore, tonsillitis often occurs against the background of acute respiratory infections, flu, etc.);
- with chronically weak immunity, a certain amount of pathogenic bacteria and viruses always remains in the tonsil lacunae, which tend to periodically accumulate, provoking recurrent exacerbations of sore throat.
Lacunar tonsillitis occurs more often in children, but adults also suffer from this disease. The ratio of cases is approximately 60% and 40%, respectively.
Causes
The main and main reason is weak immunity. Whether its weakening occurs episodically or is a chronic phenomenon does not matter for the development of lacunar tonsillitis. Or a large number of pathogens entered the body at once. For example, during close and prolonged communication with a person who has a sore throat. Moreover, it is not at all necessary that it be a lacunar form, because The main forms of this disease have the same bacteriological picture.
Immunity is suppressed by a large set of factors:
- recent other infectious diseases;
- drug therapy that has an immunosuppressive effect as a main or side effect (mainly hormonal drugs and immunosuppressants used, for example, for autoimmune diseases);
- chemotherapy and radiation therapy for oncology;
- injuries of any kind (the risk of tonsillitis is especially increased by excessive blood loss and hypothermia);
- structural features of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils (increased looseness, which creates cavities where pathogenic microflora can settle);
- negative environmental factors (unfavorable environmental conditions);
- unhealthy lifestyle, constant stress, poor nutrition, bad habits.
Impaired immune defense makes the body more vulnerable to pathogens of lacunar and other tonsillitis.
Such pathogens include:
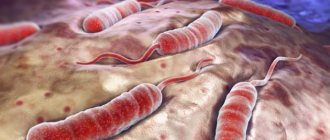
- streptococci (especially group A beta hemolytic streptococcus);
- staphylococci (especially Staphylococcus aureus and hemolytic Staphylococcus);
- hemophilus influenzae;
- pneumococci and meningococci (rather rare);
- opportunistic gram-negative enterobacteria - Klebsiella (also quite rare);
- pathogens of typhoid fever and anthrax (extremely rare).
Lacunar tonsillitis can also be caused by a viral infection:
- adenoviruses,
- enteroviruses,
- herpes viruses (for example, cytomegaloviruses).
Many of the listed pathogens can live in the body in small quantities for years.
Sources
- Chronic tonsillitis: different views on an old problem. / G.R. Kaspranskaya, A. S. Lopatin. // Medical advice. - 2013. - No. 5-6. — P. 69-71.
- Immunological aspects of chronic tonsillitis associated with Ebstein-Barr virus infection / A.S. Krasnitskaya, N.A. Borovskaya. // Fundamental research. – 2012. – No. 4-2. – pp. 299-305.
- Belov, V.A. Modern methods of microbiological diagnostics for exacerbation of chronic and acute forms of tonsillitis in children. / V.A. Belov. // Issues of modern pediatrics. - 2012. - T. 11, No. 2. - P. 128-131.
Symptoms
It is necessary to clarify that pronounced symptoms may not be observed in some cases: in the chronic course of the disease and in many adults. It is guaranteed that the most complete set of signs will be detected in a child during an acute primary attack of the disease.
The entire main clinical picture appears on the first day of the disease, which demonstrates the transience of its development.
At the initial stage (the first few hours), lacunar tonsillitis can be confused with influenza or an acute respiratory infection:
- a sharp increase in body temperature to febrile (38 degrees) and pyretic (above 39 degrees) values (although the rapidity of the temperature increase immediately gives rise to suspicion of a sore throat);
- the throat begins to sore and ache; upon visual examination, hyperemia of the soft and hard palate, palatine tonsils is noted (small, pinpoint, epithelial hemorrhages are possible);
- headache, weakness, weakness, loss of appetite;
- myalgia and arthralgia, aches in the lumbar region and calf muscles are often observed (a common symptom of the onset of influenza).
Read also: Sinusitis - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Then by the end of the day the following appear:
- high temperature turns into hectic fever, when low-grade or even normal temperature in the morning (after sleep) rises to 39-40 degrees in the evening;
- characteristic skin changes on the face: unhealthy, bright blush on the cheeks and cheekbones with severe pallor of the nose and lips;
- the most important and characteristic sign is that purulent formations are found on the surface of the palatine tonsils, visualized as dirty yellow or white plaques; later the plaques are highly likely to cover the entire surface of the tonsils with a purulent film;
- the sore throat intensifies, which in combination with swelling makes the swallowing process problematic;
- despite the pain syndrome, the voice, as a rule, remains normal, not hoarse or hoarse, unless the person is forced to speak much more quietly (hoarseness is a symptom of laryngitis);
- cervical lymph nodes increase in volume and become painful on palpation;
- against the background of a general headache, specific pain may appear, for example, behind the eyeballs, in the jaw joint, etc.;
- in the sternum and behind the sternum, in the area of the heart, a burning sensation, unpleasant heaviness may occur, the pulse when measured even in a calm state of the patient is increased (tachycardia, reaching up to 100 beats per minute).
What you need to know about the disease
What is lacunar tonsillitis and what are its characteristics? This pathology is a form of acute tonsillitis - bilateral inflammation of the palatine tonsils, which are one of several components of the lymphadenoid ring of the pharynx. They contain a large number of the mentioned lacunae. When the latter become overfilled with waste products of pathogenic microorganisms and dead epithelial cells, fairly large areas of tonsil tissue become covered with an easily detachable yellow-white coating. It is this sign that allows you to visually distinguish the lacunar form from the follicular form, in which single pustules appear on the lymphatic formations. Lacunar tonsillitis of moderate severity is very common in both children and adults; it develops more rapidly and is more severe than follicular tonsillitis.
Is the disease contagious?
To the question of whether lacunar tonsillitis is transmitted from person to person, the answer is clear: yes, and infection occurs quite easily and quickly. The main routes of transmission are airborne and household contact. Everyone who comes into contact with the patient, as well as objects he uses (including children's toys), are susceptible to infection. That is why the sick person must be completely isolated from others, provided with separate dishes, linen and towels. To prevent the spread of infection, it is necessary to temporarily exclude direct contact of an infected person with healthy people.
Important: the disease is very dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, since the infection can enter the child’s body through the mother’s blood, causing serious pathologies in the fetus and even causing its death.
Diagnostics
All diagnostics for this form of angina comes down to three points:
- a throat smear is the main component of diagnosis; it is done not only to determine the causative agent(s) of the disease, but also to exclude other infections, for example, diphtheria, which in its symptoms can be very similar to lacunar tonsillitis (hence the alternative name for this sore throat). Also, sore throat can be confused with the initial phase of scarlet fever or infectious mononucleosis;
- examination of the patient, taking note of his complaints, simple pharyngoscopy;
- blood test - allows you to clarify the diagnosis due to characteristic changes (the number of leukocytes can reach up to 35*109/l, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate up to 60 mm/h).
The importance of a simple visual inspection should not be underestimated. For example, diphtheria on the tonsils gives a grayish coating, which almost always extends beyond the tonsil zone. With lacunar angina, purulent plaques are easily washed off, but with diphtheria it is noticeably worse. In lacunar angina, the mucous membrane of the tonsils under the purulent layer is not damaged, but in diphtheria, erosions are detected.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the antibiogram, which clarifies not the diagnosis, but the sensitivity of the pathogen to certain antibiotics. When paper mugs impregnated with various antibiotics are placed on the nutrient medium with the isolated pathogen. And based on the degree to which bacteria avoid this or that piece of paper, the required drug is determined.
In diagnosis, it is necessary to determine the nature of the sore throat - bacteriological or viral. Because antibiotics do not work on most viruses. The difference between viral and bacteriological sore throat is clearly determined by a blood test. With viral tonsillitis, leukocytes almost do not increase, band neutrophils do not increase, but the level of lymphocytes is very high. With bacteriological tonsillitis, all of the above points are exactly the opposite.
Preventive measures
Prevention of lacunar tonsillitis consists of limiting contact with people who have this pathology or any cold, using personal protective equipment, strengthening the body with physical exercise, maintaining a high level of immune defense, eating well, washing hands frequently and ventilating the premises.
Lacunar tonsillitis of moderate severity is a fairly common occurrence, especially during the cold season. Both adults and children suffer from inflammation of the tonsils caused by pathogenic bacteria, but in the latter the disease is quite severe and is more likely to cause complications. That is why it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible and begin treatment with antibiotics.
Treatment of lacunar tonsillitis
Treatment of lacunar tonsillitis is represented by the following points:
- antibacterial (systemic and sometimes local antibiotics);
- anti-inflammatory and antiseptic (rinsing, irrigation, lubrication and inhalation);
- antipyretics and painkillers;
- antiviral drugs (possibly, especially if viral tonsillitis occurs);
- antihistamine action (possibly, especially when a child is sick).
The standard course of treatment is 10 days, but varies depending on the age and condition of the patient. Semi-bed rest is recommended. Lacunar tonsillitis is treated conservatively. In Soviet medicine, lacunar tonsillitis was often considered an indication for tonsillectomy, but later this approach was abandoned. There is much more harm from removing tonsils than benefit. Today this is only used for recurrent abscesses.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
This type of therapy is always considered auxiliary, additional. And it is used after the peak period, when the most severe condition is over.
However, its therapeutic effect is undeniable:
- Ultraviolet irradiation of the tonsils (quartzization of the tonsils). The healing factor here is short electromagnetic waves: they disinfect and inhibit inflammation (for example, they slow down the migration of leukocytes).
- Centimeter wave irradiation (CW). Electromagnetic waves are also used here, but of much greater length (around 1 cm). Ceramic emitters are applied to the area of closest impact on the tonsils (usually the submandibular area). It has been proven that SMV has a warming, regenerative and anti-inflammatory effect on the tonsils.
- Infrared radiation (IR). It penetrates deeper than all others used in physiotherapy, but the therapeutic effect is similar to SMV.
- Electrophoresis. A method in which a small amount of medicinal substances is introduced into the body directly through the skin or mucous membrane using an electromagnetic field.
This is the main set of physiotherapeutic techniques. But there are also many additional ones that are not included in official medicine on other grounds. For example, treatment with a Minin reflector, better known as a blue lamp.
Rinsing and irrigation
With lacunar tonsillitis, rinsing with various solutions, decoctions and infusions plays an important role. Not only due to its antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, but also because rinsing itself helps remove purulent discharge from the tonsils.
There are a huge number of rinsing products. Here are just a few:
- sea water is perhaps the most famous, very easy to prepare, and at the same time very effective remedy (for 200 ml of boiled lukewarm water, 1 level teaspoon of baking soda, a pinch of salt and 1-2 drops of 5% iodine solution);
- a weak solution of potassium permanganate - carefully (this is important) dissolve a few grains of potassium permanganate in 200 ml of boiled lukewarm water, the crystals of the substance must completely dissolve, otherwise there is a considerable risk of getting a chemical burn to the mucous membrane;
- dissolve the nitrofural tablet (furatsilin) in the same way in 200 ml of water;
- garlic infusion - pour 2 cloves of garlic into 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 60 minutes, after which you can gargle with the resulting infusion;
- calendula solution - dilute 1 teaspoon of calendula in alcohol in 200 ml of boiled water, the rinse is ready;
- Brew any herb (chamomile, St. John's wort, sage or a mixture of herbs) (instructions are on the package), the resulting “tea infusion” can be further diluted with water, or can be used ready-made - for rinsing or for ingestion.
Read also Hoarseness (hoarseness of voice) - causes, diagnosis, treatment
Rinsing must be done at least 4-5 times a day, and after the procedure, do not eat or drink anything for at least 20 minutes.
Lubricating the mucous membranes of the tonsils
There are otolaryngologists who claim that in case of lacunar tonsillitis, lubrication of the tonsils and removal of purulent films from their surface, on the contrary, are contraindicated. Because this can lead to generalization of the infectious process to the entire throat. There is a lot of reliable clinical evidence for this statement. Probably, in individual cases with powerful attacks of tonsillitis, disruption of the purulent film leads to a sharp release of a large amount of pathogenic microflora into the throat. But this does not unequivocally discredit the method of treatment itself.
To be on the safe side, it is recommended to resort to lubrication already at the stage of decline of the disease. And, of course, after consulting a doctor. Especially when it comes to a child’s sore throat. For lubrication, use a long stick with a cotton or gauze swab at the end (all this can be purchased at the pharmacy).
You can lubricate the surface of the tonsils with rotokan, chlorhexidine, miramistin (it copes very well with fungal infections). Methods of dilution and dosage are indicated in the instructions, but usually we are talking about weak aqueous solutions, which are used to moisten the tampon. If you resort to Lugol's solution, then only at the final stage of treatment, since iodine can burn the already inflamed mucous membrane.
Inhalations
Inhalations do not remove purulent plaques from the tonsils, but can have a noticeable anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and analgesic effect. The peculiarity of inhalation is that here the drug enters the tissues in the form of a finely dispersed medium - an aerosol. Which causes very fast absorption. The choice of inhalations is also quite large: Ingalipt, Kameton, Hexoral, etc. Recently, a device for home inhalation - a nebulizer - has gained great popularity among consumers. A huge plus is that you can load any healing mixture into its working container. And the device will turn the solution into an aerosol.
Pills
Antibiotics for tonsillitis are almost always used systemically, i.e. inside the body. And in fact, in terms of therapeutic effect, there is not much difference between oral administration (swallowing tablets) and intramuscular injections. Simply, oral administration may be difficult due to severe pain in the throat. Or a serious stomach disease (ulcer).
It is immediately worth noting that independent choice of antibiotics is not recommended. Such prescriptions must be made by the attending physician. We must remember that antibiotics also attack beneficial microflora. In certain cases (viral tonsillitis), standard antibiotics will not work.
For lacunar tonsillitis, the following series of antibacterial drugs are used:
- Ampicillin, Amoxicillin and other penicillin derivatives successfully destroy a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including all cocci, diphtheria, hemophilus influenzae, etc., but there is a serious drawback - bacteria can become resistant (often with chronic tonsillitis).
- Antibiotics of the cephalosporin series, especially representatives of the first and third generations (Cefalexin, Cefadroxil, Cefotaxime, Cefoperazone, Ceftibuten, Cefixime) are considered the second line after the penicillin series, when penicillin derivatives show insufficient antibacterial activity against specific pathogens.
- Macrolides (Spiramycin, Amoxiclav, Flemoxin, Sumamed) are the third line in antibacterial therapy for lacunar angina, they are characterized by a low level of toxicity and hypoallergenicity (thus, the risks of cross-allergy with beta-lactams are eliminated).
In addition to antibiotics, “tablet” therapy includes antipyretics and painkillers. As a rule, these are NSAIDs: Analgin, Nurofen, Pentalgin, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, etc. If there is a viral sore throat, then the main ones are antiviral drugs - Cycloferon, Arbidol, Ingavirin, Fluconazole, Acyclovir, etc.
Finally, antihistamines, antiallergic drugs: Suprastin, Loratadine, Erius (Desloratadine). Antiallergic drugs are needed to prevent possible drug allergies, which are especially common in children. Sore throat is inflammation, allergy is inflammation. One strengthens the other.
Needle aspiration, abscess incision, tonsil removal
For lacunar angina, none of the listed surgical procedures are used or needed. But lacunotomy (surgical or laser) for recurrent forms may be indicated: the tissues near the lacunae are dissected so that with further fusion the depth of the lacunae noticeably decreases. This prevents the accumulation of pus.
Diet
There is no special diet for this disease. Food should be such that the mucous membrane is not subjected to mechanical, thermal or chemical irritation. Plenty of warm drinks are recommended.
Treatment with folk remedies at home
It should be borne in mind that folk remedies are just an addition, and the backbone of treatment includes taking antibiotics and consulting a doctor.
Read also Eustachitis (tubo-otitis) - causes, symptoms, treatment
A few “folk recipes”:
- grate fresh beets (1-2 pcs.), squeeze to get at least 150 ml of beet juice (can be diluted a little with warm boiled water), gargle with this juice (at least 3 times a day, week);
- An alcohol or vodka compress helps against swelling of the tonsils (moisten a bandage or gauze, apply it around the neck and wrap a dry bandage on top for an hour or two);
- cover your neck with fresh cabbage leaves and wrap a scarf for a couple of hours;
- Pour 4 fresh plantain leaves into 200 ml of boiling water, leave for an hour, then rinse (every 3 hours until the final phase of recovery);
- any consumption of aloe leaves and juice - in ground form, with tea, with honey, with milk, 30 ml of juice or one ground leaf per day is enough (but aloe is not recommended for allergy sufferers and children under 3 years of age);
- 4 g of Rhodiola rosea root pour 500 ml of vodka, keep in a dark place for at least 4 days, 10 ml of the resulting tincture is diluted with 100 ml of boiled water - another folk remedy for rinsing is ready (due to the duration, it is better to prepare such a tincture preventively).
Recommendations
It is difficult to give specific recommendations here. Is it just that lacunar tonsillitis requires the involvement of professional doctors: a pediatrician, an otolaryngologist, a therapist, an infectious disease specialist, and sometimes a rheumatologist. Letting the disease take its course or self-medicating is unacceptable. Taking antibiotics requires maintenance therapy to restore beneficial microflora. Therefore, in parallel, you need to take probiotics and prebiotics (Enterol, Eubicor, Bifiform, Linex, Inulin, etc.). Sore throat is especially dangerous for people under 13 years of age.
Folk remedies
The most effective and popular means are:
- Honey, apple cider vinegar. Dilute one teaspoon of each component in a glass of warm water and gargle with the resulting solution 4 times a day.
- Butter, soda, honey. Melt one spoon of butter, add the same amount of honey and a pinch of baking soda. Mix the resulting mass thoroughly. The product should be consumed warm, a teaspoon three times a day, dissolving it.
- Beet juice, apple cider vinegar. Grate the vegetable on a fine grater and squeeze the juice from the resulting mass. Add a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar to one glass. Then heat everything up and gargle for 1 minute. Repeat the procedure 4 times a day.
- Ginger and lemon tea. Brew tea in the classic way, add one small spoon of ginger root, previously grated, and a slice of lemon. You can drink the drink after 20 minutes, holding it in your mouth for a while.
It is recommended to do inhalations at home. For the procedure, you can purchase a special nebulizer or use a regular kettle. For inhalation, use tincture of chamomile, calendula or various essential oils. They help relieve pain, swelling and redness.
Complications and consequences
There are two points to note here:
- Phlegmonous paratonsillitis is a very formidable disease, since it can itself give new, even more formidable complications (occurs against the background of a chronic, recurrent course of lacunar tonsillitis), the consequences can be very sad, including disability and death (for example, if paratonsillitis provoked purulent meningitis or blood poisoning).
- In children, swelling of the larynx can occur and, as a result, suffocation (this condition is called false croup), here it is necessary to urgently relieve inflammation (often you have to resort to hormonal droppers) to prevent hypoxia.
Prevention
To prevent the re-development of lacunar tonsillitis, you should take care of its prevention:
- eat well, do not forget about fruits, vegetables and other fortified foods;
- harden;
- be physically active;
- avoid hypothermia;
- cure teeth, restore the health of the nose, gums, etc.;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- try not to contact people with tonsillitis.
To prevent lacunar tonsillitis from becoming chronic, you must constantly monitor your health, have moderate physical activity and give up bad habits.
Is it contagious and how is it transmitted?
Because Lacunar tonsillitis is of an infectious nature in 99% of all cases (not counting unique autoimmune reactions); naturally, it is contagious. A person becomes contagious during the incubation period (1-2 days before the first symptoms appear) and remains so until complete recovery.
Methods of infection:
- airborne - if you just stay near the patient for enough time;
- through shared utensils;
- through food (therefore you cannot finish eating or drinking anything while sick).
In particular, contact of the patient with children and people already suffering from something (for example, acute respiratory infections) is unacceptable.
Forecast
With timely and correct treatment, lacunar tonsillitis completely disappears within 2 weeks maximum and the patient returns to normal life. If the disease is neglected, the risk of complications is quite high. The consequences of a sore throat are dangerous not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient. It happens that the disease recurs and becomes chronic.
If conservative treatment does not help, surgical intervention is necessary. A laser is used to cut the tissue around the lacunae, allowing the pus to be removed. If this method does not produce results, then doctors recommend completely removing the tonsils.
Follicular tonsillitis Purulent tonsillitis Chronic tonsillitis Tonsillitis Psoriasis Sinusitis: symptoms and treatment in adults
Treatment of lacunar tonsillitis
The acute course of the disease requires bed rest. In case of severe illness, hospitalization of the patient .
In order to eliminate a disease such as lacunar tonsillitis, treatment is carried out in three directions:
- Symptomatic therapy . As a rule, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, immunomodulators, vitamins, and medications to normalize the functionality of the heart and blood vessels, nervous, digestive and genitourinary systems.
- Therapy against the pathogen . The basis of treatment for such bacterial etiology is etiotropic therapy for a week or two. The dosage of drugs is calculated depending on the sensitivity of the pathogen. Penicillin antibiotics, macrolides and cephalosporins are applicable against lacunar tonsillitis. Secondary tonsillitis can be treated with antifungal and antiviral agents.
- Local treatment . For such therapy, antiseptics and physiotherapy are applicable - after the acute symptoms of lacunar disease have subsided. For localized abscesses, puncture of the purulent formation is required.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapy sessions for purulent sore throat include UHF currents or microwave therapy. The doctor may suggest a hardware method such as suctioning out pus using the Tonsilor device. During the procedure, ultrasound and vacuum are applied; after removal of purulent foci, the inflamed area is washed with antiseptics, which reduces swelling, relieves pain and inflammation.
During treatment, it is necessary to observe bed rest, since physical activity during toxic poisoning of the body can lead to serious cardiac pathologies - endocarditis and myocarditis. Even with visible improvements, the child should remain in bed. It is also necessary to carry out wet cleaning twice a day, ventilate the room and isolate the patient from healthy family members.
Lacunar tonsillitis: complications
With incorrect and unprofessional treatment of this form of angina, supplemented by a general decrease in the resistance of the immune system, the disease can cause the following symptoms and complications:
- Retropharyngeal abscess.
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
- Peritonsillar abscess.
- Chronic tonsillitis.
- Kidney damage.
- Inflammation of the middle ear.
- Ear pain.
- Damage to the heart muscle.
- Inflammation of lymphoid tissues.
- Joint damage.
Such conditions can be provoked by untreated or neglected lacunar tonsillitis. Complications are fraught with deep damage to organs, followed by prolonged therapy and long-term treatment.
Processing of pharynx
With this disease, local treatment of foci of infection is necessary. Decoctions of medicinal herbs, such as chamomile, calendula or sage, as well as solutions of antiseptics, such as Miramistin, Iodinol, Chlorophyllipt or Furacilin, are used. You can use sprays that help relieve inflammation and reduce pain; for this, Hexoral, Bioparox, Ingalipt or Tantum Verde are used.
To reduce pain and relieve inflammation, it is useful to dissolve special Stop-angin and Faringosept plates.