Perioral dermatitis - in medicine it is also called rosacea-like or perioral dermatitis. This is a rare disease, occurring in approximately 1% of the population, most often in women 20-40 years old.
With perioral dermatitis, small papules and pimples appear on the skin around the mouth and on the chin, the skin turns red, irritation appears and papules grow over a larger area. This creates considerable aesthetic, physical and psychological discomfort for a person. This is how most patients describe the onset of the disease - “... recently I noticed that several small red pimples had formed on my chin, I began to use acne cream and wash my face more often, but this only made it worse.
Within a few months, the skin around the mouth and chin became simply red, and when the acne healed, it left dark spots. Moreover, between the lips and the affected areas around the mouth there is a clear strip of healthy skin without redness...”
Traditional methods of combating facial skin disease
Along with traditional treatment, folk therapy is often used.
This comprehensive approach allows you to quickly get rid of skin rashes and speed up the process of regeneration of damaged areas. At the initial stage of development of oral dermatitis, traditional healers recommend using herbal decoctions for lotions. In this situation, it is appropriate to use wormwood, chamomile, linden, and string.
Herbal decoctions based on St. John's wort, calendula, and celandine are recommended for daily wiping of the affected areas of the skin of the face.
Alternative therapy also includes oral medications. Usually they are taken according to the same “scenario”: three times a day, 1/3 cup.
For example, you can prepare a decoction according to the following recipe. Mix in equal proportions plantain leaves, elecampane root, the flowering part of chamomile and calendula, as well as horsetail, St. John's wort and sage. Then pour 100 grams of the resulting plant material with a liter of boiling water and leave to infuse. You can also prepare a medicine based on birch buds. Pour 1 tablespoon of the herbal component into 250 ml of boiling water and take according to the traditional regimen.
Ointments prepared with your own hands are very effective for oral dermatitis. For example, you can mix onion juice, natural honey and flaxseed oil in a ratio of 1:2:2. Or prepare a medicine from pre-melted propolis (4 tbsp) and vegetable oil (1 tbsp).
In most cases, with timely and competent therapy, the skin disease can be eliminated within a few weeks.
However, do not forget that after drug treatment it is important to observe prevention. Eliminate from your life all possible causative factors of skin disease (cosmetics, detergents), stop using corticosteroids and hormonal creams, properly care for your facial skin - and then the disease will not bother you again
Prevention measures
In order not to encounter unpleasant signs of oral dermatitis in the future, it is necessary to take the following preventive measures:
- do not use ointments or cosmetics of the corticosteroid type;
- Avoid using fluoride toothpastes;
- try not to use household chemicals for a while, especially if they contain allergenic substances;
- give up bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle - this will prevent most skin diseases;
- Maintain oral hygiene.
Prevention of perioral dermatitis
The prognosis for perioral or perioral dermatitis is positive, but only in cases where the diagnosis is timely and treatment is prescribed by an experienced specialist.
How to cure a disease: drug treatment
It is immediately worth noting that therapy for this disease is a labor-intensive and rather lengthy process. Depending on the severity of the course of treatment, the course of treatment can take from 45 days to 3 months. The sooner you start therapy, the faster and more effective the results will be.
Therapy for oral dermatitis begins with eliminating the causative factors, that is, eliminating all used cosmetics, creams and ointments, as well as replacing fluoridated toothpaste with regular one. At the same time, drug treatment is carried out, which may include the use of:
- antihistamines: Loratadine, L-ceta, Suprastin, Cetrina, etc.;
- drugs of the imidazole group: Metronidazole, Trichorol;
- antibiotics: Oxalicin, Erythromycin, Metacycline, etc.;
- antiseptic solutions: Decasan, Chlorhexidine;
- vitamins: Riboflavin, Ascorutin, vitamin C, group B, nicotinic acid, etc.
Dietary nutrition is an important part of comprehensive treatment. For patients diagnosed with oral dermatitis, doctors recommend excluding salty, spicy, spicy, sour foods and dishes from their nutritional diet during therapy. In addition, there is a “taboo” on alcohol, tea and coffee.
Unfortunately, even with proper treatment, it is not always possible to avoid relapses of the skin disease. However, repeated outbreaks of the disease are much easier and are cured faster.
Nutrition when sick
A special diet for perioral dermatitis plays an important role in treatment. It is important to exclude certain foods and make the diet hypoallergenic. The following products should not be used for dermatitis on the face:
- any fish, seafood and fatty meat;
- oranges, lemons, tangerines;
- soy products;
- tea or coffee;
- mushrooms;
- baked goods and sweets;
- chicken eggs.
You should not add seasonings to your diet and it is better to limit salt. Let's eat more vegetables and fruits. It is also recommended to avoid meat broth; during treatment, the soup should be prepared in vegetable broth. The ban applies to sweet soda and alcoholic beverages. They should be replaced with fruit drinks, compotes, green tea and clean water. The volume of liquid drunk should be at least 1 liter.
The rash around the lips looks unpleasant and gives a person a lot of discomfort. At the first sign, it is better to consult a doctor and find out what it is. Do not be afraid of visiting several doctors at once - a comprehensive examination is sometimes necessary to make a diagnosis. During treatment, it is recommended to review cosmetic skin care products and diet; compliance with all doctor’s recommendations guarantees a quick recovery. Perioral dermatitis during pregnancy requires care; it is better not to experiment and discuss the problem with a specialist.
You can ask your question to our author:
Diagnostic features
In principle, there is nothing complicated here. A simple external examination by a specialist and a description of other symptoms is enough. However, for treatment to be effective, the causes of the disease must be determined. To do this, you may have to undergo additional tests:
- Blood and urine.
- Allergy test.
— Be examined by a therapist, who should take an anamnesis regarding the frequency of occurrence of infectious diseases. Data from a cardiologist and endocrinologist may be required.
If you are diagnosed with oral dermatitis, treatment, reviews of which are mostly positive, will be carried out comprehensively.
Symptoms of the disease
This form of dermatitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of itching, hyperemia, pain and burning in the mouth and chin (pictured);
- small pimples may have a head, upon opening of which, in the initial stage, a separation of transparent exudate is observed. In the future, it can develop into purulent;
- rashes can group together, forming colonies.
Rosacea-like dermatitis is accompanied by the appearance of scales on the inflamed areas, which may subsequently fall off on their own. This manifestation of the disease occurs quite often with this type of dermatitis.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose perioral dermatitis, a bacterial culture for rosacea-like dermatitis should be performed.
Quite often, diagnostics reveal the presence of fungi of the genus Candida on the skin, causing oral candidiasis. However, to date it has not been possible to identify the specific infectious agents that cause perioral dermatitis.
Histology of the skin is not recommended due to the fact that there are no specific signs of perioral dermatitis. As a rule, there is a subacute inflammatory process and isolated areas of altered skin, which can be confused with similarly manifested skin diseases.
Steroid dermatitis: classification of the disease
There are 2 main classifications of the disease: according to the severity of symptoms and according to the location of the rash.
According to the location of the rash, they are distinguished:
- perioral dermatitis itself. The rash is located around the mouth and on the chin.
- periorbital dermatitis. The rash may appear on the bridge of the nose, cheeks and around the eyes. mixed form. Combines the symptoms of perioral and periorbital dermatitis. This form is more common than others.
- Steroid dermatitis, like all other diseases, is also classified by severity. But to determine the severity of the disease, there is a special index (PODSI) - it includes characteristics of such signs as redness, papules (nodules) and peeling. Each of these symptoms is rated on a scale from 0 to 3 points. Intermediate values can also be used, for example, 1.5 or 2.5 points. The scores are then summed up to form the PODSI index, which can be used to determine the severity of the disease.
With a mild degree of the disease, the index is in the range of 0.5-2.5, with perioral dermatitis of moderate severity this value is 3.0-5.5, and if the index is in the range of 6.0-9.0, then we can conclude that the disease is severe.
Patterns of disease development
Perioral dermatitis is a common condition, affecting 1 in 100 adults. Typically, patients aged 20-30 years are affected, with women 12 times more likely than men. However, the pathology is observed in both preschool children and the elderly. Among children, the pathology is more common in teenage boys.
The causes of perioral dermatitis are unknown. Scientists suggest that the prerequisite for the development of the disease is an allergic predisposition. The triggering factor is the too frequent use of moisturizing cosmetics or creams with glucocorticoids (especially fluoridated ones), as well as the use of fluoride toothpaste.
Factors provoking and maintaining exacerbation:
- prolonged exposure to the sun or excessive use of solariums;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- foci of chronic infection in the body (chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries);
- hormonal imbalance;
- tuberculosis and other severe infections;
- pregnancy.
Sometimes microorganisms of the genus Fusobacteria can be obtained from the contents of the vesicles, which indicates the participation of infection in the development of perioral dermatitis. It is believed that in some patients the disease is associated with Demodex mites and Candida fungus.
Constant use of moisturizers leads to the accumulation of fluid in the stratum corneum of the skin, resulting in swelling. The protective (barrier) properties of the epidermis are weakened, and microorganisms are introduced into the skin.
The infection is localized primarily at the openings of the hair follicles. Inflammation of the skin occurs - dermatitis. Seeing swelling and redness of the skin, many patients begin to use glucocorticoid ointments on their own. After short-term positive dynamics of the condition, these drugs lead to a significant and long-term worsening of the course of perioral dermatitis.
In many cases, patients use fluorinated glucocorticoids on the advice of a dermatologist for long-term seborrheic dermatitis, acne, and rosacea.
The main role in the appearance of symptoms of the disease is played by opportunistic microflora of the skin, which normally does not harm a person. Its pathogenic qualities appear under the following conditions:
- deterioration of the natural bactericidal properties of the skin due to prolonged use of external glucocorticoids;
- deterioration of immunity;
- allergic reaction to bacterial antigens;
- hormone imbalance due to side effects of external medications or gynecological diseases;
- thinning of the skin under the influence of hormonal ointments.
Is perioral dermatitis contagious or not?
The pathogenic microflora involved in its development can be transmitted to a healthy person. But in the absence of other conditions for the development of the disease (for example, the use of hormonal creams), microbes will not lead to inflammation.
What is oral dermatitis?
oral dermatitis on the face treatment
Usually they are located symmetrically, but their localization can also be unilateral. Papules and pustules do not immediately affect the skin; they can grow over several weeks or even months.
Oral dermatitis can be distinguished from other facial skin lesions due to the characteristic border in the form of an area of healthy skin around the lips. Granulomatous oral dermatitis occurs mainly in children. It differs in the color of the papules: they can be pink, yellowish-brown or flesh-colored.
In addition to typical locations, papules may be located around the ears, on the scalp, on the labia majora, on the skin of the arms and legs. Papules can be located separately or merge into groups.
Skin lesions usually do not cause significant discomfort to the patient. The main cause for concern is cosmetic discomfort. In some cases, there may be a feeling of skin tightness, a slight itching or burning sensation. Patients also complain of intolerance to certain types of cosmetics and moisturizers.
The first cases of oral dermatitis were reported in the 1950s. Recently, the number of cases of the disease has decreased significantly. This is due to the fact that corticosteroid drugs are increasingly used in the treatment of skin diseases.
Women (from 20 to 45 years old) are primarily at risk. Less commonly, oral dermatitis is diagnosed in men and children. Children suffer from oral dermatitis regardless of gender and race. Prepubertal children are more likely to develop granulomatous oral dermatitis.
Some believe that oral dermatitis is a type of rosacea, but these skin lesions differ in the nature of the rash. Additionally, perioral dermatitis usually develops at an earlier age than rosacea.
To date, doctors cannot determine the exact cause of the development of oral dermatitis. It is assumed that oral dermatitis is provoked by corticosteroid hormones contained in tablets, ointments, creams or inhalants for bronchitis.
The disease can develop even after taking weak corticosteroids (for example, hydrocortisone) or their short-term use. If corticosteroid drugs are used to treat inflammation or cosmetic problems on the skin, this can also lead to the development of dermatitis.
Eye ointments containing corticosteroids can cause perorbicular dermatitis. Another possible cause of the development of the disease is dentures and toothpastes containing fluoride. Interestingly, after the patient is cured of perioral dermatitis and starts using this paste again, a relapse may not occur.
The formation of skin rashes can be caused by sun exposure, improper use of cosmetics, the use of synthetic substances, etc.
Development of the disease in childhood
In children, areas of the skin affected by red nodules with rashes may experience peeling where the blisters break. The disease can manifest itself against the background of asthma, during inhalation therapy. Early treatment of atopic dermatitis, accompanied by corticosteroid drugs, can provoke the development of perioral dermatitis on the face. Thus, steroid dermatitis develops. These drugs cause addiction to the skin and contribute to the transition of the disease to a chronic form. The use of even such a mild drug as hydrocortisone can have a negative impact. Stopping steroid ointments for children abruptly can be dangerous due to the fact that the child’s skin is very delicate and withdrawal of the drug can be difficult to tolerate. It is necessary to discontinue the drugs gradually; for this reason, treatment of perioral dermatitis in a child can take up to a year or more. To alleviate the unpleasant consequences of withdrawal, lotions with mineral water are prescribed to the affected areas.
What does perioral dermatitis look like on the face?
The external manifestations of perioral dermatitis are similar to many other skin diseases, so only a dermatologist should make a diagnosis.
The main symptom is the appearance of small rashes and pimples, which have the following features:
- The main affected areas may be areas around the lips, nasolabial fold and chin area.
- The location of all rashes is usually symmetrical.
- The sizes of pimples can be very different and vary from very small to quite large, and also merge into a single lesion.
- At the initial stage, the rash is red or has a light pink tint, but over time they become brown.
- The rash can develop into a purulent irritation if third-party infections enter it.
- After the rash passes, hyperpigmentation remains in its place for a long time.
- A small strip 1.5-2 mm thick remains near the lip border, which is not subject to inflammation. This is the hallmark of perioral dermatitis, which is observed in most patients.
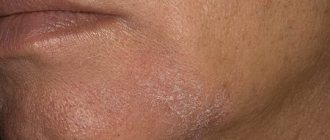
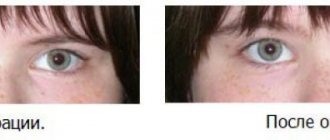
Photo
In order to better understand what perioral dermatitis looks like, below is a photo of dermatitis that depicts the main manifestations of this disease:
Characteristic symptoms
This type of dermatitis can be asymptomatic for several months. After this period, redness (erythema) and small papules appear on the skin. Over time, large pathological foci are formed from the resulting papules, which doctors call plaques.
In this case, the patient may experience the following clinical signs:
- dry skin;
- peeling;
- the appearance of crusts on the perioral part of the face;
- the formation of a clear boundary between the affected area and the lips.
Symptoms of perioral dermatitis
The main symptom of perioral dermatitis is a rash that also affects the chin area and nasolabial triangle. The resulting papules are whitish in color and can reach a diameter of 1 to 3 mm.
Causes of perioral dermatitis in adults
Perioral dermatitis has been studied by specialists for a very long time, after which they came to the conclusion that the main reason is a decrease in the basic protective functions of the skin, after which it cannot withstand aggressive external influences.
Among the factors that can provoke such a phenomenon are:
- Too long and frequent use of toothpastes with a high concentration of fluoride in the composition.
- Systematic use of cosmetics that have a harsh effect on the skin, for example, various scrubs.
- Undergoing potentially harmful and dangerous cosmetic procedures, primarily this concerns chemical exposure and mechanical peeling.
- The use of pharmacological or cosmetic products that contain hormonal components.
- Use of corticosteroids for medical reasons.
- Presence of seborrhea.
- Disruption of the functioning of the digestive, vegetative-vascular or endocrine system.
- Frequent exposure to direct sunlight or exposure to excessive amounts of ultraviolet radiation in other ways.
- Change of residence, implying a sharp and radical change in climatic conditions.
- Taking contraceptives that lead to hormonal imbalance in the body.
- General deterioration of the immune system.
Causes of perioral dermatitis in children
As already mentioned, perioral dermatitis can also occur in children, in which case immediate consultation with a pediatrician is always required.
The causes of this disease in younger patients may be the following factors:
- Hormonal changes that occur in the body and are associated with the process of growth and maturation of the child.
- Age-related changes in the structure of the skin, which can cause a number of dermatological problems.
- Other lesions of the facial skin, most often accompanied by purulent inflammation. In the most difficult cases, hormonal ointments are prescribed for topical use, which provokes the parallel occurrence of perioral dermatitis.
- Disturbances and deterioration of the immune system, which is typical for a growing organism.
- Increased need for nutrients, acute lack of vitamins, minerals or any chemical elements in the body.
Types of skin dermatitis
Each type of disease has different causes.
Allergic
Allergic dermatitis is the body's reaction to an allergen.
Allergic dermatitis can be caused by:
- Food (fruits, berries, nuts and other highly allergenic products).
- Plant pollen.
- Street or household dust.
- Medications.
- Chemical substances.
- Household chemicals.
- Cosmetics and care products.
- Animal fur.
This type of dermatitis occurs more often in people whose bodies are more prone to allergies.
Atopic
Atopic dermatitis is the most severe form of the disease. Symptoms first appear in childhood and later recur in adulthood. In adults, this form of the disease most often occurs due to constant stress or exposure to allergens.
The occurrence of atopic dermatitis is due to a genetic factor.
If one of the parents has experienced acute dermatitis, then with a 50% chance the child will develop atopic dermatitis. If the father or mother has atopic dermatitis, then the risk of this disease in the child is 80%. In many cases, atopic dermatitis is accompanied by bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis.
External manifestations of the disease and causes
This disease can be called differently - perioral, rosacea-like, steroid, perioral dermatitis. In any case, it manifests itself as redness of the skin around the mouth, with the appearance of pink-red convex papules in this area. The skin becomes dense and rough to the touch. Subsequently, these rashes spread to the chin, nasolabial folds, and cheek area. In advanced cases, the rash can spread to the skin around the eyes and temporal area. The rashes are usually symmetrical, concentrated in different areas, but do not merge. These rashes do not itch and do not physically bother the patient. In rare cases, a slight burning sensation may be felt in areas of redness of the skin.
The following reasons can provoke oral dermatitis:
- Diseases of the endocrine system, stomach, intestines, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Predisposition to allergic reactions.
- Infectious diseases, in particular candidiasis.
- General decrease in immunity.
- Sensitive facial skin.
- Creams and ointments containing hydrocortisone or prednisolone. To activate the disease, it is not necessary to use these hormonal drugs on the face; they can be applied to any part of the body.
- Fluoride toothpastes.
- Cosmetics - creams and lotions for facial skin care, foundation, powder, which contain paraffin, isopropyl myristate, petroleum jelly, sodium lauryl sulfite.
- Oral contraceptives. The disease is often provoked by the withdrawal of such drugs.
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or prolonged exposure to severe frost.
During the period of treatment, you should exclude exposure to provoking factors on the skin: do not use cosmetics and ointments, avoid any hormonal products and fluoride-containing paste, protect your face from the sun or bad weather when going outside, do not visit baths and saunas, and do not steam your skin.
Possible complications
Aesthetic problems and discomfort that arise with the development of perioral dermatitis can provoke various psychological problems, cause depression or neuroses. This is a chronic disease, so relapses may be accompanied by more severe symptoms (discomfort and skin rashes).
Complications of perioral dermatitis
Incorrect or untimely treatment can cause acne scars or pigment spots to appear on the skin. In addition, the affected areas of the skin become drier, pale and tight.
Treatment of perioral dermatitis
Treatment of this skin disease is quite long, the duration of therapy ranges from 1.5 to 3 months and depends on the severity of the manifestations of perioral dermatitis. Treatment of perioral dermatitis is prescribed by a dermatologist, and the sooner you contact a specialist, the more effective the result will be. Even with proper treatment, relapses of the disease are possible in the future, but they are much easier and are eliminated faster.
Zero therapy
The first thing that is recommended to be done after diagnosis is called zero therapy. That is, cancel all ointments, creams, cosmetics used, especially with corticosteroid substances, and also change the toothpaste to regular one. In this case, the condition may worsen for some time, and then after a few weeks it should improve.
Antihistamines
At this time, it is possible to use antihistamines (Suprastin, Cetrin, etc., see All allergy tablets), sodium thiosulfate, calcium chloride.
Antibiotics
For oral dermatitis, treatment with antibiotics is quite effective. The administration of Metronidazole gel or cream 0.75% or Erythromycin gel 2% stops the progression of the disease. Apply the product 2 times a day until the rash stops.
The doctor may prescribe an oral antibiotic - this is Minocycline or Doxycillin 100 mg 2 times. per day until the rash goes away, then for a month, 100 mg once a day and another month, 50 mg per day. And also taking Metronidazole orally (this is not an antibiotic, but an antiprotozoal drug).
Or Tetracycline according to a similar regimen, only 500 mg/2 times, then 500 mg/1 time and 250 mg/1 time. After starting the use of antibiotics, deterioration may occur, but after 3 weeks the condition of the skin usually improves noticeably.
Elidel Cream (Pimecrolimus)
Pimecrolimus can be used for oral dermatitis only as prescribed by a doctor when other treatments are ineffective.
Elidel is a cream that has long-term adverse effects; the effect of the drug has not yet been fully studied, but it is believed that pimecrolimus suppresses the secondary immune response and there have been cases of the development of skin tumors and lymphomas after its use
Therefore, the use of this product should be treated with caution.
Skin care for perioral dermatitis
For this disease, gentle facial skin care is recommended. After washing, you should not wipe your face with a towel, but only blot it. The doctor can select for you indifferent powders, cooling, moisturizing creams that do not contain substances that aggravate the symptoms of the disease. (see Allergy creams, dermatitis ointments)
Herbal infusions
In the case of an acute process, to relieve symptoms, you can use cooling lotions made from chamomile infusion (if there is no allergy) or 1% boric acid, as well as from infusions of St. John's wort, celandine, and calendula.
Normalization of the general condition of the body
If there are foci of infection, then treatment of concomitant diseases is necessary, as well as normalization of the endocrine and nervous systems, and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If necessary, general strengthening, immunostimulating drugs, and drugs that normalize the function of the central nervous system are prescribed. Monthly courses of vitamin therapy, B vitamins, vitamin C and A, and folic acid are recommended.
Sun protection
During the treatment period, you should protect yourself from direct sunlight, since ultraviolet radiation aggravates the symptoms of perioral dermatitis. In summer, you should use sunscreen daily with a protection factor of at least 30.
Normalization of the general condition of the body
It is important to remember that a positive result is observed only when, along with symptomatic therapy, it is possible to cure chronic foci of infection. In addition, the functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems and the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract should be normalized.
As necessary, medications are used to normalize the immune system, medications to strengthen the central nervous system, vitamin therapy (folic acid, vitamins B, A and C).
During the summer, sunscreen should be used, as direct ultraviolet rays can aggravate symptoms. It is necessary to use a cream with a high protective factor. In addition, cryomassage has a positive effect.
Warning! The use of corticosteroids (Elocom, Advantan, etc.) for this type of dermatitis is contraindicated. External treatment with glucocorticosteroids (Elocom, Advantan) can lead to the development of glaucoma.
Treatment of perioral dermatitis
Treatment consists of two stages:
The first stage is “zero”. All hormonal medications are canceled, and the negative symptoms that appeared after their discontinuation are removed.
It is recommended to avoid using cosmetics and hygiene products for the face, otherwise it will be impossible to establish the exact picture of the disease.
At this stage, the patient's condition worsens for a short period of time, but then gets better.
During this period, you need to properly care for your face. For mild stage disease, you can use a decoction of chamomile or sage. For a more complicated form, special oil-based emulsions will be required. For acute symptoms, 2% naphthalene-tar paste is used.
The following drugs are used externally:
- Products containing Trichopolum (ointment, cream, gel). The drug is applied twice a day. If a positive effect does not occur, 2% Erythromycin and Metronidazole gel are used. The first enhances the effect of other drugs.
- Body and face milk (Protopic 0.01% - 0.03%). The topical product relieves inflammation and does not provoke skin atrophy. Adults and adolescents over 16 years of age are prescribed Protopic ointment 0.1% - 0.03%. Children from 2 to 16 years old 0.03%. The drug is prohibited for use during pregnancy and lactation.
- Any external preparations containing zinc. They dry out and relieve itching.
- Adapalene is camelolytic and anti-inflammatory, stimulating epithelial production. Available in the form of gel and cream. Gel for oily skin, cream for dry skin.
- Elidel relieves inflammation and cannot be used for a long time. Prescribed for adults and children from three months.
- Rozamet is a drug for external use, practically not absorbed. When using, avoid direct sunlight.
At the “zero” stage, Erius, Parlazin, Telfast and others can still be prescribed. For swelling, diuretics are prescribed: Veroshpiron, Furosemide, etc.
Calming drugs Novo-Passit and Valerian are used in severe cases.
The first stage of treatment is completed by acupuncture and cryomassage.
The second stage of treatment is getting rid of microorganisms that cause the disease. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed: Metronidazole and Doxycycline, Azelaic acid and Isotretionine, Monocycline and others.
The drugs should be used for about two months. It all depends on the severity of the disease. Trichopolum is most often prescribed. It is characterized by a wide spectrum of action.
The second most commonly used drug is Doxycycline. The medicine gets inside and blocks the pathogen. It begins to work two hours after ingestion. The drug may reduce the bactericidal effect of taking penicillins. Expectant mothers should not take the medicine.
For effective treatment, inhibitors are sometimes prescribed: Pimecrolimus or Tacrolimus.
Drug treatment: indications, names of drugs, instructions for use
Initially, the causes that contribute to skin irritation are eliminated. For this purpose, it may be sufficient to use only anti-allergenic drugs and a hypoallergenic diet. In severe cases, intravenous detoxification therapy is prescribed.
Local treatment includes the use of ointments and antiseptics. Burning and itching are eliminated with the help of sedatives. In case of pancreatic dysfunction, which was the cause of dermatitis, enzyme replacement therapy is prescribed.
Glucocorticosteroids
For the past 40 years, corticosteroids have been the mainstay of treatment for atopic dermatitis. For this purpose, Hydrocortisone, Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus were used, but they are not effective in all cases. Many are associated with side effects, although they clear the rash within the first few days.
Initial therapy consists of 1% hydrocortisone powder in an ointment base applied twice daily to the affected areas. A medium strength steroid ointment (Triamcinolone or Betmenasone Valerate) is applied 2 times a day to the affected areas until the eczema lesions subside. Some steroids penetrate the skin into the bloodstream.
Hydrocortisone
Their number is small, but can have a negative effect on the body:
- increase AD;
- thin the bones;
- promote fluid accumulation in the legs;
- influence weight gain.
The amount of steroid applied to the affected areas is measured in FTU fingertip units. One FTU is the amount of ointment that is squeezed out of the tube along the finger from its limb to the first phalanx. Typically, 1 FTU is enough to treat an area of skin twice the size of an adult's palm. Two FTU equals approximately 1 g of steroid.
How much ointment should be applied to the affected areas:
| Area of skin to be treated | Dose units in FTU |
| Palm and fingers, front and back | 1 |
| Front chest and abdomen | 7 |
| Back and buttocks | 7 |
| Face and neck | 2,5 |
| Full hand | 4 |
| Full leg | 4 |
Antihistamines
Drugs that reduce itching and block chemical processes during an allergic reaction are always prescribed in the treatment of dermatitis. They are secondary to itching and should not replace treatment for dermatitis. Sedatives such as Zyrtec, Benadryl, Claritin improve sleep quality and reduce allergic rhinitis.
Immunosuppressants of the macrolide class
Macrolides are xenobiotics produced by soil fungi that have immunosuppressive properties. They help well in the treatment of inflammatory dermatoses. Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus are immunomodulators that act as calcineurin inhibitors.
Cyclosporine
When applying them, patients experience a slight burning sensation, which disappears within 2-3 days. For children over 12 years of age they are used in 0.03% and for adults in 0.1% composition. Pimecrolimus, produced on a cream basis, helps well. It is used once a day for moderate dermatitis. Can be used for children over 2 years old.
Moisturizers
The best preventive measure is to moisturize the skin, which improves the function of the skin barrier. Healthy skin is less likely to become inflamed and better protected from allergens and irritants. This could be Vaseline, Aquaphor ointment containing ingredients such as lanolin, beeswax, and silicones.
Aquaphor ointment
Such basic components should be present in daily skin care, especially in the presence of changes in the epidermal barrier and reduced water content in the epidermis. Moisturizers should contain substances: glycyrrhetinic acid, telmestein, lipids that have anti-inflammatory properties.
Drugs that help with dermatitis:
- Aloe vera increases skin hydration.
- Shea butter, whose stearic and oleic acids contain anti-inflammatory and antitumor substances.
- Bisabolol, based on chamomile, contains anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic substances.
- Liquorice root. Helps reduce dryness, itching, inflammation.
- Niacinamide improves skin barrier functions, reduces inflammation and water loss in the epidermis.