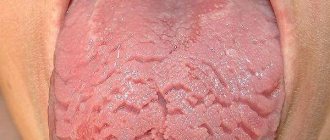
The tongue of a healthy person should have a pale pink color. The formation of a certain amount of light plaque on the surface of the tongue is allowed; it should be loose and the texture should be visible through it. If the natural color of the tongue is not visible through the layer of deposits, this means that it has formed too thick.
A coated tongue does not require treatment; the plaque will go away on its own as soon as the cause of its formation is eliminated. You need to fight the reason that causes it!
Etiology
As noted above, often plaque on the root of the tongue and other parts of this organ is the first sign of the development of a pathological process in the human body. The appearance of plaque can be a physiological phenomenon if the following points coincide:
- absence of foul odor from the oral cavity;
- color is pale yellow or barely noticeable white;
- transparency, i.e. the surface of the tongue is clearly visible behind the coating;
- absence of signs of inflammation in the tongue;
- easy cleaning of the tongue from plaque;
- no changes in the papillae covering the tongue.
Physiological reasons for the appearance of such a sign include:
- lack of fluid in the body. This is often due to the hot season, when water evaporates from the body much faster. Against this background, a change in the structure of saliva occurs - it becomes thicker, and the components contained in it lead to the formation of a slight white coating;
- insufficient or irregular adherence to oral hygiene rules. At the same time, the bacteria that make up the microflora of the mouth begin to multiply, which leads to the appearance of a pale yellow color of the tongue;
- addiction to bad habits.
Physiological plaque on the tongue mainly appears in the morning. There are several ways to get rid of plaque on the tongue, which has nothing to do with diseases. You just need to thoroughly clean your mouth, drink enough water and eat. After breakfast, the plaque of physiological etiology should completely disappear. However, in situations where it does not go away throughout the day, it is necessary to consult a clinician.
There are several pathological factors why plaque appears on the tongue:
- dental ailments;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- kidney or liver disease;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases;
- chemical poisoning;
- indiscriminate use of medications. Most often, plaque appears on the tongue after antibiotics.
Causes of plaque on the tongue
Oral diseases include:
- candidiasis is the most common cause of the appearance of this symptom, which is caused by the spread of microscopic fungi throughout the oral cavity, tonsils and back wall of the pharynx. Such a disorder, in turn, is formed against the background of a weakened immune system and conditions that lead to this, for example, HIV or diabetes;
- Glossitis is the development of an inflammatory process on the mucous layer of the tongue. It can be an independent disease or develop against the background of other diseases. This disease can be caused by thermal irritants or pathogenic microflora.
Causes of plaque on the tongue in adults associated with gastrointestinal ailments:
- esophagitis;
- GERD;
- gastritis, regardless of the reasons for its formation;
- colitis;
- chronic inflammation of the pancreas;
- acute appendicitis.
Other pathological reasons for the appearance of plaque on the tongue include:
- hepatic colic;
- renal failure;
- diabetes;
- Addison's disease;
- Graves' disease.
Against the background of such predisposing factors, patients with one disorder or another very often have a question: how to clean the tongue of plaque? To do this, it is only enough to begin treatment of the disease that became the source of such a symptom.
What to do if your tongue is bluish?
To get rid of the blue color of your tongue, you need to find out why it became that way. To do this, you need to contact the following doctors: gastroenterologist, dentist and therapist. Only after consultation with these specialists, who will conduct a visual examination and collect anamnesis, will you be prescribed appropriate treatment.
READ ALSO: Why might a child have a blue tongue, and what to do about it?
If it turns out that you have problems with the digestive system, the doctor will most likely prescribe antibiotics, antispasmodics, and anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of vitamin deficiency, a complex of vitamins will be prescribed and changes will be made to the diet. If the problem arose due to dentures, the dentist will correct them. If the cause of the blue organ is some kind of infection, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics or antifungal drugs.
In addition to treating identified diseases, it is necessary to:
- quit smoking, as this addiction damages the surface layer of the oral cavity and impairs blood circulation, and this causes further development of the disease,
- brush your tongue and teeth twice a day using antibacterial toothpaste,
- rinse the mouth with solutions of soda, furatsilin, potassium permanganate.
READ ALSO: what to do if your tongue stings and burns badly?
For rinsing, you can also use decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs:
- chamomile: steam 3 g of dried flowers in 200 ml of boiling water and let it brew for about 40 minutes, then strain and rinse 2 or more times a day,
- calendula: pour 5 g of dried flowers with cold water and put on low heat, after boiling - cool and strain, rinse your mouth after each meal,
- cloves and cinnamon: pour boiling water over 2 g of cinnamon powder (1 stick) and 5 clove buds and let steep for 20 minutes, rinse while warm.
Classification
During the initial diagnosis, plaque on the tongue can tell the doctor a lot - this is explained by the fact that the shade, structure and location will be characteristic of a particular disease or internal organ, which greatly simplifies diagnosis and saves the patient from undergoing unnecessary examinations.
What does plaque on the tongue indicate, depending on the place of its occurrence:
- tip of the tongue - indicates damage to the intestines, namely the rectum;
- a stripe strictly in the center of the tongue - indicates diseases of the spine;
- right side – liver pathologies;
- middle – stomach diseases;
- left side – damage to the spleen;
- root – inflammatory processes of the throat or nasopharynx. But the most common cause of plaque on the root of the tongue is ailments of the digestive system.
Localization of plaque on the tongue
The coating on the tongue in adults may differ depending on its shade:
- white or white-gray - indicates the effect of toxins on the body, pathology of the large or small intestine, serious diseases of the bladder, as well as inflammation of the lungs or kidneys;
- green - may indicate yeast infection of the oral mucosa and serious immunodeficiency;
- gray – indicates dehydration or stomach diseases;
- yellow – a signal of liver or gastrointestinal disease. In addition, doctors pay attention to the intensity of the shade. Pale yellow indicates the beginning of the development of the disease, and dark yellow indicates the late stage of the disease;
- brown - taking certain medications or a blood disease, gastritis or peptic ulcer, GERD or cholecystitis, hepatitis or dysbacteriosis;
- black – acidosis or severe fever;
- blue – dysentery or typhus;
- purple – blood stagnation;
- blue – stroke and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
According to the structure, coating on the tongue can be:
- fatty;
- dry;
- curdled;
- wet.
Depending on thickness:
- surface;
- heavily lined;
- spots.
How to clean plaque
The substrate must be removed after brushing your teeth.
Instructions:
- Turn the toothbrush over to the other side.
- Place it on the root of the tongue.
- Remove deposits using gentle, top-to-bottom movements. Force cannot be used.
- Rinse your mouth with any disinfectant.
Instead of a brush, you can use a special scraper.
Symptoms
The manifestation of clinical signs directly depends on why the plaque appeared on the tongue. If the cause of this is dental ailments, then there can be only a few manifestations:
- dry mouth;
- the appearance of a foul odor;
- bleeding gums;
- change in taste.
The symptoms will be much wider in cases where the coating on the tongue was caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- severe pain in the projection of the affected organ or spreading throughout the abdomen;
- heartburn and burning in the chest area;
- belching with a sour and unpleasant odor;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- pale skin;
- increased hair fragility;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- increased gas formation;
- abdominal enlargement;
- heaviness and discomfort in the stomach;
- exhaustion;
- yellowness of the skin - with liver damage;
- strong thirst;
- dry skin;
- increased sweating;
- increase in body temperature.
Symptoms accompanying plaque on the tongue
These are just the main symptoms that will accompany a coating on the tongue. The clinical manifestation of a particular disease will be individual for each patient.
Infectious diseases
This is primarily scarlet fever, dysentery, diphtheria, tonsillitis, gonorrhea, HIV infection.
If a person is sick with one of these infectious diseases, he is unlikely to find out why there is a white coating on his tongue. These are quite serious diseases that bring suffering primarily with their main symptoms: high fever, pain, rashes, discomfort, diarrhea and others.
The doctor may see a red tongue with a white coating, pinpoint rashes on the tongue, ulcers also covered with a white coating and other changes that will be secondary to these infectious pathologies. After infection with HIV in the AIDS stage, a white coating on the tongue appears due to fungal, bacterial, viral infections, which, in the normal state of the immune system, do not make themselves felt.
Diagnostics
A dentist or gastroenterologist knows what plaque on the tongue means and how to remove it. Diagnostics is complex and consists of a wide range of laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Primary diagnostic measures include:
- conducting a detailed survey;
- a specialist’s examination of the patient’s medical history and life history;
- performing a thorough physical examination.
Such manipulations will make it possible to find out more about the causes of the main symptom, as well as determine the presence and intensity of the manifestation of concomitant symptoms.
The second diagnostic stage will consist of:
- general and biochemical study of blood, urine and feces;
- specific tests to detect pathogens;
- radiography and ultrasound;
- biopsies and FEGDS;
- CT and MRI;
- other individual examinations;
- consultations with a dentist.
Only by studying the results of such diagnostic procedures will the clinician be able to formulate the most effective treatment tactics and prescribe ways to remove plaque from the tongue.
Once again about attention to language
Based on the above, it should be noted that the color of the tongue is a kind of beacon for every person. Therefore, it should be given close attention, especially to the mucous membranes in children. Doctors recommend examining it daily for changes, especially in color. Various types of blue discoloration on it indicate a serious malfunction in the body system.
It should be noted that the tongue will show signs of illness approximately 1–2 days before the body organs themselves begin to ache.
Be healthy!
Treatment
Clearing the tongue of plaque completely depends on why such a symptom appeared.
If plaque on the tongue occurs due to physiological reasons, then it will only be enough to regularly perform oral hygiene procedures, and in some cases, change your diet.
When the appearance of the main symptom was due to any disease, treatment will be aimed at:
- diet therapy;
- taking medications - to eliminate other manifestations of the clinical picture and the inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract;
- physiotherapy;
- medical intervention – if conservative methods are ineffective, if the patient’s condition is serious or there are serious indications for medical intervention.
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent the appearance of plaque on the tongue; it is only necessary:
- brush your teeth morning and evening;
- rinse your mouth after every meal;
- give up fatty and spicy foods, as well as smoked meats and sodas, which irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- brush your teeth with a paste with an antibacterial effect.
In addition, it is recommended to undergo examination by a dentist and gastroenterologist every six months.