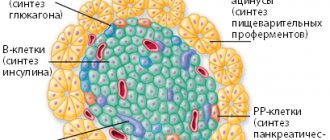
Insulin acts as the most important hormone produced by the pancreas from the cells of its tail. The purpose of insulin is to control blood sugar levels based on active metabolism.
When the hormone malfunctions, glucose levels begin to rise, resulting in a person developing diabetes mellitus. To maintain their health, a sick person must follow a diet and carry out the necessary procedures.
These procedures involve the regular use of drugs based on a specially developed laboratory method of insulin. Today there are a large number of varieties of this medicine. Therefore, you should understand what types of insulin exist, how they differ from each other and how they work.
General information about the hormone
As we have already noted, insulin is a hormone that affects metabolic processes in the body; without its participation, these processes are disrupted, which leads to irreversible consequences, as a rule, diabetes mellitus develops. When the production of the hormone is disrupted, the sugar level rises, and when it rises to a critical level, a person develops signs of hyperglycemia, which is dangerous by the development of coma.
To maintain normal levels, patients are prescribed replacement therapy. Depending on the type of diabetes, patients are forced to take tablets or injections.
Important. Due to its peptide nature, a critical deficiency of the hormone cannot be resolved with food.
The numerous functions of the hormone are as follows:
- facilitates the penetration of sugar through cell membranes;
- activates enzymes that promote glucose oxidation (glycolysis);
- enhances the production of glycogen substances by liver cells, as well as adipose and muscle tissue (the energy reserve in the body formed due to the entry of glucose into the blood);
- stimulates fat and protein metabolism;
- weakens the effect of components that promote the breakdown of fats and glycogen.
The above functions are basic, but insulin also has additional capabilities:
- improves the absorption of amino acids by cellular tissue;
- increases the amount of magnesium and calcium entering cellular tissue;
- has a beneficial effect on the process of ester production.
The pancreas is responsible for the production of an important hormone.
Thanks to its important function - transporting sugar from the blood to the liver cell tissue, muscle and fat tissue, insulin contributes to the formation of additional energy in the body. It is the only hormone that helps regulate glucose concentrations in the body.
Important. Insulin plays a significant role in the life of the whole organism, which is expressed by the regulation of all metabolic processes. Thanks to its effect, the resulting glucose is processed into the energy substance glycogen and deposited in liver cells, fat and muscle tissue. The body thus receives an additional supply of energy and maintains a balance of saturation with various nutrients.
Let's now turn to our topic; insulin, due to its important functions, is necessary for the body. With the development of diabetes mellitus, its deficiency should be compensated for by replacement therapy.
Injections are prescribed to patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. Modern pharmaceuticals have developed a huge variety of drugs whose active substance is insulin.
Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2: relationship with insulin
In type 2 diabetes, there is a change in the normal production and functionality of insulin. Most often, the disease manifests itself in elderly people who suffer from obesity. With excess accumulation of fat in the body, the number of lipoproteins in the blood increases. This helps reduce cell sensitivity to insulin. As a result, the body begins to produce it in smaller quantities. The level of insulin in the blood drops, and the level of glucose begins to rise, because there are not enough hormones to utilize it.
If your blood glucose level is elevated, then you need to start following a diet and get rid of fat deposits. In this case, the risk of developing diabetes mellitus is reduced, which means a person can avoid serious health problems.
Type 1 diabetes develops differently. With this type of disease, there is a lot of glucose around the cells, but they cannot absorb it, since there is not enough insulin in the blood for these purposes.
As a result of such disorders, the following pathological changes begin to occur in the body:
- Fat reserves from the reserve are not utilized in the Krebs cycle, after which they are sent to the liver. There, fat takes part in the formation of ketone bodies.
- The higher the blood glucose level, the more thirsty a person is. At the same time, sugar begins to be excreted in the urine.
- Carbohydrate metabolism begins to occur along the sorbitol pathway, which is an alternative pathway. This entails negative consequences, since excess sorbitol begins to accumulate in the tissues. When it accumulates in the eye lens, a person develops cataracts, when it accumulates in nerve fibers - polyneuritis, and when it accumulates on the walls of blood vessels - atherosclerotic plaques.
The body tries to prevent these disorders and begins to break down fats. This entails an increase in triglycerides in the blood and a drop in good cholesterol. Hyperlipidemia contributes to a decrease in immunity, an increase in fructosamine and glycosylated hemoglobin in the blood, and a change in its electrolyte balance. The person begins to feel worse and worse, while he is constantly tormented by thirst and urinates frequently.
Diabetes mellitus affects the functioning and condition of all internal organs, which explains the variety of clinical manifestations of the disease.
Classification of insulin
The classification of insulins depends on:
- origin and species characteristics;
- number of components;
- degree of purification;
- duration.
First of all, we note that such drugs, depending on their origin, are divided into two types:
- Obtained artificially . They are created in laboratory conditions by combining the main substance with additional components.
- Obtained naturally . The hormone is obtained from the pancreas of animals or human E. coli cells.
Attention. Artificially produced insulins are most often used in practice, since components that can cause an allergic reaction in humans are replaced using genetic engineering.
An allergic reaction may occur to artificially produced insulins.
Let's take a closer look at all types of insulin.
Types of insulin by origin
Taking into account the classification of the drug, the doctor selects the optimal treatment regimen for the patient.
Based on their origin, the following types of insulin are distinguished:
- Insulin obtained from the pancreas of cattle . Animal insulin, unlike human insulin, has three amino acids that can cause a severe allergic reaction in humans.
- Porcine insulin . The structure of such a hormone is close to the structure of human insulin, with the only exception of one amino acid present in the protein chain of the animal.
- Whale insulin . This type is used quite rarely in practice, since its structure differs even more from the hormone of large horned animals.
- Analogue of a human hormone . This hormone is produced by two methods. The first uses human E. coli. In the second method (genetic engineering), the “unfavorable” amino acid contained in the pig hormone is replaced.
The best drugs are those produced by genetic engineering.
By component
Depending on the components, drugs are divided into two types.
Table No. 1. Classification depending on the content of components:
| Type of insulin | Description of composition |
| Monotype | These are drugs based on insulin obtained from one type of animal, for example, only a bull or only a pig. |
| Combined type | The drug contains simultaneously several extracts of animal insulin, for example, bovine and pig combined. |
By degree of purification
The hormonally active substance obtained from the pancreas of an animal, whale or human E. coli needs to be purified.
Depending on the degree and method of purification, the following types of insulin are distinguished:
- Traditional drug. Using acidic ethanol, the substance is diluted to a more liquid state. After filtration, the substance is salted out and crystallized. This purification method is not perfect, since after all laboratory manipulations many impurities remain in the drug.
- Monopeek. This method goes through two purification phases. The first phase takes place in the traditional way, after which in the second phase the substance is filtered using a special gel. Impurities remain, but their number is several times less than with the first cleaning method.
- Monocomponent. This method differs in that the laboratory creates conditions for deep cleaning using molecular sieving and ion exchange chromatography. This cleaning method is the most advanced; such preparations are more suitable for the human body.
Interesting. Tablet medications for diabetes are an indispensable part of the treatment of diabetics with the development of diabetic foot. Regular use of tablets can reduce swelling of the limbs and even reduce the risk of developing a dangerous pathology - gangrene.
Tablets for insulin-dependent diabetics help avoid the development of gangrene in diabetic feet.
When prescribing injections to children and the elderly, you should be extremely careful and careful, since at this age patients are prone to adverse reactions. That is why knowing what types of insulin there are and their effect is very important not only for medical workers, but also for the patients themselves.
By speed of impact
According to the speed of action, drugs are divided:
- ultra-short;
- short;
- average;
- long;
- extra long lasting.
Each of the above types of insulin has a different effect on the human body, which must be taken into account when calculating the injection dose.
Side effects
The most common and most common side effect in people taking insulin is lipodystrophy . This is a pathology of the tissue where the patient receives the injection. There are cases when taking insulin in a patient causes hypoglycemia, which should be immediately eliminated with chocolate or a glass of juice. These side effects occur when you take pure insulin (in its most purified form). If a person takes insulin in a less purified form, he should be prepared for allergic reactions.
Insulin is a very important substance that is necessary for a person to live a full life. And when the body itself cannot produce it on its own, a person needs an artificial supply. This is a very important point, because each person needs his own dose of insulin. In this case, consulting a doctor is simply mandatory, otherwise you risk harming your health.
For diabetics, all of the above information is very important, because knowledge about the correct use of these drugs, their origin, methods of maintaining sugar levels and the duration of action will help many people choose their insulin.
Return to content
Factors influencing the action of insulin
The action of insulin also depends on many indicators, such as:
- injection sites (subcutaneously, into a vein, into a muscle);
- body temperature (lower body temperature slows down the effect of the drug, increased body temperature, on the contrary, enhances it);
- massage movements in the injection area increase the rate of absorption of the drug;
- individual tolerance of the drug.
If we talk about the injection site, this is an important factor when taking into account the effect of the drug:
- abdominal area – the hormone is absorbed in 90% of the received volume of medicine;
- extremities area – up to 70% of the received volume of the drug is absorbed.
When calculating the exact dose required to compensate for the carbohydrates entering the body, the patient must take into account factors such as: taking a hot shower, exposure to the sun, drinking hot tea, etc. They contribute to a sharp decrease in sugar levels, which can manifest as attacks of hypoglycemia (dizziness, nausea, confusion, weakness).
After the injection, a light massage is recommended to remove the accumulation of hormone in one place.
Important. After an injection, a reserve of hormone can form in the muscle tissue, which will manifest itself only after a day. Therefore, diabetics may experience hypoglycemia in some cases. Patients should always have with them foods rich in fast carbohydrates, for example, lumps of sugar, buns, a sweet drink, as they can quickly replenish the lack of sugar in the blood.
Common drugs
The most common ICD is called:
- insuman rapid,
- actrapid,
- actrapid NM,
- actrapid MS,
- humulin regular,
- Iletin regular, etc.
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to use large doses of ICD.
For a better effect and to avoid allergic reactions, this drug should be administered in smaller doses, but more often. Intermediate-acting insulin has the abbreviation ISPD . It is prescribed for the same diseases as the above option. This also applies to other types of drugs. The most common ISPD drugs are called:
- insuman basal,
- Protafan, etc.
Attention!
This type of insulin can be mixed, but only with similar short-acting drugs in any ratio. It is desirable that the additional drug that is mixed with ISPD be based on neutral protamine Hagedorn (I-NPH). Be careful when mixing this type of insulin with long-acting drugs, because this should not be done. The most common IDD drugs are called:
- humulin ultralente,
- glargine,
- ultratard nm.
Attention!
Long-acting insulin preparations can be mixed with short-acting (simple) acting insulin preparations. Such mixtures are sold in ready-made form in almost all pharmacies. Their ratios can be very different (10:90; 20:80...50:50). This makes it easier for older people with poor vision to take the drug and administer the required dosage as accurately as possible. Such insulins begin to act soon and the effect lasts quite a long time. Well, the most commonly purchased ultra-fast acting insulins have the following names:
- Humalog,
- Apidra,
- Novolog.
Return to content
Ultra-short insulin
This type of insulin is the fastest acting of all. Its action begins immediately after subcutaneous administration; after 1 hour, the maximum accumulation of the active substance is noted in the body. Moreover, its effect also ends quickly, that is, 3-4 hours after the injection.
The video will tell our readers in more detail what the insulin injection technique should be. By following the rules for administering the drug, a diabetic will eliminate possible consequences such as the development of hypoglycemia.
Ultra-short-acting insulin injections should be given immediately before meals or immediately after. It should be noted that the time of day does not matter.
The onset of action of the ultra-short drug is a few minutes after the injection. The patient feels the maximum effect within an hour. The duration of exposure occurs during the period of food digestion.
In this case, you should pay attention to the pattern: as the dose of the drug increases, the period of exposure increases, but within the limits specified in the instructions. In fact, the effect of the fast hormone lasts up to 4 hours with an administered dose of insulin up to 12 units.
Attention. It is strictly not recommended to administer insulin in a dose exceeding 20 units. With this option, the risk of hypoglycemia attacks increases, because excess hormone is not absorbed by the body and negatively affects the functioning of the body.
Side effects may occur in the patient if the dose of the medicine was incorrectly calculated. It must be said that when calculating the dosage, the doctor conducts a full examination of the patient’s body; the sugar level must be measured using a special algorithm. If the dose of insulin is calculated correctly, then there is no need to be afraid of the body’s reaction.
Attention. One of the most important disadvantages of this method of therapy is the unpredictability and instability of the drug's response to glucose levels. Due to the high potency of the medication, blood glucose levels may drop sharply. 1 unit of ultra-short-acting insulin reduces sugar concentration 2 times faster than the same dose of other types of insulin.
In what cases are ultra-short insulins recommended?
Due to the characteristics of the body, hormonal metabolism can occur quite rapidly, which in frequent cases, both insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetics may experience morning attacks of hyperglycemia. This syndrome is not uncommon and cannot be eliminated, so doctors recommend early morning injections of ultra-short insulin in a dose of up to 6 units.
Also, these types of drugs are used with food, as they have a super-rapid effect. However, ultra-short types force the patient to take injections several times a day, imitating natural hormonal synthesis in the pancreas (up to 6 times a day, depending on the number of meals).
Another important circumstance in which these types of drugs are used is the patient’s pre-comatose or comatose state, when the action of rapid insulin is able to compensate for the critical deficiency of the hormone.
Short insulins can compensate for a critical deficiency of the hormone.
Ultra-short-acting insulin preparations
Table No. 3. The most common drugs with ultra-short effects:
| Name | Type of insulin | Indications for use |
| Natural (analogue of human hormone) |
|
| Analogue to human hormone. Produced on the basis of insulin aspart. | pregnancy and breastfeeding. |
| Recombinant analogue of human hormone. | only children over 6 years of age and adults (contraindications – pregnancy and lactation). |
Ways to Maintain Insulin Levels
This effect can be achieved if you use a pump. It is a kind of apparatus that ensures a constant supply of the drug to the human body. Some doctors nicknamed this device an “artificial pancreas.”
The principle of operation of the pump is to supply insulin, which has two modes:
- Basal (background) mode. It is needed to replace constant insulin injections. In one hour, the pump independently administers a certain dose of the drug.
- The bolus regimen is characterized by a one-time administration of the substance only in the case of a meal (when the patient takes a certain amount of carbohydrates). This process is very similar to a one-time injection with a syringe.
All pumps differ in the speed of insulin delivery. Pumps from different companies can deliver the drug at different speeds (from 0.01 to 0.05 units/hour). It is very important to individually select a pump for each case.
You can maintain the desired insulin level not only with the help of a pump - syringes and syringe pens help many people. Their advantage over pumps is their price. The patient injects insulin intramuscularly with a syringe and then throws it away. Syringe pens are reusable.
Return to content
Intermediate- and long-acting insulins
Doctors classify intermediate-acting insulins as drugs with long-lasting effects on the body. The duration of the effect of the drug is from 12 hours.
Often, diabetics are prescribed combination therapy, including short- and medium- or long-acting agents. At the same time, medium ones are recommended for the night, as they can prevent high jumps in glycemia.
The onset of action is noted after 4-5 hours, and the maximum accumulation of the active substance is achieved after 8 hours. The patient only needs 2-3 injections per day to compensate for the lack of a daily dose of the hormone.
Medium- and long-acting insulin preparations
Table No. 5. Common intermediate- and long-acting drugs:
| Name | Type of insulin | Indications for use |
| The basic substance of the drug is glargine. Analogue of human insulin. | adults and children over 6 years old. |
| The basic substance of the drug is insulin detemir. Analogue of human hormone. |
|
| The basic substance is insulin glargine. An analogue of a human hormone, produced by recombination of the DNA of Escherichia coli bacteria. |
|
Causes of increased and decreased insulin in the blood
The following pathologies can lead to increased insulin levels in the blood:
- Insulinomas are tumor formations of the islets of Langerhans. They produce insulin in large quantities. At the same time, on an empty stomach the level of glucose in the blood will be reduced. To detect a tumor, doctors use a formula to calculate the ratio of insulin to glucose. In this case, the level of insulin in the blood is divided by the level of glucose in blood taken on an empty stomach.
- Early stage of type 2 diabetes mellitus. As the disease progresses, insulin levels will decrease and glucose levels will increase.
- Excess body weight. Sometimes it is the increased level of insulin in the blood that provokes the development of obesity, as a person’s appetite grows, he overeats and accumulates fat. Although it is not always possible to track the cause of obesity.
- Tumor lesion of the pituitary gland (acromegaly). If a person is healthy, insulin helps lower glucose levels. This, in turn, promotes the production of somatotropin. When acromegaly develops, such production does not occur. This feature is used when conducting stimulation tests aimed at determining hormonal balance. When insulin is administered in the form of intramuscular injections, the level of somatotropin does not increase either one or two hours after the injection.
- Hypercorticism. With this disease, there is an increased production of glucocorticoids in the body, which suppress the processes of glucose utilization. As a result, its values remain elevated despite high levels of insulin in the blood.
- Muscular dystrophy. It develops against the background of metabolic disorders, and the insulin level will be increased.
- The period of pregnancy can lead to an increase in insulin levels if a woman overeats.
- Hereditary diseases associated with fructose and galactose intolerance.
If a patient in a hyperglycemic coma is given an injection of fast-acting insulin, this will bring him out of this state. Insulin injections are also used to treat patients with diabetes, since its administration helps reduce blood glucose levels. In this case, the level of insulin itself will be increased in a person.
You can reduce insulin levels if you focus your efforts on treating the underlying disease that leads to disturbances in metabolic processes.
Low insulin levels are observed in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this case, non-insulin-dependent diabetes causes a relative decrease in insulin in the blood, and insulin-dependent diabetes causes an absolute drop in the hormone in the blood. Serious stress, physical activity and other factors that have an adverse effect on the body can also lead to its decrease.
Biphasic combined
Biphasic combined insulins are drugs that combine short-acting and long-acting insulins in certain combinations. Using these types of drugs, the patient limits the daily number of necessary injections by 2 times.
Table No. 6. Combination drugs:
| Name | Type of insulin | Features of application |
| Semi-synthetic insulin | Subcutaneous administration only, prescribed for type 2 diabetes (if indicated). |
| Semi-synthetic insulin | Injections are given 1 to 2 times a day 30 minutes before meals. The drug is administered only subcutaneously. |
| Produced using genetic engineering method | It is allowed to administer insulin both subcutaneously and intramuscularly. Intravenous administration of the drug is prohibited. |
| Produced by genetic engineering | Injections are carried out only subcutaneously. Activation of the substance begins 30 minutes after injection. The duration of action of the drug is up to 20 hours. |
| The basic substance of the drug is insulin aspart. | It begins to act 15-20 minutes after the injection. The effect lasts up to 1 day. It is administered only subcutaneously. |
Instructions for using insulin
Specifics of insulin administration
Insulin is administered by subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous injection. Only short-acting drugs can be injected into a vein for certain medical indications - hyperglycemic coma or pre-comatose state.
Insulin in suspension form is used exclusively intramuscularly. Injecting the drug into a vein is prohibited! Before administration, the insulin ampoule is warmed to room temperature for faster absorption. For insulin injections, a plastic syringe is used, which has virtually no “dead space”, unlike glass instruments. A set of the drug in a plastic syringe ensures that the exact dosage is maintained.
Experienced diabetics prefer syringe pens into which cartridges with insulin solution are installed. The main advantage of these syringes is that the solution does not need to be drawn up before each injection. They can be used for injections of short-, medium- and combined-acting drugs. The needles of insulin syringes are small in size - length 8 -12 mm, thickness 0.3 - 0.4 mm. These features help minimize pain during injections.
Insulin injection areas
With the question: “Where should I inject insulin?” Patients with a newly diagnosed diagnosis and relatives of patients turn to an endocrinologist. The fastest way for the hormonal drug to enter the bloodstream is when administered subcutaneously in the area of the anterior abdomen. The outer upper arm and anterior thigh area are suitable for subcutaneous injections, but absorption is slower here. The slowest absorption occurs when insulin is injected into the subscapular region or into the subcutaneous fat of the buttocks.
The preferred area for subcutaneous insulin injection depends on the type of drug. Short-acting solutions are transparent. They must penetrate the blood quickly, so the front surface of the abdomen is suitable for injections, except for the area around the navel. Long-acting insulin is produced as a cloudy solution. Its slow absorption allows for administration into the surface of the thigh and buttocks.
The patient must follow a strict sequence of changing injection sites. A specific area must correspond to a specific time of day. A morning injection of short-acting insulin can be performed in the abdomen, an afternoon injection in the thigh, and an evening injection subcutaneously in the buttock area. This rule is due to the need to calculate XE (bread units) for different times of the day.
Rules for subcutaneous insulin administration
- Check the validity period of the drug, type, dosage on the bottle.
- Wash your hands with soap and treat the injection site with an antiseptic solution.
- Heat the bottle with the solution in your hands to the optimal temperature. Do not shake the preparation under any circumstances to prevent the formation of air bubbles.
- Treat the bottle cap with an alcohol solution.
- Air is drawn into the syringe as much as the required units of the drug. Release it into the bottle and collect the required amount of insulin (in units). Considering the features of the syringe, you can draw a little more solution, about 10 units.
- Adjust the dose by fixing the syringe at eye level.
- In order to remove air bubbles, lightly tap the body of the syringe.
- When injecting the drug, count to 5 or 10 and remove the needle. Massaging the injection site is strictly prohibited! Massage promotes rapid absorption, and too active absorption can cause hypoglycemia.
It is not recommended to treat the surface of the skin with an alcohol solution. Ethyl alcohol destroys insulin, which after its administration can cause lipodystrophy. Before injection, it is enough to wash and dry the corresponding area of skin with a napkin, if necessary. In certain cases, insulin is administered through clothing.
For the injection, choose a place 2.5 cm from the navel or 3 cm from the shoulder, thigh, upper gluteal region. If the injection site is the shoulder or thigh, use your thumb and index finger to form a triangle from the skin, without grasping the muscle. The needle is inserted into the base of the formed triangle with an upward cut at an angle of 45°. It is important to ensure that the needle does not enter the muscle layer, since absorption of the drug here occurs much faster than from subcutaneous fat. For an injection in the stomach or buttock, it is not necessary to form a fold. In this case, the needle is inserted at an angle of 90°
The optimal time for insulin injections is 30 minutes before meals. This is due to the fact that the drug is absorbed into the blood within an hour. The best time to eat is 15-30 minutes after the injection.
How to choose the best insulin?
It is impossible to give a general answer to this question. The selection of insulin, the selection of dosage and the method of its administration is carried out by the treating endocrinologist during the patient’s hospitalization. This takes into account the clinical symptoms of the disease, the severity of the patient’s condition, the time of appearance of signs of a decrease in glucose levels, and the duration of the glucose-lowering effect.
Rules for calculating the dose and administration of insulin
For each patient, the dose of the drug is selected individually. Short-acting insulin begins to act very quickly, but the drug effect lasts for a short time. The solution can be administered both subcutaneously and intramuscularly. In some cases, intravenous injections are indicated.
Short-acting insulin can be injected once or several times a day. The number of injections depends on the clinical picture of diabetes. The injection is given 15-20 minutes before a meal. After this time, a sugar-lowering effect begins to appear, the peak of which is recorded after 2 hours. Its duration is approximately 6 hours.
Scope of application of short-acting insulin:
- In a hospital setting.
When selecting the required therapeutic dose in case of hyperglycemic coma, precoma. The precomatose state is urgent to change the patient's insulin activity.
- In combination with a course of anabolic drugs.
The dosage in this case is 4-8 units 1-2 times a day. The amount of insulin is minimal and cannot cause any serious consequences.
Long-acting insulins are divided into several types, depending on the duration of the effect:
- Semilong.
- Long.
- Ultralong.
Injections of long-acting drugs are performed much less frequently, due to the fact that the therapeutic effect lasts from 10 to 36 hours.
The long-acting drug is available in the form of a suspension. It is injected only subcutaneously, intramuscularly. Intravenous administration of long-acting insulin is prohibited. Due to its pharmacological characteristics, this type of insulin is not used during coma or precoma.
When selecting a drug, the doctor takes into account the time of maximum glucose-lowering effect. It is at this time that you need to eat. If necessary, mixing two long-acting drugs in one syringe is allowed.
The combined administration of long-acting and short-acting insulin is necessary when the patient needs to maintain optimal sugar levels for a long time. A combination of drugs with different effects is used to quickly normalize blood glucose. Long-acting insulin is usually recommended for morning injections. The injection is given in the morning, before breakfast. In some cases, long-acting medications can be given at other times of the day.
Patients with diabetes must adhere to a special diet. This requirement is mandatory when treating with insulin. The calorie content of food depends on the patient’s weight and lifestyle. If the patient is underweight, but at the same time there is daily physical activity, at least 3000 kcal per day should be supplied to the body along with food. Excess weight and a sedentary lifestyle means consuming no more than 1700-2000 kcal.
How to draw medicine into an insulin syringe?
Correctly drawing one type of insulin into a special syringe is not particularly difficult. To do this, you need to do several sequential steps:
- Fill the syringe with air until the required number of units of the drug is marked.
- Puncture the cap of the bottle and release air from the syringe inside.
- Holding the bottle upside down at eye level, draw a little more than the required amount of the drug into the syringe.
- In order to remove the formed air bubbles, lightly tap the syringe barrel with your finger and move the piston to the desired mark.
To correctly draw insulin from the bottle, a puncture must be made in the center of the stopper, preferably with a needle from a regular syringe. All subsequent steps are performed with an insulin syringe, inserting a needle into the previously made puncture.
Insulin dose calculation
According to the rules for calculating the drug, the daily dosage should be no more than 1 unit per kilogram of the patient’s weight. The therapeutic dose depends on the type of disease and the characteristics of the clinical picture.
For type I diabetes, the following recommendations have been developed:
- 0.5 IU per 1 kg - in the case of a newly diagnosed disease;
- 0.6 units per 1 kg - with compensation within 12 months;
- 0.7 units per 1 kg - with unstable compensation;
- 0.8 units per 1 kg - for decompensation;
- 0.9 IU per 1 kg - complicated course of the disease, phenomena of ketoacidosis;
- 1.0 units per 1 kg - for women in late pregnancy.
In order not to make a mistake in dosage calculations, you can consider one of the examples. If a patient needs to be administered long-acting insulin at a dose of 0.6 units with a weight of 75 kg, then the volume will be 0.6 x 75 = 45. Half of the resulting amount is taken, rounded down, i.e. the dose is 20 units. In the morning, before breakfast, 12 units are administered, before dinner - 8 units.
Short-acting insulin with the same parameters (weight 75 kg, dose 0.6 units) is calculated according to the rule: 0.6 x 75 = 45, 45 - 20 = 25. For a morning injection, take 9-11 units, before lunch - 6- 8 units, in the evening - 4-6 units.
Differences between short-acting and long-acting insulins
Short- and long-acting insulins have distinctive features that are taken into account when calculating the daily dose of the drug.
Table No. 7. Distinctive features of short- and long-acting drugs:
| Short acting insulin | Intermediate- and long-acting insulin | |
| Injection site | Injections are performed subcutaneously in the abdominal area. Such drugs are distinguished by their rapid effect, so injections are given immediately before meals (ultra-short) or 15-20 minutes before meals (short). | Due to the fact that drugs of this type are absorbed more slowly, injections are carried out intramuscularly, in the thigh area. |
| Time mode | Injections are given before each meal. Time is determined by duration:
| Injections are made systematically in the morning and evening at the same time. A short-acting medicine is administered together with the morning dose of medium and long-term effects. |
| Relationship with food intake | After administering a dose of short (ultra-short) insulin, food must be taken. Lack of food intake leads to the development of an acute attack of hypoglycemia. | Intermediate- and long-acting insulin is not associated with meal timing. |
As we can see from the table above, insulins have different effects and main distinctive indicators, which must be taken into account by the doctor when calculating the daily dose, and by the patient when calculating the single dose of the drug.
Why do we need many different types of insulin?
Many types of insulin are produced and used because it is impossible to get by with just one drug. Different drugs have opposite properties that cannot be combined together. Almost all diabetics, except those with mild type 2 diabetes, need to use two types of insulin at the same time:
- Extended
- Fast.
A person should have some concentration of insulin in his blood around the clock, at least a small one. The main thing is that insulin is still needed around the clock, continuously, even during sleep, even when fasting. If there is no sugar in the blood at all, sugar increases greatly and the body begins to destroy itself. This is called diabetic ketoacidosis.
This situation is deadly. If left untreated within a few hours, the person will lose consciousness and may die. That is, there must always be a background concentration of insulin so that ketoacidosis does not occur and you do not have to call an ambulance.
In addition to this, when you eat a food, it spikes your blood sugar almost immediately. Especially if you ate carbohydrates, but also proteins. After eating, sugar rises quickly and strongly. It is advisable to bring it back to normal as quickly as possible, otherwise it will damage the kidneys, eyes and other organs.
To suppress a spike in sugar after a meal, a large dose of insulin is required immediately. Where does it come from? In healthy people, the pancreas stores insulin in advance to inject it into the blood during meals. In diabetics, insulin production is insufficient or completely absent. That is, there is no way to accumulate supplies and prepare for meals. Therefore, you need to take insulin injections that cover food.
The goals of diabetes treatment are:
- It is necessary to continuously maintain the background level of insulin in the blood.
- It is also advisable to prevent sugar levels from rising after meals.
- If your blood sugar has jumped, you need to bring it back to normal as quickly as possible.
To achieve these goals, insulin drugs must have opposite properties. On the one hand, you need potent insulin that starts working quickly, preferably immediately after the injection. On the other hand, insulin is required, each injection of which will act smoothly and for a long time, preferably from morning to evening. And it is especially important that it lasts all night and that you do not have to give additional injections in the middle of the night, because this is very inconvenient. Read more about how to reduce sugar to normal in the morning on an empty stomach.
Fast onset and long-lasting action are mutually exclusive properties. They cannot be combined in one type of insulin. Either one or the other. Therefore, there are different types of insulin, which are discussed in detail below.
It will also be useful for you to familiarize yourself with the professional terms of endocrinologists.
- The basis is the background concentration of insulin in the blood, which is relatively small.
- A bolus is a fast-acting insulin, usually short or ultra-short, which is used with meals or when you need to quickly reduce high sugar levels.
- Basal-bolus insulin therapy is when a diabetic uses two insulin medications at the same time to achieve two goals.
Doctors love to use these terms when they want to confuse patients and squeeze more money out of them. To do this, it is advisable for doctors to appear smarter than they are. However, in reality the meanings of the terms are not complex. They can be understood even by people without medical education.
Basis-bolus insulin therapy - this means that one insulin preparation is not enough, but two must be used, otherwise it is impossible to achieve good control of diabetes. This is true for most diabetics, except those lucky ones who have the mildest form of type 2 diabetes.
Rules for subcutaneous administration
The administration of insulin subcutaneously has some important features that every insulin-dependent diabetic should know about. First of all, it should be noted that beginners make a big mistake and direct the needle deep under the skin, which leads to the drug entering the muscle, as a result of which the medicine does not have the necessary effect.
Thanks to modern medicine, the task of giving an injection is made easier by short insulin needles. Such needles are thinner and have a length of 4 to 8 mm. With their help, you do not have to worry about the medication getting into the muscle tissue.
Below are the rules for administering an insulin drug:
- The medicine is administered only subcutaneously, trying to insert the needle into the fatty tissue. But, if the skin at the injection site is thin, then it is necessary to make a fold: two fingers (thumb and index or thumb and middle) grab a section of skin and slightly compress it. Common injection areas are the abdomen, upper and lower extremities.
- When using a needle less than 8 mm in length, the needle angle should be 45 degrees. It is important to note that if the injection is performed in the abdominal area, it is not recommended to use short needles.
- When using a syringe pen, you need to know that the needle in it is disposable and needs to be changed every time after use.
- Before giving the injection, you should wash your hands well with antibacterial soap. The injection site is not wiped with alcohol, as it contributes to the destruction of the active substance. If you decide to wipe the injection area, you need to wait until the alcohol has completely disappeared.
- If necessary, make a fold of leather.
- With a quick jerk, insert the needle at an angle of 45 or 90 degrees.
- Inject the drug by slowly pressing the syringe plunger.
- The needle must be removed from under the skin after a 10-second break. This is necessary to ensure that the injection liquid does not leak out.
The rate of absorption depends on the area of injection, as well as the type of drug itself.
Depending on the length of the needle, insulin is injected under the skin at a right angle or at an angle of 45 degrees.
Our readers will be able to learn how to administer insulin; the video will provide detailed explanations on this issue.
Important. Before giving the injection, you need to make sure that no air gets into the syringe and needle. If this is allowed, the drug will not have the desired effect, and this can lead to attacks of hypoglycemia.
What is a syringe pen and how to use it correctly?
A syringe pen is an injector used for subcutaneous administration of various types of medications, in particular insulin. This instrument was invented back in 1983.
Today, syringe pens are produced by a huge number of different pharmaceutical companies. The instrument got its name due to its similarity to a regular ballpoint pen. Its convenience lies in the fact that the patient can independently inject himself and dose the medicine correctly.
Benefits of a syringe pen
With the help of a syringe pen, a diabetic will be able to independently calculate the required number of units of medication. The instrument is designed in such a way that with each injection of 1 unit of insulin a characteristic click is produced, and the injection itself is done with one press of a button.
Syringe pens are equipped with needles, which are included in the package, and in the future they can be purchased in pharmacies separately from the instrument itself. This is a very convenient design that can be easily carried with you and used if necessary.
Syringe pens are equipped with a special push-button dispenser, which allows you to regulate the amount of the administered drug.
Rules for using a syringe pen
The syringe pen package includes:
- medicine cartridge;
- syringe pen body;
- automation used as a piston;
- needle;
- needle cap.
In addition, the design is equipped with a dosing mechanism and an injection button.
Using the tool is quite simple:
- remove the syringe from the case and install the needle on it, then remove the cap from it;
- shake the medicine in the syringe;
- Click to count the required dose of medication;
- by pressing the injection button, release the needle from air;
- make a fold of skin and inject into the desired area (hold the button for 8-10 seconds, then release and release the syringe).
Important. The rate of absorption of the drug is affected by the temperature of the drug. Thus, at low temperatures the drug is absorbed more slowly than at higher temperatures. In addition, the speed of action slows down if the injection is given in the same area several times, since the accumulation of the hormone in one place slows down the absorption process. In such a situation, it is recommended to perform a light massage in the injection area.
We have provided our readers with an explanation on how to use an insulin pen, the video will give a clear example.
Disadvantages of using a pen
In addition to the great advantages of using pens, they have some disadvantages.
This:
- a syringe pen is a tool intended for reusable use, but which cannot be repaired;
- the cost of the design (depending on the manufacturer) is quite high, despite the fact that diabetic patients require at least 3 units;
- many manufacturing companies produce syringes with a non-replaceable cartridge, which leads to a constant need to replenish the number of pens;
- Patients using a syringe pen need to be more strict in their carbohydrate intake, since they do not have the ability to independently mix and change the number of insulin units, taking into account food consumption.
Despite all the advantages of syringe pens, their use for some is a labor-intensive and complex process, and some individuals even experience psychological pressure from performing an injection “blindly”.
Area of administration and absorption efficiency of the drug
As we mentioned above, there are 3 injection zones:
- stomach;
- upper limbs;
- lower limbs.
All these zones have varying degrees of absorption.
Table No. 8. Efficiency of insulin absorption in different injection zones:
| Injection area | Stomach | Outer part of arms (from shoulder to elbow area) | Front thigh | Spatula |
| Suction efficiency,% | 90% | 70% | 70% | 30% |
For clarity, let's present a diagram:
Efficiency of insulin absorption at various injection sites.
Attention. The highest absorption efficiency of the drug is observed in the abdominal area at a distance of 2 fingers from the navel.
It should be noted that it is not recommended to inject into the same area several times in a row; you should alternate injection sites. A second injection in one area can only be done after 14 days. In this case, the minimum distance between the first injection and the next one should be at least 2 cm.
Dose calculation
The daily dose of the drug is calculated only by the attending physician after a complete examination of the patient and laboratory tests.
The dose volume depends on many indicators, such as:
- patient's body weight;
- duration of the disease;
- type of diabetes and severity of pathology;
- presence of complications.
Table no. The daily requirement of a diabetic for insulin:
| Insulin requirement, units/kg | Course of diabetes |
| 0,5 | Diabetes was diagnosed less than 12 months ago |
| 0,8 | The patient has been suffering from diabetes for 1 to 10 years |
| 0,9 | The disease is more than 10 years old |
| 1 | With the development of ketoacidosis or various infections |
For clarity, let's present a diagram:
Daily requirement of a diabetic for insulin.
Important. When determining a patient’s daily need for short-acting insulin, it is important to take into account additional units of the drug to suppress carbohydrates consumed by a person, that is, the dose is calculated using a table of bread units. How many units are needed to cover 1 XE is decided by the endocrinologist, since each body is individual and reacts differently to treatment. For example, the dose of a hormone required by an adult may well be lethal for a teenager or child.
The approximate distribution of the daily dose is presented as follows:
- before breakfast and lunch – 2/3;
- before dinner – 1/3.
The daily dose is adjusted based on glycemic levels.
The patient independently monitors the sugar concentration using a glucometer, this happens as follows:
- 8 am;
- 2 hours after breakfast;
- 00;
- 2 hours after lunch;
- 00;
- 2 hours after dinner;
- 00;
- 3 a.m.
During the period of self-monitoring of glycemic levels, the daily dose does not change. If the patient experiences instability in sugar levels, the doctor changes the dosage of the drug and glycemic control is carried out again.
Rules for storing insulin
Such medications require strict adherence to storage rules. Thus, insulins of any type are stored in the refrigerator at a temperature no higher than 8 degrees Celsius.
Attention. Freezing medications is strictly prohibited; at low temperatures it loses its special functions. After defrosting, administering medications is strictly prohibited.
If, under the correct storage standards, the drug has changed its properties, for example, it has become cloudy, a sediment has appeared in the form of flakes or other impurities, then it is considered unsuitable for use. However, it is worth noting that long-acting insulins are often cloudy, which is not considered spoilage, the main thing is that no sediment appears in the mixture.
An open bottle (cartridge) should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 30 days. If this period has expired, the drug loses its medicinal properties and becomes harmful to the body.
Insulins should be stored in the refrigerator; at high temperatures the drug loses its properties.
Bottles (cartridges) should only be moved in special refrigeration chambers; if this is not possible, refrigerants such as helium or ice should be used. But it is important that the drug itself does not come into contact with these substances.
Attention. In Russia, as well as in the CIS countries, all patients diagnosed with insulin-dependent diabetes are registered with an endocrinologist. Such patients are provided with government assistance; insulin medications are provided to them free of charge.
Consequences in the absence of an injection
The consequences of the lack of systematic injections will depend on the severity of the disease and the patient’s lifestyle. Lack of insulin can cause glucose levels to skyrocket and cause serious health complications.
For example:
- in older people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, there is a high risk of hypoglycemic coma;
- Patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes are at high risk of ketoacidosis.
In the absence of systematic insulin therapy, a diabetic develops signs of hypoglycemia.
The most severe consequences that can threaten patients who neglect systematic treatment are:
- renal and liver failure;
- loss of vision, up to the development of blindness;
- severe diabetic foot, and subsequently gangrene and amputation;
- hypoglycemic attacks;
- diabetic coma.
For a large number of diabetics, insulin therapy is an indispensable part of life, and if you neglect treatment, you can lead your body to death.