Lymphoma is an oncological lesion that originates from lymphoid tissue or degenerated lymphocytes. Considering that the blood flow is involved in the process, over time all lymph nodes are affected, as well as other organs, including the bone marrow. The disease is diagnosed equally in both adults and children. If you seek medical help in a timely manner, the disease can be eliminated. Treatment of lymphoma abroad takes place taking into account new standards.
Taking into account the fact that the entire process is localized in the lymph nodes, the first symptoms of the disease can be observed precisely from them. In adults, the axillary and submandibular nodes often increase in size. At this stage, identifying the problem is not difficult. If you perform an ultrasound, it turns out that the entire section has darkening. With normal inflammation, there are gaps in some places. Any good doctor will refer a person for further examination, where the diagnosis will be confirmed or not confirmed (this happens extremely rarely). If the diagnosis is confirmed, the cost of the examination will be included in the total price for cancer treatment abroad.
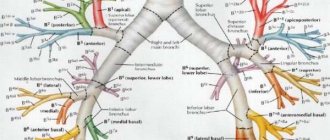
The structure of the lymphatic system in pictures
The human lymphatic system (a diagram in pictures will be presented below) is a complex mechanism that includes several structural components: vessels, nodes, lymph. And to understand this, it is worth considering the links of this chain separately.
Vessels
The human lymphatic system (a diagram in pictures will clearly show the location of its main nodes) has some structural features. Its branches resemble plant roots. The vessels penetrate into the tissues of organs. The exception is the brain, spinal cord, parenchyma of the spleen, lens, inner ear, sclera, placenta, cartilage tissue, and epithelial tissue.
The diagram shows how the human lymphatic system works.
Biological fluid flows from the cells into the capillary processes of the system, one end of which is completely closed. That is, the movement occurs only in one direction - up. The walls of the capillaries have good permeability, which allows liquid to easily penetrate inside.
Capillaries converge into vessels equipped with valves that prevent the reverse movement of lymph. They completely envelop the internal organs and flow to the lymph nodes located throughout the body. The stems coming out of them are directed into the ducts, and ultimately end up in the veins. In this way, lymph enters the blood.
Nodes
Lymph nodes consist of lymphoid tissue. It is in them that B-lymphocytes are formed and develop, whose role is indispensable in immune processes. Thanks to them, antibodies are produced to fight various pathogens.
In addition, T-lymphocytes are located in the lymph nodes, where their differentiation takes place after contact with the antigen. Lymph nodes not only serve as a connecting link, but are also an active participant in the formation of immunity at the cellular level.
Lymph
Lymph is a liquid of biological properties, which contains lymphocytes. It consists of water, salts, fats and other substances. The viscosity of lymph is provided by colloidal proteins. Its composition is in many ways similar to blood.
The volume of lymph in the body is 1-2 liters. The movement of the substance occurs under pressure, which is formed as a result of contraction of the cells of the vascular walls. Significantly affects the speed of lymph movement, adjacent muscles, breathing phases, and body position.
How dangerous is the pathology?
Having understood what serous and reactive lymphadenitis is, as well as diseases of specific and nonspecific etiology, you should be aware of their potential complications.
The dangerous consequences of lymphadenitis are purulent inflammation with the development of an abscess and the spread of the pathological process beyond the lymph node. In such cases, irreversible changes in the lymphoid tissue develop, which require surgical intervention.
Among the complications:
- fistula formation;
- thrombophlebitis;
- lymphogranulomatosis.
Changes in lymph node tissue are potentially dangerous due to the onset of cell malignancy. As a result, the risk of developing lymphoma increases. Lymphoma can be distinguished from lymphadenitis by the absence of acute symptoms during a malignant process, but cancer can be accurately excluded only after a comprehensive examination.
Abscessing lymphadenitis is dangerous for infection of the entire body in case of rupture of the capsule of the inflamed node. In this case, purulent contents penetrate into the general bloodstream and can cause blood poisoning, known as sepsis. In the most advanced cases, sepsis can cause death.
The problem with chronic inflammation is its long duration. However, the cause of the disease may remain hidden. The mere presence of a focus of infection in the body is dangerous, as it creates conditions favorable for the development of various pathological processes.
Chronic lymphadenitis, the treatment of which is not started on time, is accompanied by weakened immunity, so the frequency of various infectious diseases increases many times over.
Basic functions in the body
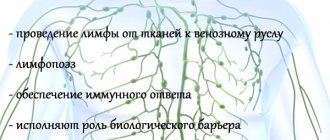
The human lymphatic system (the diagram in pictures shows the relationship between the lymphatic and circulatory systems) plays an important role in the body. Immunity, metabolic processes, and protective function depend on how well it functions.
Important tasks assigned to the LS:
- Delivery of fatty acids, fats of the small intestine to all organs and tissues that need them.
- Cleansing the body of harmful substances.
- Synthesis of lymphocytes that increase resistance to the negative effects of harmful microorganisms.
- Removal of tissue fluid, which allows you to remove harmful substances from tissues.
What is lymph
Lymph is a transparent liquid of viscous consistency that takes part in metabolic processes. It consists of lymphocytes. The lymphatic system, like the bloodstream, has vessels and capillaries, but the walls of which are poorly developed. Unlike blood circulation, it works without a closed cycle and is formed from intercellular fluid. Lymph is popularly called ichor, and each of us has seen it when it oozed from a wound.
This liquid moves slowly from bottom to top. Unlike the circulatory system, the heart does not take part in its movement, and its speed depends on breathing, pressure drop in the vessels and capillaries, as well as muscle contraction. The total volume of lymphatic fluid in the human body is 1-4 liters.
The lymphatic system performs the following functions:
- purification of interstitial fluid, as well as its redistribution;
- removal of toxins and protection from pathogenic microorganisms, viruses, fungi and parasites;
- return of water, metabolic products, salts and proteins to the bloodstream.
If we consider the functioning of lymph, then its work consists of collecting fluid between cells and transporting it through vessels and capillaries to places of purification - lymph nodes, in which bacteriophages and T-, B-lymphocytes are present. They act as filters and utilizers. Lymph nodes also work like pumps, pushing fluid further. After purification, it partially goes back into the circulatory system. Harmful substances come out through the skin pores along with sweat.
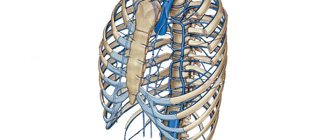
Diagram of human lymph movement
There are about 500 lymph vessels and nodes in the body. The movement of lymph in them occurs strictly from bottom to top, from the peripheral endings to the center. The fluid enters the lymph nodes through multiple vessels and exits through 1-2 channels. The movement of lymph thus reaches the main lymph vessels - the pillars.
The largest of them is the thoracic duct, which is located near the aorta. This vessel allows fluid collected in the organs on the left side, located below the ribs, in the head, chest, and arms. Ultimately, the lymph from the left thoracic duct enters the subclavian vein.
Similarly, there is a right duct of the LS. Its function is to collect lymph from the right side, which extends from the head, arm and chest. This division of the flow allows you to divide the load on the vessels and nodes, as a result of which the lymph is able to move freely in the body. Any blockage of lymph vessels threatens swelling and the formation of tissue tumors.
What are the main symptoms of lymphadenitis?
An acute nonspecific process begins with pain in the area of regional lymph nodes and their enlargement. In hyperplastic and catarrhal forms, enlarged nodes are easily palpable, their pain is insignificant, and general disorders are mild.
When suppuration occurs, the node becomes painful and dense, intoxication develops - loss of appetite, fever, headache, weakness. Local manifestations increase - swelling and hyperemia in the area of the affected node, its contours become unclear. If the formed abscess is not opened in time, pus may leak out or into adjacent tissues.
Lymphadenitis (according to ICD-10 - L04) in children occurs with high fever, loss of appetite, malaise, and sleep disturbances.
Organs of the lymphatic system
The human lymphatic system (the diagram in pictures clearly depicts the location of lymph nodes in the body) in addition to vessels and nodes, also includes organs. Each of them performs a specific function, which allows you to strengthen the body’s defenses.
The coherence of their work affects the level of immunity of the body.
- Bone marrow. This organ consists of soft tissue that is located in the cavity of the bone. It is in it that white and red blood cells are formed. Despite the fact that its mass is only 250 g, it produces 5 million blood cells daily, replacing obsolete ones with them.
- Thymus. The organ is located behind the sternum. Its function is to provide protection against pathogens. It takes stem cells and converts them into T lymphocytes. The laying of an organ occurs in the embryonic state, but as a person grows, it gradually decreases. With the achievement of puberty, the thymus gland loses its peculiarity and redistributes its function between other organs.
- Spleen. The function of this organ is to cleanse the blood of damaged red blood cells, foreign components and bacteria. The spleen also contributes to the formation of antibodies when an infection enters the body. The connection of this organ in metabolic processes has also been established, which contributes to the accumulation of iron in it, necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin.
Symptoms of lymphoma depending on its type
There are several types of lymphoma, and the symptoms vary for each one. It’s not for nothing that Hodgkin’s lymphoma is treated abroad according to one scheme, while non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, for example, is treated completely differently.
Symptoms for different types are as follows:
- Lymphedema . This type is characterized by damage to the extremities due to the leakage of lymph fluid into the layers of the skin. In this case, there is very severe swelling of the soft tissues, and the lesion is always symmetrical. At advanced stages, people find it unbearable to walk; they feel full and heavy.
- Hodgkin's lymphoma . In people with this disease, small bumps can be felt under the skin, especially in the back of the head, above the collarbones, in the neck or groin. In addition, when the lymph nodes of the chest are affected, shortness of breath and severe coughing begin. When the spleen and liver are damaged, the back hurts, and when the bone marrow is involved in the process, weakness and pallor of the skin makes itself known.
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. In this case, severe sweating, general weakness, weight loss and headache are constantly present.
- Lymphangiosarcoma. The disease is extremely rare and is observed against the background of lymphostasis. The symptoms are all the same as described above.
Types and groups of diseases
Dysfunction of drugs provokes the development of a number of diseases. All of them are divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory. The first type includes infectious and non-infectious diseases. The second includes toxic, allergic, autosomal pathologies.
According to the nature of development, they are acute, subacute and chronic. Depending on the scale of tissue damage, diseases of the lymphatic system can be limited or widespread. With constant progression, the pathological process eventually develops into a generalized one.
Main types of diseases:
| Group name | Pathologies |
| Developmental defects |
|
| Tumors |
|
| Inflammation |
|
| Injuries |
|
Causes of disorders in the body
Damage to the lymphatic system can occur for a number of reasons. Experts highlight the most basic ones.
- Heredity. The likelihood of developing the disease is very high if close relatives have been diagnosed with such diseases.
- Virus infection. Many viruses, such as influenza, measles, and HIV, are able to penetrate the lymphatic system, provoking the development of inflammation.
- Bad environment, bad habits. Both factors contribute to increased contamination of the body with toxins and harmful substances. As a result, the load on the lymphatic system significantly increases, which leads to its failure.
Lymphadenitis: a brief description of the pathology
Lymphadenitis (ICD-10 code L04) is a specific or nonspecific inflammatory lesion of the lymph nodes. The disease is characterized by pain and enlargement, headache, weakness, malaise, and fever. The inflammatory reaction in lymphadenitis is the barrier function of the lymphatic system, limiting the spread of infection throughout the body. Typically, lymph node disease occurs as a complication of inflammation of a certain localization. Infectious pathogens penetrate the regional lymph nodes with lymph, which flows from the original purulent focus. In other cases, the disease occurs when infection directly enters the lymphatic network through damaged mucous membranes or skin.
Symptoms of the onset of diseases
Despite the fact that the diseases can be different, in most cases they have the same primary signs of damage to the drug.
Main symptoms:
- annoying itching of the skin;
- elevated temperature;
- chills;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- swelling of the limbs;
- weight loss;
- skin pigmentation that was not there before;
- enlarged spleen;
- fast fatiguability;
- general weakness;
- irritability;
- sudden change of mood.
Subsequently, others are added to the existing symptoms, depending on the type of pathological process.
Diagnosis of the condition
When making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the results of various examinations and tests. Only a specialist can say what specific measures will be required based on the patient’s complaints and the symptoms identified when interviewing the patient.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Visual inspection. In this case, the doctor examines the lymph nodes and also uses palpation to determine the likelihood of inflammation of the spleen.
- Blood analysis. This examination allows you to determine the leukocyte formula.
- Lymphography. The method is used to confirm or refute cancer diseases. It is carried out by introducing a radiopaque component into a vessel of the lymphatic system. Subsequently, the movement of the liquid is monitored using images.
- Biopsy, histological examination. The method involves taking fluid and tissue to identify a malignant tumor. Subsequently, the samples are sent to the laboratory to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Based on the collected data, the doctor determines the form of the disease and the degree of tissue damage, which allows him to prescribe the appropriate course of treatment.
What is the treatment for lymphangitis?
In case of acute lymphangitis, it is necessary to eliminate the main focus, through which inflammation is maintained in the lymphatic vessels. Treatment of wounds, opening of phlegmons, abscesses, felons, their sanitation and drainage are carried out. The affected limb is fixed in an elevated position. With lymphangitis, massage and heating of the inflamed area should not be performed. Rubbing in various ointments is also contraindicated. Drug therapy includes the use of antibiotics (cephalosporins, semisynthetic penicillins, lincosamides, aminoglycosides), antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs, infusion treatment, and ultraviolet irradiation of the blood.
For sluggish chronic lymphangitis, local dressings with ointments, compresses with dimethyl sulfoxide or semi-alcohol, ultraviolet irradiation, and mud therapy are prescribed.
What other diseases cause enlarged lymph nodes?
Treatment Options
Therapy is carried out depending on the established disease, as well as the nature of the pathological process.
Treatment methods:
- Drug treatment. Prescribed for enlarged lymph nodes as a result of bacterial or viral damage. No special therapy is required, since the inflammation will go away on its own after the underlying disease is eliminated. It is allowed to take antiviral and antibacterial medications. If the provoking factor is an allergen, then therapy is carried out using antihistamines.
- Surgery. This method is prescribed when an abscess or tumor forms in the lymph node, which should be eliminated in order to avoid serious complications. Surgery to remove the spleen (splenectomy) is also used when an abdominal injury occurs that causes its rupture.
- Sclerosis with alcohol. This method is used to detect benign neoplasms of small diameter. To remove them, alcohol is introduced into the tumor tissue, which leads to their necrosis and subsequently death.
- Chemotherapy. Prescribed when malignant tumors are detected. The principle of its action is based on the destructive effect of toxins and poisons on neoplasm tissue. The drug is introduced into the body periodically after a certain number of days, since its action is aimed at destroying tumor cells, so the administration is associated with the cell cycle.
- Radiation therapy. The procedure is prescribed for cancer. The principle of its operation is based on the use of high-dose ionizing radiation. Thanks to this technique, the growth and division of malignant tumor cells is stopped, which subsequently leads to its destruction.
- Combination therapy. In some cases, the doctor prescribes several treatment methods. This technique is used when the disease continues to progress despite steps taken.
Causes of lymphadenitis
The causative agent of this disease of the lymph nodes is pyogenic flora - streptococci and staphylococci, as well as the toxins secreted by them. They penetrate the lymph nodes by hematogenous, lymphogenous or contact route. The initial focus may be purulent wounds, boils, felons, carbuncles, erysipelas, phlegmon, trophic ulcers, caries, thrombophlebitis, osteomyelitis. Local inflammatory processes are often accompanied by a regional form.
What is the cause of lymph node disease in children? This disease is often associated with influenza, chronic tonsillitis, otitis media, childhood infections, and skin diseases. The cause of specific lymphadenitis is the pathogens of syphilis, tularemia, tuberculosis, gonorrhea, plague, actinomycosis, anthrax, etc.
How to cleanse the lymphatic system
The human lymphatic system cleanses the body of harmful substances and toxins. On the schematic representation of its organs and nodes, which is presented in the pictures above, you can see how important it is for the full functioning of the internal organs. A negligent attitude towards one's health leads to increased contamination of the lymph.
This negatively affects its functionality. The liquid begins to linger in the vessels, and the concentration of toxins in its composition increases. As a result, the lymphatic system begins to work to the detriment of the body. This leads to a decrease in immunity, as a result of which the body’s susceptibility to the effects of pathogens increases.
Signs indicating lymph pollution:
- colds, infectious diseases;
- failure of kidney, liver, spleen function;
- regular exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- skin rashes, pigmentation;
- allergy;
- obesity;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- joint inflammation;
- diseases of the reproductive organs;
- psoriasis.
To cleanse the lymph, you can use several methods: medications, massage, folk remedies. Each of them gives a stable positive result. Therefore, it is worth understanding the features of each procedure separately.
General recommendations
Experts highlight some rules for lymph cleansing that should be taken into account when carrying out the procedure. Ignoring them may render the event futile.
Basic recommendations:
- During the week before the procedure, you should visit the bathhouse twice.
- Carry out a cleansing enema every 3 days.
- Increase daily water intake to 2.5 liters.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Cleaning should be done once every six months, in spring and autumn.
- Take frequent walks in the fresh air.
- Enrich your diet with healthy foods. Give preference to greens, walnuts, flax oil, fresh fruits and vegetables, eggs, berries, and dairy products.
- Avoid fried and fatty foods, alcohol, animal fats, flour products, canned food, smoked foods, pickles, and sweets.
- It is recommended to eat food often, but in small portions.
- You can’t go hungry, you need to eat as much as you want, but the food should be healthy.
- Eat meals at the same time every day.
Causes of lymphangitis
The disease occurs secondary, against the background of a deep or superficial purulent-inflammatory focus - a boil, an infected wound or abrasion, an abscess, or phlegmon. The main pathogens in this case are beta-hemolytic streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, and sometimes Proteus and Escherichia coli. Specific lymphangitis is caused by the presence of tuberculosis in the patient.
Microbial agents enter from the lesion into the interstitial space, then into the lymphatic capillaries, and along the lymph flow to large lymph nodes and vessels. Reactive inflammation of the vascular walls is expressed in swelling of the endothelium, increased permeability, the occurrence of exudation, intravascular thrombus formation, and loss of fibrin clots. Such changes provoke lymphostasis - a disorder of local lymph circulation. As inflammation progresses, purulent lymphangitis and fusion of blood clots occur.
Medicines
In some cases, medications are prescribed to cleanse the lymphatic system. The need for this procedure is determined by the doctor in case of frequent cases of damage to the body by viruses and infections. Medicines have a targeted effect on increasing immunity. The dosage, frequency of administration, and course of treatment depend on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Main types of medications:
- Herbal preparations (Immunorm, Immunal). Helps activate the protective function.
- Medicines that contain weakened bacilli (Broncho-munal, Likopid, Bactisporin, Broncho-Vaxom). Their use causes the body to produce antibodies to fight pathogens, which significantly improves immunity.
- Products with nucleic acid (Derinat, Poludan, Sodium nucleinate). They have a complex effect on the body: improve wound healing, activate the bone marrow, and enhance the synthesis of leukocytes.
- Medicines based on the thymus gland of animals (Tactivin, Timalin, Thymogen). Strengthen immunity, normalize metabolism in cells.
- Interferon preparations (Anaferon, Arbidol, Viferon). Increases resistance to viruses and infections.
Massage
To restore the function of the lymphatic system, it is also recommended to use massage. The choice of technique for its implementation is made by the doctor, depending on the form of the pathological process.
Main types of massage:
- Lymphatic drainage. The massage is carried out using a soft bristle brush. The skin should be dry, clean and warm. Movements should be superficial, wavy. Their direction should correspond to the movement of lymph in the vessels.
- Vacuum roller procedure. The massage is carried out with a special device, which allows you to create a vacuum environment to expand the lumen in the blood vessels.
- Pressotherapy. For the procedure, a special suit is used, into which air is supplied. Under its pressure, the body initially contracts, and when released, it relaxes. Despite the feeling of discomfort during this massage, its effectiveness is much higher than other methods.
- Microcurrents. The procedure is carried out with a special device that affects the body with low-frequency current pulses. This helps to activate the flow of blood, as well as the outflow of lymph. As a result, stagnation of biological fluid is eliminated.
The effectiveness of massage directly depends on the professionalism of the master. Therefore, it is recommended to contact medical institutions that have proven themselves positively over many years.
Swelling on the face
Puffiness of the face and bags under the eyes cause dissatisfaction, especially among the fair sex. However, serious congestion threatens health and requires treatment.
Lymphatic drainage massage, aimed at normalizing lymph outflow, increasing skin tone, and improving complexion, will help get rid of facial lymphostasis.
Watch this video in which professional massage therapist Margarita Levchenko shows you what movements to do.
Lymphatic drainage facial massage. Margarita Levchenko.
It is important to eat right, do not abuse fatty salty foods, alcohol, and stop smoking.
Folk remedies
To cleanse the lymphatic system, as well as to prevent diseases, it is recommended to use traditional medicine. This method is not only accessible, but also effective.
Effective recipes for restoring the function of the lymphatic system:
- Liquorice root. Pour boiling water (250 ml) over the dry crushed component (20 g). Keep the mixture in a water bath for 15 minutes. Cool, clean, bring the volume of liquid to the original volume. Drink the medicine 100 ml 2 times a day for 1.5 weeks.
- Infusion of yarrow. Pour 70 g of medicinal plant collection into 1 liter of boiling water. Keep in a thermos for 50 minutes. Clear the drink. Take 3 times a day, drinking 100 ml. The course of therapy is 10 days.
- Echinacea decoction. Steam 20 g of dried herb with 500 ml of boiling water. Keep the mixture in a thermos for 10 hours, so it is better to prepare it overnight. In the morning, clear the drink of impurities. Drink the medicine 100 ml three times a day for 30 minutes. before meals. Course - 10 days, break - 5 days. Repeat therapy 3 times.
- Kvass based on horse chestnut buds. Heat 3 liters of whey slightly. Add 200 g of chestnut buds, 20 g of crushed celandine, 100 ml of honey and 300 ml of sour cream. Place the mixture in a warm place for fermentation for 72 hours. After the time has passed, clean the kvass and bottle it. Take 3 times a day, drinking 100 ml. Full course - 60 days.
The function of the lymphatic system (diagram in pictures) in the human body should not be underestimated. Schematically, it represents a separate organ, parts of which are located throughout the body, which can be seen in the drawings given earlier in the article. The functioning of all internal organs depends on how effectively it copes with its tasks.