Rubella is a viral disease caused by tagovirus (a family of viruses with single-stranded, non-segmented infectious RNA), which primarily affects children of preschool or primary school age, adolescents and young people aged 20 to 30 years.
Characteristic symptoms are a maculopapular rash throughout the body, a short-term increase in body temperature to subfebrile (38°C) or febrile levels (39°C), generalized lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes).
In childhood, the disease is mild, often not accompanied by a febrile syndrome, and if medical recommendations and the prescribed treatment regimen are followed, it is cured in 10-14 days. In adults, rubella is more severe, with severe symptoms, and there is a possibility of bacterial infection and the development of severe complications. Infection with the rubella virus is extremely dangerous during pregnancy, because transplacental infection of the fetus is fraught with serious malformations.
What signs are characteristic of the onset of rubella in adults?
The incubation period from the entry of the virus to the appearance of the first symptoms of infection lasts on average about three weeks, but can be 10 days and four weeks. The first signs of rubella in adults are quite pronounced: increased body temperature and catarrhal symptoms, like a cold.
In adults weakened by chronic diseases or with reduced immunity, the temperature may be high, muscles ache and a headache. Most adults have a sore and sore throat, watery eyes, and strong irritation from bright light.
The difference from a cold is an enlargement of the lymph nodes, mainly on the back of the head and back of the neck; regardless of treatment, this symptom of rubella lingers for almost 3 weeks, while the entire catarrhal period lasts no more than three days.
A specialist with extensive clinical experience needs modern equipment and the ability to perform complex tests; only in such conditions can an accurate diagnosis be made. All this is available at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, you can verify this personally, we work seven days a week and seven days a week. Make an appointment by phone: +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Mechanism of disease development
After the virus enters the body, the disease goes through several stages of development. Initially, the infection affects the tissue cells of the nasopharynx and larynx. After this, it moves further and moves to the cervical and mandibular lymph nodes, where it begins to multiply intensively. After 1 week after the virus enters, it spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body.
Within a week after this, red spots appear on the skin. They indicate the appearance of protective bodies in the body. In the future, their number will only increase, which will help overcome the virus. The patient recovers completely in the next 2-3 weeks. The period depends on individual characteristics.
What symptoms appear later?
A characteristic symptom of rubella is a rash, which may appear after the end of catarrhal symptoms, or may accompany them, appearing literally on the first day. This sign is called “exanthema” - red-pink spots that do not rise above the rest of the skin, often merging into fields. Before the rash, itching of the skin may bother you, but it is not necessary. And it is also not necessary that skin symptoms begin on the face and move down to the torso. There are no spots on the soles and palms, but on the back and buttocks there is solid redness, hence the “rubella”. They can even be in the mouth. The rash covers the skin very quickly, in just a day, lingering for four days, and disappearing without a trace.
During the period of exanthema, the temperature may return to normal, but symptoms of intoxication, pain in muscles and joints, abnormal stool, and discomfort in the abdomen are possible. Some people have muscle pain, others have dyspepsia, the combination and manifestations are varied and unsystematic.
If the symptoms described above occur, you must immediately contact a specialist who is seeing you at the Medicine 24/7 clinic. Early initiation of therapy will avoid irreparable consequences.
Folk remedies
Measles rubella in adults is a serious test for the body, with dangerous possible consequences. At the first signs of it, you should consult a specialist, and simple folk recipes will help alleviate severe symptoms.
- An infusion of nettle, rose hips and dandelion root with honey has immunomodulatory properties and will help strengthen your defenses in the fight against complications.
- An herbal mixture, including clover and yarrow flowers, string, dandelion roots and birch buds, in the form of an infusion, will relieve itching, have a calming effect and help in the fight against the virus.
- A decoction of coltsfoot and linden blossom is an excellent anti-inflammatory agent.
- The infusion of lingonberries and St. John's wort will enrich the body with many vitamins and nutrients. It also has anti-inflammatory and calming, antidepressant effects.
- Tea made from rose hips with the addition of currants or lingonberries will perfectly strengthen the body.
Immunity to the disease after an illness, unfortunately, is not always lifelong. Therefore, in adults, symptoms of the disease have become much more common. Let us note once again that older people and pregnant women need to be especially careful. Rubella is extremely dangerous for them, and the symptoms in adults of this disease require high-quality and timely treatment.
What manifestations of rubella occur in pregnant women?
Pregnant women do not have any special symptoms of rubella, and they require treatment exactly as much as it helps all other adults. It can also occur easily and even unnoticed, but the virus penetrates through the general bloodstream into the pregnant uterus, where it damages the inner lining of the blood vessels, disrupting the blood supply to the fetus. The virus inserts itself into the DNA and changes the division of fetal cells, as a result of which it develops with defects. The greatest damage is caused to organs and systems developing during viremia, especially in the first weeks of pregnancy. The probability of congenital pathology is close to 100%.
Symptoms and signs
After entering the human body, the rubella virus goes into short-term hibernation. It begins to actively attack the immune system in the first days after the rash appears. In adults, the first symptoms resemble a mild cold.
During the incubation period, the rubella virus penetrates the mucous membranes of the body and attaches to their surface. Soon after this, it also settles in the submucosal tissues. The virus then quickly spreads through the lymphatic system. There is a significant increase in the cervical lymph nodes; when they are palpated, the patient experiences pain.
From this moment, the disease enters a prodromal period, the duration of which ranges from several hours to two days. The incubation period ends with the appearance of rashes.
The characteristic rash is the first and key sign of rubella. It first appears on the skin of the face and behind the ears. Subsequently, the rashes spread to the scalp, after which they affect the entire surface of the body. Elements of the rash may also occur in a different sequence.
The rashes have a round or oval shape. Their color varies from pink to red. The size of each speck is from 2 to 3 millimeters. The rash does not rise above the skin and looks more like stains from spilled paint. Upon manual examination, the rash appears smooth to the touch.
In some cases, rubella is accompanied by a confluent rash. In this case, solid red fields appear on the body. Because of this symptom, the disease can be difficult to distinguish from scarlet fever or measles, which can subsequently lead to a false diagnosis.
But there is a visible difference: with confluent rashes, the patient’s face and body look the same as with measles, while the limbs are covered with a rash that is similar to scarlet fever. It is important to know that the rash with rubella is slightly larger in diameter than with scarlet fever, and slightly smaller than with measles.
In adults, rashes are more pronounced than in children. They completely cover the body, with the spots being as close to each other as possible. Often they combine into one large spot. Entire erythematous areas may appear on the skin of the back and buttocks.
In some patients, rubella passes without a rash, with weak or moderate manifestations of intoxication and catarrhal syndromes (atypical course). According to some data, rubella without a rash occurs in 30-50% of patients, according to others, this is a very rare form of the disease, and more often such a diagnosis is the result of an insufficiently thorough examination of the patient.
The course of rubella in children and adults, including pregnant women, is not significantly different. Asymptomatic forms of rubella are recorded in adults more often than in children. The condition of children changes a day before the rash appears. They are capricious a lot, get tired quickly, and may complain of discomfort and general malaise.
In children, rubella can occur in completely different ways:
- with the presence of rash and fever;
- exclusively with a rash;
- with the simultaneous presence of rash, fever and catarrhal symptoms.
In childhood, severe forms of rubella and moderate rubella are diagnosed 10 times less often than in adult patients.
One of the first symptoms of the virus is damage to the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. In combination with the rash or long before it, enanthema appears on the mucous membrane - a dermatous change in the form of pale pink spots. This phenomenon is also called Forxheimer's spots. In children, this symptom is usually mild.
With rubella, the patient is accompanied for some time by an elevated body temperature (no more than 38 degrees Celsius). It indicates two things at once: the inflammatory process in the body and the fight of the immune system against infection. There is no need to artificially lower the temperature if it does not rise above 38.5 degrees.
Rubella is invariably accompanied by a deterioration in general health. The patient is concerned about the standard manifestations of an infectious disease:
- malaise;
- headache;
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- body aches.
In some cases, changes appear in the blood test - slight leukopenia and lymphocytosis may occur.
Rubella can also manifest itself in an atypical (erased) form. The patient is not bothered by the rash or other manifestations of intoxication. The only symptoms are a sore throat and fever. Due to its uncharacteristic symptoms, the erased form of rubella is often confused with a sore throat or acute respiratory infection. In this case, the disease can only be detected using laboratory tests.
Despite the absence of a rash, a patient with atypical rubella still spreads the virus. This is the most common cause of epidemics and outbreaks of infection in groups.
Rubella in pregnant women: symptoms of congenital rubella
Rubella is especially dangerous for pregnant women. It often leads to catastrophic events:
- frozen pregnancy;
- miscarriages;
- stillbirth;
- formation of fetal development pathologies.
The virus most threatens a pregnant woman and child in the first trimester of pregnancy. It enters the fetus through the placenta. After this, it gradually affects all tissues and organs that are just beginning to form, which leads to their improper development.
The degree of damage to the fetus depends on the form in which the disease occurs. Often a woman can only be bothered by catarrhal manifestations: runny nose, sneezing, lacrimation. But the fetus may suffer much more at this time. Therefore, any symptoms during pregnancy, even the most minor ones, are a reason to consult a doctor and get the necessary tests.
The shorter the pregnancy, the greater the likelihood of serious complications. For example, at 3-4 weeks it is 58-62%, and at 14-15 it is already 8%. The nervous system of the fetus most often suffers: hearing, vision, conditioned reflexes. Congenital heart defects, underdevelopment and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract often occur.
At 9-12 weeks from the moment of conception, rubella can lead to the most terrible consequences. As a rule, during this period it entails miscarriage or intrauterine fetal death. Even if the pregnancy can be maintained, the possibility of its normal course in the future is almost excluded.
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the baby’s organs are already fully formed, therefore, the rubella virus does not pose such a serious danger to his life and health.
Depending on which organs and systems of the fetus were affected by rubella viruses, congenital rubella syndrome can clinically manifest itself as disorders from:
- hearing organs - complete or partial, uni- or bilateral deafness, and deafness may not appear immediately, but several years after birth;
- organs of vision - one- or two-sided cataracts, microphthalmia, glaucoma, chorioretinitis, pigmentary retinopathy;
- heart - pulmonary artery stenosis, aortic valve defects, atrial or ventricular septal defect, ductus arteriosus disease;
- musculoskeletal system - open anterior source, osteoporosis of tubular bones, joint diseases;
- nervous system - microcephaly, meningoencephalitis, impaired consciousness, diseases of the language apparatus and psychomotor reactions, mental retardation, convulsive syndrome;
- endocrine system - diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, growth hormone deficiency;
- genitourinary system - cryptorchidism, hydrocele, cereal buds, prostate diseases;
- gastrointestinal tract and abdominal organs - pyloric stenosis, hepatitis, hepatosplenomegaly.
In addition to the listed disorders, characteristic signs of congenital rubella syndrome are low birth weight of the child, thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia, interstitial pneumonia, inguinal hernia, and various dermatoglyphics anomalies.
Visual impairment manifests itself in different ways. With cataracts, clouding of the crystal is observed (in one or two eyes). The eyeball may increase or decrease in size. In general, vision diseases are recorded in 85% of cases.
Heart or arterial defects are diagnosed in 98% of newborns with “minor” rubella syndrome. The remaining 22% are hearing pathologies (most often complete or partial deafness). It is usually accompanied by disorders of the vestibular apparatus.
More serious damage to organs and systems is called “major” rubella syndrome. Children often experience dropsy of the brain - hydrocephalus. The main symptom is a significant enlargement of the skull, which is caused by the accumulation of fluid inside it. Sometimes the opposite disease can develop - microcephaly, which is characterized by a decrease in the volume of the brain and skull.
In the presence of such congenital pathologies, doctors' prognoses are disappointing. Infants are often diagnosed with severe mental disorders, and in the future - developmental delays. The congenital form of rubella also leads to disorders of the musculoskeletal system, convulsions, and paralysis.
If a woman has had rubella in late pregnancy, the likelihood of visible disorders in the child is significantly reduced, but is not completely eliminated. Instead, the infection may become chronic. In this case, the pathology is difficult to detect at birth - it appears later and can periodically worsen.
Features of rubella symptoms in adults
All infections that must be overcome in childhood are more severe in adults.
- Symptoms during the catarrhal period are more pronounced than in children.
- The temperature is higher and the signs of intoxication are more intense.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in adults are less common and develop more slowly.
- The duration of the catarrhal period is longer; children usually cope within a day.
- The rash is more abundant and does not disappear in children.
However, for every adult patient with severe manifestations of rubella, there are two patients in whom all symptoms went unnoticed, and the disease was discovered only through a special diagnosis of antibody levels.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic has everything you need for effective treatment and effective recovery; all programs are individualized and based on world standards of diagnosis and treatment. Specialists from the Center for Infectious Diseases are ready to help, call
The World Health Organization is confident that rubella will not last forever for humanity, so at the end of the last century it set the task of reducing the incidence to a minimum value, and the congenital infection should not affect more than one baby out of 100 thousand newborns.
Diet and nutrition
If the disease is severe and has complications, the patient is prescribed diet No. 13, which is effectively used for acute infections, pneumonia, and during the recovery period after major operations. Nutrition is aimed at reducing intoxication of the body, removing microbial toxins, and restoring defenses.
Food should be gentle both thermally, mechanically, and chemically. It is prepared only by steaming or boiling. It is prohibited to stew food, let alone bake or fry it.
The temperature of cold dishes should not be lower than 15 degrees, and hot ones should not exceed 65. Spicy or fatty foods and spices are excluded. The amount of salt consumed is also reduced. To quickly remove toxins, it is recommended to consume liquid in large quantities - up to two and a half liters per day. Food should have a liquid or puree consistency.
How can you become infected with rubella?
How rubella manifests itself is clear from the name - red skin from a profuse rash, but there are other symptoms. Rubella is caused by a tiny virus, similar to a soccer ball, with RNA twisted inside it. It can fly around a room alive for several hours; it does not like ultraviolet radiation from sunlight or heat, but when alive it can withstand frost.
The pathogen is evil, but not as aggressive as measles and chickenpox, which are practically transmitted without contact. The cause of rubella is fairly close contact with a patient with an obvious or hidden infection; transmission occurs when a microscopic drop of saliva infected with the pathogen is inhaled or gets on the skin.
It is assumed that in childhood the infection can be caused by licking a sick child's toy, but in adults there is no such contact method of transmission. It’s strange, because adults can kiss, however, for serious adults, only one cause of the disease is indicated - airborne infection with an aerosol of saliva.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic uses high-precision equipment to conduct round-the-clock examinations, which allows you to quickly make a correct diagnosis and begin treatment without delay, and this is possible on holidays and weekends.
We will call you back
leave your phone number
Diagnostics
Only a specialist can make a diagnosis.
This is usually done based on the following diagnostic measures:
- Conducting a patient interview and visual examination are the primary measures to identify the characteristic signs of rubella and establish the frequency of the onset of symptoms;
- A neurological examination is necessary to determine muscle tone and sensitivity of the skin;
- Taking a blood test , with rubella there is a decrease in the concentration of white immune cells. Usually several tests are carried out, between which there is a break of 2-3 days, which allows you to study the dynamics and determine the form of the disease;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is required in some cases with severe disease; the procedure is aimed at studying the state of the brain structure and identifying possible complications in the presence of neurological symptoms.
A basic set of diagnostic measures is needed to make an accurate diagnosis and exclude diseases with a similar clinical picture, primarily these include scarlet fever, measles and enteroviral infections; Sometimes rubella is confused with an acute allergic reaction of the body.
How does the infection enter the body?
The reason for the introduction of an infectious agent is its entry into an environment favorable to it, where the program laid down by nature forces it to multiply. Once on the moist and warm mucous membrane of the nose or mouth, tiny pores are formed in the virus shell, through which the RNA is introduced into human cells suitable for further life. The particle has a special predilection for epithelium and lymphatic tissue.
Having entered the blood through an epithelial cell, the pathogen migrates to the lymph nodes, where it temporarily takes root to reproduce and accumulate its own army, therefore one of the first manifestations of rubella is enlarged lymph nodes. The cause of the appearance of the red rash, which gives the name of the disease and the most striking symptom, is the travel of multiplied viral particles throughout the body with accumulation in the skin. Having settled in the skin, the pathogen gradually dies.
The infectious disease specialist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, having a broad clinical horizon, has at his disposal the most modern diagnostic equipment with the ability to perform complex tissue tests, which affects the patient’s favorable prognosis.
Does the rash itch when you have rubella?
Regarding the main question – itching during illness, doctors give a clear answer: “Skin covered with a rash does not itch.” Of course, there have been cases where itching was still observed, but this is only an exception to the rule. This phenomenon can be explained by subjective sensations and, of course, individual susceptibility. Another answer to the question whether the skin itches with rubella is the addition of a new disease or an incorrect diagnosis. The disease can be confused with the following pathologies:
- chicken pox;
- deprived;
- dermatitis;
- roseola;
- scabies.
When is a patient most dangerous to others?
The release of an infectious agent into the external environment begins when neither the carrier himself nor those around him even suspect infection. A seemingly healthy person, but already filled with pathogens inside, throws out infected saliva a week before the rash develops.
And after the rash appears, when everyone is already shying away from it as a possible cause of future health troubles, it also releases infectious agents, for a total of at least two weeks the patient is dangerous for healthy and unvaccinated people. Children born with congenital rubella can cause infection in adults from a year to a year and a half, during which time the infectious agent lives in their saliva and secretions.
Degree of susceptibility to the disease
Now we know whether rubella is transmitted through third parties. Now let's talk about how susceptible people are to this disease and how long the patient remains infectious after infection.
Unfortunately, rubella is a highly contagious disease. Patients are able to shed the virus all the time before the onset of the rash and for at least 4 days after its onset. Infants with congenital rubella may be contagious for several months. But immunity after an illness lasts for life.
Children born to women with immunity to the disease are usually protected from it for up to 7-9 months. But this is only provided that the child is not bottle-fed. In order to understand how protected your baby will be in utero and after birth, you can conduct a special test for the presence of IgG antibodies. Blood is taken from women who are already pregnant or preparing to conceive. Based on the results, a risk group is identified, that is, seronegative women.
Therefore, it is advisable for anyone planning a pregnancy to take this test. If immunity is low, vaccination is necessary. Vaccination during pregnancy is prohibited. Therefore, if you have any doubts about the strength of your immunity, eliminate them before conception.
Why is rubella so scary for pregnant women?
Only a previous infection provides permanent immunity. Rubella is highly contagious, but unless you had it in childhood, vaccinations do not promise 100% protection. The reason for this insecurity is that immunization is not always carried out as it should: the intervals between vaccinations increase, an insufficient amount of antibodies is formed, that is, there are a lot of different reasons.
When examined, every third young woman does not have antibodies to the virus, and the virus itself “loves” young and pregnant women very much. In the first trimester of pregnancy, exposure to an infectious agent causes the formation of genetic defects in the fetus and disruption of its blood supply in almost 100% of cases, so rubella during this period is an objective reason for artificial termination of pregnancy.
During a comprehensive examination, specialists at the Medicine 24/7 clinic identify risk factors and objective causes that can lead to the development of an infectious disease, which allows them to begin preventive measures. If you get sick, don’t rely on chance, seek help from a specialist at the Center for Infectious Diseases, call by phone.
Diagnosis of rubella in most cases occurs without special tests; clinical symptoms are sufficient, although these symptoms are very similar to infectious diseases caused by other pathogens. But it is impossible to make a diagnosis with a regular blood test; in many processes there is a decrease in leukocytes and an increase in ESR.
What infections does rubella resemble?
When examining a patient suspected of rubella symptoms, differential diagnosis is carried out:
- with measles, but with almost similar manifestations, with rubella everything goes easier and faster, there are no such distinctive measles signs as cough in the first days of the disease and Filatov-Koplik spots on the mucous membrane of the cheeks;
- with scarlet fever, in which the damage to the tonsils is much more pronounced - sore throat and the condition is much more severe;
- with infectious mononucleosis, in which the symptoms are more pronounced and all manifestations last longer, in addition, specific changes are found in the blood, which are not present with rubella;
- There are very few differences with enterovirus infections, and in this case everything is decided by a special diagnosis of the infectious pathogen.
Infectious diseases specialists at the Medicine 24/7 clinic have undergone specialization and have extensive clinical experience, which allows them to make the correct diagnosis in a short time and at minimal cost.
Vaccination against measles
The vaccine against rubella can be simultaneously administered against measles and mumps at the age of 1-1.5 years and 6 years. This procedure is free and is carried out in medical institutions at the place of registration. But sometimes parents, fearing fictitious side effects, do not give permission for it, thereby endangering the health of their child.
In adult women, the vaccine is recommended to be used at the age of 22-30 years, since at this age the desire to give birth to a child increases. Vaccination can be carried out for men up to 40 years of age, which helps reduce the further spread of infection and also protects women and children with whom they come into contact. The vaccine preserves human immunity for 10 years.
There is no special preparation before the procedure, but experts recommend following some recommendations:
- If the body is prone to an allergic reaction, it is necessary to take an antihistamine in accordance with the age-specific dosage 2 days before vaccination.
- People with weakened immune systems should take general strengthening medications 7 days before the procedure, having agreed with their doctor.
- It is not recommended to have a large breakfast on the day of vaccination.
- After the procedure, you should not immediately leave the clinic. The patient should remain under the supervision of medical staff for half an hour, which will help provide timely treatment in case of allergy development.
- During the week after vaccination, you should beware of new foods, and you should also limit your intake of fatty foods.
- After the procedure, it is recommended to drink more fluids, as it helps remove toxins from the body.
- After vaccination, you should not drink alcohol for 1 week, as this prevents the development of stable immunity to the pathogen.
Acceptable body reaction to vaccination, which is not a cause for concern:
- slight redness, swelling and pain at the site of vaccine administration;
- temperature within 38-39 degrees for 2-3 days;
- the presence of a runny nose, sore throat, otitis media and pain in the eyes;
- a rash on the body resembling rubella and measles spots, which goes away on its own within 2-3 days.
Who needs a special diagnosis for rubella?
The danger is not in the disease itself, it is quite mild, but in pregnant women it leads to miscarriages, forms deformities in the fetus, and is transmitted through the general bloodstream to the unborn child with the formation of congenital rubella syndrome.
All young women need diagnostic screening, which detects the presence of antibodies to the rubella virus in the blood. Diagnosis is possible in several ways. If antibodies are detected, it means there is immunity. If antibodies are not found, then preventive vaccination is indicated.
The most modern diagnostic equipment of the Medicine 24/7 clinic allows you to conduct an in-depth examination in a short time and find out the cause of the disease, and, based on error-free information, create an individual therapeutic strategy.
What diagnostic methods are used in pregnant women?
After contact with a patient, a pregnant woman must be examined, determining the concentration of antiviral immunoglobulins M and G in the blood. This is done in the first 10 days; if immunoglobulin G (IgG) is found, then a conclusion is drawn about the presence of immunity and the woman is left alone.
In the absence of immunoglobulins, re-diagnosis is carried out after 10 days; if immunoglobulin M (IgM) is found, it is considered that the woman is already sick and the issue of terminating the pregnancy must be decided. Even in the second half of pregnancy, when the fetus is fully developed and may not develop defects, the likelihood of congenital rubella is high.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Prevention of rubella in adults
Treatment for infection is nonspecific, so preventing infection is the best defense. Rubella is always bad for a pregnant woman, so it is necessary to take care of developing immunity in advance.
With vaccination, which uses a weakened virus, a mild form of the disease occurs, so there may be unpleasant reactions. Every fourth woman in the second week develops pain in small joints - arthralgia, there may be a slight enlargement of the lymph nodes and a rash. Formally, vaccination is contraindicated during pregnancy, but if the woman did not know about her status, then abortion after vaccination is far from necessary.
Transmission routes
So, how is rubella transmitted in children? We list the main variants of transmission of the virus:
- Airborne method, the most common and well-known. Everyone has probably heard about him.
- Through direct contact, that is, handshakes or objects that a sick person passed on to a healthy person.
- Nasopharyngeal secretions can also be excellent vehicles for the virus.
The average incubation period (the time when the disease does not manifest itself) lasts on average from 14 to 17 days. In some cases, this period may be extended to 21 days.
What is emergency prevention, in what cases is it needed?
The infection is not easily tolerated, so children and pregnant women need emergency immune protection, and they are given anti-rubella immunoglobulin.
If a person knows for sure that he has been vaccinated against rubella, he can undergo diagnostics and find out the level of protective antibodies in the blood. All other adults, if they have not had an infection or do not remember whether there was or was not an illness and vaccination, are vaccinated in the first three days. Before vaccination, it would also be possible to carry out diagnostics in order to know for sure whether it is advisable to do it, but there is no time for this.
Diagnostics consists of a professional analysis of the entire set of information, based on world standards and rich clinical experience. Doctors at the Center for Infectious Diseases work only in this manner. Get help from an infectious disease specialist by calling.
Until the end of the 19th century, even doctors did not really distinguish between rubella, measles and scarlet fever, which is not surprising given the same symptoms, but very different degrees of severity. Understanding improved the accumulation of knowledge and its systematization, while pathogens could be seen almost a century after the division of infections.
How are measles and whooping cough transmitted?
Is rubella transmitted? Of course yes. But what about other infectious diseases like it? Let's talk a little about measles and whooping cough. These diseases are also very dangerous.
The mechanism of infection for whooping cough and measles is exactly the same as for rubella. That is, the virus is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. But it can also spread through things that belonged to an infected person. These pathologies have one more thing in common - they mainly affect children, and they have a fairly long incubation period, during which the infected person spreads the infection. Therefore, if you do not want to become infected, refrain from contact with them. This primarily applies to pregnant women. All infectious diseases are extremely dangerous for the development of the fetus and can cause irreparable harm.
Measles, rubella, and whooping cough are transmitted by touch, as well as by airborne droplets. In general, avoid visiting areas where small children frequent. Then the risk of infection will be minimized, and you will not have to undergo treatment for this unpleasant and dangerous disease. Be especially careful of dangerous places while you are expecting your baby.
How common is rubella in adults?
Until the present century, rubella was considered a childhood disease; it was tolerated in kindergarten, acquiring lasting immunity for life. In the last decade of the existence of the USSR, children got sick much less often, because pediatricians did not ask their mother “to vaccinate or not,” but sent them to the vaccination office. In the 90s, in every thousand there were already two adult patients and cases of congenital infection began to be identified. Today, vaccination against the rubella virus is mandatory for girls from 18 to 25 years of age, so the disease affects men.
If you do not know what is happening to your body and what diseases are possible, undergo an in-depth examination. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, the latest equipment is at your service, any tests are carried out and, most importantly, a team of highly professional specialists will give the examination results a correct and error-free interpretation.
Complications
Before the advent of the vaccine, most patients suffered from rubella in childhood, after which the body developed lifelong immunity to the virus (you only get the disease once). Since the introduction of mass vaccination, the incidence of rubella in children has decreased, and the incidence of rubella in adults has increased because the vaccine does not provide lifelong protection. If you suffer from the disease after the age of 20, failure to follow medical recommendations and self-medication can lead to the following complications:
- meningoencephalitis, encephalitis and encephalomyelitis;
- arthritis;
- pneumonia;
- otitis;
- convulsions
Articles on the topic
- Normal blood pressure in adults - influencing factors and how to measure correctly at home
- Guttate psoriasis - signs and stages of the disease, treatment with medications and folk remedies
- Endoscopy of the stomach - in what cases and to whom it is prescribed, types and techniques of examination, contraindications
During pregnancy
Infection during the first trimester of a woman's pregnancy is a medical indication for abortion , since if transplacental infection of the fetus occurs, there is a high probability of serious developmental defects (central and peripheral nervous system, hearing and hematopoietic organs, other internal organs and tissues) that cannot be corrected. There is a danger of intrauterine death of the child. In the later stages, due to infection, it is necessary to take immunoglobulins and continuous monitoring of the condition of the mother and fetus.
Due to the high risks of developing severe consequences in the absence of a history of rubella exposure in childhood, it is recommended that both partners be vaccinated against the disease at the stage of pregnancy planning. A person infected with the disease in utero is an active carrier of the virus and is epidemiologically dangerous to others.
Is it true that the disease is mild?
For adults, infection is not always easy; for every patient, there are two people who have had an asymptomatic infection or a very mild one, which was mistaken for a common cold. For an organism burdened with chronic diseases, in principle, any infection is dangerous, and the rubella virus also causes intense clinical manifestations that can hardly be called mild. There is a high temperature, a severe rash, and prolonged enlargement of the lymph nodes, as well as completely nonspecific pain in the muscles and joints.
Incubation period
The most favorable conditions for the development of the disease are low temperatures and high humidity levels. Therefore, infection is most often diagnosed in autumn and winter. The incubation period for rubella is 11-25 days, but in some cases the disease develops within 16-20 days.
At this time, the person does not even suspect that he himself is a virus carrier and therefore does not carry out any therapeutic measures.
The disease is characterized by a period of rash, the duration of which is 3-4 days. The peculiarity of rubella is that a person who has had the infection once cannot become infected again due to lifelong, stable immunity.
What complications of rubella can occur during pregnancy?
The disease in a pregnant woman is no different from other adults, but the gestating fetus has poor prospects.
- Miscarriages occur in every third case, every fifth is stillborn, every fourth newborn dies.
- In the first trimester, the infection penetrates the fetus in 8 cases, in the second and third trimesters - in 3-5 out of ten.
- Infection of a 9-12 week fetus guarantees that every third newborn will have malformations; up to 20 weeks, deformities are observed in every tenth.
- Every tenth newborn with developmental anomalies is caused by the rubella virus.
- Congenital infection syndrome is guaranteed 60% when the mother is infected at 3-4 weeks of pregnancy, by 12 weeks the frequency decreases to 15%, by 14 weeks - to 7%.
Rubella - what kind of disease?
Rubella is an infectious disease of viral origin and transmitted from person to person. The risk group primarily includes children aged 2 to 9 years who have not received appropriate vaccinations.
In adults, especially women, the risk of infection increases in their 20s and 30s. Rubella poses the greatest danger to girls in the first 2-3 months of pregnancy, since the disease can provoke irreversible changes in the development of the fetus.
Thanks to the vaccination program, rubella is becoming a less common disease, and the number of infections in developed countries is decreasing every year.
Treatment of rubella in adults
Treatment of uncomplicated rubella is symptomatic - reducing unpleasant symptoms, drugs that kill the virus do not yet exist.
After contact with a sick person, an adult who has not previously been vaccinated and has not had the disease with a high probability of complications will be offered a rubella vaccination. Vaccination at any age is the best prevention of the disease and associated complications, but a woman planning to have children is simply obliged to find out her immunological status by testing for rubella and, in the absence of immunity, undergo immunization.
Many diseases come unexpectedly, and a person is unable to prevent them, but this does not apply to rubella and other “related” infections; they can be stopped with simple vaccinations.
If you value your own health, get tested for immunity against infectious diseases, and specialists will calculate an individual preventive strategy. Contact the Center for Infectious Diseases of the Medicine 24/7 clinic by phone +7 (495) 230-00-01
The material was prepared by an infectious disease specialist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, Doctor of Medical Sciences Margarita Vasilievna Nagibina.
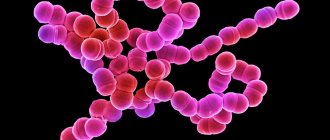
The causative agent of the disease
The disease develops as a result of the penetration of a certain virus containing ribonucleic acid into the body. The pathogen is a member of the Rubivirus genus and belongs to the Togavirus family. Its peculiarity is the ability to glue red blood cells to each other, as well as destroy them with the help of enzyme proteins.
In addition, the virus has the enzyme neuraminidase, which has a negative effect on nerve tissue. The size of the causative agent of the virus is 60-70 nm. On top it is covered with a protein shell with villi, which helps it attach to healthy cells.
The pathogen is unstable to environmental conditions, therefore it is destroyed in the presence of the following factors:
- ultra-violet rays;
- change in acidity level below 6.8 and above 8.0 pH;
- treatment with disinfectants;
- elevated temperature (over 30 degrees);
- interaction with ether or formaldehyde.
The rubella virus is able to withstand freezing down to -60-70 degrees, maintaining viability for 30-40 days, and at room temperature it persists for 8-10 hours. People aged 21-30 years, mainly women, are at risk, in the future the likelihood of infection is significantly reduced.