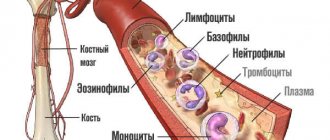
Dihydrotestosterone is the most powerful male sex hormone. The steroid component is produced from testosterone due to the action of certain enzymes. Affects the development of the genital organs and prostate, supports normal erectile function and high libido. Produced predominantly in the testicles of men, a small part is produced by the adrenal glands. The maximum concentration is detected in the skin of the genitals and in the hair follicles. Let's take a closer look at what dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is and what is its function?
What is DHT
DHT stands for dihydrotestosterone, which is an endogenous androgenic sex hormone. In addition to DHT, it is sometimes called DH or 5α-dihydrotestosterone.
This hormone, which is converted from testosterone (another androgen, which basically means "male hormone"), is associated with many male physical characteristics. Harvard Medical School explains that the word androgen comes from words meaning “man-maker.”
This androgen also contributes to the changes that occur during puberty and affects sexual arousal.
According to the Endocrinology Society, "nearly 10% of the testosterone produced by adults each day is converted to dihydrotestosterone, from the testicles and prostate (in men), ovaries (in women), skin and other parts of the body."
DHT is more potent than testosterone and is present in smaller quantities. The level of DHT depends on the amount of testosterone present. The more testosterone available, the more it is converted into dihydrotestosterone.
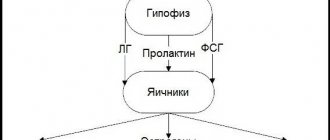
Testosterone production is controlled by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which are considered the “control centers” of the brain.
Dihydrotestosterone and its effect on hair
How to lower dihydrotestosterone in men
As we wrote above, the DTG norm in men is in the range of 250–990 pg/ml. It is strictly forbidden to treat elevated DTG on your own. You need to contact a urologist and endocrinologist. It is they who, depending on what is causing the increase in DTG, will prescribe appropriate treatment. This is mainly drug treatment, which can also be accompanied by physiotherapeutic procedures.
Bifidumbacterin for women: application, analogues, price and reviews.
Pros, cons and side effects of birth control Janine: read more.
Types of cervical erosion and its treatment: https://venerolog-ginekolog.ru/gynecology/diseases/vidy-erozii-sheyki-matki-i-ee-lecheniya.html
DHT and its functions
While this hormone is often associated with thinning hair, acne, and other unpleasant symptoms, we know that there are also benefits of DHT that apply to both sexes. Below are some important functions that DHT performs as described:
- Helps with the onset of puberty in boys and girls, leading to genital development, deeper voice, and changes in body composition (less is known about how it affects puberty in women compared to men)
- Leads to the growth of body hair, including pubic hair
- Causes prostate growth in men
- Increases male sexual performance (in combination with testosterone or testosterone boosters)
Does DHT Build Muscle? To some extent, it helps adults maintain muscle mass as they age, much like testosterone does.
It also benefits reproductive health and sex drive.
Reduced hormone levels - causes, symptoms, treatment options
The production of DHT in a man’s body can decrease under the influence of various factors:
- dysfunctional disorder of the gonads;
- prostatitis;
- diabetes;
- tumors in the adrenal glands;
- androgen deficiency;
- with Morris syndrome;
- hypogonadism – insufficiency of the gonads.
Hypogonodism in men
You can pay attention to your health and get tested to determine your hormone levels if you experience the following symptoms:
- sudden hair loss, cessation of hair growth;
- obesity, manifested by the female type (stomach, chest, thighs);
- erectile dysfunction;
- lack of sexual desire;
- increased sweating;
- decrease in muscle mass;
- dry skin;
- fatigue, depression, insomnia;
- infertility.
Traditionally, doctors advise undergoing an examination if at least three of the above signs are present.
In boys, low hormone levels manifest themselves as follows:
- lack of muscle mass;
- slow hair growth, absence of hair on the face, armpits, groin;
- a reduced penis or its abnormal structure;
- there is femininity in the figure;
- disproportionate development of the limbs.
Role of DHT in hair growth and hair loss
The American Hair Loss Association states, "While testosterone underlies the balding process, DHT is considered the main culprit."
DHT is now believed to contribute to androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness) by binding to receptors in the sebaceous glands of scalp follicles, causing them to shrink.
The conversion of testosterone to DHT requires the enzyme 5-alpha reductase type II. This enzyme is stored in the sebaceous glands of the hair follicle.
DHT affects hair growth and hair loss because this hormone causes follicles to miniaturize and shorten their lifespan, eventually causing them to stop producing hair altogether. When DHT is suppressed, for example due to medications/interventions aimed at stopping hair loss, hair follicles continue to develop and grow new hair, working as a natural hair loss therapy.
It is estimated that approximately two-thirds of American men will experience noticeable hair loss by their mid-30s. By the time a man reaches 50 years of age, this figure will increase to approximately 85%.
Here's how androgenetic alopecia contributes to hair loss:
- This usually causes thinning in all areas of the scalp in women.
- In men, thinning usually manifests itself as a distinct balding pattern that includes a receding hairline and a thinning crown. This is because the temples and the middle of the front of the head are considered to be the most sensitive to the effects of DHT.
- Some women may have a combination of the two patterns described above.
- The amount of hair loss that adults develop is closely linked to genetics, meaning you are likely to lose the same amount of hair as your parents. Genetics play a role in the formation of androgen receptors in the follicles, causing some people to be more susceptible to hair thinning caused by hormonal changes than others.
Women typically have much lower levels of testosterone and DHT in their bodies compared to men. But when levels rise, they can suffer from DHT-induced hair loss just like men. Even if a blood test shows that DHT levels are in the "normal" range for a woman, even slightly elevated levels can contribute to hair loss in some women who are sensitive to the effects of androgens.
This sometimes occurs when levels of female hormones (such as estrogen) decrease, meaning that the effects of androgen hormones are not as balanced.
What causes androgenetic alopecia in women? Some causes of hair loss associated with high androgen levels include:
- ovarian cysts
- high androgens
- taking contraceptive drugs (COCs)
- pregnancy
- menopause
- genetic susceptibility
- stressful life events
How does it affect people
It is possible to produce either too much or too little DHT. Men are more likely to experience symptoms if they produce too little DHT, while women are more likely to experience symptoms if their body produces too much.
On the other hand, in men, high levels cause little detectable change, while low levels in women have the same result.
High levels of DHT are usually the result of excess testosterone production. This can happen in both women and men.
This is usually more obvious if a woman has high levels of DHT because it causes physical changes that are considered masculine. For example, among women, symptoms of high DHT levels may include:
- Increased hair growth on the body, face and pubic area (hirsutism)
- Irregular periods or cessation of menstruation (amenorrhea)
- The appearance of acne, often on the chin, jaw and back
- Abnormal changes in the genitals
Men with low DHT levels may experience some of these symptoms:
- Delayed onset of puberty (this may also affect women)
- Reduction of pubic and body hair
- Abnormal development of the genitals (he may be born with ambiguous genitalia that resemble female genitalia)
In the past, it was believed that high levels of DHT in men posed a health risk, but according to recent research, this is not entirely true.
There are links between high DHT levels and prostate enlargement, an increased risk of prostate cancer, and an increased risk of coronary heart disease. However, a number of long-term studies have failed to show that increasing DHT has these negative effects.
The role of DHT in these conditions remains controversial, and studies are currently being conducted to explore whether DHT blockers and inhibitors may work as treatment options. What seems clear is that DHT stimulates prostate cell growth, which is normal during puberty but can cause problems in older men.
Diagnosis of hormonal disorders
An examination for suspected disorders of DHT synthesis includes, in addition to the hormonal examination itself, a study of hereditary history, a urological or gynecological examination, ultrasound, and genetic analysis.
A blood sample for dihydrotestosterone testing is taken from a vein. The test is taken on an empty stomach; at least eight hours must have passed since the last meal. You are allowed to drink water. On the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude increased psycho-emotional and physical stress, fatty foods, alcohol, smoking, ultrasound and x-ray examinations. Women are advised to test their DHT levels at the beginning of their menstrual cycle. To assess the androgenic status of the body, it is necessary to take the test several times at certain intervals.
The most significant increase in dihydrotestosterone levels is observed in adolescence, with peak production occurring at 25 years of age. With age, the secretion of the hormone gradually decreases.
If it is necessary to exclude tumor processes, a CT scan of the adrenal glands, brain and other organs is performed.
How to correct DHT levels
Measures aimed at reducing hair loss target both the production of DHT and the binding of DHT receptors in the hair follicles.
What do DHT blockers do?
- Blockers prevent the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone and also help stop DHT binding to 5-alpha reductase receptors (5-AR) in hair follicles. In other words, they can help remove DHT from the scalp.
- The most popular example of an oral DHT blocker is finasteride (sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia). It is taken orally and is available by prescription only.
- DHT blockers are intended for use by men only and should never be taken by a woman or child, as this can lead to various hormonal complications during pregnancy and development.
Will reducing DHT affect hair growth according to research? One study found that most men taking finasteride experienced improvement in their hair loss.
The study also states, “Currently, FDA-approved minoxidil and finasteride and FDA-approved HairMax LaserComb are the only treatments recognized by the FDA as treatments for androgenetic alopecia.”
Another study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that more than 80% of men taking finasteride maintained their original number of hair follicles and more than 65% began to grow new hair. Finasteride is usually taken in doses of 1 mg per day.
Another treatment option is a DHT inhibitor, which reduces the amount of DHT the body produces, helping less reach the scalp, and also reduces the effects of DHT elsewhere. Medicines that improve blood flow to the scalp can also be used in combination with blockers and inhibitors to stimulate hair growth.
5-alpha reductase inhibitors are also used as a treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia (or BPH, which is characterized by the growth of the gland with aging). In doses of about 5 mg, Proscar helps some men with BPH.
This type of medication appears to reduce prostate volume, improve symptoms, and reduce the risk of acute urinary retention and the need for surgery associated with BPH. New research suggests that DHT blockers may also play a role in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Natural Remedies to Lower DHT
Although less research has focused on this topic, there are some natural DHT blockers that naturopaths and naturopaths find helpful. Natural remedies for hair loss include:
special shampoos and creams,
green tea
Now Foods, EGCg, Green Tea Extract, 400 mg, 90 Vegetarian Capsules
pumpkin seed oil
Health From The Sun, Pumpkin Seed Oil, 90 Vegetarian Softgels
biotin
Life Extension, Biotin, 600 mcg, 100 Capsules
omega-3
zinc
adaptogenic herbs
herbal supplements such as saw palmetto.
Like all naturopathic remedies, they are slower-acting and less effective than prescription medications like finasteride. However, their great advantage is that they have virtually no side effects and can be used safely by most people for long periods of time.
Low-level laser therapy is another treatment option that some people may find more convenient and promises to stimulate hair growth. It works by increasing blood flow to the scalp and stimulating catagen or telogen follicle metabolism.
Finally, consider trying essential oils—rosemary, cedarwood, and bay oil, which some aromatherapists believe stimulate hair growth, slow graying, and treat scalp conditions such as dandruff.
Sports and DHT levels
According to some experts, exercise may influence whether you experience symptoms associated with irregular DHT levels, including hair loss or hair growth.
Exercise can be both a natural DHT blocker and a potential means of increasing DHT/testosterone levels (and therefore hair loss), depending on what kind of exercise you do and how often.
Doing a lot of aerobic/cardio exercise, such as endurance exercise (biking or running for several hours), can reduce blood flow levels. While strength training, weightlifting can increase testosterone levels and therefore DHT levels. Building muscle mass leads to increased testosterone levels.
However, large amounts of cardio have been shown to lower testosterone levels because it increases cortisol secretion.
The best way to avoid exercising that causes hormonal imbalance is to:
- make sure you take enough rest days
- combine exercise with lifestyle changes that manage stress
- make sure you eat a balanced, healthy diet
Can any food block DHT?
There is some evidence that if you include "DHT blocking foods" in your diet, hair loss may be reduced, although more research is needed to confirm how well this works.
For example, zinc, the antioxidant lycopene, the amino acid L-lysine, biotin, high-fiber foods, and plant foods with certain other phytonutrients may be able to inhibit DHT to some extent.
Foods that can potentially block the effects of high DHT include:
- pumpkin seeds (excellent source of zinc)
- tomatoes
- watermelon
- carrot
- mango
- nuts such as almonds, walnuts, peanuts, pecans
- seeds such as chia and flax (high in healthy fats, fiber and minerals)
- wheat germ
- greens (spinach, chard and kale)
- berries
- bananas
- eggs
- fish - mackerel, sardines, tuna and salmon (high in omega-3)
- caffeine/coffee
A diet high in processed foods, added sugar, and trans fats may also contribute to metabolic problems, inflammation, and hormonal imbalances, which can exacerbate health problems caused by DHT. Consuming supplements/protein powders that contain growth hormones can do the same by increasing testosterone production.
Risks and side effects of DHT blockers
Because DHT is a hormone that has multiple functions in the body, blocking its action can cause a variety of reactions. Possible side effects of DHT blockers include:
- Sexual dysfunction/erectile dysfunction
- Fat accumulation in the chest area
- Skin rashes
- Indigestion and sometimes vomiting
- Darkening and thickening of hair on the face and upper body
As mentioned above, women and children should never take DHT blocking medications.
Final Thoughts
- What is DHT? This abbreviation stands for dihydrotestosterone, which is an endogenous androgenic sex hormone that is formed from testosterone.
- DHT is the main hormone responsible for male pattern baldness. It may also contribute to thinning hair in women and other symptoms such as changes in body hair, acne, and sexual dysfunction when levels are too high or low.
- What is a DHT blocker? This is a medicine or supplement that prevents DHT from binding to 5-alpha reductase receptors in hair follicles, preventing them from shrinking and causing hair loss.
- Besides medications, here's how to lower DHT levels: eat a healthy diet, manage stress, consider laser therapy, and try supplements such as green tea, pumpkin seed oil, biotin, and herbs such as saw palmetto.
Drugs that lower androgens in women
If dihydrotestosterone is high in women, the attending physician may prescribe the following medications:
- spironolactone;
- metformin.
These two drugs not only suppress the action of androgens, but also interfere with their production.
Doctors may often prescribe certain contraceptives:
- Jeannine;
- Diana-35
- Yarina.
When reducing hormone levels through medication, it is recommended to use herbal decoctions:
- chamomile;
- mint;
- sage
Chamomile infusion