The body spends energy on digestion, brain activity, heart beats, muscle contraction and other physiological processes. This energy turns into heat, which is released by the body. The physiological mechanism responsible for body temperature is thermoregulation. Heat balance is controlled by a small region in the brain called the hypothalamus. It monitors the body’s energy expenditure: it can increase or decrease heat transfer.
Normal body temperature ranges from 36.5 to 37.5 0C in different parts of the body. During the day, the temperature can fluctuate: at 4–6 am it drops to 35.5–36 0С, in the evening it can rise to 37 0С. This is a daily rhythm, which is caused by different hormonal activity in the evening and morning.
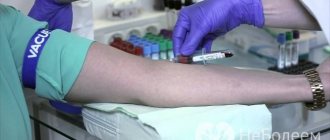
Body temperature is measured in the anus, mouth and armpit. The last option is the most common: when it comes to body temperature, we usually mean measuring the temperature in the armpit. There the average is 36.6 0C.
Stable normal temperature of internal organs and blood maintains the constancy of biochemical reactions, the movement of electrolytes, the viscosity of intracellular fluid and the transport of biological fluids. Temperature also affects the processes of excitation and inhibition in the nervous system, protective reactions of the immune system, the release of hormones and the absorption of nutrients in the digestive tract.
In diseases and pathological conditions, body temperature increases (fever or hyperthermia) or decreases (hypothermia). Based on the dynamics and daily temperature fluctuations, one can suspect the type of infection, the stage of the disease and the degree of its severity.
Myth one: heat kills viruses, so you shouldn’t knock it down, let the body fight
“Temperature is indeed one of the first signs of the body’s fight against a pathogen: a virus or bacteria. At the same time, before you give yourself the opportunity to burn out, you need to evaluate a number of parameters. If the temperature is 38 degrees or lower, and you do not feel unwell and it is not difficult to tolerate, for example, there is no sensation of body aches, this temperature does not need to be brought down,” says the immunologist.
But there are exceptions to all rules. “If a person does not tolerate the temperature well, even with a reading of 37, he feels bad, hard, has weakness, lethargy, body aches, feels terrible, in this case it is necessary to bring down even 37,” says Shulyaeva. The fever itself does not kill the virus, the doctor notes.
Extremely low. At what body temperature can a person die? More details
Local damage caused by exposure to low temperatures
Local damage, or frostbite, can occur during prolonged stay in a cold room or outside in frosty conditions, as well as when the human body is exposed to liquids or gases of extremely low temperatures (for example, liquid nitrogen). Frostbite is divided into the following stages according to the extent of the damage they cause:
- First degree (I). Swelling forms and the skin turns purple. After 5-8 days, frostbite heals without consequences. Increased sensitivity to cold in the area may persist.
- Second degree (II). Bloody blisters form, accompanied by inflammation and swelling. They heal within 10-20 days without the formation of scar tissue.
- Third degree (III). Necrosis (death of tissue) develops, accompanied by blanching of the skin and inflammation at the border of the necrosis area. Necrotic tissue is rejected and scars form.
- Fourth degree (IV). Bone necrosis occurs, dead body parts (fingers, feet) are rejected.
Examination of exposure to extreme temperatures examines the impact of frostbite on overall health, and also examines the factors and circumstances associated with frostbite.
Myth two: the more severe the disease, the higher the body temperature
Temperature readings cannot judge the severity of the disease. “The point of assessing temperature is different: we look at how the body fights the pathogen. At the same time, the struggle can be either active or not very active. As a result, the temperature can be either below 40 or 37. And this does not at all indicate the number of viruses or bacteria, it only speaks about the strength of the body’s immune response,” notes Anna Shulyaeva.
Accordingly, any temperature requires attention and control, and is also a reason to start therapy and consult a doctor.
Prevention
Prevention of P. o. is to prevent the body from losing water and salts. A water-salt regime has been developed for those working at high ambient temperatures. If you lose more than 4-4.5 kg of body weight (over an 8-hour work shift), additional intake of table salt is recommended. Water consumption should be sufficient to quench thirst; The most appropriate is considered to be fractional intake of water in small quantities (see Drinking regime). The population of Central Asia drinks green tea in the summer, which is eliminated from the body more slowly than black tea, being a good thirst quencher. When drinking hot tea, the evaporation of water from the surface of the body is much higher than when drinking cold tea. The best state of water-salt metabolism is achieved by consuming carbohydrate and carbohydrate-protein foods; According to a number of researchers, it contributes to less water consumption and greater retention in the body. In connection with oppression during P. o. for the secretory and motor functions of the stomach and intestines, decoctions of dry and fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as kvass, fruit juice and tomato juice are recommended; in this case, preference is given to easily digestible foods. In areas with a hot climate, it is necessary to take into account the selectivity of appetite - hot, spicy snacks, borscht, cabbage soup from fresh or salted cabbage, okroshka, beetroot soup, fried potatoes, stewed vegetables, compote, and lactic acid products are better eaten. For those working in high temperatures, it is advisable to reduce the caloric content of lunch and increase the caloric content of dinner or breakfast. To prevent overheating and dehydration of the body, those who arrived in the summer in a region with a hot climate from other climatic zones and perform physical work in the open air during the initial period of acclimatization (see) should be under intensive medical care. control (thermometry, weighing).
To protect against the adverse effects of high temperatures, those working outdoors periodically need a short rest (10-15 minutes) in places protected from direct solar radiation, close to the place of work (canopies, awnings, as well as portable houses or vans equipped with fans, air conditioners, shower units). To protect from direct solar radiation, the windows of the premises are equipped with wide cornices and canopies. Workers must be provided with sufficient quantities of drinking water, drinks, as well as air- and vapor-permeable clothing. It is advisable to plan outdoor work for cool morning and evening hours, and reserve the hottest time of the day (from 13 to 16 hours) for rest and work indoors.
For the prevention of P. o. In production areas with high temperatures, spraying water and blowing air is recommended. Rest rooms should be equipped with panel cooling or air conditioning and ventilation systems.
Myth four: when the temperature is high, you need to wrap yourself up and sweat actively
There is an opinion that you need to let yourself sweat so that your temperature readings go down. However, you should not overheat and increase the temperature further; you can wrap yourself up only if your body requires it.
“A rise in temperature is always a sign of the immune system’s response to fight something, be it a virus, bacteria, or some kind of inflammation. It's a question of how the body reacts. If he responds to an increase in temperature with chills and cold, he needs to be warmed up. This means that there is a spasm of peripheral vessels, the arms and legs should be warmed. If there is a fever, then there is no need to wrap the person up even more and let him sweat,” says the immunologist.
So you need to look at the needs of the body, then the fight against the pathogen will be better and more effective.
Measurement to the degree. Why are electronic thermometers not always accurate? More details
Meteopathological syndromes
In recent decades, many studies have been conducted with the participation of people with increased weather sensitivity. This allowed specialists to identify some typical symptoms of dependence on the weather situation. Researchers call them meteorological syndromes or symptom complexes. In different people, the syndromes can appear either individually or in combination with other symptoms.
Today, patients most often experience the following meteopathological symptom complexes:
- rheumatoid (fatigue, general weakness and fatigue, various inflammatory reactions, pain);
- cerebral (irritability, general excitability, headaches, sleep disturbance, respiratory dysfunction);
- vegetative-vascular (blood pressure surges, autonomic disorders);
- cardiorespiratory (cough, increased respiratory rate, increased heart rate);
- dyspeptic (unpleasant sensations in the stomach, intestines and/or under the right ribs, nausea, lack of appetite, stool disturbance);
- immunological (impaired protective reactions of the body, tendency to colds and fungal diseases);
- skin-allergic (skin rashes, itching and other reactions typical of allergies);
- hemorrhagic (bleeding rashes on the skin, bleeding of mucous membranes, rushes of blood to the head, nosebleeds, increased blood supply to the conjunctiva, changes in the blood formula).
Sometimes, if the body’s reactions to certain meteorological factors are very pronounced and are repeated quite often, they speak of the development of a general adaptation-meteotropic syndrome. In this case, the balance of the whole organism is disturbed. Problems arise in the field of metabolism and energy metabolism, enzymatic activity, tissue structure and blood formula change.
Myth five: if your body temperature is elevated, you can’t wash yourself.
The issue of washing during illness, when the temperature rises, when a person sweats, is acute. Giving up hygiene is not particularly pleasant. However, many do not take risks, fearing that they will catch up even more.
“Washing at a temperature is, of course, possible and even necessary. Moreover, with the help of washing, other problems can be solved, for example, if a person is cold, he can warm up, as well as cool down,” says Anna Shulyaeva.
Naturally, doctors emphasize, it is necessary to approach the issue responsibly, do not splash around in the bath for an hour and do not try to adjust the water incorrectly, then the result of washing will be positive.
Infectious diseases
Thus, the main infectious causes may be:
- Viral infections of ARVI and influenza;
- Mononucleosis;
- Meningitis;
- Malaria;
- Gastroenteritis;
- HIV.
Particularly dangerous infections and their causative agents: cholera, plague, yellow fever, anthrax. Respiratory tract infections: rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, tuberculosis, pneumonia. Diphtheria, dysentery.
Infections of the genitourinary system:
- gonorrhea, candidiasis, chlamydia, herpes;
- chicken pox;
- Tetanus.
Urgent medical attention is needed if one or more of the following accompanying symptoms are detected:
- high drowsiness;
- rash;
- headache;
- severe sore throat that makes it difficult to swallow;
- increased salivation;
- chest pain;
- labored breathing;
- frequent vomiting;
- blood in stool;
- abdominal pain;
- confusion and loss of consciousness;
- inflammation or swelling of any part of the body.
Some of these dangerous diseases, in addition to high fever, may be asymptomatic.
Myth six: you shouldn’t bring down the temperature with the help of drugs, it’s better to use traditional methods
There is no point in experimenting and abandoning what was created in an industrial environment. Moreover, there are quite a few different drugs that have proven their effectiveness: ibuprofen, paracetamol. But you should be more careful with rubdowns, notes the immunologist. “Rubbing in the heat can lead to vasospasm; for example, vasospasm of the heart vessels can develop, which is not only unpleasant, but also dangerous. But it may not be possible to recognize and cope with the consequences at home; you will have to call an ambulance. Herbs, decoctions and infusions can also be fraught with an unpredictable situation, for example, an allergy,” says Anna Shulyaeva.
At the same time, she emphasizes that if you really want to try traditional methods on yourself, then you should do this only under the supervision of a doctor.
There are contraindications, you should consult your doctor
How weather affects our health
How weather conditions affect the body depends on its adaptive abilities: some react to them, others don’t notice them at all, and there are also those who can predict the weather based on how they feel. It is believed that people with an unbalanced nervous system - melancholic and choleric people - are especially susceptible to dependence on weather conditions. In sanguine and phlegmatic people, it most often manifests itself either against the background of weakened immunity or with a chronic disease. However, meteosensitivity as a diagnosis is typical specifically for those who already suffer from some kind of illness. As a rule, these are pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, diseases of the nervous system, and rheumatoid arthritis.
What weather factors affect our well-being? The head of the neurology department of the 122nd Clinical Hospital, Professor Alexander Elchaninov, considers the most significant meteorological factors to be: air temperature, humidity, wind speed and barometric (atmospheric) pressure. The human body is also influenced by heliophysical factors - magnetic fields.
Air temperature
It has the most noticeable effect on a person’s well-being in combination with air humidity. The most comfortable is considered to be a combination of temperature 18-20C° and humidity 40-60%. At the same time, fluctuations in air temperature within the range of 1-10°C are considered favorable, 10-15°C are considered unfavorable, and above 15°C are considered very unfavorable. - explains Professor Elchaninov. — Comfortable temperature for sleeping — from 16°C to 18°C.
The oxygen content in the air directly depends on the air temperature. When it gets colder, it becomes saturated with oxygen, and when it gets warmer, on the contrary, it becomes rarefied. As a rule, in hot weather the atmospheric pressure also decreases, and as a result, those suffering from diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems feel unwell.
If, against the background of high pressure, the air temperature drops and is accompanied by cold rains, then it is especially difficult for hypertensive patients, asthmatics, and people with kidney stones and cholelithiasis. Sudden changes in temperature (8-10 °C per day) are dangerous for allergy sufferers and asthmatics.
Extreme temperatures
According to Sergei Boytsov, director of the State Research Center for Preventive Medicine, during abnormal heat people feel best with a normal thermoregulation mechanism, in which the cardiovascular system is actively involved, increasing blood circulation directly under the skin. But if the air temperature exceeds 38 degrees, it no longer helps: the external temperature becomes higher than the internal one, and the risk of thrombosis arises against the background of centralization of blood flow and blood thickening. Therefore, in the heat there is a high risk of stroke. Doctors advise that during abnormal heat, stay indoors as much as possible with air conditioning or at least a fan, and avoid the sun and unnecessary physical activity. Other recommendations depend on the person’s health status.
An anticyclone is an increased atmospheric pressure that brings with it windless, clear weather, without sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
A cyclone is a decrease in atmospheric pressure, which is accompanied by cloudiness, high humidity, precipitation and increased air temperature.
In extremely cold weather, the body can become hypothermic due to increased heat transfer. The combination of low temperature with high humidity and high air speed is especially dangerous. Moreover, due to reflex mechanisms, the feeling of cold arises not only in the area of its influence, but also in parts of the body that seem to be far from it. So, if your feet are frozen, your nose will inevitably freeze, and a feeling of cold will appear in your throat, as a result of which ARVI and diseases of the ENT organs develop. In addition, if you are cold, say, while waiting for public transport, another reflex mechanism is activated, in which spasm of the kidney vessels occurs, circulatory disorders and decreased immunity are also possible. As a rule, extremely low temperatures cause spastic-type reactions. Any procedures and actions that increase blood circulation help to cope with them: gymnastics, hot foot baths, sauna, bathhouse, contrast shower.
Air humidity
At high temperatures, air humidity (saturation of air with water vapor) decreases, and in rainy weather it can reach 80-90%. During the heating season, the air humidity in our apartments drops to 15-20% (for comparison: in the Sahara Desert the humidity is 25%). Often it is the dryness of the home air, and not the increased humidity outside, that becomes the cause of the tendency to colds: the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx dry out, reducing its protective functions, which makes it easy for respiratory viruses to “take root.” To avoid increased dryness in the nasopharynx, allergy sufferers and those who frequently suffer from ENT diseases are recommended to rinse with a solution of slightly salted or still mineral water.
With high humidity, those suffering from diseases of the respiratory tract, joints and kidneys are most at risk of getting sick, especially if the humidity is accompanied by cold weather.
Fluctuations in humidity levels from 5 to 20% are assessed as more or less favorable for the body, and from 20 to 30% as unfavorable.
Wind
The speed of air movement - the wind is perceived by us as comfortable or uncomfortable depending on the humidity and temperature of the air. So, in the thermal comfort zone (17-27C°) with a calm and light wind (1-4 m/s) a person feels good. However, as soon as the temperature rises, he will experience similar sensations if the air movement becomes faster. Conversely, at low temperatures, high wind speed increases the feeling of cold. Both the mountain-valley wind and other wind regimes (breeze, foehn) have a daily periodicity. Day-to-day fluctuations in the wind regime are important: a difference in air speed within 0.7 m/s is favorable, and 8-17 m/s is unfavorable.
Atmosphere pressure
Weather-sensitive people believe that atmospheric pressure plays a major role in their reaction to the weather. This is both true and not true. Because it mainly affects our body in combination with other natural phenomena. It is generally accepted that a meteorological state is observed at an atmospheric pressure of about 1013 mbar, that is, 760 mm Hg. Art., says Professor Alexander Elchaninov.
If, with a decrease in atmospheric pressure, the oxygen content in the atmosphere sharply decreases, humidity and temperature increase, a person’s blood pressure drops and the speed of blood flow decreases, as a result, breathing becomes difficult, heaviness appears in the head, and the functioning of the cardiovascular system is disrupted. When atmospheric pressure drops, hypotensive people feel the worst, which is manifested by severe pastiness (swelling) of tissues, tachycardia, tachypnea (frequent breathing), that is, symptoms characterizing the deepening of hypoxia (oxygen starvation) caused by low atmospheric pressure. For hypertensive patients, such weather improves their well-being: blood pressure decreases, and only with increasing hypoxia do drowsiness, fatigue, shortness of breath, and ischemic heart pain appear, that is, the same symptoms that hypotensive patients immediately experience in such weather. When the temperature decreases with an increase in atmospheric pressure, the oxygen content in the air increases, hypertensive patients feel unwell because their blood pressure rises and the speed of blood flow increases. Hypotonic people live well in such weather, they feel a surge of strength.
Solar Activity
We are the children of the sun; if it were not there, there would be no life. Thanks to the notorious solar wind and changes in solar activity, the Earth's magnetic field, the permeability of the ozone layer, and the standards of meteorological conditions change. It is the sun that influences the cyclical functioning of the human body, which works in accordance with the seasons. We have an innate need for a certain amount of sunlight, sunlight and warmth. It is not without reason that with short winter daylight hours, almost everyone suffers from hyposolar syndrome: increased drowsiness, fatigue, depression, apathy, decreased performance and attention. We can say that the number of sunny days per year is much more important for the body than changes in, say, atmospheric pressure. Therefore, residents of coastal, for example, Mediterranean countries, or high mountains, live more comfortably than residents of St. Petersburg or polar explorers.
Weather in the house
We cannot influence weather conditions. But we can reduce the health risks associated with the influence of the external environment. The main thing to remember is that weather sensitivity does not manifest itself as an independent problem; it, like a carriage behind a locomotive, follows a certain disease, most often chronic. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to identify and treat it. In case of exacerbation of the disease due to bad weather, you should take medications prescribed by a doctor for the underlying pathology (migraine, vegetative-vascular dystonia, panic attacks, neuroses and neurasthenia). And besides, in accordance with the weather forecast, you need to develop certain rules of behavior for yourself. For example, “heart patients” react sharply to high air humidity and the approach of a thunderstorm, which means that on such days it is necessary to avoid physical activity and be sure to take medications prescribed by a doctor.
- It is important for everyone whose health changes due to changing climatic conditions to take more care of their health on such days: do not overwork, get enough sleep, avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, as well as physical activity. Put off, for example, your morning jog, otherwise, say, in hot weather you can run away from a heart attack and run into a stroke. Any emotional and physical stress in bad weather conditions is stress that can lead to disruptions in autonomic regulation, heart rhythm disturbances, surges in blood pressure, and exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Monitor your barometric pressure to understand how to control your blood pressure. For example, with low atmospheric pressure, hypertensive patients need to reduce their intake of medications that lower blood pressure, and hypotensive patients should take adaptogens (ginseng, eleutherococcus, lemongrass) and drink coffee. In general, it should be remembered that in summer, in warm and hot weather, there is a redistribution of blood from internal organs to the skin, so blood pressure in summer is lower than in winter.
- Residents of St. Petersburg, like any other metropolis, spend most of their lives indoors. And the more time we “hide” in comfort from external climatic factors, the more the balance between the human body and the external environment is disturbed, and its adaptive capabilities are reduced. We should increase the body's resistance to adverse weather changes. Therefore, if there are no contraindications, train the autonomic nervous and cardiovascular systems. A contrast or cold shower, Russian bath, sauna, walking, preferably before bed will help you with this.
- Organize yourself physical activity - it increases blood pressure, decreases the level of oxygen in tissues, increases metabolism, heat generation and heat transfer. The cardiovascular and respiratory systems are well trained by brisk walking for 1 hour, light jogging, and swimming. Trained people easily tolerate weather changes, which have a similar effect on the body.
- It is recommended to sleep with the window open. Moreover, the sleep should be sufficient - when you wake up, you should feel that you have had enough sleep.
- Monitor the level of humidity and artificial light in the apartment.
- Dress “for the weather” so that your body is comfortable in all weather conditions.
- If you notice that you feel dependent on the weather, forget about traveling to distant countries “from winter to summer” or “from summer to winter.” Failure of seasonal adaptation is dangerous even for practically healthy people.
Irina Dontsova
© Dr. Peter
Weather sensitivity in adults and children: who is at risk
During evolution, the human body has learned to adapt to changes in weather conditions. If the weather situation changes evenly and insignificantly, healthy people, as a rule, do not notice it. Persons suffering from chronic diseases are a different matter. In this case, in response to changes in weather conditions, a person may experience a pathological (meteotropic) reaction. By the way, if earlier experts believed that mainly older people suffered from weather sensitivity, in recent years they have recorded a significant “rejuvenation” of the disorder. This is associated with acceleration (accelerated development of the body) of modern people. In addition, some researchers suggest that this disorder may be hereditary, and it is also worth remembering the meteosensitivity of infants.
As observations show, the level of manifestation of meteosensitivity depends on various factors:
- age and gender of the person;
- form and stage of the disease (chronic);
- type of nervous system;
- level of adaptive capabilities of the body.
It is known that residents of different climatic zones may have their own characteristics and manifest themselves in different ways. A weather-sensitive person does not necessarily react to all the vagaries of nature (changes in atmospheric pressure, magnetic storms, humidity, etc.); only one of the factors can cause deterioration in well-being, while others go unnoticed by the body.
Recently, researchers have become seriously interested in the impact of meteorological factors on human sensory organs (vision, hearing). It turned out that visual weather patterns (clouds, rain, rainbows, etc.) can influence the external behavior (actions, speech) of a weather-sensitive person. While auditory meteorological images cause changes in internal behavior (thinking, motivation, imagination, faith). Interestingly, a person can perceive weather sounds at a distance of more than 50 km from the source.
Treatment of weather dependence
Increased weather sensitivity pushes people to look for the most effective ways to improve their well-being. It is useful for people who respond to magnetic storms and other atmospheric phenomena to know how to deal with weather sensitivity.
Therapy for magnetic storms
If your health worsens due to magnetic storms, then during this period it is better not to engage in heavy mental and physical work. To make it easier to cope with the period of solar flares, it is useful to get a good night's sleep, spend time in the fresh air more often, do not overindulge in heavy foods and take vitamins. In addition, a few days before the start of a magnetic storm, it is useful to play sports, give up bad habits and switch to a healthy diet.
Therapy for high atmospheric pressure
The answer to the question “How to get rid of weather sensitivity?” is also of interest to people who respond to increases in atmospheric pressure. The same recommendations mentioned above are relevant for them. In addition, it is useful for such people to do light exercises in the morning and take a contrast shower. For breakfast, it is preferable to eat foods rich in potassium (for example, cottage cheese with dried apricots, raisins and bananas). On such days, you should absolutely not overeat, work hard physically, and it is also useful to avoid excessive emotionality.
During periods of high atmospheric pressure, doctors advise going to bed earlier than usual.
Treatment at low atmospheric pressure
First aid for weather sensitivity caused by a decrease in atmospheric pressure is to normalize the blood pressure of a weakened person. As a preventive measure, on such days it is useful to reduce physical activity, and after every hour of work, take 10 minutes to rest. You should start the day with coffee, then drink a lot of fluids, including green tea with honey, and it is useful for heart patients to take special herbal tinctures (with the permission of the attending physician). Before going to bed, you can take a contrast shower and go to bed 1-2 hours earlier than usual.