Many people are accustomed to paying attention only to an increase in temperature, but most often they simply do not pay much attention to its decrease. And this phenomenon, in turn, can signal the development of pathological conditions and certain diseases, including serious ones.
First, it must be said that the norm is considered to be a fluctuation in body temperature from 35.8°C to 37°C. Other indicators will be a deviation. For example, a body temperature that has dropped to 29.5°C can lead to loss of consciousness, and up to 27°C - the onset of coma, when a malfunction of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems of the organs occurs.
To identify the cause of low body temperature, it is necessary to understand how thermoregulation processes occur in the body, which maintain a person’s body temperature at the desired level (about 36°C). It is also important to know what types of thermoregulation exist. Types of thermoregulation and causes of their violations
1. Behavioral When behavioral thermoregulation is disrupted, a person ceases to adequately perceive the temperature of the environment. The reason for such a violation may be:
- effects of alcohol on the body;
- mental disorder;
- effects of narcotic substances on the body.
For example, under the influence of drugs or alcohol, a person may not feel cold. As a result, he will become hypothermic and simply freeze, which often leads to a significant drop in body temperature (up to 25°C). This condition is dangerous not only for health, but also for life.
2. Physical As a result of functional failures of physical thermoregulation, the human body loses heat due to excessive expansion of blood vessels, which remain in this state for a long time. This condition often affects hypotensive people - people with low blood pressure. Also, the cause of disturbances in physical thermoregulation can be endocrinological diseases, which are accompanied by symptoms such as increased sweating. Minor disturbances of this type of thermoregulation are observed in people during emotional stress. But this condition is easily cured.
3. Chemical The causes of violation of chemical thermoregulation include:
- intoxication of the body;
- pregnancy period;
- weakening of the immune system;
- chronic asthenia of the body;
- endocrine diseases;
- decrease in hemoglobin level in the blood;
- overvoltage.
Is low temperature dangerous?
It is generally accepted that normal values on a thermometer are 36.6°C. In fact, readings can fluctuate throughout the day, depending on meals, menstrual cycle and even mood. Therefore, a temperature from 35.5 to 37.0 is considered the absolute norm for each individual person.
True hypothermia, dangerous to health and sometimes life, begins at temperatures below 35°C. If the numbers on the thermometer are between 35 and 36.6 degrees Celsius, then most likely nothing threatens the person’s health.
Body temperature 35 - 35.5 reasons and what does it mean? Recommendations from specialists and methods of treatment
The normal temperature of the human body is designed to provide an optimal background for the occurrence of many processes. It becomes a real indicator of the functioning of various internal life support systems. In addition, it is a regulator of the interaction between the internal and external environment of the body.
The normal human body temperature for an adult is between 36.4 and 37.4 degrees Celsius. On average this means the usual and traditional 36.6.
Small fluctuations in one direction or another are not considered pathological. They can only be alarming if they approach the border marks.
Most often, these changes pass rather quickly within a short time, as they are caused by functional reasons. When repeated measurements are taken, they usually shift towards the norm.
Body temperature 35 - 35.5 what does this mean?
When the numbers on the thermometer show that an adult patient has a temperature of 35.5 or lower, then this unusual condition is defined as hypothermia.
This is not at all a harmless state of affairs. The patient's functions of the main organs and systems are disrupted, metabolism changes significantly and brain activity suffers.
Such changes have a particularly noticeable effect on the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Therefore, you need to know exactly the symptoms of this condition in order to be able to accurately determine them even before measuring the temperature in order to provide timely help to the person. This is especially important when it comes to chronically ill people, alcoholics or drug addicts.
Hypothermia usually manifests itself:
- Severe chills;
- feeling of freezing;
- general weakness;
- pallor;
- fatigue;
- feeling unwell;
- severe drowsiness;
- decreased blood pressure;
- bradycardia;
- sudden change in mood;
- dizziness;
- confusion.
These symptoms are explained by a significant slowdown in blood flow in the body, a strong dilation of blood vessels, and a change in the course of processes in the brain. A person's metabolic rate decreases, the level of production and release of hormones drops significantly, and the overall load on the cardiovascular system increases.
Often, secondary symptoms of a sharp decrease in body temperature to 35.3 - 35.5 in an adult are tactile disturbances due to a failure in reflex activity, weakening of intellectual activity, and vestibular disorders.
Due to cerebral ischemia, difficulties with hearing and vision may arise; it becomes difficult for a person to speak and even hold the body in a horizontal position.
Due to multiple malfunctions in the central and peripheral nervous systems, illusions or hallucinations may even occur.
Causes of hypothermia
A significant decrease in temperature can occur due to various factors. These can be random reasons that affect a person only for a short time.
These include nervous strain, taking certain medications, hypothermia, insomnia, severe hunger, prolonged dieting, loss of strength, and alcohol intoxication.
In such cases, the temperature, as a rule, normalizes after the unfavorable factor ceases. Sometimes correction of the patient’s condition is required in order for the situation to stabilize as quickly as possible. Usually, this does not require medical assistance, since the person himself has the power to change it for the better.
For many people, a temperature of 35.7 - 35.9 is the norm.
Do not be alarmed at a temperature of 35.7 - 35.8 degrees. It may be enough to dress warmly, cover yourself with a blanket and drink a cup of hot tea. After this, you need to get a good night's sleep and have a hearty lunch. Hypothermia usually goes away after such measures. If even after this nothing can be improved, you need to contact a specialist.
This should be done, since low temperature (35.3-35.5) in adults is often a symptom of diseases such as:
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- venous insufficiency;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- drug addiction (overdose);
- diabetes;
- coma;
- adrenal diseases;
- hormonal disbalance;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- renal failure;
- disturbances in the activity of the cerebral cortex;
- depression;
- anorexia;
- diseases of the spine;
- hematological diseases.
In these cases, low body temperature can be caused by the damaging effects of drugs or alcohol, loss of strength, or malnutrition.
Hormonal deficiency provokes a significant slowdown in the flow of processes in the body, a drop in the level of endocrine activity, as well as in the absorption of nutrients.
Cardiovascular pathology causes symptoms such as weakness, decreased general activity, and ischemia of the limbs. All this provokes a temperature drop to 35.2 degrees and below.
The body tries to balance the situation and therefore attacks of irritability, aggression or, conversely, severe inhibition are often possible.
Thermometry is carried out using thermometers:
- Mercury (traditional, usually placed in the armpit for five minutes);
- Electronic (it gives a signal when the body temperature is set. In doubtful cases, it is recommended to keep it for about a minute to clarify the results.
In cases where they are clearly increased or decreased, the measurement continues).
It is very important to record the temperature correctly. Most often, the thermometer is placed in the armpit. This method is generally considered insufficiently accurate, but it is convenient and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
The error when measuring temperature is several tenths of degrees, usually on the smaller side, so a result of 35.8 - 36.2 for an adult can be considered normal.
In Western countries, the thermometer is placed in the mouth. This is the most reliable way to obtain data, but it is also dangerous, since with severe chills or in an unconscious state, a person may bite or drop the thermometer. In addition, it is completely unsuitable for measuring the temperature of infants or people with weakened mental health.
Sometimes thermometry is performed by placing a special device into the rectum. This is most often done in young children or in adult patients who are in a coma.
However, it should be borne in mind that the internal body temperature is slightly higher than the external one, so an allowance must be made here. Therefore, this method is not entirely suitable in case of hypothermia.
Methods to combat hypothermia
Body temperature should not remain too low for long. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will carry out the necessary diagnostic procedures.
You should do a clinical and biochemical blood test, a general urine test, check plasma glucose levels, determine thyroid hormone levels, and identify the presence of certain toxic substances.
In addition, it is necessary to measure blood pressure, do an Echo-KG, EGC, electroencephalogram, ultrasound, etc.
If no serious diseases are detected, then you need to measure your temperature several times a day.
If a persistent decrease in temperature to 35 degrees or below is detected, you should:
- Take a course of vitamin E;
- take immunostimulants;
- give an intensive massage of the body, as well as arms and legs;
- prepare hot milk with honey;
- drink tea with raspberry jam;
- take a contrast shower or bath;
- warm up the room;
- dress warmly;
- drink hot coffee;
- brew rosehip infusion;
- stop taking medications not prescribed by a doctor;
- allocate at least eight hours of sleep;
- drink sedatives of herbal origin;
- take a brisk walk;
- eat a bar of chocolate.
These comprehensive measures will make it possible to significantly activate metabolism, significantly dilate blood vessels, and stimulate general blood supply.
They will allow you to cleanse yourself of toxins, relax, warm up the body, and increase lymph flow. Honey, raspberry jam and dark chocolate will allow a person to sweat well, thereby regulating the heat exchange between the internal environment of the body and the external environment.
After this, you need to take measurements again. If everything returns to normal, then you should observe the patient for several days. If the temperature within 35.2-35.5 resumes, you should contact a specialist.
In general, the fight against hypothermia should be a fight against the cause that caused it.
If this is a serious illness, then treatment or an urgent call to the Emergency Department will help. If it is caused by external factors, then home remedies will help restore normal body temperature.
Can there be a low temperature with coronavirus?
A full-blown infectious process is almost always accompanied by a rise in temperature due to the large number of biologically active substances that enter the blood and have a pyrogenic effect.
This is a kind of protection: at high temperatures, many bacteria, viruses and fungi die. Or at least they begin to reproduce more slowly. But sooner or later, without adequate treatment, a rapidly developing infection leads the body to a state where all defense mechanisms fail.
Can coronavirus cause a low temperature? Yes, if it is:
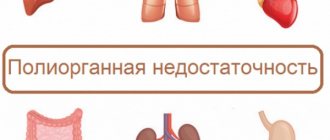
- Severe conditions: sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, multiple organ failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
- Asthenia after a long viral-bacterial process in the lungs
- Another paradox is low temperature during coronavirus in women over 50 years old
- The safest situation is when the temperature is 1-2 degrees below normal in adults after taking antipyretics against a background of low fever (37-37.5). An antipyretic, designed to reduce temperatures of 38 degrees and above, works effectively, and the temperature drops sharply.
Urgent conditions
These are life-threatening conditions in which low body temperature becomes the result of extensive organ dysfunction and disruption of the constancy of the internal environment of the body. They require resuscitation and treatment in ITAR conditions.
- DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome) is a type of hemorrhagic diathesis. At the same time, the coagulation system is strengthened, and multiple blood clots form in small vessels. The result is oxygen starvation of organs and tissues and their dysfunction. At the same time, the risks of poorly controlled external and internal bleeding increase sharply. This leads to decreased blood pressure, metabolic disorders and, as a consequence, hypothermia.
- Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response to microbial toxins. The developing failure of the cardiovascular, respiratory, urinary, and endocrine systems leads to the fact that elevated temperature and fever are replaced by cooling of the body. Sepsis can result in shock, which often causes patients to die.
- Respiratory distress syndrome is acute respiratory failure against the background of rapidly developing extensive inflammation of the lungs. The release of cytokines leads to massive effusions into the pulmonary alveoli, making gas exchange in the lungs almost impossible. Increasing oxygen starvation slows down metabolism and, as a result, the temperature drops.
Asthenia
A prolonged infectious-inflammatory process depletes the body's adaptive capabilities. Therefore, when viral and bacterial aggression have already been defeated, a person still continues to be haunted by weakness and low temperature. May be observed:
- pallor,
- decreased appetite,
- dizziness, especially with exertion or sudden standing up,
- general loss of strength.
This is a period when additional rest and recovery time is required. It is worth paying attention to adequate sleep, good nutrition, and maximum intake of fresh air.
Postmenopausal women
If menopause becomes a time for women when vascular hot flashes and increases in temperature are not uncommon, then after its end, low levels of estrogens and progestins contribute to a slowdown in metabolism. Age-related involution of the thyroid gland and partial hypothyroidism may also occur. Against the background of infectious viral aggression, in this case the usual rise in temperature does not occur.
Primary signs of a decrease in temperature
Symptoms that may indicate a decrease in temperature include:
- increased drowsiness;
- apathetic state, general malaise;
- loss of appetite;
- slowness of thought processes;
- irritability.
If a decrease in body temperature is observed in a small child, it should definitely be shown to a doctor. If an adult maintains a temperature of about 36°C for a long time, but during the examination no pathologies were identified, the person is cheerful and feels great, his condition can be regarded as normal.
Reduced human body temperature: causes depending on diseases and other pathological conditions
1. Exacerbation of chronic diseases
Often, body temperature decreases if chronic diseases are in the active stage. This is directly related to a decrease in the body’s defenses (immunity), which are directly involved in the thermoregulation of the body. After some time, symptoms of the underlying chronic disease begin to appear and the temperature may, on the contrary, increase. This occurs due to the development of inflammatory processes in the body. That is, a drop in temperature is the primary signal of exacerbation of a chronic disease.
2. Brain pathologies
A decrease in temperature may be one of the symptoms of tumor growths in the brain. The fact is that these tumors put pressure on the brain, disrupting blood circulation in it, which leads to a disorder in the body’s thermoregulation.
In addition to a decrease in temperature, brain tumors can manifest themselves by the presence of other symptoms, namely a violation of:
- speech abilities;
- sensitivity;
- levels of certain hormones;
- work of the autonomic system;
- intracranial pressure (increasing). This is accompanied by attacks of nausea, vomiting, dizziness;
- memory;
- cerebral circulation, accompanied by severe headaches that are difficult to eliminate by taking analgesics;
- coordination of movements;
- hearing;
- psyche (auditory and visual hallucinations, etc.).
3. Thyroid diseases
Often, a decrease in body temperature is accompanied by a disease such as hypothyroidism, which is characterized by functional disorders of the thyroid gland, as well as insufficient production of thyroid hormones. These hormones support the normal functioning of the entire body, including the functioning of the nervous system.
The most common manifestations of hypothyroidism are:
- brittle nails;
- weight gain;
- fast fatiguability;
- chilliness;
- memory problems;
- dry skin;
- frequent constipation.
4. Previous infections
A frequent companion to conditions that occur after viral and bacterial infections is low temperature. As a result of the disease, the body's resources are depleted. First of all, this applies to the nervous and immune systems. And the thermoregulation center, located in the hypothalamus, is known to belong specifically to the nervous system.
5. Pathologies of the adrenal glands
Often a symptom in the form of a decrease in temperature occurs in the presence of adrenal diseases. First of all, this concerns adrenal insufficiency, in other words, Addison's disease. It develops asymptomatically for quite a long time and makes itself felt when it enters the chronic stage. This condition is characterized by the following manifestations:
- weak potency;
- depressive states;
- frequent urination;
- irritability and short temper;
- muscle aches;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- low blood pressure;
- tingling and numbness in the limbs;
- increased thirst.
6. Vegetative-vascular dystonia
People suffering from this pathology experience disturbances in thermoregulation due to fluctuations in blood pressure, which leads to heat loss. With vegetative-vascular dystonia, both a persistent slight increase in temperature and a decrease in temperature can be observed.
Common symptoms of this disease include:
- disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory system;
- pain in the heart area;
- tachycardia;
- sleep disorders;
- chilliness of the limbs;
- dizziness;
- fainting.
7. HIV infection As a result of the development of an immunodeficiency state, a person experiences various symptoms, including low body temperature. The reasons why manifestations become more pronounced are most often due to associated bacterial, parasitic and viral infections.
An immunodeficiency state, in addition to low temperature, is accompanied by:
- chills;
- an increase in the size of lymph nodes;
- frequent colds;
- loose stools;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- disruptions in the digestive system;
- development of tumor neoplasms;
- increased sweating (especially at night);
- weight loss;
- weakness throughout the body.
8. Intoxication
As you know, during intoxication the temperature usually rises. But in some cases it can decrease significantly. This is due to inhibition of the nervous system, which takes part in the processes of thermoregulation of the body.
Severe intoxication, in addition to low temperature, can manifest itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness;
- neurological disorders. For example, when a person falls into a “deep” sleep, which is replaced by periods of extreme excitement;
- liver and kidney damage;
- vomiting, nausea, diarrhea;
- weakness;
- hemorrhages of varying severity (from single small spots to extensive bruises);
- lowering blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- impaired blood flow in the extremities;
- marbling of the skin.
9. Neurocirculatory dystonia
A disease such as neurocirculatory dystonia is characterized by disorders of the vascular system, which entails the development of hypotension - low blood pressure. In this condition, there is an expansion of the vascular beds, which is followed by heat loss and a decrease in body temperature. In addition to hypotension, this disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath;
- tachycardia;
- tremor in the limbs;
- panic attacks;
- hyperhidrosis;
- dizziness.
10. Exhaustion of the body (cachexia)
With this condition, a significant weight loss is observed (sometimes up to 50% of the total body weight). The layer of subcutaneous fat virtually disappears, causing the skin to become wrinkled and take on a gray, “earthy” tint. There are also symptoms of vitamin deficiency. In addition, when the body is exhausted, nails become brittle and hair becomes thinner and dull. Frequent constipation often occurs with cachexia. In women, the volume of circulating blood decreases, which causes the absence of menstruation.
Also, with exhaustion, mental disorders can occur. At the very beginning, asthenia occurs - tearfulness, resentment, irritability, weakness and depression. If the pathology is successfully cured, asthenia will still be present for some time, and will also be accompanied by a decreased body temperature.
11. Anemia
These conditions are usually the result of an improperly balanced diet. For example, insufficient consumption of foods containing iron.
Symptoms that appear in iron deficiency:
- difficulty swallowing. It seems to a person that there is a foreign body in his larynx;
- addiction to pickles, smoked meats, spices and spicy dishes;
- atrophy of the papillae located on the surface of the tongue;
- deterioration of hair, nails and skin;
- tachycardia;
- dry mouth;
- decreased performance, rapid fatigue.
12. Radiation sickness In the chronic course of radiation sickness, when the body is exposed to ionizing radiation for a long time, a low body temperature is also often noted. As for the acute course of this disease, this condition, on the contrary, is characterized by an increase in temperature.
Symptoms accompanying low temperature during radiation sickness:
- dry skin;
- development of dermatological diseases;
- the presence of compactions in the area of the irradiated areas;
- cataract;
- the appearance of malignant neoplasms;
- depressed genital area;
- decrease in the body's defenses.
13. Significant blood loss As a result of injuries, large arteries can become damaged, which leads to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood. This entails a violation of thermoregulation and, accordingly, a decrease in body temperature.
Internal bleeding is considered the most dangerous. For example, in the ventricles of the brain, in the pleural and abdominal cavities. Such bleeding is quite difficult to diagnose and, as a rule, surgical intervention is required to stop it.
14. Hypoglycemia Low blood sugar also leads to a decrease in body temperature. This condition can occur with physical exhaustion of the body and with an unbalanced diet, which contains a large amount of flour products and sweets. Often this condition becomes a harbinger of developing diabetes mellitus. Other symptomatic manifestations of a hypoglycemic state:
- headache;
- dilated pupils;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- hyperhidrosis;
- inappropriate behavior;
- tachycardia;
- disruption of the respiratory system;
- slow blood circulation;
- muscle tremors;
- motor dysfunction;
- confusion (the consequence may be fainting and/or coma);
- tachycardia;
- loss of sensitivity.
15. Overwork
Chronic fatigue, which may be associated, for example, with constant emotional stress or lack of sleep, can cause a decrease in body temperature. If, after prolonged overload, the body does not receive compensatory recovery, a failure may occur in any of the organ systems. This also entails the development of exhaustion.
16. Shock states
All shock states are usually accompanied by a decrease in body temperature. In medicine, there is a classification of such conditions depending on the nature, severity and location of the damage. The following shock states are distinguished:
- neurogenic (central nervous system disorder);
- cardiogenic (impaired cardiovascular activity);
- infectious-toxic (acute intoxication);
- combined (a combination of different types of shock conditions);
- septic (mass blood poisoning);
- traumatic (pain syndrome);
- anaphylactic (allergic reactions).
With almost any type of shock, the victim experiences the following symptoms:
- disruption of the respiratory system;
- tachycardia;
- moist skin that becomes pale or bluish;
- low blood pressure;
- confusion (lethargy or, conversely, agitation);
- reduction in the volume of urine excreted.
How to measure temperature correctly?
- In the armpit is the most common method of measuring temperature in our country. It is simple, but also quite inaccurate. So, the norm with this method ranges from 35°C to 37.0°C. In children under one year of age, low-grade fever is considered normal.
- Thermometry in the oral cavity is the norm in Europe and the USA, but rare in Russia. It may also not be effective in children, as they often open their mouth when taking measurements, which is not recommended.
- The rectal method (in the rectum) is very accurate, but is more often used in children. It is not recommended to measure the temperature of newborns rectally (to avoid intestinal damage). The average temperature in the rectum is half a degree higher than the armpit.
- Ear thermometry is popular in some countries, but is highly inaccurate.
Mercury thermometer - to correctly measure the temperature in the armpit, the mercury thermometer must be held for at least 5 minutes.
Hold the electronic thermometer until the beep and check the temperature. Then hold for another minute - if the temperature has not changed, then thermometry is completed. If it has increased further, continue to hold for 2-3 minutes.
The main rule : no need to measure the temperature of a healthy person! This leads to increased anxiety for no reason. If you feel the urge to take your temperature every day, this may be a symptom of depression or anxiety. In this case, you need to consult a psychotherapist.
What causes a change in body temperature?
An area of the brain called the hypothalamus regulates body temperature. If the body temperature rises above 38 or falls below 35, the hypothalamus begins to regulate temperature.
If the body is too cold, the hypothalamus sends signals, causing a shiver, warming the person. If the body is too hot, it sends signals to start sweating, which helps cool the body.
Infections cause most fevers. Fever develops as the body's natural way of responding to and fighting infection.
Causes of hypothermia
A significant number of people around the world have an average body temperature that differs from standard norms. Some people see 37°C on the thermometer all their lives, while for others the readings often drop below 36°C. Therefore, hypothermia is a sign of illness only if other symptoms are present. Causes of low body temperature may include:
- previous viral or bacterial infection
- anemia or hidden iron deficiency
- hormonal imbalances - hypothyroidism, diseases of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus
- external influences (frost, prolonged stay in water)
- fasting, dieting
- psoriasis and other extensive skin lesions
- Iatrogenesis (medical actions, drug overdose)
- alcohol and drug use (barbiturates)
- sepsis (blood poisoning)
Normal body temperature in children
Sometimes babies and young children have higher body temperature ranges than adults. Body temperature may rise slightly when a baby is teething. A baby's temperature is higher because he or she has more body surface area relative to body weight. The baby's body is more metabolically active, which leads to the production of heat. Babies' bodies do not regulate temperature in the same way as adults' bodies. Children sweat less when it's warm, which means their bodies retain more heat. It is also more difficult to cool a child down during a fever.
Past viral or bacterial infection
Any infectious disease, even a very mild one, forces the body to mobilize all its defenses. After illness, recovery occurs gradually. The fever is replaced by low-grade fever (see causes of low-grade fever 37.2 -37.5 C), and then by low temperature. This is accompanied by general weakness, the person feels not fully recovered. This condition may last two to three weeks after the end of the illness.
When a temperature of 35.5 is considered normal
The officially recognized norm for body temperature is 35.7-37°C.
A low temperature at which a person continues to feel well is observed in the following cases:
- individual characteristics of the body;
- aged people;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- time of day (morning);
- for a short time, after exposure to cold air.
Anemia
A low temperature, accompanied by weakness, dizziness and some other symptoms, may indicate a lack of iron in the body. A blood test for hemoglobin, as well as a determination of ferritin, helps to identify this pathology. The main signs of anemia and latent deficiency include:
- Thinning hair
- Striated and brittle nails
- Predilection for raw meat and other unusual tastes
- Inflammation of the tongue
- Weakness and decreased performance
- Pale skin
- Coldness of hands and feet
- Urinary incontinence
After prescribing iron-containing drugs (Ferretab, Sorbifer and others, see iron supplements for anemia), the above symptoms usually disappear within 2-3 months, including chilliness and a decrease in temperature.
Reduced thermometer readings
Today, several types of thermometers are used to measure body temperature: mercury, electronic, less often infrared, and each thermometer has its own range of normal temperatures, differing from others by tenths of a degree.
- The guideline (optimal values) for most measuring instruments is the interval 36.0–37.0 for axillary measurement and 36.1–37.8 degrees C for rectal measurement.
- Reduced thermometer readings are considered to be values from 36.0 to 35.0 degrees C.
- Low values are thermometer readings of 35.0 degrees and below.
All the following indicators in the article are given for axillary measurements.
Minor drops in temperature (slightly above or slightly below 36 degrees) with normal health usually act as a physiological response of the body to certain influences and are not a sign of pathology.
Hormonal imbalances
The human endocrine system influences absolutely all processes, including thermoregulation. Thus, tumors and brain injuries can cause disruption of the hypothalamus, which in turn is responsible for the temperature of the “core,” that is, a person’s constant internal temperature. Such conditions always clearly manifest themselves as disturbances in consciousness, speech, vision or hearing, problems with coordination, headaches and vomiting. Fortunately, serious brain diseases are rare. Much more often the cause of low thermometer readings is hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is an insufficient functioning of the thyroid gland, a deficiency of its hormones. A similar failure occurs during autoimmune inflammation of the gland, surgery on it, or treatment with radioactive iodine. The disease occurs quite often (according to some data, in 1-10% of the population) and manifests itself with a variety of symptoms:
- Weakness, decreased performance
- Weight gain, swelling
- Chilliness, low temperature
- Dry skin, itching
- Brittle hair and nails
- Drowsiness, memory loss and general lethargy
- Chronic constipation
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
To diagnose hypothyroidism, you need to check your TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) level. If it is higher than normal, then the likelihood of this disease is high. This is especially true for women over 40 years old whose relatives have problems with the thyroid gland. After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes replacement therapy (Eutirox), which allows you to return to normal health and get rid of symptoms.
Causes of severe headache and low temperature
Unfortunately, due to our unfavorable ecology and variable atmospheric temperature and pressure, quite a lot of people, and often, suffer from headaches. Headache, because We feel it immediately, from the moment of its appearance; the phenomenon is already quite familiar to us.
But, if a headache is accompanied by a low body temperature (below 36.6), then in this case it is worth not only taking a painkiller pill for headaches, but also seriously concerned about the condition of your body.
In this case, doctors are rarely consulted, which is the reason for the lack of knowledge of the problem. We will try to understand the causes, consequences and methods of treatment, because... These symptoms are dangerous for the body.
Causes of these symptoms
The causes of symptoms - headache and low body temperature are: - malfunction of the body; - decreased immunity; — acute or activated chronic diseases; - stress; - pregnancy; - general exhaustion of the body;
- and many others.
Let's take a closer look at the main reasons, which should promptly consult a doctor:
Acute or chronic diseases
These symptoms can cause diseases such as diabetes, asthenic syndrome, psoriasis, and skin inflammation. In this case, symptoms may be accompanied by constant thirst and require urgent treatment of the underlying disease.
For inflammation and tumors in the brain, both malignant and benign, due to deterioration of cell movement in the hypothalamus or oncology in other organs. Chills, low body temperature, headache and general weakness are also observed. To identify the cause of the disease, you need to consult a doctor. In this case, changes in the brain are diagnosed using MRI.
Also, reasons such as alcohol intoxication can cause a headache and a decrease in body temperature. In case of chronic alcoholism, it is worth paying special attention to these factors.
Thus, there can be many reasons for the manifestation of factors. First of all, you should observe the frequency and duration of their manifestations, and then consult a doctor. Since the symptoms may quickly disappear, indicating the restoration of the body’s performance. But it’s still worth paying attention to them!
Iatrogenic hypothermia
Physician-associated hypothermia typically occurs in patients undergoing surgery. If you leave a patient without a blanket after a long surgical procedure, the risk of hypothermia will be high. Anesthesia suppresses shivering, which prevents the temperature from dropping. Therefore, careful attention to postoperative patients is extremely important.
Overdose of antipyretic drugs - quite often, especially in children, the temperature drops sharply after an overdose of antipyretic drugs. Concerned parents, when they see numbers above 38 on the thermometer, begin to actively “bring down the temperature.” The consequences of such actions can be not only disturbances in thermoregulation, but also severe stomach diseases, as well as bleeding. Therefore, under no circumstances should you abuse antipyretic drugs.
An overdose of vasoconstrictor drops is another cause of low body temperature in a child. Due to the general effect on all vessels, such drugs can lead to hypothermia. Therefore, with a normal runny nose, without complications, it is better to rinse the child’s nose with a banal saline solution, sold in any pharmacy.
Differential diagnosis
A body temperature of 36 in an adult (the cause may be related to the presence of serious diseases) often indicates possible pathologies in the body. Therefore, it is recommended to carry out differential diagnosis. This method allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis based on a set of other symptoms.
Diagnostics is carried out in 3 stages:
- First, the patient’s medical history is carefully studied and the reasons for the appearance of low temperature (for example, hypothermia) are determined.
- At the 2nd stage, a direct examination of the patient is carried out, and concomitant symptoms are also studied in detail.
- The final step is to conduct laboratory and other tests to confirm a particular diagnosis.
Sepsis
The active proliferation of bacteria in the blood and poisoning of the body with their waste products is called sepsis. As with any bacterial infection, with septic complications, a rise in temperature is more often observed, and to very high numbers. But in some cases (in weakened and elderly people), damage to the nervous system occurs, including the thermoregulation center.
In such a paradoxical situation, the human body responds to the invasion of bacteria by a sharp drop in temperature to 34.5°C and below. Hypothermia during sepsis is a rather unfavorable sign. It is combined with a severe general condition, depression of consciousness, and dysfunction of all organs.
Low body temperature - reasons for the decrease and how to raise it
Cases when a person has a low body temperature, i.e. below normal are much less common than fever. Many people do not pay due attention to this, but this manifestation may indicate serious problems with the body that need to be addressed immediately.
What body temperature is considered low?
A person has a thermoregulation center in the brain area, and with the slightest disturbance in its functioning, body temperature begins to change. It is impossible to accurately determine the low temperature in the same way for all people due to the individual characteristics of each organism.
The norm is considered to be a temperature of 36.4–36.8C. But doctors increase the range from 35.5C to 37C. Anything below or above this norm is already a deviation. You can raise the low temperature barrier yourself at home. But if the problem lasts more than a day, it is better to go to a general practitioner to determine further actions.
A decrease in temperature exposes the body to malfunctions of all systems and threatens to disrupt normal metabolism.
Exacerbation of chronic diseases can be manifested by a temperature of 35C. A decrease in temperature to 29.5C leads to loss of consciousness, and with an indicator of 27.0C the patient falls into a coma.
Causes of low body temperature
Temperature 35.5C – a person feels tired, cold, lethargic and drowsy, and the cause may be:
- The presence of chronic diseases that have begun to progress. A doctor's help will be required.
- Regular overwork due to lack of sleep, constant worry, physical or mental stress.
- A weakened immune system, which may be caused by a recent serious illness or diet.
- Lack of vitamin C in the body. When drinking hot tea with lemon, you need to know that this vitamin loses its properties at a high temperature of the drink.
- Self-medication. Many people, having made a diagnosis for themselves, begin to use the medicine at their own discretion. Taking some medications can cause a decrease in temperature.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
- Stressful situations. Their influence leads to a weakening of the immune system and disruptions in the functioning of most important body systems.
- Pregnancy, during which a woman's hormonal levels change.
- A tumor could appear in the area of the hypothalamus (thermoregulation center), which leads to malfunctions in the brain, which leads to heat transfer disturbances.
- Low body temperature is observed more often in people who are bedridden. The reason is a weakened body.
- Minor injuries to the head can lead to a drop in temperature (if the thermoregulation center is affected).
The temperature in the body is maintained with the help of fats consumed in the form of food. Their processing provides heat transfer energy, and a shortage leads to hypothermia (a decrease in body temperature).
What to do if your body temperature is low - 34,35,36
In case of frequent hypothermia, the following rules should be followed to activate the body's protective features:
You can increase your immunity and improve your vitality with the help of a sweet delicacy, consumed daily, 1 teaspoon, prepared at home.
To prepare you will need:
- raisin;
- prunes;
- dried apricots;
- walnut kernels and honey.
All ingredients (except honey) are crushed (stick to an approximate ratio of 1:1). Afterwards, the delicacy is poured with honey and taken daily before breakfast.
How to increase the temperature?
First of all, you need to understand whether the decrease in temperature is normal or a deviation from it.
- If you accidentally, just like that, measured your body temperature and found a decrease in it, without experiencing any other symptoms, then calm down. Remember if you have recently had ARVI or another infection. Perhaps these are residual effects.
- Or maybe the reason is the active ventilation of the apartment on a frosty day. In this case, you need to close the windows, dress warmly and drink hot tea.
- If these reasons are excluded, then, most likely, such numbers on the thermometer are your individual feature.
- If, in addition to hypothermia, you experience weakness, depression, or find many other symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor.
Most likely, after additional tests, anemia or reduced thyroid function will be found. Prescribing appropriate treatment will help raise the temperature. In children, it is necessary to discontinue antipyretics and vasoconstrictors.
Temperature 36°C: what does it mean?
This temperature indicator can also be present in completely healthy people. The reason for this condition may be:
- recent illness;
- morning time, when all processes in the body proceed more slowly than usual;
- pregnancy;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- insufficient supply of vitamin C to the body;
- overwork, fatigue.
Also, a body temperature of 36°C may indicate the development of certain diseases and be observed in such conditions as:
- disorders of the adrenal glands:
- decreased thyroid function;
- prolonged fasting, as a result of which the body is depleted (often observed with improper dieting);
- brain pathologies;
- significant blood loss;
- chronic bronchitis.
When is urgent medical attention needed?
Mandatory contact with a specialist is necessary in cases where:
- Man unconscious
- Body temperature is 35°C and continues to decrease.
- Low body temperature in an elderly person combined with poor health
- The presence of serious symptoms such as bleeding, hallucinations, uncontrollable vomiting, speech and vision disturbances, severe jaundice.
Remember that true hypothermia, which is life-threatening, occurs in people who are seriously ill or hypothermic. A slight decrease in temperature will not harm your health. Moreover, at low temperatures all metabolic processes proceed more slowly. Therefore, many experts believe that people with this feature live somewhat longer.
Author:
Evtushenko Anna Aleksandrovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Normal body temperature in adults
In adults, the following temperature indicators divide fever into:
- weak (up to 38.5 C),
- moderate (up to 39 C),
- high (up to 41 C),
- hyperpyretic (above 41 C).
Scientists have studied individual differences between normal body temperatures. The study, which included nearly 35,500 people, found that older adults had the coldest temperatures, and African-American women had higher temperatures than white men. Scientists have also discovered that certain diseases can affect body temperature. For example, with insufficient activity of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), there is a decrease in body temperature, while with cancer, the body temperature is high.
Actions to take when the temperature drops
The physical condition of a person who has a low temperature should be adequately assessed. If you are not afraid, there is no weakness or other signs of illness, you need to remember whether you have recently had hypothermia or illness. A slight drop in temperature may be a residual symptom. In this case, there is no need to see a doctor. In addition, it is possible that low temperature is the normal state of a particular organism.
If the temperature has dropped due to hypothermia, then you need to put the victim in bed, cover him, paying special attention to the limbs, but leave the head and chest open. Wet clothes need to be changed. If your extremities are frostbitten, you cannot warm them up with water, but you can apply a warm heating pad to your chest. The victim needs a hot drink, but alcohol or coffee is contraindicated. You can use baths (water temperature up to 37 degrees Celsius) to warm up.
A decrease in temperature caused by malnutrition requires normalization of the diet. The patient also needs ascorbic acid, which has a good effect on the immune system, and children are additionally recommended to be given vitamin E.
If the mark on the thermometer is low due to illness or other reasons, and other symptoms of the disease are observed, then you should call a doctor. Before the doctors arrive, the patient must be put to bed and covered with a warm blanket. It is necessary to provide the person with complete peace of mind, give him warm tea to drink, and put a heating pad under his feet. This will allow the body to establish the process of thermoregulation; in most cases, the temperature will begin to rise to normal.
Recommendations from experts
When identifying evidence of a decrease in temperature, it is necessary to adhere to certain recommendations of specialists. It is necessary to increase the capabilities of the immune system in every possible way, carry out hardening, and start the morning with exercises. You need to optimize your own nutrition and consume 2 liters of fluid or more daily.
If possible, you should avoid nervous breakdowns, have a good background, and avoid overwork. You can achieve maintaining your condition not only through rest, but also through meditative practices and yoga.
Living conditions also influence body temperature, for example, at night the room should not be too hot or cold, and when going outside it is necessary to dress in such a way as to ensure the required level of thermal comfort.
It is also recommended to follow a daily routine that involves eating, going to bed and waking up in the morning at the same time. Having proper rest and doing your favorite things has a positive effect on your emotional state and nervous system. Quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages is an important element of maintaining good health, and taking medications should be carried out solely on the basis of specialist recommendations.
It is also worth taking into account such a moment as congenital predisposition. Some people have a low body temperature, but for them this is a normal condition, they do not experience any problems or discomfort. However, such people also need to undergo medical examinations for timely detection of existing diseases.