Diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract occur in many people and are considered the most common among all other organ diseases. Statistics say that 90% of citizens need constant consultation with a specialist, as they experience regular stomach problems.
Among the main symptoms indicating pathology of the digestive system, pain in the abdominal area of varying intensity, nausea, constipation, heartburn, vomiting, poor appetite, and sudden weight loss are most often observed.
The main reasons for the development of stomach diseases include poor nutrition, bad habits, excess weight, infectious diseases, and diabetes.
Types of gastrointestinal diseases and their diagnosis
In recent years, gastrointestinal diseases have become very common in the world, compared to the situation before. Cases have become especially frequent among children and adolescents. Such diseases lead to partial destruction of certain organs: the stomach, liver, intestines and pancreas.
The most widespread among gastrointestinal diseases are the following ailments:
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, gastritis).
- Various diseases of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
- Liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis).
- Dysbacteriosis.
Diagnosing peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum is quite simple. To determine it, esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed. This procedure is an effective method for identifying ulcerative defects and possible complications of the disease at an early stage. It is also necessary to be tested to detect the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. In accordance with the data obtained, treatment is prescribed.
Irritable bowel syndrome is the presence of digestive problems that are caused by instability of the nervous system. To determine intestinal diseases, as a rule, the first step is to take a stool and blood test to exclude organic pathologies. Diseases of the digestive system are not fatal, but can lead to serious consequences.
To detect cholecystitis, an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder is required. If necessary, they can also examine the abdominal cavity and perform an MRI. If gastritis is suspected, the doctor’s first priority is to exclude acute surgical pathology. To determine the “seriousness” of the disease, laboratory diagnostics and functional studies are performed, and then, based on the result, a decision is made on treatment and possible hospitalization.
In the process of diagnosing liver diseases, it is necessary to assess the general condition of the organ, as well as identify or exclude the presence of cancer. For this purpose, a huge number of laboratory tests of blood and urine are used (for example, the study of protein metabolism and urine bilirubin).
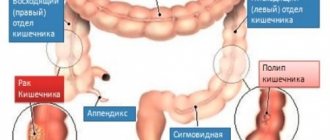
Anatomy
In its anatomical structure, there are two intestines: large and small. The small intestine, which occupies an intermediate position between the stomach and the large intestine, got its name due to the smaller (compared to the large) diameter of the internal lumen and the smaller thickness and strength of the walls.
The small intestine consists of three intestines:
The large intestine, which is the lower part of the digestive tract, also consists of three intestines:
- Blind, having a vermiform appendix.
- Colon, the sections of which are represented by the ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and sigmoid colon.
- Straight, in the structure of which there are: an ampulla and a gradually narrowing anal canal ending in the anus.
The most famous causes of gastrointestinal diseases
Currently, in large cities, every fourth person by the age of 28 suffers from various stomach diseases. This is due to many factors, the basis of which is stress and a lifestyle that is far from ideal. Let's highlight some of the most significant reasons that will eventually lead to stomach diseases:
- Wrong diet. Excessive secretion of gastric juice has a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the intake of spicy, peppery, over-salted foods. Cold food, overeating, and irregular nutrition also lead to the formation of gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- Bad habits. An equally significant factor that is present in at least half of cases of esophageal diseases. These include alcohol addiction, smoking and drinking large amounts of coffee. Smoking affects the mucous membrane and can lead to spasms of the stomach and duodenum. Alcohol affects the human liver and pancreas, and also leads to other gastrointestinal diseases.
- Medications. Some medications that contain salicylates (aspirin, etc.) lead to gradual destruction of the gastric mucosa, which leads to serious diseases of the esophagus.
- Helicobacter pylori infection. It is now generally accepted that spiral-shaped bacteria are one of the main causes of diseases of the digestive system. Its main function is the effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa, leading to a decrease in its protective properties.
How to identify a disease in time: symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases
For the most part, the symptoms of various diseases of the stomach and intestines are similar to each other. They help find the problem and begin treatment immediately. Let's consider the main symptoms of diseases of the intestines, stomach and other organs:
Nausea. An unpleasant condition of the human body, which can be caused by food poisoning or is a sign of intestinal disease, gastritis and other similar diseases. In many cases, nausea leads to vomiting.- Vomit. A fairly constant phenomenon in diseases, which is accompanied by the forced ejection of the entire contents of the stomach through the pharynx. Usually after this process the person feels better. The presence of blood or bile in the vomit indicates serious problems with the stomach and other organs, which require timely medical assistance.
- Heartburn. The process of excessive secretion of gastric juice, which provokes release into the upper part of the esophagus, is accompanied by a burning sensation. A characteristic symptom of esophageal disease. Regular occurrence of heartburn can lead to the formation of ulcers or even cancer in the digestive system.
- Stomach ache. A constant symptom of absolutely all gastrointestinal diseases, which becomes the first sign of the development of the disease. The pain can be either nagging or cramping. The presence of pain indicates serious problems with the intestines, stomach and pancreas. Also, this sign indicates an enlarged liver and its partial damage.
- Diarrhea. It speaks of problems with the human digestive system and manifests itself in the form of frequent liquid bowel movements. This condition occurs due to a large number of bacteria and viruses, and is caused by diseases of the small intestine.
- Bloating. The formation of a large accumulation of gases leads to distension of the gastrointestinal tract. Talks about stomach problems and colon disease.
There are several other symptoms characteristic of this or that disease:
- jaundice (hepatitis, cholecystitis);
- constipation (intestinal obstruction, irritable bowel syndrome);
- bitterness in the mouth (diseases of the liver, gall bladder);
- hiccups (problems with the esophagus);
- dysphagia (tumors and narrowings, inflammatory diseases of the esophagus);
- false urges (inflammatory diseases of the large intestine).
All of the listed symptoms and signs are a reason to visit a doctor. We strongly do not recommend self-medication; immediately seek help from qualified personnel.
Pancreatitis
Yes, you didn’t see it in the top of the most common reasons for visiting a gastroenterologist. But gallbladder diseases often go hand in hand with pancreatitis. The fact is that the bile and pancreas have a common excretory duct. If problems arise in the biliary tract, for example due to a stone, the pressure in the common channel also increases.
This threatens that bile will flow under pressure into the pancreatic ducts. The pancreas produces enzymes that help dissolve food. These enzymes are activated only in the intestines upon contact with intestinal juice and bile.
If enzymes and bile meet earlier, then it is not the food that begins to dissolve, but the delicate cells of the pancreas. This is how pancreatitis begins. This disease is characterized by constant girdle pain and repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief. An attack of pancreatitis is a serious reason to call an ambulance.
The most common gastrointestinal diseases and how they are characterized
The most famous stomach disease is chronic gastritis. Scientists believe that the cause of the disease in 90% of cases is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. There are many ways of infection: from kissing to using common things in everyday life. Stomach pain, poor appetite and belching are characteristic signs of the disease.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is considered no less common in the world. Develops due to stress, bad habits and poor nutrition. Even working night shifts can contribute to this disease. It is characterized by night pain, malaise after eating, and constipation. If you ignore the first symptoms, complications of gastric ulcer are possible.
Cholecystitis is becoming another popular disease, especially among women. This is an inflammation of the gallbladder due to blockage of the ducts by a stone formed in them. It manifests itself as biliary colic, which is characterized by a severe attack of pain in the right hypochondrium, which lasts about an hour. Nausea and vomiting are possible.
Pancreatitis is considered to be another disease that indicates a problem with the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms include pain in the upper abdomen, general malaise, flatulence, vomiting and rapid heartbeat. Infections, abdominal injuries, and heavy alcohol consumption usually cause pancreatitis.
Last on the list is irritable bowel syndrome. The main reason is an increased reaction to stressful situations. However, it's not just about psychological disorders. An increase in the response of pain receptors and biological substances in the intestines can lead to inflammation.
There are still quite a few gastrointestinal diseases that are similar in symptoms and causes. To accurately diagnose the disease, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination, after which the correct treatment will be prescribed.
What are the consequences of problems with the digestive system?
Any disruptions in the functioning of these organs will ultimately negatively affect overall health. Gastrointestinal diseases are often caused by such phenomena as:
- Decreased immunity, since the organs responsible for the protective function do not receive enough nutrients.
- Deterioration of the condition of the skin, nails and hair. Irritation occurs on the skin, hair and nails become brittle.
- Muscle pain and numbness of the limbs - all this is also affected by gastrointestinal diseases.
- Metabolic disorders and, as a consequence, the problem of excess weight or, conversely, lack of it.
- Development of allergic reactions.
- Dysfunction of the organs of the reproductive system, further difficulties with conception and pregnancy.
- Complications from the cardiovascular system, including an increased risk of heart attack.
- Diseases of the endocrine system - thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
- Oral diseases, including stomatitis and glossitis, also develop with gastrointestinal diseases.
- Skin diseases - neurodermatitis and eczema.
- In severe cases, death occurs due to the progression of gastrointestinal diseases and associated pathologies.
General methods of treating gastrointestinal diseases
It is very important not to delay the treatment of diseases of the stomach and intestines, as they tend to develop into chronic forms with constant manifestations of complications. In this regard, any disease requires timely and comprehensive treatment. It includes:
- strict diet;
- use of medications;
- colon cleansing;
- rejection of bad habits;
- strengthening the immune system;
- physiotherapy.
For example, for gastric and duodenal ulcers, doctors recommend following a diet that excludes fried, fatty, sour and salty foods (irritating factors). Based on the recommendations of Maastricht 5, experts prescribe drugs to reduce the secretion of gastric juice and protect the gastric mucosa (proton pump inhibitors). Antibiotics are also used to combat Helicobacter pylori (beta-lactams, macrolides). In case of serious complications, treatment of gastric ulcer requires surgery.
It is worth remembering that stomach problems can cause serious damage to health, even death, if the recommendations of doctors are not followed. Be attentive to your health and do not ignore the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease.