What are the ovaries in women and where are they located?
The ovary (ovarium) is a paired internal female reproductive organ.
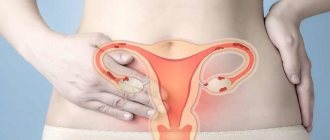
Normally, a woman has two ovaries. They are located in the pelvic area: asymmetrically “suspended” on ligaments on both sides of the uterus; the left ovary is on the left, the right ovary is on the right.
The uterine pole of the ovary is connected to the uterus by its own ligament of the ovary.
Articles about ovarian diseases
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer, how to diagnose the disease
04/06/2020 3471 No comments
Why is ovarian cancer so dangerous? Is it possible to make a diagnosis using the CA-125 eye marker? The first signs and symptoms of an ovarian tumor. Diagnostic methods, treatment and prognosis. How to recognize a relapse...
Read more
Chronic oophoritis
12/05/2018 23230 2
What is chronic oophoritis? How to recognize the disease, what are the symptoms? How to treat low-grade inflammation of the ovaries? Dangerous consequences of the disease...
Read more
With its tubal pole, the ovary faces the infundibulum of the fallopian tube.
Location of the ovaries
Ovarian sizes
Sizes of the ovaries in women (average norm): - in newborn girls: 1.5-2 x 0.5 x 0.1-0.35 cm - by the first menstruation: 3-3.5 x 1.5-2 x 1 -1.5 cm - in childbearing age: 3.0 x 2.0-2.5 x 1.0-1.5 cm
The size of the ovaries can vary within certain limits depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the age of the woman. The right and left ovaries are often not the same: one is slightly smaller or larger than the other.
Dimensions of the right/left ovary according to ultrasound for women over 18-20 years old:
| Ovarian parameter | Permissible minimum | Allowable maximum |
| Length | from 2.0 cm | up to 4.5 cm |
| Width | from 1.8 cm | up to 3.0 cm |
| Thickness | from 1.6 mm | up to 2.2 cm |
| Volume | from 4 cu. cm | up to 10 cu. cm |
After menopause and the decline of reproductive function, the ovaries become smaller.
Dimensions of the right/left ovary of a woman according to ultrasound during the postmenopausal period
| Ovarian parameter | Permissible minimum | Allowable maximum |
| Length | from 2.0 cm | up to 2.5 cm |
| Width | from 1.0 cm | up to 1.5 cm |
| Thickness | from 0.5 cm | up to 1.0 cm |
| Volume | from 1.5 cu.m. cm | up to 4.0 cu.m. cm |
Return to contents
Structure and structure
- The basis of the organ is the string and the trigger substance.
- In addition, there is also a medulla containing a neurovascular component.
- The follicular apparatus develops in the cortical tissue. It is here that the stage of maturation of follicles and subsequent development of the egg occurs.
Ovarian size
Normally, a woman's ovary size should be approximately the same throughout her life. In some cases, it may increase during the ovulatory process.
Normally, the domina should not exceed 5 cm, and the width should not exceed 3 cm. With minor deviations, this should not be considered a pathology. But if the values are dramatic, then additional diagnostics will be required to exclude diseases. Read more about the size of the ovaries here.
Popular questions
I have inflammation of my left ovary.
The doctor prescribed me several injections and suppositories. Can I replace injections with tablets? I recommend that you consult your doctor regarding this issue to select adequate therapy and change the method of administration.
Good afternoon, polycystic ovary syndrome, the thyroid gland is normal, thyroid hormones too, hormones on days 2-4 of the cycle (it seems only DHEA-SO4 is increased): DHEA-SO4 354.8,
E2 28,
HFSH 2.46, HLH 2.19, PRL 10.99, TESTO 1.25, PROG 0.30, 25-OH 69.87, FT3 2.63, FT4 1.16, T3 1.65, T4 7.59,
TSH 1.790,
TP0AB 8.10, HSBG 28.6 26 years old, normal weight, I had my first menstruation at the age of 16 and came once every six months; I don’t plan to have children.
What treatment can you recommend? If, according to the result of ultrasound, there are more than 10 follicles in the ovaries and the volume is increased by more than 8.5 cm3, then it is recommended to take combined oral contraceptives. Considering the results of hormone levels, I would recommend taking a combination of ethinyl estradiol and cyproterone for at least 6 months.
How to treat an ovarian luteal cyst, if I’m pregnant, what should I do?
Hello! During pregnancy up to 16 weeks, such cysts require only dynamic monitoring and ultrasound control once a month.
Hello! For inflammation, can Reosorbylkat 200 be instilled?
Hello!
This drug is used only as prescribed by a doctor for severe, life-threatening conditions. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
How does the ovary work?
It should be noted that a woman’s ovaries work only for a certain period of time and this is due to hormonal changes in the body, as well as the supply of necessary tissue.
Their functioning in a woman begins during puberty with the arrival of menstruation and ends with the onset of menopause. Every month there is a single-phase process of maturation of the egg, until the moment of fertilization. Every month, the supply of cells in a woman’s organ decreases.
Where to get examined and treat ovarian dysfunction in St. Petersburg
If you notice signs of improper ovarian function, be sure to contact the Diana Clinic. Our address: St. Petersburg, Zanevsky Prospekt, 10. Here you can undergo a set of tests, undergo all types of ultrasound, and then get advice from experienced gynecologists and endocrinologists. Cost of examination and treatment of ovarian dysfunction: ultrasound - 1000 rubles, doctor's appointment - 1000 rubles. The cost of tests can be found by calling toll-free: 8 (800) 707-1560
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Functions of the ovaries
The ovaries are a functionally complex organ. This is due to the fact that it has a fairly strong effect on the woman’s body.
Functions:
- Initially this is a function of reproduction. In a woman’s ovaries, germ cells—eggs—are formed, which combine with sperm and the process of fertilization occurs.
- It is also a hormonal product. The most important hormones are formed in the ovary, these are estrogens and progesterone, and in small quantities these can also be androgens. They promote the development and functioning of the mammary glands, prepare the uterine cavity for implantation, and also influence many metabolic processes in the body.
Ovarian diseases
Cyst or polycystic
This is the formation of cavity formations in a woman’s ovarian tissue, filled primarily with liquid inclusions.
These formations can be of different nature, most often they are benign ovarian cysts in women.
In most cases, these are functional elements that have collapsed due to disruption of their development during the menstrual cycle.
They occur equally often at any age, but mainly in the reproductive age, when the ovaries are actively working.
Symptoms:
- In some cases, it may not manifest itself in any way; this usually occurs when the ovarian cyst is small.
- In most cases, the formation of an ovarian cyst is associated with menstrual irregularities; this is mainly a delay.
- A pain syndrome appears, characterized by either aching or stabbing character on the affected side.
- In this case, irradiation occurs in the leg area or tailbone.
- There is no violation of the general condition.
Treatment tactics are selected based on the clinical picture of the pathological process. If severe pain and complications do not occur, then waiting several menstrual cycles and determining tumor markers is sufficient.
If the process does not go away on its own, it initially requires medical treatment using anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs. If there is no response to treatment, an attempt is made to surgically remove the cyst.
If the process is multiple in nature, only drug treatment is required, provided that the woman’s ovarian cysts are benign.
Dysfunction
This is a process of hormonal failure in the ovaries. It can occur in various types of pathologies. This can manifest itself as irregular bleeding from the genital tract, its abundance, and also, on the contrary, scarcity.
This may also be associated with pain and the inability to bear a child. Treatment in this case is medicinal and includes pathogenetic therapy for the underlying pathology.
Apoplexy
This is an acute gynecological pathology that requires immediate surgical treatment.
It occurs quite often and is associated with the development of hemorrhage and infarction in the ovarian tissue.
This problem can be observed during the reproductive period; the risk group is women aged 20 to 30 years.
Predisposing factors for the development of this condition are follicular or corpus luteum cysts in the ovary, inflammatory and adhesive processes in women.
Apoplexy manifests itself as a pronounced pain syndrome, which is noted by the woman. It develops acutely, the pain has a dagger-like and stabbing character. A woman can often name the time when the manifestation began; usually it does not exceed a day.
Determination depending on the day of the menstrual cycle is very important. Palpation of the ovarian area in a woman causes difficulty due to severe pain.
In addition, a clinical picture of hemorrhagic shock may develop, expressed in pallor, increased heart rate and pallor of the skin, as well as a decrease in blood pressure.
Diagnosis is usually not difficult:
- The basis of ovarian apoplexy in a woman is ultrasound diagnosis. With its help, as well as Dopplerometry, the source of bleeding is revealed, as well as the structure of the organ and its size. In addition, the volume of free fluid in the abdominal cavity is determined.
- One of the available methods is puncture of the posterior vaginal vault. It can be carried out in any medical institution and determines the contents that have accumulated in the lower abdomen. If the doctor receives blood, then by its nature it can be determined whether the bleeding continues or has already stopped. The puncture is performed under local anesthetics, the most popular is novocaine.
- In addition, the technique of laparocentesis and diagnostic laparotomy can be tried on . In better equipped hospitals this will be laparoscopy.
Treatment in this case is predominantly surgical. The doctor performs the scope of the operation after examining the affected ovary; if it is extensive, then in such cases complete removal of the organ from the woman is required. If there are fragments of healthy tissue, then they try to save the ovaries. Prescription of hemostatic substances and antibiotics is also required.
Adhesive process
This is a disease that is characterized by the replacement of functional tissue in the ovary with connective tissue.
It does not perform functions, but can also lead to disruption of the organ.
It occurs in women of any age, but it is predominantly encountered by representatives of the fair sex between the ages of 25 and 40.
Inflammatory processes, especially in a chronic course, as well as previous operations and the consequences of cystic growths can lead to adhesions in the ovary.
Symptoms:
- The disease manifests itself in the development of pain, which in some cases interferes with the normal functioning of a woman.
- Exercise tolerance, sex life, and performance are impaired.
- The pain has the character of pulling or aching manifestations. There is constant discomfort in the lower abdomen, as well as the ovaries. It can intensify during ovulation and menstruation.
- The affected ovary in a woman is prone to disruption of the menstrual cycle, as well as the formation of cystic growths in women.
Therapy varies and depends on the degree of manifestation of the pathological process. If these are minor changes, then conservative therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs or fibrinolytics is sufficient.
If a woman’s standard of living is significantly reduced, then this may include surgical interventions with possible removal of adhesions or excision of the woman’s affected ovarian tissue. In most cases, prevention of the process may be required.
Teratoma
This is a voluminous formation that forms in the ovary.
This process is most often congenital in nature and is associated with a violation of the formation of embryonic tissues. But this pathology is most often diagnosed in young people.
It consists of the rudiments of connective tissue, as well as fragments of hair and teeth, in some cases cartilage.
A woman may experience pain from the lesion, disturbances in urination and defecation, especially as the size increases.
Treatment in this case should be exclusively surgical with strangulation and possible preservation of ovarian tissue.
Endometriosis
Currently, this is one of the most common diseases in gynecology.
Great importance is attached to it due to the fact that the exact cause of its occurrence has not yet been established and, at the same time, no etiopathogenetic treatment has been selected that will be aimed at eliminating the disease.
It is characterized by the fact that the inner lining of the uterine cavity, the endometrium, grows beyond the limits of their anatomical areas.
Similar tissue can also land on a woman’s ovaries, which leads to the formation of hormonally dependent cysts, which can change in size over the course of menstrual cycles.
Symptoms:
- This pathology is characterized by pain, even with small lesions in the ovaries in women, of a pulling or aching nature, as well as infertility.
- Increased pain in a woman occurs several days before and continues for several days after menstruation.
- In some cases, sexual intercourse becomes painful, and in addition, exercise tolerance sometimes worsens.
In this case, diagnostic methods include ultrasound examination, as well as the determination of one of the tumor markers that is sensitive to an increase in endometrioid tissue in the body, this is ca 125.
The basis of therapy is surgical removal of the formations followed by the administration of anti-relapse therapy.
Drug therapy will primarily include hormonal drugs from the group of estrogen antagonists, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that eliminate pain. The prognosis is more favorable compared to other forms of endometriosis of the reproductive system.
Ovarian cancer
This is one of the most dangerous pathologies that occurs in women. It can appear at any age, but most often it is the period after puberty and before the onset of menopause. Very often it is hereditary in nature, in most cases it occurs in women with hormonal disorders.
At present, the exact cause of the development of this pathology cannot be established, but it is known that very often such pathology occurs under the influence of predisposing factors. The main ones are hazardous industries, living in unfavorable areas, exposure to radiation, carcinogenic products and uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs.
Symptoms:
- The disease poses a great danger due to its long asymptomatic course. Subsequently, when the tumor grows, the woman’s menstrual cycle is disrupted, and a pain symptom appears in the lower abdomen.
- The nature of the pain is predominantly nagging or aching; due to compression of neighboring organs, urination and defecation may be impaired; women note a tendency to constipation.
- Also, the clinical picture of ascites and damage to internal organs subsequently develops.
- In addition, one of the most common signs of ovarian cancer is metastasis from the stomach. A woman may not be bothered by pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis and treatment:
- The basis for the treatment of ovarian malignancy in women is an integrated approach. To do this, in the initial stages of oncology, it is necessary to do chemotherapy to inhibit the increase in cell growth, and then to surgically remove the tumor formation, most often with the entire ovarian tissue. This is followed by chemotherapy and radiation exposure.
- The basis of diagnosis is ultrasound examination and determination of tumor markers ; specific reagents for malignant ovarian lesions in women have now been identified.
- After these studies, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the lesion with histological examination , most often this is performed during surgery in order to immediately determine the extent of the surgical intervention.
The risk of death, as well as possible manifestations after a few years, is very high.
Adnexit
This is an inflammatory disease of ovarian tissue in women.
The pathology is common, at the same time, a very large number of women do not undergo treatment on time and adnexitis becomes chronic with the development of complications.
The main reason for its development is the bacterial flora, which enters the tissues through the bloodstream or through lymph and direct transfer from the uterine cavity through the fallopian tubes.
As a result, edema develops and normal hormonal processes are disrupted, resulting in a change in the woman’s menstrual cycle.
This process may be further characterized by the replacement of the sling and parenchyma with connective tissue, which does not carry functional activity.
This process is manifested not only by changes in the cyclicity of menstrual flow in women, but also by pain in the lower abdomen, as well as in some cases by the development of intoxication with an increase in body temperature.
Treatment:
- In order to treat the disease, antibiotics are prescribed, preference is given to determining the sensitivity of the pathogen; this can also include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins.
- In case of a purulent process, surgical intervention is required to remove the affected tissue and install drainages.
In most cases, a course of preventive treatment may be required to avoid complications and relapses. Many women are faced with the development of complications in the ovaries, among which the most important are chronic inflammation, adhesions and infertility.
Features of reproductive age
The shape is elongated, almond-shaped. The surface may be smooth, but closer to ovulation, bumpiness is noted due to the formation of follicles. On the outside, the ovary is covered with a thin tunica albuginea containing nerves, arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels.
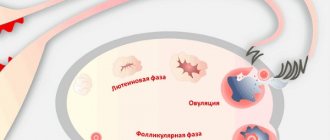
Important. During the cycle, a group of follicles is stimulated, but only one or a few reach the final stage with the formation of a dominant one.
After the egg is released from the follicle, the corpus luteum is formed in the luteal phase, which produces the hormone progesterone. Further, everything depends on whether fertilization has occurred or not. If the fusion does not occur, then the gland decreases in size, stops producing the hormone, and scar transformation occurs. There may also be degenerative changes with the formation of a corpus luteum cyst, which is complicated by hemorrhage due to the abundant blood supply.
If fertilization has occurred, the corpus luteum remains functional for 12 weeks and synthesizes progesterone. This hormone is necessary to stimulate the endometrium, since it is in this area that the fertilized egg is fixed.
What do the ovaries look like during pregnancy?
During this period, a slight increase in volume is possible due to the presence of the corpus luteum in the structure of one of them. It gradually decreases after fulfilling its purpose - the production of progesterone. As the uterus enlarges, the ovaries move upward towards the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis of ovarian pathologies
Ultrasonography
Currently, this is one of the most common research methods in gynecology.
The advantage is high diagnostic accuracy, as well as non-invasiveness and the risk of side effects.
If it is necessary to diagnose the ovaries, ultrasound can be used even for pregnant women.
This method determines not only the location of the organ, but also its size and the quality of the follicular apparatus.
Evaluation of follicles is one of the most necessary studies performed for women, especially for cysts, discormonal disorders and infertility.
In this case, the number and nature of follicles in the ovary, their size, as well as the determination of dominant formations are calculated. In some cases, the doctor can conduct a differential diagnosis of ovarian formations in women by genesis, for example, distinguish the nature of the cyst.
Also, using a Doppler unit, blood flow in a woman’s ovary is assessed. Particular importance is given to this when recognizing a malignant process. In some cases, the doctor can determine the adhesive process in the ovaries or the nature of hormonal imbalances.
Even with the development of emergency conditions, often accompanied by bleeding, a study is carried out to determine the presence of free fluid in the pelvis and determine the source of bleeding.
This is especially important if such a condition develops in a woman during pregnancy, since any surgical intervention or invasive procedure can cause harm to the fetus.
Stimulation
This is the process of prescribing medications to enhance the functioning of the ovaries and create the process of egg maturation.
In this case, increased release of hormones is necessary to increase the functional functioning of the organ.
The ovaries increase in size and the formation of a large number of eggs may occur.
Puncture
This is a diagnostic, invasive procedure that is performed to obtain the contents of ovarian tissue. In some cases, this is necessary to clarify the contents of space-occupying formations and select treatment tactics.
It can also be a method of obtaining eggs that mature after stimulation for a subsequent IVF procedure.
Physiological changes during menopause
At the onset of menopause, the volume of the ovaries decreases by approximately 2 times. The outer contour becomes lumpy, the structure becomes more dense. The stromal apparatus begins to predominate, the number of follicles gradually decreases. This process is physiological and is called involution. It is possible to preserve single follicles for 5 years after the last menstruation. If during menopause, during preventive examinations, cyst-like inclusions are detected, then they must be dynamically monitored, and if they increase, they must be promptly removed.
At this time, hyperplasia (increase in size) is possible, accompanied by clinical manifestations - obesity, lability of blood pressure, diabetes mellitus. It is explained by increased production of androgens by the ovarian stroma.
Important. In contrast, there is also atrophy with pronounced fibrosis. In this case, they are quite difficult to detect during an ultrasound or MRI of the pelvic organs against the background of intestinal loops.
Types of treatment for ovarian pathologies
Cauterization
This is a new and quite popular method of treating ovarian diseases.
The principle of operation is laparoscopic access to the organ and with the help of a special device, cystic formations are removed, which not only disrupt the woman’s hormonal levels, but also lead to pain.
The advantage of this type of treatment is the low traumatic effect on tissue, as well as the rapid rehabilitation of the woman.
With the help of ovarian cauterization, it is possible to quickly achieve pregnancy. But at the same time, the risk of recurrence of cystic changes in the ovary remains high.
Resection
This is the process of partially removing ovarian tissue. This usually occurs during apoplexy or removal of space-occupying formations. It can be performed either by laparotomy or laparoscopic access.
In this case, the method is more traumatic, since it captures not only the affected, but also healthy tissue.
As a result, a large scar is formed and the woman’s follicular apparatus is lost. But the advantage of this method is the low percentage of possible complications and relapses. Recovery usually occurs without any significant disturbances in well-being.
Removal
This is a surgical intervention with complete removal of the organ and ligation of the vessels involved in its blood supply. In this case, this is done in case of extensive damage, when saving the tissue is either impossible or does not make sense.
At the same time, the process is quite complex, and the woman’s rehabilitation is also difficult. This is due to extensive intervention, as well as hormonal imbalance, which, as a rule, occurs suddenly.
In the future, maintenance hormone replacement therapy may be required.
Folk remedies
Various folk remedies are used to treat ovarian diseases, and the forms of use are very different.
Hog queen
This is one of the most common medications used in gynecological practice.
Its spectrum of action is quite wide and the onboard uterus can be used for various ovarian diseases:
- Unlike many other herbs, it is able to normalize the disrupted menstrual cycle due to hormonal imbalance.
- In addition, it copes with inflammatory processes or space-occupying formations, including malignant ones.
Used in the form of decoctions or tinctures.
Recipe and instructions for use:
- For the decoction, take 30 grams of dry boron uterus grass per 300 ml of water at high temperature, but not at a boil. Leave the resulting mixture until it cools. Subsequently, it is filtered and consumed internally. The decoction is drunk in small courses for no more than 20 days.
- The infusion is prepared at the rate of 10 grams per 100 ml of vodka. The tincture is left for 3 weeks in a dark place. Use no more than 30 drops.
- During menstruation, the course is stopped. In most cases, the duration of therapy should be at least 3 months, especially for dyshormonal pathologies.
Red brush treatment
This medicinal plant effectively fights such ovarian diseases in women as inflammatory processes, hormonal disorders, cysts of various origins, as well as infertility.
That is why this plant is widespread in gynecological practice.
Recipe and instructions for use:
- The decoction is prepared from the ratio of 10 grams of dry herb per 100 ml of water. Fill with hot water and leave until completely cooled, consumed in small portions several times a day. The course is also long; for diseases such as infertility and chronic inflammation, it can be several months.
- In some cases, a tincture can be prepared ; for this, 100 grams of dry herb is poured into 500 ml of vodka or ethyl alcohol, after which the mixture is put in a dark, cool room for one month. Women with chronic or recurrent processes are recommended to constantly store the resulting mixture at home for a systematic course of administration. It should be used no more than 10-15 drops 2-3 times a day. Alcohol infusion may have restrictions on its intake.
Basil
This plant is famous for its beneficial properties; many experts recommend regularly including it in your diet for both men and women.
In gynecology, it is used for such ovarian diseases in women as corpus luteum cysts, polycystic changes in the ovaries against the background of dyshormonal disorders, as well as inflammatory chronic processes.
Can be used fresh as a food additive or by preparing a decoction.
Recipe:
- To do this, dry grass is poured into 100 grams of hot, but not boiled, water.
- The mixture is infused until it cools to room temperature, after which it is filtered and drunk. A fresh solution must be prepared each time for use.
- The frequency of use, as well as the time, can be any, but no more than three. You can drink at any time, regardless of meals.
Basil has the best healing properties when eaten fresh. During pregnancy, it should be consumed fresh with caution, especially during the first trimester, as well as in women with mass formations of the pelvic organs.
Licorice
This is an equally effective remedy in the treatment of ovarian pathologies in women. Copes with inflammation, as well as ovarian cysts.
The advantage of this plant is that it can be used both in cooked and dry form:
- To do this, just add a dry plant to food, for example, to a salad.
- To prepare the decoction, you need to mix 30 grams of dry herb with boiling water and leave for several hours. It is recommended to consume the resulting mixture no later than 30 minutes before meals; in the worst case, this can lead to heartburn or poor absorption of nutrients. Also, the course of treatment for ovarian diseases in women should average two weeks.
- In combination with licorice, you can also use wintergreen ; for this, an alcohol tincture is prepared from 50 grams of dry herb per 100 ml of vodka, after which the mixture is infused and consumed for a course of at least 15 days. Coltsfoot, as well as motherwort and chamomile with calendula, have worked well for inflammation and ovarian cysts.
Prevention of ovarian diseases
These are complex measures that will be aimed at preventing the occurrence of ovarian pathologies in a woman or possibly reducing the number of relapses:
First of all, this is regular visits to specialists, in particular a gynecologist.- If a woman or girl has a hormonal imbalance or cycle, treatment is required.
- Inflammatory diseases should be avoided. This requires maintaining control over sexually transmitted infections, as well as avoiding hypothermia or the appearance of foci of chronic infection.
- A woman also needs a plan for pregnancy , because its interruption leads to disruption of the ovaries.
- When a disease of the pelvic organs is detected, urgent and comprehensive treatment is necessary in order to prevent the development of complications or a possible chronic course.
- You also need to eat a nutritious diet of healthy foods and avoid the ingress of potential carcinogens into your food. A regime of rest and physical activity must be observed.
- Avoid staying in environmentally unfavorable areas.
Probability of pregnancy
Ovarian dysfunction is not a death sentence for women who want to have a child. Pregnancy is possible, but only with medication support. Preparation and attitude towards it must be especially attentive.
The duration of treatment is about 6 months and is carried out under the close supervision of a gynecologist-endocrinologist. The woman is prescribed a course of hormonal therapy aimed at restoring the ovulatory menstrual cycle. When the mature follicle reaches 18 mm, and the thickness of the endometrium is 8-10 mm, the woman is injected with hCG, which provokes ovulation. Ovulation is monitored using ultrasound of the follicles, basal temperature measurements and blood tests.
According to statistics, therapy is successful for 90% of women and it is possible to achieve conception. Further pregnancy is carried out under careful supervision.