Recently, you can increasingly hear that diabetes is an epidemic of the 21st century, that every year it is getting younger and more and more people are dying from its consequences. So let's understand what diabetes is, what types of diabetes exist, and how they differ from each other.
Diabetes is a whole group of diseases, the peculiarity of which is the release of large amounts of urine.
What types of diabetes are there? Diabetes is of two types due to its causes: diabetes mellitus, associated with high levels of glucose in the blood, and diabetes insipidus. Let's take a closer look at them.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease associated with elevated blood glucose levels for various reasons.
According to the World Health Organization, every 11th person in the world suffers from diabetes.
Depending on the cause of diabetes mellitus, the following types are distinguished:
- Diabetes mellitus type 1.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2.
- Specific types of diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes mellitus.
Let's look at the types of diabetes and their characteristics.
What is diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes
is a metabolic disorder in the body, which is based on either a deficiency in the formation of its own insulin, or the appearance of cell resistance to it. As a result, hyperglycemia develops - a persistent increase in blood glucose.
In parallel with this, water metabolism is disrupted. The tissues cannot retain water, and as a result, a lot of defective water is excreted through the kidneys.
In the human body, pancreatic cells (beta cells) are responsible for producing insulin. In turn, insulin is a hormone that is responsible for ensuring that glucose is supplied to the cells in the required amount. What happens in the body during diabetes? The body produces an insufficient amount of insulin (type 1), while the blood glucose level is sufficient, but the cells cannot absorb it due to hormone deficiency. In the second type of diabetes, the picture is the opposite: the pancreas produces enough insulin, but the cells do not see it, and again cannot absorb glucose.
From a lack of insulin, pustular and other skin lesions develop, teeth suffer, atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, hypertension develop, the kidneys and nervous system suffer, and vision deteriorates.
Code - ICD
ICD-10: E10-E14
ICD-9: 250
Consequences of diabetes in women
Without timely treatment, you risk getting serious complications, getting rid of which will be extremely difficult. The main dangers plaguing diabetics who do not adhere to doctor’s recommendations are:
- Constant swelling. Persistent swelling throughout the body is a consequence of excessive fluid retention in the body.
- Trophic ulcers. They are characteristic of a long course of the disease, which did not respond to appropriate treatment.
- Gangrene. Damage to the blood vessels of the extremities results in amputation. This outcome is typical for an advanced form that has been going on for many years.
- Coma. An extremely rare consequence of a severe form of the disease. This state is preceded by clouding of consciousness and loss of a sense of reality.
Why does diabetes develop?
The most significant causes of diabetes are:
- Heredity.
If at least one parent suffered from diabetes, then the risk of diabetes is 30%; if both parents were sick, then – 60%.
- Obesity.
If a person knows that his parents had diabetes, then he should monitor his weight to minimize the risk of developing this disease in himself. At the same time, not everyone who is obese, even in severe form, develops diabetes.
- Pancreatic diseases
, which contribute to the damage of beta cells responsible for the production of insulin. Such diseases include pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
- Viral infections
(rubella, chickenpox, epidemic hepatitis and other diseases, this includes influenza). These infections are the starting point for the development of diabetes mellitus. Especially for people who are at risk.
- Nervous stress.
People who are at risk (heredity) should avoid nervous and emotional stress.
- Age.
With age, the risk of developing diabetes doubles for every ten years.
This list does not include those diseases in which diabetes mellitus or hyperglycemia are secondary in nature, being just a symptom. In addition, such hyperglycemia cannot be considered true diabetes until full clinical manifestations or diabetic complications develop. Diseases that cause hyperglycemia (increased sugar) include tumors and hyperfunction of the adrenal glands, chronic pancreatitis, and increased levels of contrainsular hormones.
Diabetes mellitus occurs mainly in those who abuse sweets - just a myth! Diabetes can also appear in a person who does not consume sweets at all. However, you need to understand that sweets contribute to excess weight gain and can lead to obesity, which can pose a risk of developing diabetes.
Signs in women over 40
After 40 years of age, there is a danger of developing both type 1 and type 2 disorders. The main reasons for developing this pathology are a sedentary lifestyle and overeating. The autoimmune system begins to attack the pancreas, where insulin is produced. It's not known why, but thin women have a higher risk of developing diabetes without actively developing symptoms.
Insulin injections are rarely required. The main focus of treatment is on a low carbohydrate diet. A healthy lifestyle will help support the body in the fight against the problem. The main thing is not to get caught up in unhealthy sweets and other temptations. Otherwise, all previous treatment will go to waste.
Diabetes type 1 and 2: what is the difference?
There are two varieties of it, which are fundamentally different from each other. Although modern endocrinologists call the division of diabetes mellitus very conditional, the type of disease still matters in determining treatment tactics. Therefore, it is advisable to dwell on each of them separately.
It's important to understand
that not all hyperglycemia is true diabetes mellitus, but only that which is caused by a primary violation of the action of insulin!
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 (insulin dependent).
With this type of disease, the body produces antibodies that destroy the cells of its own pancreas that produce insulin. It is almost impossible to completely recover from type 1 diabetes, although there are cases of restoration of pancreatic function, but this is only possible under special conditions. To maintain health, you need to inject insulin into the body using a syringe. Since insulin is destroyed in the gastrointestinal tract, taking insulin in tablet form is impossible. Insulin is administered along with meals. It is very important to follow a strict diet; easily digestible carbohydrates are completely excluded from the diet.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2 (non-insulin dependent).
This type of diabetes is insulin-independent. The cause of the disease is loss of cell sensitivity to insulin. The use of insulin for treatment is not necessary for every patient. To begin with, such patients are prescribed a diet. It is very important to completely follow the doctor's recommendations. It is recommended to reduce weight slowly (2-3 kg per month) to achieve a normal weight, which must be maintained throughout life. In cases where diet is not enough, sugar-lowering tablets are used, and insulin is prescribed only as a last resort.
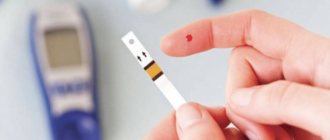
In type II diabetes, it is important to constantly monitor glucose levels. At home, such an examination can be performed independently using a glucometer - a device for measuring blood sugar levels. Accuracy of measurement and ease of use are important in a glucometer.
OneTouch Select Plus Flex® is suitable even for inexperienced users and retirees who find it difficult to understand new gadgets. It is no coincidence that this glucometer has become the best-selling in Russia. What makes this device different?
It is convenient - color hints help you understand at a glance what the number on the screen means.
This is a simple glucometer - easy to learn how to use and easy to measure blood sugar.
OneTouch Select Plus Flex® delivers accurate results, proven through years of clinical research.
Forecast
If left untreated, diabetes can cause severe complications and death. Poorly controlled type 1 diabetes is a risk factor for chronic complications such as blindness, kidney failure, amputations and heart attacks.
Overall, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in diabetes. Over time, the treatment plan will change. This is because insulin resistance increases with age, and the cells that produce insulin in the pancreas wear out as the pancreas tries to meet the body's additional insulin needs.
The prognosis depends on how well the sick person controls his glucose levels and how well he follows the doctor's recommendations.
Signs of diabetes
Clinical signs of the disease in most cases are characterized by a gradual course. Rarely, diabetes manifests itself in a fulminant form with a rise in glycemia (glucose content) to critical levels with the development of various diabetic comas.
Early signs
With the onset of the disease, patients develop:
- Constant dry mouth;
- Feeling thirsty and unable to quench it. Sick people drink up to several liters of daily fluid;
- Increased diuresis - a noticeable increase in portion and total urine excreted per day;
- Decrease or sharp increase in weight and body fat;
- Severe itching of the skin and dryness;
- Increased tendency to pustular processes on the skin and soft tissues;
- Muscle weakness and increased sweating;
- Poor healing of any wounds;
Usually the listed complaints are the first sign of illness. Their appearance should be a mandatory reason for an immediate blood test for glycemia (glucose content).
As the disease progresses, symptoms of diabetes complications may appear, affecting almost all organs. In critical cases, life-threatening conditions with impaired consciousness, severe intoxication and multiple organ failure may occur.
Late signs
The main manifestations of complicated diabetes include:
- Visual impairment;
- Headaches and neurological abnormalities;
- Heart pain, liver enlargement, if they were not noted before the onset of diabetes;
- Pain and numbness of the lower extremities with impaired walking function;
- Decreased sensitivity of the skin, especially the feet;
- The appearance of wounds that do not heal for a long time;
- Progressive increase in blood (systolic and diastolic) pressure;
- Swelling of the face and legs;
- The appearance of the smell of acetone from the patient;
- Confusion of consciousness.
The appearance of characteristic signs of diabetes or the development of its complications is an alarm signal that indicates the progression of the disease or insufficient drug correction.
Signs in women over 30
At this age, as a rule, type 1 develops, a rather severe autoimmune disease.
The development and manifestation of the disease occurs rapidly and most often does not depend on the lifestyle of the sick person. This type is considered hereditary. Its development is almost impossible to prevent. Acute symptoms and early signs for this type of disease:
- nausea and vomiting,
- numbness of the limbs,
- smell of acetone from the mouth,
- thirst and hunger.
If you have these signs, you should not hesitate to get tested in the laboratory. However, you can check your sugar level with a home glucometer. However, do not forget that such a check will not give you the complete picture.
Once you are diagnosed with diabetes, do not delay consulting your doctor. You will be prescribed a special diet and treatment that will help eliminate the severe course of the disease and protect you from disability.
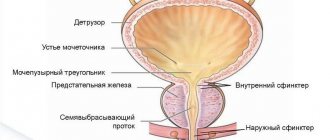
Blood sugar levels in diabetes mellitus
The very first and most informative method for the primary diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and its dynamic assessment during treatment is the study of blood glucose (sugar) levels. This is a clear indicator from which all subsequent diagnostics and treatment measures should be based.
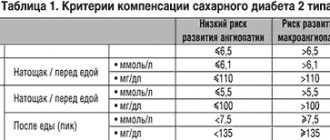
Experts have reviewed normal and pathological glycemic values several times. But today their clear values have been established, which shed true light on the state of carbohydrate metabolism in the body. They should guide not only endocrinologists, but also other specialists and patients themselves, especially diabetics with a long history of the disease.
| State of carbohydrate metabolism | Glucose level indicator | |
| Normal blood sugar | On an empty stomach | 3.3-5.5 mmol/l |
| 2 hours after carbohydrate load | <7.8 mmol/l | |
| Impaired glucose tolerance | On an empty stomach | 5.5-7.0 mmol/l |
| 2 hours after carbohydrate load | 7.8-11.0 mmol/l | |
| Diabetes | On an empty stomach | >7.0 mmol/l |
| 2 hours after carbohydrate load | >11.0 mmol/l | |
As can be seen from the table above, diagnostic confirmation of diabetes mellitus is extremely simple and can be carried out within the walls of any outpatient clinic or even at home if you have a personal electronic glucometer (a device for determining blood glucose levels). In the same way, criteria have been developed for assessing the sufficiency of diabetes therapy by one or another method. The main one is the same level of sugar (glycemia).
According to international standards, a good indicator of diabetes treatment is a blood glucose level below 7.0 mmol/l. Unfortunately, in practice this is not always feasible, despite the real efforts and strong desire of doctors and patients.
Find out more:
normal blood sugar, how to determine the exact level?
Symptoms in a child
Diabetes can manifest at any age, including early childhood. Even newborn diabetes occurs. This is a rare case of a congenital disease. Most often, manifestation in children occurs between 6 and 12 years of age. Metabolic processes in children during this period proceed much faster, and the state of the unformed nervous system can affect the level of glucose in the blood. The younger the baby, the more difficult diabetes is.
Among the main symptoms that parents need to pay attention to in order not to miss the development of diabetes, doctors identify in children:
- thirst and dry mouth;
- nausea with vomiting;
- frequent urination with sticky urine;
- weight loss and high appetite;
- drop in visual acuity;
- high fatigue, weakness and irritability.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
If a child has at least one of the above symptoms, this is a reason to consult a doctor. If several symptoms are detected at the same time, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Symptoms in children may also include typical and atypical signs of diabetes. Doctors include polyuria, which parents of babies often confuse with age-related urinary incontinence, polydipsia, polyphagia, dry and itchy skin, itching of the genitals after urination, and the amount of sugar in the blood more than 5.5 mmol per liter on a fasting blood test. Timely diagnosis in case of suspicion will help to identify the disease at an early stage and begin the necessary therapy, which will not allow complications to develop.
Stages
A very important classification of diabetes mellitus is its division into stages of severity. This distinction is based on blood sugar levels.
Stages of development of diabetes mellitus:
- First stage.
Blood glucose increases slightly and remains within 8 mmol/l (when tested in the morning). Daily glucosuria is mild; in some patients, only traces of sugar are found in the urine. The maximum value at the first stage does not exceed 20 g/l. You can normalize blood glucose levels with diet. However, already at this stage of the disease development, the patient is often found to have asymptomatic vascular damage.
- Second stage.
The blood sugar level in the morning rises to 14 mmol/l, daily glucosuria is 40 g/l, and ketosis or ketoacidosis periodically develops. It is not possible to control the progression of the disease with diet therapy alone, but compliance with it is a prerequisite. At this stage, patients are most often prescribed tablet medications to control diabetes. Insulin injections are indicated for the development of secondary sulfonamide resistance. The maximum daily dose is 40 units. The second stage is characterized by the fact that patients are diagnosed with angioneuropathies of various organs and systems.
- Third stage.
The glucose level on an empty stomach exceeds 14 mmol/l, and daily glucosuria indicators are 40-50 g/l. Without regular insulin injections, severe complications develop. The daily dose is 60 units or more. The patient is diagnosed with multiple angioneuropathies.
Complications
Diabetes mellitus is dangerous due to its complications, including:
- Diabetic angiopathy.
Vascular walls become brittle, thin, their permeability increases, which is associated with the formation of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques with the further development of coronary heart disease, intermittent claudication and diabetic encephalopathy.
- Diabetic retinopathy.
The patient's retina is destroyed, and the vessels that supply it suffer. Vision begins to decline. As the disease progresses, retinal detachment occurs and the person becomes blind. This complication makes itself felt after 10-15 years in type I diabetes and even earlier in type II diabetes. No more than 5-15% of patients manage to avoid retinopathy.
- Diabetic polyneuropathy.
Destruction of peripheral nerve nodes causes symptoms such as: swelling and chilliness of the hands and feet, deterioration of sensitivity, paresthesia. This complication develops in 75% of patients and is more common in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. The clinical manifestation of polyneuropathy occurs in the 10-15th year of development of the underlying disease.
- Diabetic foot.
Due to malnutrition of the lower extremities, its bone structures and joints are destroyed, intractable ulcerative defects are formed, and pain occurs.
- Diabetic nephropathy.
The vessels supplying the kidneys suffer, which eventually leads to kidney failure. This complication occurs in approximately half of patients with diabetes. It develops 10-15 years from the onset of the disease.
[Video] Dr. Berg - How does diabetes mellitus affect the vascular system?
Early signs of diabetic coma
The most serious complication of diabetes mellitus is coma. It can be hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic.
Coma due to very high sugar.
A sharp rise in blood sugar levels provokes a hyperglycemic coma.
Symptoms that precede it:
- Deterioration in general health.
- Lack of appetite.
- Headache.
- Weakness.
As hyperglycemia progresses, a person experiences abdominal pain, vomiting, and his breath smells like acetone. He becomes drowsy and apathetic, and his blood pressure drops. This symptom complex is associated with increasing ketoacidosis. If the patient is not provided with medical assistance, he will lose consciousness, fall into a coma and die.
Coma due to very low sugar.
Hypoglycemic coma is accompanied by a sharp decrease in blood glucose levels. The most common cause of this dangerous condition is an overdose of insulin.
Hypoglycemia develops quickly and is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- A sharp jump in blood pressure.
- Cooling of the skin.
- Trembling in arms and legs.
- Sudden hunger.
- Cramps.
- General weakness.
Complications of diabetes can be avoided, but this requires lifelong therapy and monitoring of blood glucose levels.
Diagnostics
If diabetes is suspected, this diagnosis must be either confirmed or refuted. There are a number of laboratory and instrumental methods for this. These include:
- Study of blood glucose levels - determination of fasting glycemia;
- Glucose tolerance test - determination of the ratio of fasting glycemia to this indicator two hours after taking carbohydrate components (glucose);
- Glycemic profile - study of glycemic numbers several times throughout the day. Performed to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment;
- General urine analysis with determination of the level of glucose in the urine (glucosuria), protein (proteinuria), and leukocytes.
All patients with diabetes must be consulted by the following specialists:
- Endocrinologist;
- ;
- Neurologist;
- Ophthalmologist;
- Surgeon (vascular or special doctor - pediatrician);
Carrying out the entire complex of these diagnostic measures will help to clearly determine the severity of the disease, its degree and the correctness of tactics in relation to the treatment process. It is very important to conduct these studies repeatedly, and repeat them over time as many times as the specific situation requires.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes - metformin
To get rid of type 2 diabetes, you must follow these recommendations:
- Go on a low carb diet.
- Start taking an inexpensive and harmless drug for the treatment of diabetes based on metformin.
- Start playing sports and increase your physical activity.
- Sometimes insulin injections in small doses may be required to normalize blood sugar levels.
These simple recommendations will allow you to control your blood sugar levels and stop taking medications that cause multiple complications. You need to eat right not from time to time, but every day. Switching to a healthy lifestyle is an indispensable condition for getting rid of diabetes. Treatment of diabetes mellitus in a simpler and more reliable way does not yet exist at this point in time.
Features of the use of metformin
Metformin does not affect the synthesis of its own insulin, and is most often prescribed during the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus. Belongs to the pharmacological group of biguanides. The main effect of this substance is antidiabetic activity. The study of the full range of its properties continues to this day. The drug significantly reduces the release of glucose from the liver depot and has a positive effect on metabolic processes at the cellular level. Thanks to metformin, active absorption of glucose by muscle fibers occurs.
In most clinical cases of taking metformin, patients do not experience the effect of hypoglycemia, in which blood glucose decreases too quickly and severely. This phenomenon is typical only for patients who receive metformin alone. If combined regimens with other antidiabetic drugs are used, a critical drop in blood sugar is observed quite often.
A therapeutic result is possible when metformin is used while following a diet. If the patient does not adhere to special dietary rules for diabetes, the effect of the drug will be insignificant or not at all. A therapeutic diet is prescribed to reduce the intake of excess carbohydrates into the body, as well as to reduce the patient’s body weight. It is important to consider that weight plays a key role in the development of diabetes.
Video: Dr. Evdokimenko - how to cure type 2 diabetes: 7 steps. Simple but effective tips:
Other medicines
For type 2 diabetes, glucose-lowering medications are used:
- Drugs that increase cell sensitivity to insulin.
These are Biguanides (Siofor, Glucophage, Metformin). Biguanides are not prescribed to people who suffer from pathologies of the heart and kidneys with severe dysfunction of these organs. Also drugs that increase the sensitivity of cells to insulin are Pioglitazone and Avandia. These drugs belong to the Thiazolidinediones group.
- Drugs that stimulate the production of insulin by the pancreas.
Prescribed in cases where the effect of metformin is insufficient, or biguanide cannot be used (hypersensitivity, side effects). These are sulfonylurea derivatives (Diabeton, Glimepiride, Glibenclamide, Gliclazide, Glyurenorm, Movogleken), as well as meglitinides: NovoNor, Diaglinide, Repaglinide, Iglinide.
Drugs in this group are capable of activating the functions of pancreatic cells. This kind of stimulation leads to increased production of your own insulin. The secondary effect of taking sulfonylurea derivatives is the inhibition of glucagon production and the processes of glucose release from the liver. Failure to comply with the therapeutic dosage can lead to the development of hypoglycemia.
- Drugs that prevent glucose from being absorbed
in the organs of the digestive system. This medicine is called "Acarbose" from the group of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
- Incretins
- These are hormones of the gastrointestinal tract that are produced in response to food intake and cause stimulation of insulin production. These include gliptins: Sitagliptin (Januvia), Vildagliptin (Galvus), Saxagliptin (Ongliza), Linagliptin (Trangenta). And GLP-1 receptor agonists: Liraglutide (Victoza) and Exenatide (Byeta).
Read more: “New generation drugs.” The cost of drugs varies from 1 to 5 thousand rubles. for gliptins, and about 7-10 thousand rubles. for GLP-1 agonists.
Read more: The most popular glucose-lowering tablets
Therapy using folk remedies
As already noted, the main ways to maintain glucose levels are diet and medication. However, no one has canceled restoration using folk remedies. It is worth noting that their use can also be harmful, so before using any drugs it is better to consult an endocrinologist. Let's consider the most popular methods of traditional treatment of diabetes:
- Clover infusion. To prepare it, you need to combine a small amount of clover with the same amount of boiling water. After three hours, the drink is ready. It should be taken before meals, 300 ml.
- Blueberry leaves. The cooking method is almost the same, except for the ratio of ingredients. Pour a cup of boiling water over a spoonful of leaves and leave for half an hour. Take one cup orally three times a day.
- Burdock roots. They should be eaten with cheese, both boiled and fried. Sometimes people add this plant to soup instead of potatoes.
Treatment of type 1 diabetes - insulin
Therapy is based on physical activity, insulin administration and control of the amount of carbohydrates consumed:
- Diet.
The nutritional system involves reducing the volume of carbohydrate foods, but it will not be possible to do without insulin injections.
- Physical activity.
It is aimed at getting rid of extra pounds, optimizing energy consumption and expenditure.
- Injection of insulin.
The dose is selected individually; the patient is prescribed short-acting or super-short-acting insulin.
Possible operations:
- Transplantation of the islets of Langerhans.
The operation is performed on patients with type 1 diabetes. The difficulty lies in the selection of a donor (the material is taken from a deceased person) and the need for serious immunosuppressive therapy.
- Pancreas transplant.
Most often, this operation is combined with a kidney transplant. Its successful implementation leads to complete relief from the disease.
How many times a day should you inject insulin?
The main goal of diabetes therapy is to maintain normal levels of insulin in the blood, so it will have to be administered at least 3-5 times a day. This regimen is indicated for young patients; compliance with it allows you to control blood sugar levels and prevent the development of complications of the disease.
The administration of insulin for pregnant patients is a prerequisite for the birth of a healthy child.
For elderly people, it is recommended to administer insulin no more than 1-3 times a day, since memory impairment increases the risk of developing hypoglycemia.
How to give an injection correctly?
The drug is injected into the skin fold, preventing it from entering the muscle. The needle is inserted at an angle of 45 degrees (if the thickness of the fold is less than the length of the needle).
Insulin should not be injected into areas with compactions; the injection area should not be changed. It is not recommended to use the skin of the shoulder.
- Short-acting insulin is administered half an hour before meals. The injection site is the anterior abdominal wall.
- Long-acting insulin is injected into the thigh or buttock.
- An ultra-short-acting drug (Novorapid or Humalog) is administered before a meal, during a meal, or immediately after its completion.
Insulin is absorbed more quickly by exposure to heat and increased physical activity. When in the cold, this period extends over time.
Read more: Insulin - types of injection, instructions for use
Treatment rules
The main goal of therapy to eliminate pathology is to reduce sugar levels and take preventive measures to prevent complications. During treatment the following rules must be observed:
- following a diet aimed at limiting carbohydrates (it is a balanced diet and does not require fasting, while the diet restores the patient’s body and returns strength to him);
- performing physical exercises;
- carrying out daily monitoring of your tests;
- administering insulin injections if necessary;
- using the most accurate glucometer, which is subject to periodic checks for serviceability;
- keeping a food diary, in which foods that cause an increase in blood sugar should be noted;
- use insulin if necessary without trying to replace it with tablets, because otherwise the pathology can lead to disability.
Prevention of diabetes
Unfortunately, not in all cases it is possible to influence the inevitability of type 1 diabetes. After all, its main causes are the hereditary factor and small viruses that every person encounters. But not everyone develops the disease. And although scientists have found that diabetes occurs much less frequently in children and adults who were breastfed and treated for respiratory infections with antiviral drugs, this cannot be attributed to specific prevention. Therefore, there are no truly effective methods.
The situation with the prevention of type 2 diabetes is completely different. After all, it is very often the result of an incorrect lifestyle.
Therefore, complete preventive measures include:
- Normalization of body weight;
- Control of arterial hypertension and lipid metabolism;
- Proper fractional dietary meals with a minimum content of carbohydrates and fats that can be easily digested;
- Dosed physical activity. They suggest combating physical inactivity and avoiding excess loads.
Severity
Currently, there is no concept of the severity of diabetes. Also, the concepts of compensation and decompensation of diabetes mellitus are outdated. Diabetes communities no longer categorize severity because such grading does not help with prognosis or optimization of diabetes treatment.
Now doctors set specific therapeutic goals for patients. These are target levels of average glucose content over three months - which must be achieved in a person depending on his age, learning ability, the presence of pathology of the heart, blood vessels, blood pressure and body weight. The goals may be more stringent if the person has underlying complications. But it is important to achieve them in order to ensure a normal level of quality of life.
Can diabetes be cured?
Today the question of the possibility of a complete cure for diabetes is considered very controversially. The complexity of the situation is that it is very difficult to return what has already been lost. The only exception is those forms of type 2 diabetes mellitus that are well controlled under the influence of diet therapy. In this case, by normalizing your diet and physical activity, you can completely get rid of diabetes. It should be borne in mind that the risk of recurrence of the disease in case of violation of the regime is extremely high.
According to official medicine, type 1 diabetes and persistent forms of type 2 diabetes cannot be completely cured. But with ongoing drug treatment, you can prevent or slow down the progression of diabetes complications. After all, they are the ones who are dangerous to humans. Therefore, it is extremely important to regularly monitor blood glucose levels, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment measures. We must remember that they must be for life. It is permissible to change only their volumes and varieties depending on the patient’s condition.
There is a special plant - Gymnema sylvestre, which slows down the absorption of glucose in the intestines, stimulates the release of insulin from the pancreas, and thereby helps the regeneration of the cells that produce it (beta cells), which are damaged in diabetes. Based on it, a study was conducted: in 27 patients with insulin-dependent diabetes, taking 400 mg of Gymnema supplement for 30 months led to a reduction in insulin dose by almost half.
As for surgical methods for eliminating diabetes mellitus with the implantation of a kind of artificial pancreas, which is a device that analyzes the level of hyperglycemia and automatically releases the required amount of insulin. The results of such treatment are impressive in their effectiveness, but they are not without significant drawbacks and problems.
Developments continue in the field of synthesis of those types of insulin that will consist of identical components specific to each patient. And although this still remains a distant reality, every person exhausted by diabetes believes that a miracle will happen.
[Video] Frolov Yu. A. will tell you in detail how to get rid of diabetes forever:
Main types of insulin
When the only option is to inject the hormone, it is important to choose the right medication.
Insulin preparations can be divided into the following types based on their origin:
- Porcine - the pork insulin molecule is almost identical in its amino acid sequence to the human insulin molecule. Produced from pig pancreas by extraction and purification. When administered, it functionally replaces human.
- Cattle insulin – is extracted from cattle material. The difference between bovine hormone and human hormone is significant and often causes allergic reactions.
- Genetically engineered - modified microorganisms are used for its production.
Now the best drugs are produced by modified microorganisms. Using DNA recombination, genes responsible for the production of insulin are inserted into them, and molecules are obtained - complete analogues of human ones. They do not cause allergies or immune reactions and are as effective as possible.
Classification by number of components
If a drug contains one type of hormone, it is called monotype. When different types of hormones are present, it is called combined.
Degree of purification of the drug
Insulin from natural sources (for example, pork) is obtained by purifying the raw material and isolating one fraction.
With standard purification, the so-called “traditional” is obtained. It contains many impurities and is less tolerated by patients.
With more thorough cleaning, the result is monopeak. It contains fewer impurities and has fewer side effects.
At the highest purification, a one-component product is obtained. It can be called the highest quality.