In the structure of gynecological diseases, cervicitis occupies far from the last place. According to statistics, the disease is detected in 70% of women who consult a gynecologist. Most often, cervicitis is diagnosed in women of childbearing age. And although this disease does not lead to the death of the patient, it can cause significant damage to health due to the development of complications. In 55% of patients, ectopia of the cervix is diagnosed against the background of chronic cervicitis. Cervicitis rarely acts as a separate disease; as a rule, it is accompanied by colpitis and vulvovaginitis.
Cervicitis - what is it?
Cervicitis is considered a complication of diseases of the lower reproductive system.
Vulvovaginitis, urethritis, and then cervicitis become successive stages of one inflammatory reaction. Endocervicitis and ectocervicitis are two forms of inflammation of the epithelial cover of the cervical canal of the uterus. The disease is characterized by the transient or permanent presence of infection on the mucous wall, which can progress and become aggressive or malignant. According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), ICD code N72 belongs to various forms of inflammatory reaction in the cervix. Due to its high prevalence, every woman should have an idea of what cervicitis is, how to identify and treat this disease. Untreated cervicitis in time means chronic erosion, ectopia and oncological tumors in the future. Cervicitis of the cervix can be suspected independently, but treatment should be carried out by a qualified obstetrician-gynecologist.
Life forecast
If cervicitis of any origin is not treated, complications may arise that adversely affect a woman’s health. These include scarring of the mucous membrane, adhesions, and the development of non-invasive cancer.
If a young woman who has not yet given birth suffers from the disease, then in the future she has an increased risk of developing infertility.
Causes
The main etiological factor of the disease is infectious invasions by bacteria, fungi and viruses. STD pathogens account for 70% of all cases, 20% are infectious-inflammatory reactions caused by opportunistic microorganisms, and only 10% are due to other causes. Although STD pathogens are transmitted through sexual contact, cervicitis cannot occur in men; this form of the inflammatory process occurs only in women.
The main pathogens contributing to the occurrence of cervicitis:
- pathogens of latent sexually transmitted infections;
- opportunistic coccobacillary flora;
- viral strains and protozoa;
- The Candida family of fungi and other types of fungi.
Cervicitis during pregnancy is caused by identical pathogenic agents. Pregnant women who already have a history of mucosal infection may experience reinfection and the addition of a new pathogen.
The causes of cervicitis are not always infectious. Some forms of damage to the cervical canal develop with endocrinopathies, when the natural hormonal balance is disrupted. Such forms of the disease are especially typical in postmenopausal women, when active hormonal changes in the body are underway. Another endocrine disease that can cause cervicitis is diabetes mellitus. Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism entail a change in blood flow in the microvasculature of the epithelial lining. Adequate oxygenation and tissue trophism are disrupted, which entails a decrease in the local immune response.
Classification
Depending on the pathogen that contributed to the development of the pathology, the disease can be:
- specific, which develops under the influence of STIs;
- nonspecific, provoked by opportunistic microflora.
According to the prevalence of inflammation, the process is distinguished:
- focal, when some areas of the endocervix are affected;
- diffuse - the entire epithelium is affected. Chronic pathology is usually diffuse.
A separate type of pathology is atrophic. It develops during menopause. In addition to the presence of an inflammatory process, thinning of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is observed.
Kinds
The main clinical classification of the disease involves dividing the pathology depending on the etiology of the pathogen that caused the inflammation.
According to this modern classification, cervicitis is divided into:
- bacterial cervicitis - caused by absolutely any microbes. They can be transmitted through sexual intercourse or enter the cervical canal from the vagina and environment;
- candidomycosis - infection with fungal microflora or active growth of own candida fungi, which are always present in the urogenital tract;
- viral - infection by virions, while any virus is considered an obligate pathogen, because healthy people do not have a single viral invasion;
- other forms of cervicitis - this category includes other rare forms of the disease (cystic, lymphocytic-infiltrative, endocrine, etc.)
All pathogens that cause cervicitis develop an active inflammatory process in the body. They colonize the mucous membranes, multiply here and lead to cell death. Due to severe destruction of the cellular lining, previous cervicitis can lead to ectopia. Ectopia is a pathological growth of the epithelium beyond the cervical canal. Cervicitis and subsequent ectopia are risk factors for oncogenic and neoplastic processes. This pathological transformation is characteristic of most viral invasions.
Purulent
This form of the disease is characterized by an aggressive course and a tendency to complications. The most common forms of purulent-inflammatory disease are caused by diplococci, myco- and ureaplasma and coccobacillary association of bacteria. In 45% of cases, acute gonorrheal cervicitis occurs with copious purulent discharge, often developing into a chronic recurrent form. The danger of this disease is manifested in the development of cervical ectopia of the cervix following chronic cervicitis, which is characterized by the spreading of epithelial cells beyond the anatomical boundaries of the cervix.
Cystic
Under the influence of various factors, especially infectious ones, the normal functioning of the glandular cells of the cervix is disrupted. Normally, they secrete a special mucus-like substance that protects the genital tract from pathogens. Cystic cervicitis appears due to blockage of the excretory duct of the gland by desquamated and dying epithelium. The natural secretory function is disrupted, and the gland itself swells, forming a cystic cavity. Such cervicitis of the cervix has a tendency to recur. Moreover, local protection against pathogens is reduced, and the reproductive system becomes vulnerable to various pathogens.
Bacterial
Bacterial cervicitis is a consequence of the invasion of pathogenic microbes into the lumen of the cervix from the vagina. In 80% of cases it is caused by STD pathogens, and in the remaining 20% - by microorganisms living in the urogenital tract. An ascending infection causes classic signs of an infectious-inflammatory reaction in the cervical canal: hyperemia, swelling and soreness. As the process becomes chronic, the symptoms subside, reminding themselves only when immunity decreases and the pathological process is activated. Inflammation of bacterial etiology can develop into purulent cervicitis in women, and therefore requires immediate pharmacotherapy.
Lymphocytic follicular
This form is characterized by the formation of infiltrative foci under the epithelial lining of the endocervix. Follicular cervicitis appears in postmenopausal women, so many experts associate this proliferative disease with changes in the concentration of hormones circulating in the blood. The endocervix is actively populated with lymphocytes, which can merge and form small clusters. The disease does not manifest itself clinically in any way, and the diagnosis is established only histologically. Lymphocytic cervicitis is considered by some doctors as a protective reaction to an infectious pathogen that was not detected by standard laboratory tests.
Atrophic
Atrophic cervicitis of the cervix is caused by natural fluctuations in hormone concentrations in the premenopausal and postmenopausal periods. A decrease in the content of estrogen in the blood leads to a proportional decrease in their effect on the epithelial cells of the reproductive system. With normal hormonal balance, active processes of proliferation and division occur, ensuring the correct histological structure of the mucous membrane. Due to a lack of hormones, degenerative and atrophic processes occur, leading to thinning of the epithelial lining, and then nonspecific atrophic cervicitis develops.
Viral
The etiological factor in inflammation is a virus. The pathogen penetrates into the epithelial cell, actively multiplies in it and causes destruction of the epithelium. The clinical symptom complex depends on the strain of the pathogen. Thus, HSV type 2 causes typical herpetic lesions in the form of painful and itchy blisters, which leave ulcerative elements on the mucous membrane. HPV leads to the formation of benign skin tumors - papillomas and condylomas, and CMV and EBV infections can exist for a long time without a single symptom.
Types of cervicitis and their treatment
In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish several types of cervicitis, it all depends on the cause of its occurrence.
Atrophic cervicitis
Diagnosed more often in older women. Its formation is usually provoked by a hormonal imbalance. Rarely, it may occur after spaying or chemical castration.
Purulent cervicitis
It is formed in most cases in young women as a result of bacterial infection. The causative agent of the disease is most often gonococcus. The disease is characterized by the appearance of abundant purulent discharge from the genital tract, increased temperature, and general weakness.
Candida
The provoking factor is fungi of the genus Candida. The appearance of cheesy discharge and itching is observed.
Forms of flow
Gynecological classification involves dividing the disease according to the degree of activity and duration of symptoms into several options:
- Acute cervicitis - the duration of the disease is no more than two months;
- Subacute - the duration of the inflammatory reaction is from two to six months;
- Chronic recurrent active cervicitis is a chronic process in the relapse stage, and the number of relapses per year is more than two;
- Moderate chronic cervicitis is the stage of attenuation of the symptoms of the disease; the total number of exacerbations per year is 1-2;
- Inactive chronic cervicitis - the diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests, clinical symptoms have been absent for more than a year.
conclusions
Treatment of low-grade chronic cervicitis is long-term and requires a responsible approach on the part of the woman. If she is interested in further having children, then she should devote a significant part of her time to her health.
Video: about colpitis, cervicitis, etc.
About colpitis, cervicitis, etc. —Dr. Elena Berezovskaya
Video: chronic cervicitis. Treatment, signs
Chronic cervicitis. Treatment, signs
Video: treatment of nonspecific vaginitis and cervicitis
Apolikhina I.A. — “Treatment of nonspecific vaginitis and cervicitis”
Complications and consequences
The most dangerous complication of the acute phase is the spread of an infectious-inflammatory reaction to the endometrium, uterine appendages and pelvic fat. In the absence of adequate pharmacotherapy, the formation of purulent foci in the small pelvis in the form of abscesses, phlegmons or swellings is possible.
Endometritis, in turn, can progress to endomyometritis and panmetritis with the involvement of all layers of the uterus in the pathological process. A rare complication is sepsis due to the pathogen entering the bloodstream. This condition is life-threatening. Sepsis occurs with multiple lesions of all vital organs and systems.
The consequences of any long-term invasion, especially viral ones, are characterized by cellular transformation in response to a constant inflammatory response. Cervical ectopia and erosion in chronic cervicitis are the most common complications. Cervical erosion and viral cervicitis lead to oncogenic transformation of the epithelium, first causing precancerous changes and then obligate oncological processes.
Pathogenesis
There are several stages during the course of the disease:
- the pathogen penetrates into the mucous membrane of the cervical canal;
- the columnar epithelium is damaged and exfoliated;
- secretion is released in large quantities;
- tissues become loose;
- the immune response is activated;
- damaged tissues are restored. In the absence of therapy, recovery will be incomplete, the process will become chronic;
- The mouths of the cervical glands are blocked, Nabothian cysts are formed.
Frequent exacerbations of the disease lead to the fact that the epithelial cells are transformed, and the stratified epithelium is replaced by its other forms.
Symptoms
Acute cervicitis has clear symptoms of an infectious-inflammatory reaction.
With severe inflammation, general infectious-toxic symptoms may appear. The manifestation of the disease begins with a slight pain syndrome in the inguinal-pubic region. As the disease progresses, the dull pain intensifies, and the main signs of cervicitis are added - pathological discharge of various types and acute pain when changing body position, sexual intercourse and physical activity. In some cases, symptoms of cervicitis include light spotting.
In 65% of patients, there is a delay in monthly menstrual bleeding or various variants of its disturbance: oligomenorrhea, polymenorrhea, algomenorrhea. Discharge from cervicitis often has a foul odor due to the presence of pyogenic bacteria in the discharge. Infectious-toxic symptoms of cervicitis are represented by low-grade fever, muscle and headache and general malaise.
Chronic cervicitis in the remission stage can occur latently, and sometimes the only symptom complex is menstrual irregularity. Exacerbation of cervicitis of the cervix has typical symptoms of acute inflammation, but their severity is much less.
An excursion into anatomy
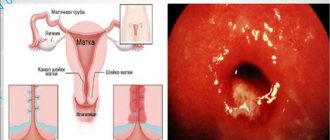
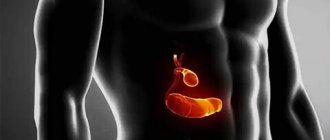
The cervix is an anatomical continuation of the lower uterine segment. It is presented in the form of a tube up to 4 cm in length and 2.5 cm in width. From the outside (in the vagina) only its part is visible - the vaginal part. The neck is covered with epithelium, which gives it a pale pink color. The cervix is the junction of the vagina and the uterine cavity, which provides the cervical canal.
The cervix acts as an anatomical and biological barrier that prevents the penetration of infectious agents into the uterine cavity, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Protection is provided due to the narrowness of the cervical canal, the mucous plug located in it, and the secretion of protective secretion by the cervical glands. When exposed to certain factors, the protective function of the cervix is disrupted, foreign microflora penetrates into the cervical canal and an inflammatory process is triggered - cervicitis.
Definition of concepts
If the vaginal part of the cervix becomes inflamed, they speak of exocervicitis. When inflammation develops in the epithelium of the cervical canal, this is called endocervicitis.
You can often hear from a woman that she has signs of cervicitis of the cervix. This is an incorrect phrase, since the word cervicitis itself means an inflammatory process of the cervix, and the result is “oil oil.” A more correct expression without any additions would be “cervicitis.”
Diagnostics
Clinical and laboratory examination data aimed at identifying the type and strain of the pathogen that caused the inflammatory reaction are of decisive importance in making a diagnosis.
General vaginal and urethral smears determine pathological deviations of the microbiocenosis of the urogenital tract, reveal lymphocytic infiltration and the presence of a large amount of desquamated epithelium.
But a general analysis is not enough to identify the pathogen, so the discharge is collected to carry out the following reactions:
- serological reactions with determination of immunoglobulins of various classes;
- polymerase chain reaction and double hybridization reaction;
- cultural examination with bacterial culture and antibiogram.
An oncocytological smear, which is performed on all patients, is of great clinical importance. It identifies atypical cells that have an abnormal structure and can potentially lead to cervical cancer.
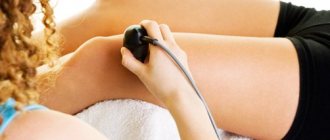
Specific echo signs of chronic or acute cervicitis are usually absent. However, ultrasound examination allows for differential diagnosis with suppurative complications, endometritis, salpingo-oophoritis and other diseases of the reproductive system.
Simple and advanced colposcopic diagnostics make it possible to visualize the mucous membranes of the cervical canal and study its surface in detail. In addition to the presence of pathological discharge, the colposcopic picture is characterized by the presence of many red dots on the surface - these are dilated capillaries. This type of mucosa is specific for an infectious-inflammatory reaction, which is manifested by hyperemia and congestion of the microcirculatory bed.
If these methods are insufficiently informative, biological material is collected for histological and morphological examination of the cervical epithelium. The search is aimed at identifying atrophy, dysplasia, hyperplasia and neoplasia of epithelial cells.
Cytogram
The most accurate diagnostic method used by doctors when endocervicitis is suspected is a cytogram. The gynecologist takes a scraping from the surface of the cervix with a sterile instrument, after which the biomaterial is examined under a microscope.
The procedure will take a few seconds to complete; there will be no discomfort or pain. The study is carried out regardless of the day of the cycle.
The method allows you to assess the condition of the epithelial cells, determine the form of the disease and its degree, detect other cervical pathologies at an early stage, and exclude dysplasia and oncology. If pathological compaction of the tissues of the cervical canal is detected, it means that the disease is chronic.
Is it possible to get pregnant with chronic cervicitis?
Most patients with the disease are interested in whether or not it is possible to become pregnant with chronic cervicitis. With this disease, there is no violation of the anatomical integrity and patency of the cervical canal. Sperm have no obstacles to meeting the egg, so the formation of a zygote is possible.
The main problem becomes the task of bearing a healthy child in the presence of a chronic infectious focus. Cervicitis of any etiology during pregnancy is a potential threat to the normal development and growth of the fetus. Cervicitis during pregnancy is subject to mandatory drug treatment, which helps prevent disturbances in embryonic development in the fetus.
Whether it is possible to become pregnant with tuberculous cervicitis is a controversial question. The ability to conceive depends on the adhesive process localized in the reproductive system. With significant adhesions, the patency of the genital tract is impaired, which prevents the reunification of reproductive gametes and the process of conception. For women with active adhesions, it is possible to use assisted reproductive technologies, in particular, in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Treatment during pregnancy
If there is a history of chronic cervicitis and pregnancy has occurred, then the main task of the obstetrician-gynecologist is to suppress the active infectious-inflammatory process and maintain constant remission for nine months.
Treatment of cervicitis in women during pregnancy must meet safety criteria not only for the mother, but also for the fetus. Some antimicrobial drugs can cause embryogenesis stigmata and developmental abnormalities in a child, so their use is prohibited. There is a special list of medications approved for use during pregnancy. These medications are absolutely safe and approved by all medical communities. In addition, pharmacotherapy requires mandatory monitoring of the condition of the expectant mother and her child.
Drug therapy is carried out according to the generally accepted scheme:
- etiotropic pharmacotherapy;
- symptomatic treatment;
- immunomodulation and increasing the immune resistance of the body as a whole.
Symptoms
If a doctor suspects that a woman has progressive chronic endocervicitis, the symptoms and treatment of this disease should be entrusted to an experienced specialist, since in the initial stages of the development of the disease women do not pay attention to the characteristic signs.
The patient needs to go for examination to a gynecologist in situations where the following disorders exist:
- A slight nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen;
- A mucous or purulent discharge appears from the vagina, which has an unpleasant putrefactive odor;
- There are minor problems with the urination process.
There is also such a type of pathology as chronic inactive endocervicitis. In this case, there is attenuation of the symptoms, and the pathology proceeds without any signs, but the infection in the body continues to increase in number and strengthen the immune system, increasing resistance to drugs.
It is also worth noting that chronic endocervicitis may have virtually no symptoms in the acute and remission stages. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo regular preventive gynecological examinations in a timely manner, since endometritis, colpitis and urethritis can develop against the background of this pathology.
Accordingly, it is impossible to say, having a history of chronic inactive endocervicitis, that this is an established remission that does not require maintenance therapy. If a sharp decrease in immunity occurs, the woman will be in a state of stress or physical overexertion for a long time, and an exacerbation will begin.
Signs of chronic endocervicitis at this stage will be as follows:
- Severe painful syndrome in the lower abdomen and lumbar back;
- Spasms in the uterus;
- A burning sensation during urination;
- Feeling of itching and burning on the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- Scanty or heavy vaginal discharge;
- Discomfort and pain during intimacy;
- Increased body temperature;
- Headache, fever, lack of appetite.
If at this time the wrong treatment is carried out, taking medications, the action of which will allow you to get rid of painful and uncomfortable symptoms, then the remission stage will soon begin again. The woman will feel relief, so she will not consult a gynecologist, but in the future, such a negligent attitude towards her reproductive health will lead to the development of serious complications.
Knowing what chronic endocervicitis is in gynecology, we can conclude that this is a very insidious disease. Often, in the absence of therapy, women are faced with the development of a severe inflammatory process in the cervical canal, which spreads to nearby muscle and connective tissue. In the future, this becomes the cause of hyperplastic and dystrophic changes with subsequent formation of cysts.
Treatment
Acute and chronic cervicitis require complex treatment prescribed taking into account the individual and age characteristics of the patient.
How long the disease is treated depends on the form, prevalence and activity of the inflammatory reaction. The average duration of a course of pharmacotherapy ranges from 7 to 15 days. Antibiotics for cervicitis are first-line drugs in case of bacterial invasion, and in case of inflammation of viral etiology, antiviral pharmacotherapy is prescribed. To remove inflammation, local therapy is prescribed using vaginal suppositories and creams. If the patient suffers from severe pain that interferes with normal functioning, then a course of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is prescribed. Antibacterial drugs have the ability to suppress the growth of normal microbial communities of the genital organs, which contributes to the development of candidomycosis. To prevent this condition, Fluconazole is prescribed.
It is impossible to cure chronic cervicitis, but you can influence its activity and the frequency of relapses. During remission, vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants, probiotic and prebiotic medications are prescribed. In case of relapse of the disease, pharmacotherapy is carried out according to the generally accepted scheme for the treatment of acute endocervicitis, with preference given to local dosage forms (ointment forms, vaginal suppositories).
Tablets and ointments
Tablet forms have a number of advantages: ease of administration for the patient, high efficiency and bioavailability, good and rapid therapeutic effect.
The main antibacterial drugs used for drug therapy in women:
- Amoxicillin and its “protected” derivatives (Amoxiclav);
- Second and third generation cephalosporins (Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone);
- Fluoroquinolone pharmaceuticals (Norfloxacin, Oflosacin);
- Tetracycline and its newer derivative, Doxycycline;
- Macrolides (Azithromycin, Roxithromycin, Josamycin);
- Aminoglycosides (Kanamycin, Gentamicin, Sisamycin).
Drug treatment includes the mandatory use of local forms that directly affect the pathological focus. This therapy helps to quickly destroy the pathogen, accelerate the processes of repair of damaged epithelium and reduce symptoms of discomfort.
Candles
Candles (suppositories) for cervicitis with an antimicrobial or antifungal agent are not inferior in effectiveness to systemic antibiotic therapy. Sometimes they are prescribed as monotherapy, but in most cases they are used in conjunction with tablet forms.
The main types of suppositories used in gynecology for local therapy:
- One-component suppositories - Hexicon, Ginezol, Milagin, Pimafucin, Metronidazole;
- Combined - Terzhinan, Betadine, Neo-Penotran.
Betadine and Terzhinan for cervicitis make it possible to simultaneously influence infectious foci of polymicrobial etiology or for any type of mixed infection. Suppositories are inserted into the vagina at night after hygiene procedures with a special instrument sold along with them. It is forbidden to insert suppositories with your hands, this will avoid new infections.
Medicines (drugs, suppositories)
Depending on the cause of the disease, the doctor selects medications:
- chlamydial infection requires the use of macrolides (Sumamed), tetracyclines (Doxycycline);
- if the pathology is caused by a fungus, it is necessary to use antifungal agents, for example, Fluconazole, Diflucan;
- if the cause of inflammation is Trichomonas, the use of antiprotozoal drugs (Metronidazole) is recommended;
- For staphylococcal and streptococcal infections, penicillins (Amoxiclav, Ampicillin) are used.
In a medical facility, medications are administered into the patient’s cervical canal. The cervix is treated with brilliant green or a solution of silver nitrate. Manipulations should be carried out once every 7 days. Suppositories or vaginal ointments (Poliginax, Terzhinan, Betadine, Mikosist) are also used for local treatment.
At home, it is recommended to irrigate the vaginal walls and cervix with medicinal solutions using a syringe. Usually protargol, chlorophyllipt, chamomile or St. John's wort are used in the form of a decoction. But procedures should be carried out only after the doctor’s permission.
Therapy for inflammation lasts 7-10 days, then it is necessary to restore the microflora of the vagina and intestines. The patient is recommended to use Vaginorm suppositories and probiotics (Bifidumbacterin). This stage of treatment lasts 1-2 weeks.
Immunomodulators and vitamins
To avoid relapse of the disease and increase immunity, immunomodulators are prescribed, for example, Cycloferon.
Such means help to increase defenses and eliminate the pathogen. The use of multivitamin complexes (AlfaVit, Pikovit) is also recommended.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Comprehensive treatment of the disease also includes the use of physiotherapy methods for the speedy restoration of affected tissues.
Physiotherapeutic procedures for illness: essence and effect
| Procedure | The essence of the method | Effect |
| Electrophoresis | The method is based on the use of electric current, with the help of which medications are administered, while the skin remains intact. | Provides tissue regeneration, eliminates inflammation and swelling, restores metabolic processes. |
| Mud therapy | A method of thermal therapy using various therapeutic muds. | It has a bactericidal effect and eliminates pain. |
| Cryodestruction | The essence of the method is the effect of cold on the affected areas. | Eliminates pathogenic microorganisms. |
| Ultrasound | The method involves the use of a device that emits ultrasonic waves of different frequencies, promoting compression and stretching of tissues and their restoration. | Prevents the development of adhesions, normalizes metabolic processes, restores blood circulation, eliminates inflammation and pain. |
| Magnetotherapy | The therapeutic effect is achieved thanks to the magnetic field affecting the affected area. | Activates blood circulation in the pelvic organs, reduces swelling and inflammation. |
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of cervicitis is also possible with folk remedies. Traditional methods, as a rule, complement pharmacotherapy prescribed by a doctor. The use of such methods requires prior consultation and approval of the attending physician. Endocervicitis and its treatment with folk remedies should be carried out only with medicinal substances with strict adherence to the proportions and concentrations of the active substances. Otherwise, the pathological process may worsen and complications may arise.
Treatment of endocervicitis and ectocervicitis with folk remedies can be carried out using the following publicly available methods:
- Carry out douching at home using water decoctions at room temperature. For this purpose, prepare a decoction from special pharmaceutical medicinal herbal infusions or collect medicinal plants yourself. Chamomile, sage, oak bark, buckthorn, and coltsfoot have pronounced therapeutic properties. Douching is carried out with a solution with a temperature identical to body temperature (maximum 38 ºC). It should be remembered that this method is not suitable for people predisposed to allergic diseases.
- Herbal tinctures and teas from lingonberry leaves and berries, dill seeds, chamomile, rose hips or mint. Drinking plenty of fluids allows you to quickly remove endotoxins from the body, reducing the symptoms of intoxication and inflammatory reaction. In addition, these herbal mixtures have a significant uroseptic effect on the urogenital tract, killing pathogenic microorganisms.
Chronic cervicitis also involves treatment with folk remedies. To prevent relapses of the disease, it is recommended to conduct two or three courses of uroseptic herbal medicine per year.
Prevention
Basic preventive measures should be aimed at identifying, sanitation and pharmacotherapy of foci of chronic infection.
Particular attention is paid to the health of the urinary and reproductive systems, which are closely related anatomically and physiologically. Timely screening diagnostics and preventive medical examinations by a gynecologist guarantee the absence of STDs and other infectious infestations in the patient. Increasing the level of sex education among the population will help stop the spread of latent sexually transmitted infections around the world. Unprotected sex with gonococcal cervicitis and other forms of STDs is prohibited. However, the use of barrier methods also does not guarantee complete safety, therefore, during treatment you should refrain from sexual contact with your sexual partner.