- Pathogenesis of the disease
- Routes of transmission
- Why and why is giardiasis so dangerous for children?
- Symptoms of giardiasis in children
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment of giardiasis in children
- Recovery period
- Prevention of giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic infection caused by the simplest single-celled creature from the genus Flagellate, Giardia. Giardia in children is quite often diagnosed completely by accident, during routine stool or scraping tests in kindergarten and school.
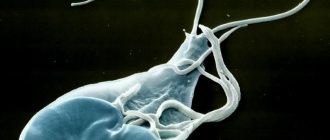
What does lamblia look like?
The parasite can exist in two forms: vegetative and cystic.
- Vegetative (mobile) form. It is a drop-shaped unicellular organism with 4 pairs of flagella and a special attachment disk. The parasite needs flagella to move through the small intestine, and the disc helps to attach tightly to the intestinal wall.
- Cystic (immobile) form. Serves as an adaptation of lamblia to unfavorable conditions. If the parasite fails to attach to the right place, it enters the large intestine. Conditions in the large intestine are not suitable for the life of the protozoan; lamblia turns into a round cyst.
In this form, the parasite enters the environment with feces. Giardia in the form of a cyst can exist for a long time, wait for suitable environmental conditions, and when exposed to such conditions, it can again turn into a vegetative form.
Where does Giardia come from in children?
Due to its ability to form cysts, Giardia lives in the environment for a long time. For example, the parasite can live in water for up to 5 weeks, on soil for about 3 weeks, and on vegetables and fruits for up to 48 hours. The parasite dies if the temperature drops below 13 degrees and when exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
The main source of infection is humans. Parasite cysts are excreted in the patient's stool. Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules and insufficiently washed hands after visiting the restroom serve as a tool for the spread of Giardia.
But giardiasis can be contracted not only from humans. Dogs, cats, cattle, and rodents are also susceptible to the disease and excrete cysts in their feces.
To become infected with giardiasis, 10-100 cysts of parasites are enough. The release of cysts from the same person occurs unevenly. The patient is most dangerous on the 9-12th day of the disease, when the most parasites are released (more than a million cysts in 1 g of feces). This period is manifested by subsidence of diarrhea and improvement of the patient’s condition.
The mechanism of transmission of giardiasis is fecal-oral, through ingestion of parasitic cysts.
Routes of infection by the parasite.
- Through the water. Giardia cysts can remain viable in water for a long time, up to 3 months. Water from natural sources, wells, and open reservoirs is dangerous for consumption. Only boiling is guaranteed to cleanse water of the parasite. Since the size of Giardia cysts is very small, not all filters are able to cope with this task.
- Contact and household path. Most often, children become infected with giardiasis through contact and household contact in preschool institutions and children's groups. A sick child does not follow the rules of hygiene and transfers parasite cysts to household items. Other children become infected through contact with infected toys, dishes, furniture, and towels. Bad habits of putting your hands in your mouth, sucking a finger, or chewing a pencil greatly increase your chances of contracting giardiasis.
- Food route. Infection with giardiasis occurs when eating unwashed foods that contain parasite cysts. Insects, flies, and cockroaches can carry cysts and contaminate food.
Giardiasis is easy to get infected by simply eating foods contaminated with cysts, drinking unheated water, or not washing your hands before eating. It is not for nothing that giardiasis is also called “the disease of dirty hands.”
Ways of infection with giardiasis
How is giardiasis transmitted? The source of infection is most often a person or animal, since cats, dogs, guinea pigs and other mammals are also giardia carriers. The main mechanism of infection by this type of infection is oral - fecal, and the pathogen spreads by water, food and contact. In other words, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, consumption of unboiled water, unwashed food, and unsanitary living conditions are the reasons for the spread and infection of giardiasis in children and adults.
How does giardiasis manifest in children?
Signs of giardiasis in children are varied and depend on the state of the child’s immunity. The disease can occur either acutely, with clear clinical manifestations, or in a mild form. Sometimes it is difficult to determine giardiasis; asymptomatic cases occur.
The disease in children most often occurs in an acute form, the main symptoms of which are the following.
- Diarrhea. Diarrhea is the most common symptom of the disease. The nature of feces with giardiasis changes, the feces become liquid, with an unpleasant odor, mixed with mucus, usually yellow. Sometimes diarrhea alternates with constipation.
- Indigestion. Intestinal function is disrupted, gas formation increases, and bloating occurs. Nausea and vomiting are symptoms characteristic of the acute form of the disease; they rarely occur in the chronic form.
- Abdominal pain. Increased gas formation, flatulence, and improper bowel function lead to cramps and pain around the navel and in the stomach area.
- Temperature increase. A slight increase in temperature is possible when Giardia first enters the child’s body. It is typical for the acute form of giardiasis and is combined with intoxication and deterioration of the baby’s general condition.
- Loss of appetite. Against the background of a general deterioration in the condition, the toddler’s appetite also changes. With an asymptomatic course, there may be no changes in appetite.
- Malabsorption. Intestinal dysfunction and frequent loose stools lead to decreased absorption of nutrients in the intestines. The baby does not receive enough nutrients, vitamins and minerals and begins to lose weight.
- Skin changes. A lack of vitamins manifests itself in skin symptoms, the skin becomes dry, pockets appear in the corners of the mouth, and cracks appear on the lips. Sometimes there is an increase in pigmentation, a marbled skin pattern.
- Deterioration in health. All this leads to a deterioration in the baby’s general condition; the baby becomes irritable, capricious, and gets tired quickly. If giardiasis is not recognized for a long time and the correct treatment is not prescribed, chronic malaise leads to a lag in the physical development of children.
- Allergic reactions. Giardia multiplies in the child's body and produces toxins that are absorbed into the blood. Toxins suppress the functioning of the immune system and provoke the development of various allergic reactions, atopic dermatitis. Why do allergies and cough occur with giardiasis in children? Giardia lives only in the intestines and does not get into the lungs, so why is coughing considered one of the signs of giardiasis? Cough serves as a response to the introduction of toxins and is often allergic in nature. And reduced immunity with giardiasis provokes the development of chronic bronchitis.
- Neurological disorders. Constant intoxication and vitamin deficiency lead to nervous system disorders. In addition to irritability and anxiety, there are nervous tics, hand tremors, and teeth grinding at night.
Diagnosis of Giardia in the liver and treatment
It can be carried out using various methods.
- Using the study of duodenal contents, this method is extremely painful for children.
- A blood test examines the presence of specific antibodies in the blood serum.
These studies are used when, with characteristic symptoms, the main analysis - scatology - does not show the presence of cysts. Feces for scatological analysis must be provided warm.
An ultrasound examination may also be required - the liver and pancreas are enlarged with giardiasis.
Treatment of giardiasis is divided into 3 stages. This process is quite long and cannot be carried out without following a strict diet.
Carbohydrates are excluded from the diet - children find it very difficult to tolerate the lack of sweets; the daily menu is based on cereals and vegetables of various types.
Stage 1
Depending on the severity of symptoms, the following is prescribed:
- choleretic drugs of various groups;
- enzyme therapy;
- enterosorbents;
- antihistamines.
Stage 2
Antiparasitic drugs are used either individually or in combination:
- "Furazolidone";
- "Trichopol" or "Metronidazole";
- "Tiberal"
- "Voormil";
- "Nemozol."
Antibacterial drugs may be required.
Stage 3
The diet is adjusted, products that enhance intestinal motility are introduced into it - baked apples, dried fruits, fermented milk products. To eliminate intestinal dysbiosis caused by treatment, probiotics are prescribed, to increase immunity - immune agents, and to restore the body - vitamins.
Each stage lasts up to 2 weeks.
It should be noted that medications that destroy Giardia have a large number of side effects.
During treatment the following may occur:
- vomit;
- intoxication;
- abdominal cramps;
- indigestion;
- neurological disorders;
- violation of hematopoietic function.
During treatment, parents should analyze how it affects the condition of their children. Correction of the therapeutic regimen, use of hormonal drugs, and symptomatic tactics may be required.
Why is Giardia dangerous in children and is it necessary to treat Giardiasis?
This issue is a source of controversy among doctors. Many consider giardiasis a dangerous disease that poisons the body, causes chronic diseases and requires immediate treatment.
Other doctors, including Dr. Komarovsky, consider only the acute form of giardiasis dangerous. The doctor insists that treatment is required for diarrhea lasting more than 10 days, or if there are no signs of other intestinal infections and Giardia cysts are detected in the stool.
What can be said for sure is that it is necessary to understand the appropriateness of treatment in each specific case. Manifestations of giardiasis in children are varied; the disease can affect many systems of the body, and can be asymptomatic.
With a small number of cysts in the intestines, the human body can cope on its own and “remove” Giardia into the environment without harm to the patient.
A doctor can recognize Giardia in a child and determine the need for treatment by assessing the results of diagnostic tests.
When is giardiasis treatment required?
Most pediatricians are of the opinion that therapy is not needed until the child begins to show symptoms of giardiasis. After all, it has long been known that the immune system itself is able to cope with a parasitic disease.
WHO also recommends starting to treat giardiasis only after its symptoms appear, that is, if cysts are found in the baby’s stool and he has prolonged diarrhea.
Diagnosis of giardiasis in children
Several diagnostic methods are used to detect Giardia in a child.
- Stool analysis. Stool analysis for scatology is considered the most reliable method for identifying Giardia. For analysis, experts suggest donating fresh feces, in which case living, mobile Giardia can be identified. But 20-30 minutes after collecting the analysis, Giardia changes into another form - cystic, in which it remains for a long time. Thus, in a pre-collected analysis, it is possible to identify parasite cysts, which also confirms infection with Giardia. To ensure the reliability of the result and prevent false diagnoses, doctors recommend checking stool for Giardia several times over a period of 2-3 weeks. Is it possible to detect lamblia in the liver? Indeed, at the beginning of the 20th century, Giardia was believed to live in the liver and bile ducts. But over time, it was found that bile has a detrimental effect on the parasite; protozoa can only live in the small intestine.
- Analysis of duodenal contents. A rather complex research method in which a special capsule with reagents is taken, attached to a nylon thread and lowered into the duodenum. The capsule dissolves in the intestine, the reagent enters the intestinal lumen and indicates the presence or absence of Giardia.
- Blood test for giardiasis. An immunological blood test for giardiasis is a controversial examination method. It identifies immune cells that were formed in response to the introduction of Giardia. But a feature of the disease is the possibility of self-healing, when the body copes with a small number of parasites.
In this case, the immune cells remain, and Giardia cysts may no longer be present in the stool.
The opposite situation is possible, when Giardia has entered the child’s body, and immunity has not yet been formed. Thus, a positive blood test for giardiasis does not indicate the need for treatment. The most reliable, simple and inexpensive way to examine a child for Giardia is a stool test.
Routes of transmission
Giardia can enter a child’s body in several ways:
- household - infection occurs through contaminated toys, shovels, buckets that a child plays with on the street, when using someone else's towels (from a patient or a carrier), through insufficiently washed hands, when biting nails;
- through water - when a child bathes in a polluted pond, accidentally swallows water or drinks water of unknown storage and origin (raw);
- through food - when eating unwashed vegetables, fruits, as well as foods that have not undergone heat treatment (raw milk, minced meat, raw fish, etc.).
Separately, it should be mentioned that flies and domestic animals that have access to the street can act as carriers of Giardia cysts.
The more “fast” carbohydrates (sweets, pastries, cakes) are present in a child’s diet, the faster and more intensely Giardia will multiply, and accordingly, the more severe the disease will be.
How to treat Giardia in children?
The main goal of therapy for giardiasis is to remove lamblia from the small intestine.
For the treatment of giardiasis in children, a scheme is used that includes three stages.
- First stage. Treatment begins with reducing intoxication and strengthening the body's defenses. An important role is played by the diet for giardiasis, which excludes bread, sweets, simple carbohydrates, milk and dairy products, and preservatives from the patient’s diet. It is recommended to include porridge, boiled meat, fruits and a sufficient amount of water in the diet. To facilitate the functioning of the digestive system and eliminate intoxication, sorbents, enzyme and antiallergic drugs are prescribed. The first stage of treatment lasts 1-2 weeks, the diet is followed for 3-4 months.
- Second stage. Antiparasitic drugs come to the fore in treatment. Please note that at the beginning of therapy, the symptoms of the disease may worsen, diarrhea may worsen, and rashes on the body may increase. This reaction is considered normal and lasts about three days. The duration of treatment and the choice of drug should be agreed with the attending physician; usually the course lasts about a week. Due to the frequent use of antiparasitic drugs, adaptation and addiction of Giardia occurs. Common medications may not be effective. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor to decide on the choice of medication.
- Third stage. Treatment at this stage is aimed at replenishing the body's strength and improving metabolism. In addition to enzyme therapy, probiotics and immunostimulants are prescribed. It is recommended to follow a diet and eat foods rich in pectin. The third stage lasts on average 2-3 weeks.
Recovery period
Occurs after completion of two courses of anthelmintic therapy. At this stage, all efforts are aimed at restoring immune function and eliminating disorders caused by poisoning of the body with decay products. To support the child’s body, he is prescribed:
- Enzymes – Mezim forte, Creon;
- Probiotics – Linex, Biogaia, Lactofiltrum, Hilak;
- Vitamin complexes – Alphabet, Kinder biovital, Revit, Undevit, VitaMishki.
It is important to follow a diet, since the body cannot yet cope with the stress. The principles of dietary nutrition are the same as at the stage of preparation for anthelmintic therapy - fast carbohydrates, fatty foods, whole milk, and sweet carbonated drinks are excluded.
The child should be encouraged to drink a lot - up to 1.5 liters of liquid per day, not counting first courses. You can also give herbal decoctions - chamomile, corn silk, immortelle herb. These decoctions have natural anti-inflammatory effects and help normalize the functioning of the gallbladder.
Treatment of Giardia in children with folk remedies
There are many folk methods of treating worms and parasites, including Giardia in children. The use of milk-garlic tinctures, tansy, birch buds and other remedies is widespread.
Unfortunately, folk remedies cannot guarantee recovery, their effectiveness has not been proven, and the harm sometimes exceeds the benefits of treatment. A lot of time is spent trying to recover in this way; the disease can progress.
Prevention of giardiasis in children
Like many other diseases, giardiasis can be prevented by knowing simple rules. In addition, the possibility of re-infection with Giardia cannot be ruled out, especially in childhood.
Therefore, it is important to follow preventive measures.
- All family members, including the child, must strictly follow the rules of personal hygiene and wash their hands regularly.
- Vegetables and fruits should be washed thoroughly before consumption.
- Drink only boiled water; not all filters can purify water from Giardia.
- Do not allow your child to swim in bodies of water if you doubt the quality of the water. A child can ingest Giardia cysts while bathing.
- Get your stool tested for Giardia regularly.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is extremely important to diagnose the pathology in the early stages, before the pathogen has yet managed to poison the child’s body with its toxins. At this stage, the disease responds well to therapy. For the differential diagnosis of giardiasis in children, detailed tests and studies are prescribed:
- stool analysis for coprogram - fecal samples are examined under a microscope for the presence of cysts in them; this diagnostic method cannot be called highly informative, since the pathogen is not always excreted in the stool. In order for the results of the analysis to be informative, you should take the coprogram several times with weekly breaks;
- serological test - a blood test that allows you to determine the presence of antibodies to Giardia, however, this study is informative when carried out only at the initial stage of the disease;
- duodenal intubation - allows you to examine bile for the presence of Giardia cysts in it, however, this diagnostic method is not used in children due to the complexity of the procedure.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the child is given a treatment regimen that can last quite a long time.
conclusions
Giardiasis is a widespread parasitic disease.
No one is safe from infection with giardiasis; there are many parasitic cysts in the environment. Symptoms of the disease are very diverse; the disease can manifest itself as severe abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs, or it can be asymptomatic. There are cases of spontaneous cure of giardiasis, when the body copes with the disease itself.
The main task of parents is to prevent the disease, teach the child the rules of personal hygiene, and monitor the purity of the food consumed. This way you can protect your baby not only from giardiasis, but also from many other infectious diseases.
Intoxication syndrome
The degree of manifestation of intoxication depends on the massiveness and virulence of the parasites.
- In some cases, the liver and spleen become enlarged (hepatolienal syndrome).
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
- With long-term giardiasis, neurological symptoms appear: bruxism (teeth grinding) and tics.
- The waste products of parasites inhibit the functioning of the central nervous system, which is manifested by the development of astheno-neurotic syndrome.
Rice. 15. Intoxication is a characteristic sign of an infectious disease.