Giardiasis is a lesion of the human intestine by single-celled protozoa - Giardia. The disease is widespread. The parasite, entering the body and feeding on the waste products of the host, can provoke pathological processes that negatively affect the functioning of the digestive tract.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Almost everyone who does not follow the rules of personal hygiene has Giardia, since the spores of the pathogen enter the body if a person neglects to wash their hands before eating or has the habit of eating unwashed vegetables and fruits.
When affected by this microorganism, adequate therapy is necessary. Patients with giardiasis may not always know that they have a pathology. In this case, they are carriers and pose a danger to others. The disease can occur in both mild and severe forms.
Giardia has high viability and high resistance to harmful environmental factors.
general description
An invasive disease that is caused by intestinal lamblia and manifests itself clinically as a functional digestive disorder is called giardiasis.
The main symptoms of the disease are abdominal pain of varying intensity, nausea, flatulence, and upset stool. In addition, there is intoxication of the patient’s body, enlargement of the liver, and asthenoneurotic and allergic syndrome may develop.
Another name for the disease is giardiasis. Diagnostics is complex and includes a number of laboratory and instrumental studies. Treatment of giardiasis includes taking antiprotozoal drugs and symptomatic therapy (enterosorbents, choleretic agents, enzymes).
Folk remedies
Drug therapy is combined with natural substances. Treatment of Giardia with folk remedies in adults is based on the action of choleretic and astringent herbs and antiparasitic compounds.
Here are some recipes:
- Horseradish and garlic tincture. Garlic and horseradish are taken in equal proportions, peeled and crushed using a blender. Then 50 g of the mixture is placed in a previously prepared, clean container and filled with a bottle of vodka. Cover the container with a tight lid and leave in a dark place for a week. The finished tincture is filtered and taken 1 tsp. half an hour before meals in the morning and evening. If the tincture seems too bitter, you can first dilute it with a small amount of water.
- Pumpkin seeds. It is important to take non-store bought ones, in bags; gut the pumpkin. Grind 300 grams of raw materials with a mortar, transfer to a glass jar, add 50 grams of honey and water. Eat this entire mass on an empty stomach within an hour, take a laxative.
- Tansy infusion. Brew 1 tablespoon of herb per glass of boiling water. Let the patient drink in small sips, 3-4 times a day.
- Remedy for Giardia from oats. Pour 250 grams of oats with a liter of boiling water, put on fire, evaporate a little less than a quarter of the total volume. Drink a glass 4 times a day.
- Rowan infusion. To prepare the remedy, pour 200 ml of boiling water over dried rowan fruits (1 tsp) and leave for 2 hours. The finished infusion is consumed before each meal in a volume of 100 ml.
- Corn silk infusion. Pour a tablespoon of plant material into a glass of boiling water and leave for 3 hours. Drink a tablespoon four times a day.
Traditional recipes are quite effective; they can be included in complex therapy after consultation with your doctor.
Classification of giardiasis
There are two main forms of the disease - giardia carriers, when a person does not have any symptoms, but is contagious to others, as he constantly releases giardia into the environment, and giardiasis, which occurs with a pronounced clinical picture.
In turn, giardiasis with severe symptoms is divided into several forms:
1. Intestinal. Symptoms of intestinal dysfunction predominate (enterocolitis, duodenitis, enteritis, dysfunction of the duodenum).
2. Hepatobiliary. The functioning of the biliary tract and liver is disrupted, and diseases such as cholecystitis and biliary dyskinesia occur.
3. Giardiasis in adults, which develops as a concomitant disease against the background of an underlying pathology (for example, celiac disease or atopic dermatitis), which reduces the body’s immune defense and allows Giardia to actively develop.
Medicines
Photo: pharmvestnik.ru
For giardiasis, the following antiparasitic drugs are used:
- Metronidazole. This drug is active against Giardia, Trichomonas, amoeba and anaerobic bacteria. Metronidazole is evenly distributed in all tissues of the body, is able to penetrate the blood-brain and placental barriers, and the half-life of the drug from the body is 8 hours. Contraindicated in people suffering from liver failure, since the drug is metabolized in the liver, as well as in children under 3 years of age and women during the first trimester of pregnancy. Occasionally, while taking the drug, side effects occur in the form of headache, nausea, abdominal discomfort, and stool disorders;
- albendazole. The use of the drug is contraindicated in children under 2 years of age, during pregnancy and lactation, as well as in people with cirrhosis of the liver. In most cases, the drug is quite well tolerated; the following side effects may rarely occur: dizziness, headache, abdominal discomfort, increased blood pressure.
In addition, drugs such as nifuratel, ornidazole or tinidazole may be used.
Of the enterosorbents, the most common and well-known is activated carbon. It has not only an enterosorbing effect, but also detoxification and antidiarrheal. The drug has virtually no contraindications; people with ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (nonspecific ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum) should be treated with caution.
For subsequent normalization of the intestinal microflora, probiotics or eubiotics are prescribed. Currently, there are a lot of different representatives of these drugs on the pharmaceutical market, for example, Linex, Enterol, Bifiform, Lactobacterin and others. These drugs usually contain from 2 to 4 strains of beneficial microorganisms, which are processed in such a way as to be able to withstand the aggressive gastric environment and end up in the intestinal tract unchanged.
To strengthen the protective properties of the human body, vitamin or vitamin-mineral complexes are prescribed. The duration of the course of treatment in most cases is 1 month. Usually this is enough to saturate the body with all the necessary beneficial vitamins and microelements.
Causes of giardiasis
The disease usually occurs after contact with a sick person, but cats, dogs, and rodents can also be carriers of giardiasis. In addition, Giardia lives in polluted water bodies and can even be found in ordinary chlorinated tap water.
For a person to develop the disease, it is enough to ingest ten Giardia cysts. Another important condition is low acidity of gastric juice.
Giardia can enter the body through household, water or food routes. Most often, the cause of acute or chronic giardiasis is the consumption of unwashed berries, vegetables and fruits, as well as insufficient heat treatment of food.
Symptoms of giardiasis
Most of the symptoms of giardiasis are associated with the gastrointestinal tract, since the parasites are localized in the small intestine. The first signs appear 7-21 days after the pathogen enters the body.
The following are the main initial signs of the disease:
- Flatulence.
- Diarrhea. The patient constantly has loose stools with a strong, unpleasant odor. It is characteristic that with giardiasis there are no impurities of blood and mucus in the stool, which distinguishes it from other gastrointestinal pathologies (for example, acute intestinal infections or dysentery).
- Stomach ache. Usually a consequence of diarrhea. The intensity of pain can vary (from mild aching to severe cramping pain). Most often, pain is localized in the epigastric region.
All of the above symptoms of giardiasis are observed for several weeks, after which they may disappear on their own or become less pronounced, which indicates that the disease has become chronic. What the outcome will be largely depends on the state of the patient’s immune system and the degree of contagiousness of the disease.
General symptoms of the disease include a feeling of weakness, general weakness, decreased performance, memory, concentration, drowsiness, and headaches.
This clinical picture is associated with the negative effect of parasites on the digestive processes. Digestive disorders lead to deterioration in the absorption of nutrients and can cause the development of the following pathological conditions in the body:
1. Weight loss. Develops during a long-term chronic course of the disease.
2. Anemia. This is a decrease in the level of red blood cells in the blood to a critical level, which occurs as a result of poor absorption of B vitamins into the blood (especially B9 and B12). It is these vitamins that take an active part in metabolism and are responsible for the synthesis of blood cells.
2. Reduced immune defense of the body. The patient becomes susceptible to various infections.
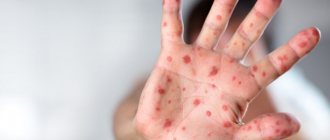
In some cases, the body develops an allergic reaction, the cause of which is lamblia and their metabolic products. Clinically, allergies can manifest themselves as the following symptoms:
- small rashes on the skin all over the body;
- skin itching;
- runny nose, allergic conjunctivitis.
Features of the parasite - Giardia
The widespread disease giardiasis is caused by protozoan parasites, Giardia, which multiply in the small intestine of humans.
What Giardia looks like can only be seen under a microscope, these creatures are so small. They are shaped like squids - the wide front end gradually turns into a pointed rear end. There is a suction cup on the bottom that allows them to attach to the intestinal wall. Motility is provided by 4 pairs of flagella.
Microorganisms exist in two forms:
- Mobile vegetative, which is the causative agent of infection. Such cells multiply in the intestines by simple division, do not require oxygen, and absorb nutrients throughout the entire surface of the body. Outside the human body they die very quickly.
- The cyst, which has a regular oval shape, is covered with a dense membrane, allowing the parasite to survive in unfavorable conditions. Cysts form in the large intestine and are present in large quantities in the stool. They prefer a warm, humid climate in which they can live for up to 3-4 months.
They are found in raw milk, chlorinated water from swimming pools and water pipes. Only boiling kills cysts.
Diagnosis of giardiasis
The diagnosis must be made by a doctor, based on laboratory data. Self-diagnosis and traditional methods are unacceptable in this case and can lead to the disease becoming chronic and the development of a number of serious complications.
The purpose of diagnosis is not only to confirm the diagnosis of giardiasis, but also to determine the degree of infection, which is extremely important for subsequent treatment of the disease.
The main diagnostic methods are:
- duodenal intubation - study the condition of the upper small intestine;
- serological analysis - detect specific immunoglobulins that are formed in the body in response to the penetration of parasites;
- stool analysis - carried out to detect vegetative Giardia and cysts, the analysis is taken weekly, at least 5 times in a row, which is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment;
- coprogram;
- blood test (general, biochemical);
- enterotest - the essence of the study is that the patient swallows a capsule with a special thread inside, when it enters the gastrointestinal tract, the capsule dissolves, and Giardia gets on the thread, which comes out with it during the act of defecation, after which the thread is examined for the presence of parasites.
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose giardiasis, feces, duodenal contents and blood are taken for analysis.
When examining formalized feces, the presence of cysts in the intestines is determined. The presence of trophozoites is determined by analyzing duodenal contents.
By means of a coprogram (detection of undigested fiber, neutral fats or muscle fibers), not only the infection itself is detected, but also the malabsorption syndrome.
To detect the presence of Giardia, such specific diagnostics as fluorescent microscopy of feces are carried out.
Blood is examined using general clinical methods:
- White blood cells above normal will indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the body;
- anemia will reveal the degree of complication of the ongoing disease.
If one family member is diagnosed with this disease in the body, then the rest of the family members also need to be tested.
Treatment of giardiasis
Therapy can be carried out in a laboratory or inpatient setting. The treatment regimen for giardiasis in adults is as follows. First, preparatory therapy is carried out, which is aimed at strengthening the immune defense, eliminating cholestasis and toxicosis.
The patient is prescribed a special diet for giardiasis, which is aimed at limiting the consumption of protein and carbohydrate foods. To restore the functioning of the biliary tract, a cleaning procedure with xylitol and mineral water is indicated.
To restore digestive function, the patient is prescribed enzymes (Mezim, Micrazim); to eliminate bile stagnation, the use of choleretic drugs is indicated.
If the body develops an allergic reaction to Giardia and their waste products, then taking antihistamines is indicated. The duration of the preparatory period depends on the current condition of the patient and is 7-14 days.
After this, they begin the second, main stage - antiparasitic treatment. To rid the patient of parasites, he may be prescribed Metronidazole, Tiberal, Macmiror, the use of which is possible only as prescribed by the attending physician.
In addition, furazolidone and drugs based on it may be prescribed. In parallel with the antiparasitic treatment of giardiasis, the patient continues to take choleretic drugs and sorbents to more effectively get rid of parasites.
Monitoring of the treatment is carried out after completion of the main course of therapy, then after 30 days and after 4-6 months.
The third stage is restorative. The patient continues to take medications to improve bile flow and sorbents. To restore the composition of the intestinal microflora, taking probiotics is indicated.
In addition, general strengthening therapy is carried out, including the use of immunostimulants, multivitamin complexes, and adaptogens. In some cases, a repeat course of treatment is required.
The main goal of treating Giardia in children is to eliminate clinical symptoms and completely destroy the parasites. It should be remembered that when a child is diagnosed with a disease, all members of his family and pets must undergo treatment.
Therapy is also carried out in several stages. The first of them includes measures aimed at eliminating cholestasis, as well as prescribing a diet for the child. In order for the treatment of giardiasis to be more effective, it is necessary to reduce the amount of fast carbohydrates in the diet, eat more baked fruits and vegetables, dried fruits, bran, and cereals.
To relieve symptoms of body intoxication, children are prescribed enterosorbents; for malabsorption syndrome, pancreatin-based enzymes are indicated. If dysbiosis is detected, therapy with probiotics and prebiotics is carried out, aimed at restoring the normal composition of the intestinal microflora.
At the second stage, etiotropic therapy is carried out, aimed at destroying the causative agent of the disease. Children are prescribed antiparasitic drugs (Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Furazolidone and a number of others).
The choice of treatment regimen, medications, their dosage, frequency and frequency of administration is made by the attending physician, taking into account the age of the child, the severity of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the general condition of the little patient.
It should be remembered that a few days after starting to take antiparasitic drugs, a child may develop an allergy. In this case, the treatment regimen includes taking antihistamines.
After completion of treatment, it is necessary to take a re-test. If it was not possible to completely get rid of the parasites the first time, then a second course of therapy with other drugs is carried out.
List of the best tablets for Giardia
The disease should be treated by a doctor who knows which drugs have a detrimental effect not only on protozoa, but also on Giardia cysts. Most often, the following drugs are used:
- Tinidazole. The dosage and duration of therapy depends on the clinical manifestations.
- McMiror. The drug has a wide spectrum of action, acts gently and does not lead to the death of beneficial intestinal microflora.
- Intetrix is an antiprotozoal agent.
- Ornidazole is a drug to combat Giardia and other protozoa.
- Nemozol. The drug is chewed one tablet per day. The course of therapy is up to five days.
- Trichopolum (active ingredient Metronidazole) is an antiprotozoal drug.
The tablets should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor, since the drugs are highly toxic and have serious contraindications and side effects.
It should be noted that Giardia is a protozoan, not a worm, and drugs such as Vermox and Pirantel are likely to be ineffective.
Giardiasis prognosis
The prognosis of the disease is favorable in most cases. In some patients, re-infection is possible. In some cases, it is not possible to get rid of parasites the first time and then a second course of treatment is carried out.
Possible complications of the disease are:
- lactose intolerance - this condition develops as a result of damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa, which leads to a deficiency in the body of the enzyme responsible for the breakdown of lactose;
- disturbance of water-electrolyte metabolism - occurs as a result of loss of microelements and fluid during diarrhea;
- weight loss - this complication is also a consequence of prolonged diarrhea;
- development of IBS;
- retardation of children in physical development;
- development of infectious diseases of the pancreas, gall bladder, joint problems.
How to identify lamblia in the body
Due to the small size of parasites, it is impossible to see them in feces with the naked eye. The primary diagnosis of giardiasis is carried out in a clinical laboratory.
Your doctor will explain how to detect Giardia. He will order a stool test and advise that the material needs to be collected in sterile containers and delivered for examination within 2-10 hours.
In the laboratory, a specialist makes a smear, which reveals Giardia (cysts and mobile forms), and writes a conclusion. As a rule, to ensure the reliability of the result, the analysis is repeated 3-5 times.
The following will help confirm the diagnosis:
- detailed blood test - with giardiasis, the number of eosinophils and leukocytes increases;
- biochemical blood test, which shows an increase in the level of alkaline phosphatase;
- modern immunological techniques detect giardiasis antigens and antibodies to them in venous blood and feces;
- The PCR method is capable of detecting parasite DNA in bile and feces.
You can undergo PCR and determine antigens for a fee in most medical centers.
Prevention of giardiasis
The main methods of preventing the disease are:
- compliance with basic hygiene rules;
- proper processing of fruits and vegetables;
- refusal to drink raw water, you need to drink only boiled water;
- When working with soil, you must use gloves;
- Pets should be regularly treated against parasites;
- hardening of the body;
- avoiding stress and other psycho-emotional disorders that weaken the immune system, which can lead to the development of giardiasis;
- regular sanitation of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- After interacting with animals, you must wash your hands thoroughly;
- avoiding swimming in polluted bodies of water with stagnant, musty water;
- if cysts are detected, all family members must undergo treatment;
- When the first suspicious symptoms appear, you must immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination - this will help to diagnose the disease in time and begin treatment, which will significantly improve the prognosis and help avoid the disease becoming chronic.
Good health to you!