Every second woman of reproductive age experiences breast tumors. That is why experts insist on regular self-examination of the breast, as well as periodic visits to a mammologist. However, most often breast formations are benign. But don't relax. Malignant neoplasms of the breast rank second among the incidence of cancer, second only to lung cancer. Therefore, you need to regularly visit your gynecologist and mammologist in order to promptly identify any formations in the tissues.
Types of disease
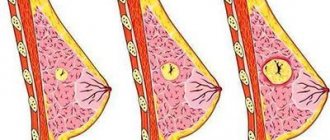
A tumor in the sternum in women most often appears in the mammary gland, which most depends on the normal hormonal balance and well-being of the patient.
A neoplasm is formed on different tissues of the mammary gland, so there are several main types:
- mastopathy;
- breast cyst;
- intraductal papilloma;
- fibroadenoma;
- lipoma;
- adenoma.
- Mastopathy is the most common type of benign tumor in the breast in women, which develops when glandular and connective tissue grows in the breast. New growths in mastopathy are heterogeneous and may contain voids - cysts. Depending on the proliferation of tissue type, mastopathy is divided into types:
- fibrocystic, which involves mostly connective tissue;
- glandular;
- mixed type.
Mastopathy can have 1 focus (node) of development (single form) or several (diffuse). With mastopathy, the neoplasm tissue becomes very dense and can protrude on the skin when located superficially, so this type of benign tumor is the easiest to diagnose.
- If a cavity forms in the connective tissue of the mammary gland and fills with fluid, this indicates the development of a mammary cyst. An elastic formation of an oval or round shape has clear boundaries that can be easily palpated and determined by ultrasound. A woman may not notice small cysts in the mammary glands for a long time. If the size is maintained, they do not require treatment. Only with an increase in the size of the cavity and suppuration of the contents of the cyst can the presence of the disease be established for further treatment.
- Intraductal papilloma is characterized by the appearance of small spherical growths inside the ducts of the mammary gland. The disease is viral in nature, in which the human papillomavirus first infects the woman's nipple. Then, moving along the ducts, the papillomas penetrate deep into the tissues, affecting an increasingly larger area. Most often, such neoplasms appear in the ducts of the mammary gland near the nipple. The disease can affect 1 mammary gland. In rare cases, intraductal papilloma affects both breasts and causes the appearance of small “warts” in its depths. Such a disease does not have the potential to progress to a more severe stage and be well treated.
- Fibriadenoma is characterized by thickening and enlargement of a separate lobe of the breast. A firm, round lump appears in the upper part of the breast due to the growth of connective tissue between the large milk ducts, which is called intracanalicular, or around them (pericanalicular). In more severe manifestations, cysts with fluid may appear at the site of the tumor. Such a tumor usually grows up to 5 cm. The formation develops in the form of a single compaction or a cluster of small formations, affecting 1 or both breasts. Only large tumors (more than 7 cm) are considered dangerous, so if such a disease is detected, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible to avoid the growth of fibroadenoma into a malignant tumor.
- Lipoma belongs to a group of rare benign tumors. When the disease occurs, a solid tumor develops from the fatty tissue of the breast. Most often, a lipoma forms on breast tissue that is stretched after prolonged feeding of a child. It grows slowly and can reach a diameter of no more than 1 cm. Depending on the composition, the disease is divided into types:
- myolipoma, in which fatty tissue is mixed with mucus;
- myelolipoma consists of fatty deposits and mostly connective tissue;
- lipofibroma is characterized by a large amount of fat and a small presence of connective tissue in the tumor;
- angiolipoma is noted when a fatty formation appears with an overgrown network of blood vessels;
- fibrolipoma (adipose tissue is gradually replaced by connective tissue).
Due to its small size, lipoma is difficult to diagnose, since it causes discomfort only when inflammatory processes in the tissues begin. In the absence of proper treatment at the time of inflammation, over time, a lipoma can cause necrosis of neighboring tissues and develop into cancer.
- Adenoma develops only in the glandular tissues of the breast and belongs to epithelial tumors. A tumor in a woman’s breast appears quickly and can be easily felt. After general tests, a diagnosis of adenoma is made, which develops in various forms. Depending on the type of formation, it is divided into:
- apocrine (develops in the mammary glands in places where they are intertwined with sweat ducts from apocrine cells);
- tubular (develops in the form of elongated formations - tubes);
- lactation (develops during feeding and is associated with the production of breast milk. Most often appears in the nipple area);
- ductal, which appears only in the ducts of the mammary glands;
- pleoform (mixed form, in which the tumor formation can be characterized by signs of several types of adenoma).
Adenoma has vague symptoms, especially in the early stages. Complete recovery without surgical intervention is possible only in the initial stages of the disease, so a routine examination by a specialist plays an important role in preventing the disease.
How to distinguish a benign breast formation from a malignant one?1
If you find some thickening or compaction, or feel nodules in the mammary gland or armpit area, do not immediately panic. Most often, benign neoplasms can be located in these places, but nevertheless, be sure to make an appointment with a doctor. First, see a gynecologist, who, if necessary, will write you a referral to an oncologist. The health of women's mammary glands is influenced by many factors: the environment, bad habits, unhealthy diet, various types of medications that we take as food, and much more. It is believed that after 35 years a woman’s breasts enter the so-called involution phase, or, in other words, become obsolete. This is also the reason why during this period women often experience a number of changes in their breasts and, during self-examination, discover new formations - cysts, thickening of tissue and other bad things. Of course, most of them are benign formations that may well disappear and reappear. Let's figure out the reasons for which tumors appear and which can be classified as malignant and which cannot.
90% of women have probably already noticed that you can often feel a small lump in your breast before your period. It usually occurs in the same place, on one breast. After menstruation, everything goes away as it never happened. In this case, there is no reason to panic; it is a simple change in hormonal levels. Lumps often appear in the breasts of nursing mothers. The reasons may be different. These include the formation of pockets with infection (abscess), and blockage of the milk ducts (lactostasis), and a general inflammatory process (mastitis). And if there is pain when pressing on the tubercle and in addition the temperature has risen, then you should not go, but run to the doctor. Self-medication will not only delay treatment, but may also deprive your baby of milk.
What is a cyst?
A cyst is a small cavity where fluid accumulates. It feels hard, smooth and moves easily under your fingers. When pressed, this spherical formation causes pain.
The sizes of cysts vary - from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The reason for the formation of this type of lump in the breast may be a hormonal imbalance. Genetic predisposition also plays a role in the occurrence of cysts. A wise decision would be to seek help from a specialist, because a cyst without treatment can develop into purulent mastitis. There can be either single or multiple formations in one or both breasts at once.
Cysts often form in women who use hormone replacement therapy, use hormonal birth control, or who have mastopathy or thickening of the mammary glands caused by dysfunction of the thyroid gland, endocrine glands, including the gonads. Injuries also contribute to the formation of cysts; even a strong blow can contribute to this, as well as operations, including implantation.
Fibroadenoma
This is a very common benign tumor in women, appearing between 15 and 35 years. Fibroadenomas also usually grow very slowly and disappear during menopause. If you do self-examination, fibroadenoma can be palpated as a round, dense consistency, painful or non-painful, neoplasm that is well separated from the border of other tissues. Depending on the size of the fibroadenoma and its location, it may also be painful. If the fibroadenoma is more than three centimeters, it will need to be removed surgically, as is the case if it is discovered after 40 years. In all other cases, the tumor is monitored by a doctor.
Lipoma
Lipoma is a benign tumor of the breast, which is derived from fat and can be either subcutaneous or deep inside the breast. Lipoma grows very slowly and can develop at any age and be of any size. The woman herself can detect this formation in herself by palpating her breasts and finding in it a certain soft-to-the-touch, round, slightly moving formation. Is it worth reminding that in this case, too, you need to go to the doctor to conduct an examination, do tests and make sure that it is actually a lipoma. A large lipoma requires surgery, but most often this is not required, and only regular monitoring of the tumor is required.
Mammalgia
You will be surprised, but this diagnosis is made in approximately 70% of women of childbearing age. These are various kinds of pain or heaviness in the chest that appear from three to seven days before menstruation. The breasts become enlarged and nodules can also be felt on them. All these symptoms usually disappear during menstruation. Even if you are familiar with these sensations, there is no reason to worry. These are simply features of your body, which reacts in this way to fluctuations in hormones. Conversely, if chest pain is not associated with the menstrual cycle, then it is called non-cyclical mastalgia. In such cases, the pain will most often be constant and may be associated with various diseases of the breast and problems in other organs, such as the muscles of the chest wall or the heart... Be sure to go to the doctor and tell us about your problem.
Intraductal papilloma
This complex name is given to a benign neoplasm consisting of connective tissue and blood vessels. This papilloma can form in the mammary gland towards the end of the breast or even further in the milk duct. If it is located near the areola, then a woman can feel her breasts and find a papilloma. Papilloma can also lead to discharge from the nipple - clear or bloody. In such cases, you should immediately go to the doctor, because, although rare, the formation can develop into a malignant tumor. If the papilloma is less than a centimeter and does not bother you at all, and also does not increase in size during examination, and the doctor’s studies did not reveal a malignant process, then there will be no need for surgery.
IMPORTANT
Almost every second woman of reproductive age experiences small lumps in her breasts. These are benign formations - by palpating the glands, you can find a benign tumor, usually a node of dense hard tissue. But if you just wait for it to go away on its own, you could be in for a lot of trouble. The main thing to remember is: if, while palpating your breasts, you come across any kind of ball or thickening that was not there before, it is better to go and get a consultation with a doctor. Your own peace and safety are most important!
Breast lumps: myths and facts
• A lump in the breast most often turns out to be cancer.
Fortunately, this is a myth. Experts assure that every woman who has discovered a tumor should not worry or panic, or immediately think that she will certainly have cancer until doctors confirm her fears or, conversely, refute her fears. Regardless of the cause, any lump in the breast should be checked. Experts advise undergoing a physical examination by a gynecologist, mammography and ultrasound examination of the breast.
• Breast cancer can always be detected by touch.
Not necessary. Quite often, doctors discover cancer after many procedures that a woman has to go through. Sometimes cancer is detected during an ultrasound examination, even before the tumor can be felt.
• When examined, a malignant tumor is always different from a benign one.
Not always. Cancerous tumors or benign growths can feel very similar to the touch. Many women are mistaken in believing that cancerous tumors are harder to the touch and immobile. Often the opposite happens - it is the soft and smooth, mobile seals that turn out to be cancerous. Experts assure that a woman will not be able to accurately determine cancer on her own. The best advice in this situation is that any lump that you find in yourself should be checked.
• If the seal is small, there is no need to worry.
This is definitely not true. The cancerous tumor can be very small. The small size of the lump is not a reason to postpone a visit to the doctor. The lump may be the size of a small pea, and this does not mean that you have a benign lump. During the examination, doctors discover tumors ranging in size from a small cherry to a grapefruit. Remember! The earlier you detect the formation, the more successful the treatment will be. If the formation is palpable, then it is already 2–3 cm in size. Therefore, it is best to undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist once a year in order to identify diseases at an early stage of development, because the effectiveness of further treatment depends on this.
• Breast cancer can only occur in women who have a history of such cases in their family.
It is a myth. Only 5–10% of breast cancer cases are inherited. Most women diagnosed with breast cancer were not at risk. But usually many representatives of the fair sex want to think the opposite. Almost everyone believes that if there are no cases of such a disease in the family, then she is unlikely to develop breast cancer.
All that is required of the woman herself, who wants to maintain the health and beauty of her breasts, is to remember to take time for herself and regularly, even without any complaints, undergo preventive examinations from specialists.
Symptoms that require attention
There are a number of signs that should force a woman to postpone everything and make an appointment with a specialist in the coming days.
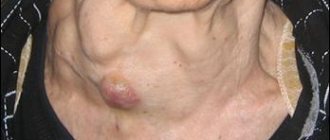
• The appearance in the mammary gland of a nodule or multiple nodules, a compaction of any size that does not have clear boundaries.
• Changes in skin color in certain areas of the mammary glands - the skin in the area of the tumor may become yellowish, bluish or red.
• Enlargement of one of the mammary glands, retraction of the skin, changes in skin density and the appearance of the so-called lemon peel.
• Changes in nipple shape and position not associated with breastfeeding.
• Discharge from the nipple outside of lactation, including clear or bloody.
• Enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes located in the axillary region.
If you notice any of these signs, do not delay contacting your doctor.
You can check your breasts at the Latgale Medical Center in Daugavpils, st. Rigas, 20. Appointment by phone. 25251010.
We will be happy to help you quickly, efficiently and confidentially!
BY THE WAY
A cyst does not mean that you definitely need surgery or drug treatment. If it is small and does not grow, then it is not touched, since over time it usually disappears or resolves itself. However, observation by a doctor in this case is necessary, because the cyst can grow and become larger, and this is dangerous. True, the cyst can increase before menstruation and decrease immediately after it. On ultrasonography, it is easy to see a cyst filled with fluid, and you can also see a lipoma, which occurs for the same reasons.
Stages and degrees
A tumor in the sternum in women, each type of which has different degrees of development and course of the disease, is distinguished into early and late stages.
- At an early stage of mastopathy development:
- A woman's lymph nodes in her armpits swell.
- shapeless formations gradually appear in the chest, which slowly increase;
- The mammary glands become harder and denser.
At a late stage:
- pain appears in the chest, which can radiate to the shoulder blade or shoulder. The pain stops for a few days after the menstrual cycle, and then appears again;
- Clear or bloody discharge begins to come out of the nipple.
- General discomfort appears in the sternum.
- When a cyst appears and develops at stage 1 of the disease, a woman does not experience any symptoms. A woman can live her entire life with small cysts in the mammary gland. But if the size of individual voids increases, the disease immediately causes a number of symptoms.
At a late stage of the disease:
- in the presence of suppuration of cystic fluid, a woman may develop and maintain a high temperature;
- a constant nagging pain occurs in the chest at the site of formation, which is practically not drowned out by painkillers.
If left untreated, a cyst in the sternum can burst, causing damage to all tissues and infection of the body.
- Intraductal papilloma in the initial stage does not have clearly defined symptoms.
Even during the period of active development of the disease at a late stage, a characteristic sign will be:
- slight pain when squeezing the breast;
- the appearance of yellow, brown or green discharge from the nipple.
The disease does not develop into cancer, but can gradually affect the entire body.
- With fibroadenoma, the symptoms of the disease are completely absent, so the disease can be diagnosed only during a routine examination.
At stage 2 of the development of fibroadenoma, small signs appear that signal the active course of the disease:
- menstrual irregularities up to infertility;
- hormonal imbalance;
- a sharp and significant change in body weight or visual acuity.
In the event of a sudden change in health status, a routine examination by a gynecologist and mammologist is recommended in order to exclude this diagnosis.
- At the initial stage of lipoma development, there are no symptoms of the disease.
At a late stage in the female breast:
- aching pain appears;
- a compaction develops, the tissue around which can become inflamed;
- When suppuration occurs, the temperature rises and remains at a high level.
A lipoma in the later stages of development is surgically removed immediately, otherwise it can cause necrotic processes in surrounding tissues and organs.
If it's not cancer, what could it be?
As mentioned above, the vast majority of newly identified formations in the mammary gland are harmless. This also applies to benign breast tumors; as a rule, they do not turn into cancer. But some of them still have a minimal risk of degenerating into a malignant disease in the future, which requires their removal.
Below we will discuss the risks of degeneration into cancer for each benign breast tumor, which leads to different therapeutic approaches for these neoplasias.
What is the difference between a benign tumor and a malignant one?
A benign tumor is a noncancerous growth of body tissue; unlike a malignant tumor, it does not spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
A benign tumor can occur in any organ and is usually the result of uncontrolled cell division in that organ. For example, the mammary gland mainly consists of glandular and connective tissue, so benign tumors most often form in it from the cells of these tissues. Fibroadenoma, the most common breast tumor, is a mixture of fibroblasts (connective tissue cells) and epithelial cells of glandular tissue. Lipoma is mainly composed of fat cells (connective tissue cells).
These cells grow only at the site of their appearance, pushing away nearby tissues without penetrating into them, which is the main difference between benign and malignant neoplasms.
Causes of benign tumors
The appearance of a benign tumor is the result of excessive cell division in the body. The body is usually able to balance cell growth and division. When old or damaged cells die, they are automatically replaced by new, healthy cells. But in the case of neoplasia, these cells do not die, but continue to grow, creating “extra” tissue - a tumor.
Often the cause of benign tumors cannot be determined, but their growth is stimulated by:
- Toxic environmental effects, such as exposure to radiation;
- Genetics;
- Diet;
- Stress;
- Local trauma;
- Inflammation or infection.
Symptoms
Almost half of the types of benign tumors in the mammary glands do not manifest themselves in any way in the female body. The growth of a tumor in the mammary glands can occur gradually over many years without causing symptoms. In such cases, a diagnosis is made only when the disease is identified during an examination.
Most tumors in the sternum in women have common symptoms that signal the need for urgent examination.
These include:
- breast tenderness during the menstrual cycle;
- discomfort in the sternum, including when lying down;
- any discharge from the nipples in the form of mucus;
- swelling of individual parts of the chest;
- change in color of the nipple areola or breast tissue;
- palpation of a lump inside the chest;
- inflammation or enlargement of the lymph nodes in the armpit.
The presence of a tumor in the mammary glands can be indicated by sudden and serious changes in the woman’s health and general well-being.
How can a doctor distinguish whether a tumor is benign or malignant?
If a clinical breast exam, mammogram, or ultrasound reveals a suspicious breast lump, a woman may be advised to undergo a biopsy, a procedure in which the doctor takes a small sample of tissue from the suspicious area and sends it to a pathologist to examine it under a microscope.
This is the only way to determine whether a lump is malignant or benign in the breast. There are several types of biopsies, which have their pros and cons:
- Excisional biopsy (removal of the entire tumor) is the most informative, but also the most invasive of all types of biopsies, requiring the removal of a large area of the breast, performed under general anesthesia;
- A fine needle or trephine biopsy (a small area is removed) is performed under local anesthesia. They are considered less traumatic, but quite often after them it is necessary to perform a second biopsy, since they do not provide a 100% guarantee that the biopsy needle entered the area of accumulation of cancer cells.
Even if the biopsy is negative (no cancerous cells), the breast lump should be monitored and removed immediately if it begins to grow.
Reasons for appearance
A tumor in the sternum in women does not occur for no reason.
Common causes of occurrence that are present in all cases during examination include:
- hormonal imbalance in the body. The ovaries, adrenal glands and pituitary gland produce different amounts of hormones in the right ratio. The level of hormone production varies depending on the age of the body and reaches a maximum during the reproductive period. In some cases, the production of hormones by organs may be disrupted due to illness (pelvic disease, diabetes) or stress. With a strong and constant disturbance in the level of hormone production (increase or decrease), various diseases begin to develop in the body, including benign tumors in the mammary gland.
- hereditary predisposition, which is determined by the genome;
- diseases of the endocrine system affect hormonal balance and can cause the development of the disease;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol, obesity, as well as poor ecology increase the likelihood of developing tumors in women in the breast.
- the absence of pregnancies by adulthood, the presence of several abortions or refusal to feed the child after childbirth provokes the development of lipoma and mastopathy after 35 years.
There are individual reasons that provoke the development of certain types of benign tumors.
The causes of the development of lipoma and adenoma are considered:
- severe injuries to the mammary glands, especially during their formation or during breastfeeding;
- frequent pregnancies, abortions and prolonged breastfeeding.
Mastopathy and adenoma often develop in cases of:
- radiation exposure, frequent visits to a solarium or sunbathing;
- damage to the body by toxic industrial poisons.
Intraductal papilloma is provoked by a lack of personal hygiene or indiscriminate sexual intercourse. A woman can get this disease at any age. Inflammatory processes in the chest can become an impetus for the appearance of cysts and the development of mastopathy.
Other benign breast lumps
In addition to the benign tumors listed above, hamartomas , hemangiomas , adenomyoptheliomas and neurofibromas . In addition, after an injury, a hematoma can form in the mammary gland.
Keep in mind that even if a benign breast lump is detected, the risk of developing breast cancer (a cancer that affects one in eight women during her lifetime) is not reduced. Although you can breathe a sigh of relief after being diagnosed with a benign breast tumor, you still need to continue screening - regular mammograms, visits to a mammologist, and performing breast self-exams.
Benign breast lumps and the risk of developing cancer Women who have a history of benign diseases are more likely to develop cancer than those who do not have any breast pathology. According to a study published in 2021 in the International Journal of Cancer, the presence of benign changes is a factor that increases the risk of developing malignant tumors, in addition to the already high likelihood of developing breast cancer due to family or individual history of the disease, as well as risk-associated mutations genes.
Find out more: From mother to daughter. How to find out if you are predisposed to breast cancer and how to protect yourself?
Diagnostics
A tumor in the sternum in women is not always easily diagnosed during a routine examination. Dense formations at a late stage of mastopathy development can be easily felt at home.
In other cases, to diagnose various types of tumors, the following is carried out:
- visual examination and thorough palpation of the mammary glands by a gynecologist or mammologist;
- mammography, which is an x-ray of the mammary glands. It is done using modern equipment and makes it easy to recognize tumors in the sternum. The study is carried out in X-ray rooms of clinics and paid medical centers. The cost of the procedure ranges from 900 to 1500 rubles;
- Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands allows you to diagnose the presence of a neoplasm, its characteristics and location. This study is carried out in inpatient clinics and medical centers. Its cost ranges from 700 to 1200 rubles;
- Computer or magnetic resonance topography is considered the newest and most effective way to diagnose the disease, which is based on a directed beam of X-rays. Such a device allows you to scan the body in thin sections, giving an accurate description of the neoplasm by content and location, if any. Such a study is carried out only in specialized oncology centers and large medical companies. The cost of the procedure ranges from 900 to 3000 rubles;
- a blood and urine test to examine changes in basic elements and the presence of inflammatory processes can be done in a regular clinic or medical laboratory. The cost of a urine test is up to 500 rubles, depending on the purpose, and up to 900 rubles for a blood test;
- A blood test for the presence of tumor markers determines the presence of proteins and other waste products of the tumor in the blood. The analysis is carried out on various types and types of contents in cancer hospitals and medical laboratories. Its cost, depending on the purpose, can range from 400 to 3000 rubles.
Diagnosis method:
| Disease | Diagnosis methods |
| mastopathy | Examination by a doctor, ultrasound, blood test |
| cyst | Ultrasound or computed tomography, general blood test and tumor markers |
| intraductal papilloma | General and detailed blood test |
| fibroadenoma | Examination by a doctor, mammography or ultrasound, blood test for tumor markers |
| lipoma | Examination by a doctor, ultrasound or mammography, general blood and urine tests |
| adenoma | Ultrasound, computed tomography, detailed blood test and tumor markers |
3.Diagnostics and treatment
Diagnosis of a benign breast tumor
A thorough breast examination by a doctor will help make an accurate diagnosis and rule out breast cancer. If the patient has nipple discharge
, they can be analyzed to help determine the presence or absence of cancer cells.
Imaging examination of the mammary glands - mammography
or ultrasound of the mammary glands - will help determine whether the tumor is a homogeneous solid mass or filled with liquid.
Sometimes a biopsy
– taking a sample of cells or tissue from the breast and further examining it under a microscope.
Treatment of benign breast tumors
The choice of treatment for a benign breast tumor depends on what type of tumor has been diagnosed.
Thus, fibrocystic changes
do not require treatment.
A simple cyst
can be treated with a fine needle, and manipulation is often performed during diagnostic procedures. A breast biopsy uses a small needle. Removing fluid from the cyst using a needle will make the cyst disappear.
Fibroadenomas and intraductal papillomas
can be removed
surgically
.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
When to see a doctor
In women, many types of benign tumors do not have clearly defined symptoms. In these cases, it is possible to determine the presence of a disease in the sternum only by undergoing a routine examination, so any woman needs to systematically, at least once a year, undergo a general examination by a gynecologist and undergo fluorography.
It is imperative to consult a doctor:
- in case of detection of a foreign formation in the chest;
- the appearance of pain in the sternum when pressed;
- mucous discharge from the nipple;
- the appearance of visible lumps on the chest;
- poor blood and urine tests that show inflammatory processes in the body.
For a more comprehensive examination and diagnosis of a neoplasm, after a gynecologist and basic tests, you need to see a mammologist, and then an oncologist for consultation.
Subspecialists will prescribe a specialized examination that will show the volume and type of tumor, its structure, as well as its location in the chest. Depending on the type of benign tumor and the patient’s condition, the doctor will determine the method of treatment.
If chest pain occurs, which is accompanied by an increase in general body temperature to or above 38 °C, you must immediately go to the hospital to take emergency treatment measures.
Malignant neoplasms of the breast
The most dangerous are malignant breast tumors. There are several types of breast cancer:
- lobular;
- metaplastic;
- colloidal;
- inflammatory;
- ductal;
- infiltrating;
- medullary;
- undifferentiated;
- low differentiated.
Separately, cancerous tumors are divided into different histological types;
- sarcomas;
- carcinomas;
- ademocarcinomas.
It should also be noted that breast cancer can be a primary or secondary tumor. In addition, neoplasms are divided into hormone-dependent, invasive and estrogen-dependent. Regardless of the type of breast cancer, it is a dangerous disease that requires treatment by a professional oncologist.
Prevention
Benign formations in the female breast always have a cause, so there is a set of preventive measures that will help maintain women's health.
To do this you need:
- lead a healthy lifestyle (adhere to the basics of a healthy diet, do not smoke or drink);
- Rest regularly, avoid stressful situations and sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- maintain systematic sexual relations with a regular partner;
- a woman should use contraceptives when having sex to avoid abortion;
- always take care of personal hygiene, systematically wash yourself using liquid soap or special gels and use cotton underwear;
- treat hormonal imbalance under the supervision of a specialist;
- After the baby is born, follow the recommended period of breastfeeding;
- Be periodically examined by a doctor and monitor your health daily.
Only in the aggregate, adherence to preventive measures can provide complete protection against the development of unwanted neoplasms in the breast.
Treatment of benign breast tumors
The benign form of breast tumors is treated with traditional methods. This includes medications and surgery. The doctor must determine the method based on a whole range of examinations. The type of tumor, its size and growth tendency are taken into account.
If the tumor grows slowly and there is no pain, conservative therapy is prescribed under the supervision of the attending physician. He will recommend vitamin therapy (A, E), preparations with iodine, selenium and plant hormones that help compensate for their deficiency in the body. Be sure to provide consultation on a healthy lifestyle and proper hygiene.
Proper balanced nutrition allows you to lose excess weight, which causes most breast diseases. 8 hours of healthy sleep and correction of physical activity are necessary. Coffee, pickles, soda, alcohol, smoking, etc. are excluded. Vegetables and fruits rich in fiber are encouraged in the diet. The amount of water you drink per day is 2 liters. When losing weight, the functioning of all organs and systems improves. It is important to treat pathologies of the genital area if problems are found there.
Surgery is used for pathological symptoms, intensive growth and signs of tumor degeneration into cancer. 2 ways to remove seals:
- sectoral resection - part of the breast is cut out along with the tumor;
- enucleation - the tumor is separated from the breast tissue and glands and only it is removed.
Doctors conduct a histological examination of the removed material, confirming or denying the malignant etiology of its occurrence. Next, the wound is sutured with a cosmetic suture.
After the operation, a rehabilitation phase follows. Here the doctor also prescribes hormonal and non-hormonal medications.
Treatment methods
Benign tumors, especially those detected at an early stage of appearance, are treated quickly and simply. You need to undergo a course of treatment only under the supervision of a specialist.
When treating benign neoplasms, the patient is prescribed:
- a light diet and adherence to the basics of a healthy lifestyle;
- medications to relieve the cause and development of the disease;
- traditional methods of influence;
- removal of the tumor surgically if it is impossible to use other means of treatment.
Medications
If benign tumors (for example, mastopathy) are detected, the woman is prescribed medications based on antibiotics. They not only allow you to treat the disease, but also prevent inflammatory processes from developing in the body.
- Maximim is considered the most effective drug, which is administered intramuscularly in 1 injection for 14 days. The exact dosage of the drug is determined by the attending physician. The price of the drug is from 350 rubles.
- Penicillin is actively used for fibrocystic mastopathy. The drug suppresses the development of the disease and eliminates inflammation, effectively removing swelling in the tissues. The drug is prescribed 1 tablet 2 times a day or in the form of injections. The cost of the drug, depending on the manufacturer, ranges from 50 to 200 rubles.
In addition to a course of antibiotics, the patient is prescribed medications to restore hormonal balance and normalize the functioning of the genital organs.
- To restore hormonal levels in breast tumors, tamoxifen, which contains antiestrogens, is actively used. Hormonal therapy allows you to adjust the level of hormones in the female body and promotes tumor resorption. The medicine is prescribed 1-2 tablets 2 times a day, depending on the patient’s condition. The exact dosage and course of treatment is determined individually by the doctor. The cost of the drug is 250 rubles.
- Actively helps restore hormone levels in the female body femoden. This broad-spectrum drug includes a combination of hormones that have a beneficial effect on reducing the number and size of tumors. Femoden is prescribed 1 tablet once a day for 1-2 months. The exact dosage and duration of treatment is determined individually. The average cost of the drug is 750 rubles.
Traditional methods
In the absence of the likelihood of developing a malignant tumor and in the early stages of the development of tumors in the breast, as well as in combination with a course of treatment, traditional methods of treatment are actively used:
For breast fibrosis, a decoction of alocasia is used:
- 50 grams of fresh or 30 grams of dried alocasia leaves are poured into a glass container.
- Add 250 ml of vodka to the leaves and mix thoroughly.
- The tincture is placed in a dark place for 20 days.
- Then filter the solution and drink 10 drops. Once a day, diluted in 50 ml of water for 10-14 days.
The tincture promotes the resorption of tumors and the elimination of inflammatory processes. A tincture of walnut peel has active properties in the fight against breast lumps.
This medicine normalizes the condition of blood vessels, restores blood circulation and reduces pain in the sternum. Long-term use of such a folk remedy promotes the resorption of tumors in the mammary glands.
- To 1 liter of vodka you need to add the green peel of 20-25 walnuts, which are first slightly crushed.
- The tincture is placed in a dark place and kept for 20-24 days.
- Drink the medicine 10 ml 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 3-4 months.
To restore hormonal levels, collecting boron uterus, which contains phytoharmones, is excellent.
Herbal infusions supplement the required level of hormones and help normalize the functioning of the entire body:
- To make an infusion, pour 35 grams of dry herb into 200 ml of boiling water.
- The solution must be mixed, closed and left for 1 hour.
- Then the medicine is filtered and drunk 50 ml 3 times a day before meals. The general course of admission is 20 days. Then you need to take a break for 14 days and repeat the course.
Propolis has anti-inflammatory properties, helps restore hormonal levels and reduce tumors in the breast:
- Take propolis 3 times a day, 5 grams 30 minutes before meals for 30 days.
Oat wraps promote the resorption of tumors:
- Ground or crushed oats (100 g) must be boiled for 20-30 minutes. in a small amount of water.
- Oats are laid out on film and applied to the chest.
- The top of the chest should be wrapped with a towel or scarf.
- The compress is kept for 40 minutes. and wash off with warm water. Wraps are used for 20-30 days.
Cabbage leaves contain vitamins and substances that have anti-inflammatory and absorbent properties. For treatment, cabbage leaves are applied to the chest for 30-40 minutes and wrapped in a towel. Repeat the procedure every day for 1-2 months.
Other methods
Other auxiliary methods are widely used to treat breast tumors:
- Doctors definitely recommend restoring immunity with a course of vitamins:
- Alphabet for women is prescribed 1 tablet 3 times a day for 20 days. The drug effectively replenishes the required level of vitamins in the body, helping to restore immunity. The price of the drug is 400 rubles.
- Complement for women includes vitamins and microelements that help restore vitamin levels and promote the production of the required level of hormones. Take the drug 1 tablet 1 time per day for 30 days. Cost 300 rub.
- Aevit is used 1-2 tablets per day for 1-2 months. The cost of the medicine is 150 rubles. The drug contains vitamins and microelements necessary for women's health.
- Taking sedatives helps eliminate stress in the body and reduce the risks of progressive development of tumors in the mammary glands.
- Valerian is prescribed 1 tablet 3 times a day for 20 days. This drug is considered the simplest and most effective way to suppress stress, which has no contraindications. The cost of the drug is 50 rubles.
- Novopassit is prescribed 1-2 tablets 2-3 times a day for 14-21 days. Already on the 2nd day of taking the drug, nervous stress goes away, the patient’s mood returns to normal. After completing the course of treatment, the drug can be taken again after a break. The cost of packaging is 230 rubles.
- Taking diuretics helps reduce swelling, remove excess moisture from the female body and reduce inflammation.
- Furosemide is taken 1 tablet 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days, depending on the patient’s health condition. The drug actively removes excess fluid, restoring vascular tone and lowering blood pressure. The cost of the drug is 40 rubles.
- Amiloride is taken 1 tablet 2 times a day for 5-7 days. The medicine effectively fights edema, helping to normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Precancerous changes in the breast
Truly benign breast tumors, as a rule, do not become malignant. Some are associated with an increased risk of cancer. Precancer is changes in breast tissue that contribute to the occurrence of malignant neoplasms. If the tumor is determined to be benign, it is either removed or left alone. But if the lump in the breast is a precancerous condition, then it must be removed.
Intraductal (intraductal) papilloma of the breast
This is a small growth inside the milk duct. There are single and multiple lesions. In the case of several growths, papillomatosis is diagnosed. There are central intraductal papillomas (located in the area of the nipple and areola) and peripheral (located remotely from the areola). The most common manifestation of intraductal papilloma is bloody or clear discharge from the nipple.
In a small percentage of cases, intraductal papillomas are diagnosed, in which areas of atypical hyperplasia are present (see below). This pathology is usually determined not by a clinician or imaging specialist, but by a cytologist or pathologist.
Radial scar
A radial breast scar is a specific growth of connective tissue that can be benign, precancerous or malignant. There are usually no symptoms. Most often, pathology is detected during a biopsy. On a mammogram, the radial scar has a star-shaped configuration. A benign radial scar should be checked regularly (ultrasound, mammography). Another option is surgical removal.
Atypical breast hyperplasia
Atypical hyperplasia is considered a precancerous condition. In other words, these tumors are not cancer, but they can become cancerous, so they must be treated before their characteristics change. Modern approaches to the management of patients with this pathology are as follows:
- detection of ductal atypical hyperplasia after biopsy requires surgical excision (cancer detection rate 15–30% or more);
- For atypical lobular hyperplasia, surgical excision is not necessary, especially if it is an incidental finding. The probability of cancer verification in this case is 0–6%;
- in patients with atypical hyperplasia, preventive treatment with antiestrogens or aromatase inhibitors . This can reduce the risk of breast cancer by 50%.
Pre-invasive cancer (“cancer in situ”, LCIS and DCIS)
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a relatively common disease, is a malignant tumor. By definition, DCIS is not considered an invasive cancer (it is a pre-invasive cancer, intraepithelial cancer) because the malignant cells have not yet spread beyond the basement membrane (the cells are still inside the duct, there is no invasion into surrounding tissues). Thanks to mammography, the detection of these malignant breast lumps is rapidly increasing, especially due to non-palpable forms.
Carcinoma in situ (carcinoma in situ, CIS, lat. carcinoma in situ - cancer in place), or stage 0 cancer - a malignant tumor in the initial stages of development. Invasive carcinoma is defined as breast cancer from stages I to IV - a cluster of histologically altered cells are detected in the underlying tissue.
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is not a preinvasive disease (precancerous, in other words, it does not develop into invasive cancer), but LCIS is an indicator of an increased risk of later developing invasive cancer. The risk of detecting invasive carcinoma increases in patients whose close relatives had breast cancer (i.e., carriers of the BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 genes), especially for women under 40 years of age.
Phylloid fibroadenoma
Phylloid (leaf-shaped) tumors of the mammary glands are rare neoplasms that develop from connective tissue. “Phylloid lumps” of the breast can be either malignant or benign. Therefore, for all leaf-shaped breast tumors, one approach is surgery.
The substrate for the formation of most malignant breast tumors is the epithelial cells that line the ducts and alveoli of the mammary gland. As for phyllodes tumors, they are formed from mesenchymal cells (connective tissue cells), so these tumors are classified as sarcomas.
Find out more: Sarcomas are malignant connective tissue tumors
Possible complications
Any tumors in the female breast must be treated immediately after detection.
It is important to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions to avoid possible complications, which include:
- transformation of the tumor into a malignant one with the further appearance of metastases in the lungs and lymphatic system;
- inflammation in the tissues of the sternum, which can cause an increase in temperature;
- severe growth of the tumor in the tissues, which requires immediate surgical removal of the tumor, as well as the mammary glands;
- the appearance of constant severe chest pain.
A tumor in the sternum, even after diagnosis in women, requires complex and complex treatment. Using only traditional methods of treatment cannot guarantee complete recovery. In the later stages, treatment without surgery does not always allow you to completely get rid of a benign tumor in the breast.
However, with timely detection of early tumors, competent and comprehensive treatment today allows women to fully recover in the fastest possible time and maintain health for many years.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
A few words from OncoInfo
Lumps in the mammary glands are quite common. It is important that you check your breasts regularly, constantly monitor their condition and make sure that no changes have occurred to them. If a lump is detected in the chest, there is no need to panic; most likely, this is a change of a benign nature. Only 5 - 6% of breast lumps are malignant tumors, the rest are benign.
However, you should not ignore the finding - you should consult a doctor. The easiest way is to make an appointment with a family doctor, who will refer you to the right specialist. Also in the clinics there are oncologists who understand all cancer diseases and will recommend the necessary examinations.
List of sources used:
- Cohen MA, Newell MS. Radial Scars of the Breast Encountered at Core Biopsy: Review of Histologic, Imaging, and Management Considerations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017
- Jha A, Agrawal V, Tanveer N, Khullar R. Metaplastic breast carcinoma presenting as benign breast lump. J Cancer Res Ther. 2017
- An important differential diagnosis in postmenopausal patients presenting with a rapidly growing breast cyst. Management and literature review. Breast Dis. 2018
4.Prevention of breast diseases
There are a number of simple rules that, if followed, will help maintain breast health and promptly identify possible problems:
- Women over 40 years of age should have an annual mammogram.
- Women at risk for breast disease should have screening mammography, starting at a younger age, at least once a year. Additionally, it is recommended to do an ultrasound of the mammary glands. In particularly high-risk cases, such as women who have a greater than 20% risk of developing breast cancer, an annual breast MRI may be required. Your doctor will help you decide on a set of specific diagnostic methods after analyzing all the information about your health.
- During an annual preventive examination of the body, women over 20 years of age should visit a mammologist who will examine the mammary glands.