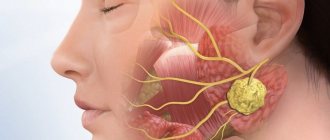
A retropharyngeal abscess is often one of the complications of nasopharyngeal diseases; if this condition is not stopped in time, it can lead to more severe consequences. It is especially common in children.
Related articles:
Post-injection abscess: causes and treatment Bartholin gland abscess - treatment Throat abscess treatment at home Peritonsillar abscess: photo and treatment Psoriasis: treatment and photos of the initial stage
Causes of the disease
Among the predisposing factors that provoke retropharyngeal abscess in adults is a weakening of the body's protective properties. Decreased immunity may be due to a history of chronic disease or cancer. The main reasons for the development of pathology are:
- exposure to infections, tuberculosis caused by Koch's bacillus or syphilis, provoking the development of dysfunction of the cervical vertebrae;
- traumatic damage to the posterior wall of the larynx, which can provoke a diagnostic examination (for example, endoscopy), endotracheal anesthesia, or ingestion of a foreign object, fish bones, or a large piece of food;
- injury to the cervical vertebrae;
- a retropharyngeal abscess may appear as a complication of an acute respiratory infection or sore throat.
Patients who have a history of thyroid dysfunction, malignant neoplasms, or HIV infection are at risk.
Why does the disease develop in children?
The main reason why the disease develops in children is associated with the influence of primary foci of infections in the form of tonsillitis, sinusitis, and rhinitis. Among the predisposing factors are the weakened immunity of a young child, who cannot yet sufficiently resist infectious pathogens. The causes of the development of retropharyngeal abscess in children are associated with exposure to:
- diseases of streptococcal or staphylococcal origin. Exacerbations of pathologies of infectious origin: measles, scarlet fever, influenza, diphtheria, as well as other childhood infectious pathologies or tonsillitis, in which there is a significant increase in body temperature, as well as the effect of inflammation on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and oral cavity. The danger is that the infection may subsequently affect the lymph nodes;
- development of purulent processes in the area of the tympanic cavity or auditory tube;
- the initial stage of mastitis in a nursing woman. During feeding, the child is often infected;
- pharynx injuries (may occur if a child swallows a foreign object or rough food).
Children with diathesis and rickets are at risk. In some cases, the disease may occur after procedures such as tonsillectomy or adenotomy.
Brief overview of medicines
Antibacterial drugs for abscess of the retropharyngeal lymph nodes are most often prescribed as intramuscular injections in significant dosages. Modern medicines are:
| Drugs | Photo | Price |
| Cefotaxime | From 24 rub. | |
| Clindamycin | From 180 rub. | |
| Josamycin | Check | |
| Amoxiclav | From 123 rub. |
Antihistamines for abscess:
| Drugs | Photo | Price |
| Erius | From 615 rub. | |
| Erespal | From 405 rub. | |
| Zyrtec | From 225 rub. |
Anti-inflammatory medications are also used for abscesses.
Nurofen - the daily dose of the drug for children over 12 years of age and adults is 200 mg 4 times a day; for the fastest results, the dosage can be increased to 400 mg three times a day.
Paracetamol - a single dose of tablets for children aged 12 years and above - 500-1000 mg, per day should not exceed 4000 mg.
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by an acute onset, in which there is an increase in body temperature above 39 degrees. If the development of a retropharyngeal abscess occurs against the background of another disease of infectious origin, the patient complains of a sharp deterioration in general health. There are a number of common symptoms that characterize this disease:
- significant tension in the neck muscles;
- increased sweating, salivation;
- the patient is forced to tilt his head in the direction that causes anxiety, or reflexively throws it back;
- increase in body temperature to 39-40 degrees;
- lymph nodes become painful and may increase in size.
Depending on the spread of the inflammatory process, the abscess of the retropharyngeal space may be accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- nasal sound, difficulty in nasal breathing - such symptoms develop when the disease spreads to the upper part of the pharynx, and are typical for adults as well as adolescents;
- if the patient is in a standing position, breathing problems may worsen due to the fact that pus flows down and blocks the lumen of the trachea;
- wheezing during breathing and difficulty swallowing;
- when the purulent-inflammatory process is localized in the middle or lower part of the pharynx, suffocation may occur;
- difficulty breathing, as well as difficulty passing food through the esophagus, development of hoarseness. Breathing becomes whistling and wheezing.
If in an adult patient the disease develops against the background of tuberculosis or syphilis, then the listed manifestations are expressed in an insignificant form, and the pathology itself can develop sluggishly.
Symptoms of the disease in children
The development of a retropharyngeal abscess in children is indicated by the same symptoms as in adults. One of the most characteristic signs of the development of the disease is a severe sore throat. There may be complaints of increased pain when eating and swallowing food. In this case, the child may refuse to eat due to intense pain and discomfort in the throat area. Characteristic manifestations of general intoxication:
- increased body temperature;
- increased fatigue;
- breathing and sleep disorders;
- increased irritability, moodiness;
- the child may refuse food, and sucking disorders are observed in infants.
When the disease spreads to the middle or lower part of the pharynx, the child’s inhalation becomes difficult, and shortness of breath may occur. Parents may notice that the neck on the affected side is swollen. If the described symptoms occur, you should consult a pediatric otolaryngologist or therapist as soon as possible.
Classification
The abscess is classified by location. The abscess can be localized in the lower, central, upper region of the pharynx.
Types of ulcers:
- epipharyngeal abscess - inflammation occurs just above the velum;
- hypopharyngeal abscess - the pathological process is located in the subradicular region of the tongue;
- mesopharyngeal abscess - an abscess occurs between the root of the tongue and the edge of the palatine arch;
- mixed abscess - covers the retropharyngeal space in several zones and is the most severe type of this pathology.
The inflammatory process appears within 5–6 days of developing infectious disease or when the symptoms have subsided a little.
Diagnostics
Predominantly retropharyngeal abscess is diagnosed in children. This is due to the fact that loose tissues and lymph nodes develop before the age of five. In adults, the lymph nodes are atrophied: significantly reduced and do not perform their function. At the first signs of pathology, you should consult an ENT specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination. When carrying out diagnostics you need:
- Collecting an anamnesis, which allows us to identify the inflammatory processes that provoked the disease, as well as the presence of past injuries to the larynx or neck.
- An in-person examination by a doctor who performs pharyngoscopy - examines the pharynx using a spatula under special lighting. The otolaryngologist evaluates the condition of the lateral walls of the pharynx, soft palate, palatine arches, uvula and tonsils, the intensity of color and smoothness of the mucous membranes, the presence of pathological formations and accumulations of lymphoid tissue.
- During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the position of the patient’s head, the presence of edema, the condition of the lymph nodes, and also performs palpation to identify painful sensations.
- A general blood test to determine inflammatory processes.
- Conducting microscopy and biological examination of a smear from the pharynx area. Such an examination will determine what exactly is the causative agent of the disease.
- Carrying out PCR diagnostics.
- It is necessary to examine sputum to identify tuberculous mycobacteria.
- Using x-rays to determine the exact location of the purulent focus.
In order to determine concomitant pathologies that could provoke the development of a retropharyngeal abscess, otoscopy, rhinoscopy are additionally prescribed, and the paranasal sinuses and cervical spine are examined.
Depending on the suspicion of what concomitant disease provokes the retropharyngeal abscess, additional consultation with a therapist or pediatrician, phthisiatrician, traumatologist or neurologist, or oncologist may be required.
Therapy methods
If a retropharyngeal abscess is detected, treatment should be carried out only as directed and under the supervision of a physician. The basic principles of therapy are based on:
- hospitalization of the patient and carrying out a complex of treatment measures in the ENT department. The main treatment method is opening the purulent focus with subsequent removal of the pus. The procedure is carried out using local anesthetics;
- prescribing antibacterial treatment after opening the lesion. The selection of the drug, its dose and duration of use is carried out taking into account the sensitivity of the infectious agent to the active component of the drug, as well as the characteristics of the patient’s body and his age. Preparations for internal administration or intramuscular administration from the group of macrolides, cephalosporins, lincosamides can be used;
- the use of antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs based on ibuprofen, nimesulide, indomethacin;
- taking antihistamines: Erius, Loratadine, Aleron;
- gargling using disinfectant solutions before and after opening a purulent lesion; Salt and soda solutions, herbal infusions based on chamomile, calendula, and eucalyptus have a good effect. The procedure must be carried out at least 5 times a day and refrain from eating for 60 minutes after rinsing;
- carrying out thermal procedures at the initial stage of development of the disease or after eliminating symptoms;
- prescribing general strengthening treatment using multivitamin complexes based on vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
To avoid complications, you must strictly follow the instructions of your doctor. The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the patient’s age and symptoms of the disease.
With timely treatment, the prognosis for the patient is favorable.
Treatment
A retropharyngeal abscess requires mandatory hospitalization. Under no circumstances should you treat the disease yourself. Treatment of retropharyngeal lymph nodes is carried out exclusively by surgery. If a spontaneous rupture of an abscess occurs, then there is a possibility that it will come out of the nose, mouth, or ears.
Surgical treatment
The autopsy technique will help remove the purulent contents. During the procedure, the doctor cuts the painful area and removes the pus. Manipulation is performed with a scalpel or special surgical scissors with a sharp tip.
Dissection of the abscess is performed in the most swollen, inflamed area. Access to the pathological area is made through the mouth. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
At the time of extraction of purulent exudate, it must not be allowed to penetrate into the throat. To prevent this from happening, use one of these methods:
- The contents are sucked out using an electric pump, introducing the tip of this device into the affected area.
- The pus is removed using a syringe; this does not require opening the abscess.
Sometimes the edges of the incision become stuck, and to move them apart you will need Hartmann forceps or a special grooved probe.
If the respiratory system is compressed, the use of a breathing tube (intubation) is strictly prohibited.
Surgical treatment of a retropharyngeal abscess may have features depending on its location, causes and complications.
To protect against the spread of infection, repeated punctures are performed instead of dissection. Pus is extracted through punctures, and medications are introduced through them to treat the main pathology.
In addition to surgical therapy, drug treatment of the abscess is mandatory.
Conservative treatment
Medicines are not the main treatment for an abscess; they are used as an adjunct to surgery. Immediately after the excision procedure:
- the use of anti-inflammatory, antipyretic drugs (Paracetamol, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen) - to relieve symptoms;
- antibiotics (Cefotaxime, Azitral, Amoxiclav);
- desensitizing, antihistamine (Erius, Zyrtec, Cetrin) drugs - reduce tissue hyperemia;
- taking vitamins, multivitamins - to strengthen the immune system during an abscess;
- treating the throat with antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, chamomile decoctions);
- after relieving the inflammatory process, perform thermal manipulations;
- UHF.
After improvement of the condition, to avoid re-formation of an abscess in the retropharyngeal tissue or lymph nodes, it is advisable to sanitize the nasopharynx and oropharynx, in particular if the tonsils are enlarged with constant complications of adenoiditis.
Complications
If the retropharyngeal abscess is not treated promptly and efficiently, there is a risk of developing the following complications:
- compression and blockage of the airways, which can lead to difficulty breathing, or in the worst case, to stopping it;
- the development of mediastinitis - an inflammatory process affecting the area of the heart and aorta. The complication may be accompanied by the development of acute pain in the heart and back, which significantly intensifies when the patient inhales and exhales or moves, loss of consciousness, increased heart rate, increased sweating;
- epidural abscess - purulent foci localized in the brain area;
- infection of the whole body (sepsis);
- damage to the walls of large arteries.
In the worst case, there is a risk of death due to cardiac arrest or suffocation.
Prevention
For prevention, the following recommendations from doctors are required:
- Timely identify chronic diseases and foci of infection. Particular attention is paid to chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, and sinusitis.
- High-quality treatment of infectious pathologies. Self-medication is under no circumstances acceptable, as it may not have the necessary therapeutic effect. The selection of drugs should be carried out only by a doctor after a personal examination of the patient and taking into account the results of the examination.
- It is necessary to direct efforts to strengthen the immune system. To do this, the patient must eat well (a large amount of vegetable fats, vitamins, microelements), sleep at least 7-8 hours a day, and observe a work-rest regime. Smoked, fried, and overly spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. It is recommended to pay attention to hardening procedures and moderate physical activity.
- Take multivitamin complexes.
- If it is necessary to carry out diagnostic procedures that can injure the walls of the pharynx, it is recommended to contact competent and qualified specialists.
Timely detection and high-quality treatment of emerging diseases, as well as surgical sanitation of purulent foci, significantly reduces the likelihood of developing a purulent abscess. And following simple recommendations contributes not only to prevention, but also to a significant improvement in the quality of life of a patient of any age.