The lymphatic system ensures the normal functioning of the body, serving as an important part of the immune system. Lymph nodes are organs of the lymphatic system that act as a filter, cleansing the body of harmful compounds. Lymph nodes are located in all parts of the body. They can become inflamed and enlarge in response to various pathological processes occurring in the body, so anyone who is concerned about their own health should understand in more detail the features of their location and functions.
What are lymph nodes, their functions and significance
The lymphoid system, like other life support systems of the body, is very similar in structure to the root system of large plants. The vessels of the lymphoid system surround the entire human body, some organs several times. They are absent only in a few human organs and tissues.
Lymph moves from tissues and organs into capillaries. The capillary lining is very thin and has very good permeability to liquid lymph, as well as ingredients dissolved in the lymph, including some small cells and even microorganisms. From the capillaries, lymph enters the large vessels of the lymphoid system.
The vessels also have easily permeable walls with internal valves necessary to prevent the back passage of lymph into the tissue.
Through these vessels, the lymph approaches the group of lymph nodes. These groups of lymph nodes are called regional and are located in places where vessels of all life-supporting systems of the human body accumulate, for example, in the groin.
The vessels leaving the lymph nodes interact with the lymphatic ducts that enter large arteries. This is how tissue fluid enters the blood and is cleansed.
Lymph nodes on the human body perform the most important biological functions, barrier and filtration, determined by the peculiarities of their structure.
What to do if the lymph nodes are inflamed?
The treatment regimen is prescribed after examination and confirmation of the diagnosis. Depending on the root cause of inflammation, various techniques and medications are used. So, if the enlargement of the lymph nodes was provoked by the initial stage of tuberculosis, getting rid of the problem will be carried out using conservative methods. The patient is prescribed anti-tuberculosis drugs and antibiotics. If the pathology has reached a chronic stage, the lymph node can be removed. Then treatment will be continued with anti-tuberculosis drugs. Often, a doctor prescribes isoniazid. This is a synthetic drug that has high activity against tubercle bacilli. However, the drug has a whole list of side effects and can even provoke the development of hepatitis. An alternative medication is pyrazinamide. It has a high sterilizing effect at the site of inflammation. The drug is well absorbed. The action is carried out through the intestines. However, the human immune system may react to the use of the medication with nausea and vomiting. Taking the drug can cause joint damage.
If a purulent form of cervical, inguinal or submandibular lymphadenitis is observed, surgical intervention is required. The specialist opens the abscess, removes the pus and treats the resulting wound with antiseptics and antimicrobial agents. Ampicillin may be used during the procedure. This is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. It can come in the form of tablets, capsules or powders. The drug is well absorbed. This allows you to get the effect already in the first hours after taking it. However, the medication has a large number of side effects. Mirasmestin may be prescribed instead of ampicillin. It is one of the antiseptics. The drug is highly effective against anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. It is often used for sexually transmitted infections. The medication is not absorbed through the damaged surface. It can be prescribed to children from the age of three.
If the lymph node is inflamed due to respiratory diseases, the causative agent of the pathology is first determined. If it is bacterial in nature, antibiotics are prescribed. If the pathogen is viral, antiviral drugs are used, and if it is fungal, antimycotic drugs are used. In parallel, the patient is prescribed immunomodulatory drugs and medications that can relieve cold symptoms. Such drugs are viferon and paracetamol. The first remedy is part of a group of popular antiviral medications that have an immunomodulatory effect. The drug is also effective against colds. With its help, you can reduce the duration of the course of taking antibiotics. For convenience, Viferon is available in several forms. Paracetamol helps reduce fever. It can be used even by children and pregnant women. The drug is available in the form of syrup, tablets and suppositories. The medication can help get rid of the pain that occurs with a cold.
To reduce the risk of inflammation of the lymph nodes, experts recommend timely treatment of all diseases. This rule is especially important to follow when purulent infections occur. Don't neglect personal hygiene. This will minimize the likelihood of infection entering the body. It is recommended to treat even minor scratches and wounds with antiseptics. To prevent inflammation, you need to support your immune system by eating right and exercising.
Internal structure of lymph nodes
Lymph nodes on the human body look like a small kidney with a diameter of 2-5 mm, are reddish in color and represent the peripheral human immune system. Various nodes are responsible for nearby areas of the body.
The lymph node is closed by a special capsule made of connective tissue, and inside it has partitions that divide it into sections. LNs within include lymphocytes, plasma cells and reticulocytes. The node contains the cortex and medulla. The first is divided into nones: superficial (follicle) and deep cortex (paracortical).
Here, the formation of T-lymphocytes, direct fighters against pathogens, occurs. There they undergo differentiation caused by contact directly with the antigen. Trabeculae, not very large bundles of connective tissue, extend from the capsule into the LN and form plates, septa, and cords that form the frame of the organ.
Internally, lymph flows through the lymphatic sinuses. This is a special filter that directly carries out cleaning. The sinuses are located between the capsule and trabeculae. Important elements of immune processes – B-lymphocytes – are formed in the lymph nodes. Modifying into plasma cells, they predetermine immune reactions, producing antibodies necessary for the human body.
Lymph nodes on the human body are the main regulators of ongoing immune processes in the human body, producing T- and B-lymphocytes. There are also small lymph nodes that are located in the intestinal wall. They are called Peyer's patches. They take part in the structure of tonsil tissue.
To what diseases are lymph nodes most often sensitive?
Lymph nodes react with enlargement to the following diseases:
- Cold viral diseases
- Autoimmune
- Venereal
- Presence of parasites in the body
- Rubella
- Tuberculosis
- Oncological
- HIV diseases
- Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes)
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking a lot of alcohol)
- Bad ecology
If you have one of the above diseases, this does not mean that all lymph nodes will increase, but only those that are closer to the diseased organ.
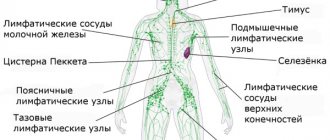
Location diagram and description of lymph nodes.
The total number of lymph nodes on the body of an adult is about 420-460. LNs are located very correctly in the body, a real filter in the path of various pathogens. The peculiarity of the lymphoid system is that it is not closed and moves in one direction.
Internal lymph nodes
Internal lymph nodes are always located in close proximity to the organs and vessels of the human body, sometimes in groups or in a chain.
Diagram of the location of lymph nodes on the human body.
- Tonsils are areas of lymphoid tissue in the mouth and throat. They perform a complex function, protecting and neutralizing incoming harmful organisms and substances from the nasopharynx.
- Mediastinal (mediastinal) lymph nodes.
- Intrapulmonary lymph nodes.
- LNs of the abdominal cavity: parietal (parietal), visceral (intrawall).
Visceral nodes
Lymph from the abdominal organs approaches the visceral lymph nodes. They are named after the organ next to which they are located. There are splenic LNs, mesenteric LNs, gastric LNs, and hepatic LNs.
Parietal or parietal nodes
These are lymph nodes located behind the peritoneum, including para-aortic and paracaval. LNs are concentrated close to large blood vessels in the form of various clusters.
External lymph nodes
External lymph nodes are lymph nodes located close to the surface of the human body. To diagnose, it is enough to simply visually inspect them and feel them. Everyone needs to know the location of external lymph nodes; this will help them independently identify changes in them in the early stages.
Superficial lymph nodes are formed into several large groups:
- LU of the head and neck.
- Supra- and subclavian lymph nodes.
- Axillary lymph nodes.
- Elbow lymph nodes.
- Inguinal lymph nodes.
- Popliteal lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes of the head and neck
LUs of the head are mainly small concentrations:
- parotid superficial;
- deep;
- occipital, mastoid;
- submandibular;
- chin;
- facial.
The picture shows lymph nodes on the head and face, information about the location of which must be known and studied for the primary diagnosis of pathologies in the medical and cosmetology field.
Cervical lymph nodes are divided as shown in the table:
| Front |
|
| Lateral |
|
| Lower | |
| Supraclavicular | |
Axillary lymph nodes
The axillary lymph nodes are very informative for diagnosis; they cause the filtration of lymph flowing from the arms and chest into them. LNs are located in the axillary zone and form 6 main groups.
- Lateral axillary.
- Medial axillary.
- Central.
- Apical (apical).
- Rear.
- Lower axillary.
The formation of lymph nodes into groups is necessary for diagnosis in oncological practice.
Lesions of certain lymph nodes may indicate the occurrence of pathology in a certain organ or life support system, the stage of the disease. Ulnar lymph nodes are less informative for diagnosis than axillary lymph nodes. Reflect the presence of harmful processes occurring in the elbow and hand; they can rarely be affected by diseases of the lymphatic system.
Inguinal lymph nodes
They are divided into deep and superficial. The second group of lymph nodes is easily diagnosed in the inguinal triangle. The location of these lymph nodes in the groin is due to the outflow of lymph from the legs, pelvis, external and internal genital organs.
The picture shows groups of lymph nodes of the pelvis and groin:
- 1 - lumbar lymph node;
- 2, 3 — external lymph nodes, internal iliac lymph nodes;
- 4 - deep groin lymph nodes;
- 5 – external lymph nodes of the groin.
Below the inguinal lymph nodes, there are popliteal lymph nodes, they are located in the fossa under the knee. They can become inflamed due to unfavorable processes occurring in the foot or in the knee joint itself.
Increase in size: causes, symptoms
An increase in the size of the lymph node is a sign of an ongoing inflammatory process. Enlargement of several nodes or their groups is a sign of a serious pathological process or disease.
Superficial ones are large; normally in adults they can be up to 1.5 cm in diameter. The internal norm is defined as 3-10 mm. The size of the capsules in young children is considered normal: 2-5 mm, depending on the location. Sometimes due to peculiarities of physiological development. Compliance with the standard is determined by the attending physician, based on the individual characteristics of the person, based on the results of medical research. Selected cases allow dimensions up to 5 cm in a non-inflamed state.
Tumors in the lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are the most vulnerable organ according to their purpose. By blocking infections and pathogenic organisms, they themselves are susceptible to inflammation. Minor changes in capsule size during filtration of an aggressive environment do not cause concern. Often the lesion turns into an independent disease and requires local treatment. Inflammation of the lymph nodes is called lymphadenitis. According to the degree of damage and severity of the course, lymphadenitis can be simple (local), destructive, accompanied by the development of the inflammatory process beyond the capsule itself through the lymph flow, and chronic.
Simple lymphadenitis shows symptoms:
- increase in size;
- change in skin color;
- pain is caused by palpation and movement;
- temperature increase;
- general malaise.
Simple lymphadenitis often takes on a purulent form and requires opening and local antibacterial treatment.
Destructive lymphadenitis complements the above symptoms with a number of signs:
- the number of nodes of one group has been increased;
- change in color and density of the skin;
- edema.
Requires immediate extensive antibacterial treatment, since suppuration and effusion of pus can lead to sepsis.
Self-medication in acute cases of lymphadenitis is unacceptable; you must immediately contact a medical facility immediately after the first signs of inflammation appear.
Chronic lymphadenitis occurs without acute symptoms; apart from an increase in the size of the lymph nodes, the person has no complaints about other manifestations. The absence of acute pain, temperature, and other signs of inflammation indicates the presence of a chronic disease that does not manifest itself in acute form. This pathology occurs unnoticed, but has serious consequences. Tuberculosis, AIDS, hepatitis C, hepatitis B can go unnoticed for a long time.
Lymphadenopathy is damage to the lymph nodes without an underlying disease. Occurs without the course of another disease. The nature of lymphadenopathy can be viral, infectious, or oncological.
Diseases that affect the lymphatic system
There are diseases of the lymphoid system itself, or a consequence of other diseases. These diseases can affect individual organs of the lymphoid system, for example lymph nodes, or they can affect the entire system as a whole. Since one of the main tasks of the lymphoid system is to cleanse the body and produce antibodies to fight pathogens, it reacts to any infection that enters the body.
Diseases affecting the lymphatic system include acute respiratory viral infections, tuberculosis, rubella, syphilis, various oncological and autoimmune diseases, HIV infections, lymphadenitis, lymphangitis and many others, as well as diseases that arise from traumatic lesions of the lymphoid system, not very good heredity, bad habits and natural environmental factors.
Lymphadenitis
The most common and most common disease of the human lymphatic system. This inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes and is caused by infection, virus, or trauma to the lymph nodes. Almost always, inflammation of the lymph nodes with lymphadenitis is manifested by its thickening, swelling, redness of the skin around the lymph nodes, and pain on palpation.
ARVI
Some of the most common infections are:
- cytomegalovirus;
- adenoviral;
- rhinovirus;
- chicken pox;
- rubella.
With infectious mononucleosis, the main symptom is an increase in cervical lymph nodes. For other viral infections, an increase in several groups of lymph nodes on the human body is typical, most often lymph nodes of the neck, less often lymph nodes of the head.
Tuberculosis
LU tuberculosis is a very serious human disease. Most often it develops together with diseases of the lungs and respiratory system. Surprisingly, but true, women are more often susceptible to tuberculosis. LU tuberculosis causes global changes in lymphoid tissue. Damage to lymphoid tissue begins when bacteria enter tuberculosis (Koch bacilli).
Tuberculosis develops in lymph nodes with a significant difference than in other tissues and organs. With lymph node tuberculosis, not only the size of the lymph nodes increases, but there is also a multiple increase in the production of lymphocytes. If, on the one hand, this improves the quality of lymph, then on the other, if there is a large amount of it in one place, granulomas may begin to form.
With tuberculosis of lymph nodes on the human body, in 70-80% of cases, cervical lymph nodes are affected, and only in 15-20% are axillary lymph nodes and inguinal lymph nodes enlarged. Only in isolated cases are other lymph nodes affected.
Syphilis
Syphilis is an infection caused by a pathogenic microbe - Treponema pallidum. A surprising feature of this disease, Treponema pallidum affects only humans. Lymph nodes on the human body become enlarged, just like with other infections. The increase in lymph nodes of that particular group completely depends on the site of infection - chancre.
When it appears on the genitals, the first reaction will be in the inguinal group of lymph nodes and the pelvic group of lymph nodes. When a chancre appears on the chest, there is an immediate reaction in the axillary lymph nodes and periosternal lymph nodes; if chancre affects the lips or tongue, the first reaction is visible on the cervical lymph nodes, facial lymph nodes, and head lymph nodes.
Less commonly, when chancre appears on the extremities, the lymph nodes of the arms or lymph nodes of the legs may enlarge. Very often, LUs are connected to each other and can form chains and entire conglomerates. Syphilis is congenital and can be transmitted from mother to child.
The consequences of congenital syphilis can be very dire. When the process develops in utero, this microbe lives and multiplies in the child’s body. Consequently, treponema circulates throughout the child’s lymphatic system, damaging his internal organs and tissues.
Rubella
The virus initially enters the nasopharynx, then into the blood and spreads through the circulatory and lymphatic systems throughout the human body. Naturally, the immune system reacts to the pathogen with inflammation of the lymph nodes, as well as numerous rashes on the skin. The lymph node is clearly defined under the skin.
In rare cases, in infected people, the spleen and sometimes the liver become enlarged due to the accumulation of the virus inside itself. The peculiarity of the virus is that a person has persistent immunity for life, after recovery.
The rubella virus has a clearly defined cytopathic effect, that is, it affects the cytoplasm and embryonic cells, which very often leads to various mutations in these cells and fetal malformations. Therefore, the disease poses a great danger to expectant mothers during pregnancy.
HIV infection
HIV infection is one of the newest diseases in the modern world. The disease is widespread on all inhabited continents of the planet, in all races and age categories of people. The clinical picture is also very diverse, with many different pathologies.
This also applies, of course, to the immune system and pathologies of lymph nodes in HIV infections. The study of the symptoms accompanying this infection, together with a quick response to the incidence, is the main direction for the prevention and diagnosis of HIV
A very common symptom accompanying HIV infection is lymphadenopathy. This disease is a direct attack on the human immune system. When the immune system is damaged, widespread inflammation of the lymph nodes on the human body occurs, since they are the first to respond to HIV and the virus directly multiplies in the lymph nodes.
The infection most affects the cells - lymphocytes.
Especially their subtype – T-helpers. These cells are responsible for the strength of the immune response. DR in HIV does not increase immediately after infection, but after a long period of time, up to several months or years. But when HIV infection gains strength, and the increase in DR occurs everywhere. Then the recovery of DR and HIV infection is significantly complicated.
Oncology
Oncology of the lymphatic system, mainly lymph node cancer, is a disease with systemic development and covering the entire body. The pathology is initially similar to an autoimmune process. The tumor can affect both superficial lymph nodes and deep lymph nodes. The most common localization of lymphoma is in the armpits, collarbone and groin.
Lymph, by cleansing and at the same time nourishing cells, helps remove infections from the body, and this is a huge burden on the body and its lymph system. Very often the immune system cannot cope with such loads. It is very important to identify signs of pathology in advance, in the early stages, namely changes occurring in the lymph nodes.
There are a lot of direct and indirect factors that accelerate the possibility of developing oncological processes associated with oncology of the lymphatic system. These include: age (with age the risk of getting sick increases), various pathologies of the immune system, heredity, environmental and natural factors.
Lymphoma is a very aggressive disease and multiplies at a high rate throughout the human body. In this case, the affected cells accumulate and concentrate in the lymph nodes.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases include those that are provoked by the person’s own immune system. With these diseases, a malfunction occurs in the body or a malfunction of the immune system, and as a result of these malfunctions, blood leukocytes begin to fight certain cells of our body, considering them harmful and foreign.
Autoimmune diseases are systemic and complex. The complex and systemic nature of these diseases is manifested by the fact that both a separate organ, some kind of life support system, and the entire body as a whole can be affected.
Failures in which autoimmune diseases can occur can be divided into several subgroups. Subgroups include external and internal causes, in which white blood cells become aggressive and multiply completely uncontrollably.
- Internal reasons. Internal causes include certain mutations that occur in genes of types I and II, when leukocytes cease to identify a certain type of cell in the body. Lymphocytes, as one of the varieties of non-granular leukocytes, are orderly cells that can begin to multiply uncontrollably and cause various autoimmune diseases. Internal causes include the consequences of very severe, long-term infectious diseases and their long-term drug treatment, after which the immune system fails and cells begin to multiply uncontrollably.
- External reasons. External causes include harmful effects from the environment, for example, radiation, electromagnetic or solar radiation; water and air pollution, industrial emissions.
The principle of operation of the lymph node
Lymph enters inward through lymphatic vessels from the convex side through the openings of the capsule in places where supporting structures emerge from the capsule. Having entered the capsule through the sinuses located between the capsule and the supporting structures, the lymph passes through the sinuses and flows out at the location of the gate on the concave side. The cavities of the sinuses are blocked by cells of reticular tissue, forming something like a mesh. This structure of the lymph node allows lymph to slowly leak through the sinuses through the lymph nodes, and differentiation, cleansing of the lymph, and production of antibodies occurs.
The products of processing and cleaning of the lymph nodes are removed through the mucous membranes of the body:
- The vagina in women and the urethra in men. During inflammatory processes occurring in the body, the appearance of fungus in these areas is a frequent occurrence. But fungal infection is a consequence, not an independent disease. A woman who treats locally exclusively for thrush, and not for the original causes, is guaranteed to get relapses. The appearance of vaginal manifestations of fungal infection requires the need to consult a doctor, undergo the necessary tests and identify the cause of the fungus.
- Nasopharyngeal mucosa. A runny nose is a typical manifestation of the results of the lymphatic system fighting viruses and infections. It is required to treat, and not suppress, vasoconstrictors.
- Intestines. Lymph nodes located in the abdominal region are open to the intestines. A lot of poisons and toxins are eliminated through the intestines as a result of the work of the lymph nodes to fight infections and viruses. The manifestation of diarrhea is the reaction of the immune system to an intestinal infection occurring in the body. Taking antidiarrheal drugs without treating the causes of diarrhea - a virus or bacteriological infection - leads to problems with the intestines, where poisons and toxins simply remain.
- Sweat glands. The release of toxins through the skin occurs through these elements. They are not located on all areas of the skin. The use of long-acting antiperspirant deodorants leads to vasoconstriction and blocking of normal sweating. As a consequence, it is impossible to remove decay products in the lymph nodes. At the same time, increased sweating indicates the active functioning of the lymphatic system, which should lead to thoughts about the reasons for this activity.
Infections and viruses enter the body through the outer integument, by airborne droplets, sexually, and through the blood, first of all they enter the lymph. Through lymphatic vessels, harmful carriers enter nodes in the threat zone and localization of the virus or infection. The appearance of a threat in the capsule is accompanied by a response - identification, recognition and production of antibodies. This process leads to an increase in size, since an accumulation of lymph forms in each zone of the capsule at each stage. An increase in size is a manifestation of the body’s immune response to one or another harmful carrier.
The condition of the lymph nodes provides information about the presence or absence of inflammation and neoplasms, which should be identified and treated. The increase in most cases is accompanied by pain. The degree and development of pain depends on the location and severity of inflammation.
Method of examination of lymph nodes
For studies of lymph nodes, the method of inspection and palpation (palpation and light pressure) is used. These techniques can only diagnose easily accessible lymph nodes, mainly superficial lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are located deeper in the human body, then it is necessary to examine the lymph nodes using modern ultrasound diagnostic methods.
When diagnosing lymph nodes, a mandatory condition for carrying out is a symmetrical examination of lymph nodes, that is, examination from both sides and simultaneously, by comparing healthy lymph nodes with lymph nodes susceptible to painful changes. It is also mandatory to record the number of affected lymph nodes in all examined points.
If a person does not experience health problems, then the reaction of the lymphoid system will not be visible, in particular, the lymph nodes are not enlarged and cannot be palpated. But if we take into account the wide incidence of various dental diseases, gum diseases, the number of seasonal and allergic irritants of the nasopharynx, then we will be able to detect submandibular lymph nodes without special skills and experience.
And already due to injuries of the lower extremities, sometimes microtraumas of the skin, palpation to determine small (the size of a small bean) inguinal lymph nodes or microdamages of the hand is indicated by an increase in the elbow lymph nodes, sometimes, with severe damage, an increase in axillary lymph nodes can be detected.
When diagnosing lymph nodes, their consistency is noted, they are palpated for pain, they are palpated and the mobility of lymph nodes to the skin and to each other is determined (adhesions of lymph nodes in the form of a chain or entire conglomerates). Painful sensations in the area of the lymph node that occur during palpation may indicate inflammatory processes occurring in the human body.
When diagnosing an inflamed lymph node, great importance is given to examining the skin above the lymph node; the absence or presence of swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, for example, a strong change in color, increased temperature of the skin over the lymph node - may indicate the presence of purulent processes in the lymph node.
Technologically, palpation of the lymph node is carried out with the tips of several fingers, slightly bent, very carefully, effortlessly, carefully without damaging the lymph node, with light movements.
Diagnosis of pathology
If a person comes to the doctor with a complaint of enlarged lymph nodes, palpation is performed first. However, the method allows checking only surface nodes. The following are taken into account:
- size;
- presence of redness;
- local temperature;
- adhesion to surrounding tissues.
If pathological processes occur in deep lymph nodes, an ultrasound examination or x-ray will be taken. Additionally, tomography and lymphography may be prescribed. The patient must also undergo general blood and urine tests. If there are indications, the therapist can refer the patient to specialists.
Examination of the lymph nodes of the head
Palpation of lymph nodes includes a certain sequence. Initially, the occipital lymph nodes are palpated, after which the postauricular lymph nodes are approached to be examined. Parotid lymph nodes are diagnosed in the area where the salivary glands are located.
Mandibular lymph nodes or submandibular lymph nodes are subject to inflammation when various harmful processes occur in the nasopharynx; they are palpated under the skin of the lower jaw. Facial lymph nodes are located quite deep and inflammation in these lymph nodes rarely occurs. For the diagnosis of diseases, they are not of great practical importance.
Complications of inflammation of the lymph nodes
Inflammation of the lymph nodes and lymphadenitis has negative consequences in the absence of proper treatment. The two most dangerous and common are sepsis and abscess.
Sepsis, or blood poisoning, is the entry of purulent masses into the blood and their spread through the circulatory system. Dangerous for health. Without antibiotic treatment, the virus quickly damages vital organs and causes death.
An abscess is suppuration, necrosis of individual areas of the skin, accumulation of blood in one place. It is treated with surgery and antibiotics.
Examination of the lymph nodes of the neck
Just as when diagnosing other lymph nodes, superficial cervical lymph nodes are palpated. LNs are examined on the side and in front of the neck, as well as, respectively, behind and in front of the edge of the sternum, clavicular and mastoid muscles.
Significant compaction of the cervical lymph nodes, prolonged over time, indicates serious processes and inflammation occurring in the human lymphatic system and are observed in tuberculosis and lymphogranulomatosis, sometimes in lymphadenitis and lymphocytic leukemia.
If you diagnose a very dense and enlarged lymph node in the area just above the collarbone, in a kind of muscle triangle (the so-called “Virchow-Troisier gland”), then this may be a sign of stomach cancer.
Which lymph nodes become inflamed during HIV disease?
HIV disease may not show itself for a long time, but only all the lymph nodes of a person enlarge, but not immediately, but gradually. First, the lymph nodes under the arms, on the neck, chest, and lower back become inflamed. And when all the lymph nodes are enlarged, then we can say that the disease can no longer be cured.
Attention . If several groups of lymph nodes are inflamed for a long time (about 1 month), it is worth checking your blood for HIV.
Examination of axillary lymph nodes
To examine the axillary lymph nodes, the patient's arms are moved in different directions. Slightly bent fingers are placed on the palpated area and inserted deep into the armpit, without pressure. Then the abducted arms are lowered, but not pressed tightly against the body.
Afterwards, the axillary lymph nodes are palpated from top to bottom. If upon palpation there is a strong enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes, these signs may indicate unfavorable processes in the arms and chest, up to metastasis, in breast cancer.
How to keep lymph nodes healthy?
There is no specific prevention of lymph node pathologies. To maintain the health of the lymphatic system, you need to:
- Healthy food;
- eliminate alcohol and smoking;
- adhere to the rules of personal hygiene;
- treat any diseases in a timely manner;
- avoid hypothermia;
- maintain immune defense at a high level.
If you discover any alarming symptom, you should consult a doctor. Only a specialist after a comprehensive examination can determine the type of disease and identify the cause of its development.
Related Articles
Lymph nodes in the neck: structure and size, causes and symptoms of inflammation
Lymph node under the arm: location and functions, causes of inflammation
Are there lymph nodes on the back: location of lymph nodes in the human body
Why does a child have enlarged lymph nodes: norm and pathology?
Lymph nodes in the groin: where are they located, how to feel them and why do they become inflamed?
Lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity: location features, causes of enlargement and inflammation
Features of treatment of lymph nodes for various pathologies
To treat lymph node diseases on the human body, it is necessary to undergo general urine and blood tests. If there are signs of pathology, additional studies are carried out, including a detailed blood test. It is necessary to determine the leukocyte formula.
And only after carrying out diagnostic procedures and examining test results, doctors can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The types of treatment for the patient are determined, which depend on the severity and stage of cancer. Several types of treatment are currently used.
Conservative treatment
The technique is applicable when there is an increase in lymph nodes in any area of the human body. Often, lymph nodes increase due to damage to the body by viruses or bacteria. After prescribing and completing a course of therapy with antiviral or antibacterial agents, the lymph nodes take on their true size, and their functionality is restored.
Sometimes treatment may take longer if a person’s immunity was weakened initially.
Surgery
The most common disease is the formation of an abscess in the lymph node area. If the abscess does not go away after conservative treatment, it must be removed surgically. After removing the abscess, it is necessary to conduct additional studies (biopsy) of the removed area.
Very often, the formation of an abscess near the lymph node is a harbinger of a tumor. The tumor is mostly benign, but if certain treatment is not taken, it can very easily turn into a malignant tumor and start an oncological process throughout the human body.
Sclerosis with alcohol
In the treatment of lymph nodes, there is a unique treatment method - sclerotherapy with alcohol. The use of this type of treatment is effective in detecting small benign tumors in the organs of the lymphatic system. The essence of the treatment is the introduction of a 70% alcohol solution into the tissue affected by the tumor, organ or lymphatic vessel.
The introduction of an alcohol solution leads, after a certain time, to sclerosis of the tumor tissue and its subsequent death. In this case, complex surgical intervention is avoided.
Chemotherapy
This type of therapy is used when malignant tumors of lymph nodes are detected on the human body. A thorough diagnosis is carried out, tests are checked for tumor markers, cytostatic medications are selected for the patient individually, taking into account many factors, which fight cancer-affected cells of organs and blood vessels.
Radiation therapy
In certain cases associated with lymph node involvement by a malignant neoplasm, radiation therapy is used. With this treatment method, radiation is given to the affected organ or tissue.
Effectively used after surgical treatment, to prevent the occurrence of malignant formations around a removed organ or tissue. Sometimes, for medical reasons, when the patient’s tumor is inoperable, radiation therapy is used in conjunction with chemotherapy.
Combination therapy
Often, for complex diseases of the lymphatic system in the human body, several types of treatment are used simultaneously. When combination therapy is carried out correctly, the effectiveness of treatment increases, recovery time is reduced, and the harmful effects of certain types of therapy are reduced.
Author: Askerovo
Causes of inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes
For what reasons can a person begin to be bothered by inflamed nodes in the neck?
Typically, lymphadenitis is a concomitant syndrome:
- some infectious and viral diseases, for example, manifests itself in chickenpox, mononucleosis, herpes, rubella;
- diseases of the oral cavity, nasal passages, respiratory tract (with sinusitis, sore throat, colds, stomatitis);
- decreased immunity;
- injury or mechanical impact on nodes;
- states of hypothermia;
- lack of vitamins and some useful microelements;
- allergies;
- nervous disorders such as stress or depression;
- sexually transmitted diseases, including syphilis or HIV.
In young children, enlargement and pain on palpation in the lymph nodes may develop during teething. Sometimes inflammation occurs in women during pregnancy.
Against the background of decreased immunity, a person may experience chronic inflammation of the lymph nodes, not only in the neck, but also in the groin, armpits, back of the head, in the collarbone area, and in the abdominal cavity.
It should be noted that normally a person may have a slight enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck - up to a size of no more than 1 centimeter, in the groin - up to 2 centimeters. As for cases where inflammation manifests itself more intensely, this condition requires mandatory diagnosis in order to determine its etiology. So, for example, if inflammation is localized in the nodes in the neck on the right and left, this may indicate the development of mononucleosis, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, lymphoma, infectious lesions of the upper respiratory tract, and also occurs with a highly sensitive reaction to vaccination against the tuberculosis pathogen. Lymphadenitis in the nodes behind and in front of the ears develops with rubella, under the lower jaw - with chronic tonsillitis or gum diseases. If gradual or sudden inflammation of all groups of lymph nodes throughout the body occurs simultaneously, that is, multiple, this pathology is characteristic of the early stage of development of HIV infection. With lymphoma, the condition of the nodes is characterized as painless, while they become mobile. If a person develops metastases in the nodes, they are felt upon palpation as dense and fused.
Development mechanism
Enlargement of lymph nodes occurs in several ways, each of which involves the accumulation of a certain type of cell in the lymphoid tissue. The reaction of peripheral lymphatic organs is often associated with increased blood flow, proliferation of lymphocytes and macrophages in response to the appearance of foreign genes. With antigenic stimulation, the node can increase 5-15 times in 5-10 days. Systemic neoprocesses are characterized by active proliferation of degenerated lymphoid cells with an increase in the size of the affected lymph node.
The stroma of lymphatic formations can be infiltrated by inflammatory elements (in infectious diseases), tumor cells located in the lymphatic drainage zone of a given node. Metastatic lesions are often accompanied by proliferation of connective tissue. In some disorders of lipid metabolism (Niemann-Pick disease, Gaucher syndrome), macrophages filled with undigested glycosphingolipids are retained in the lymph node.
Axillary lymphadenitis in a child