Young children get sick often, and, according to statistics, one of the most common diseases in childhood are bacterial infections. They occur both as a complication after viral infections and independently. To stop the growth, development and spread of pathogenic bacteria, doctors prescribe antibiotics.
For children under 12 years of age, there are special pediatric forms and medications with lower dosages than “adult” medications. One of the drugs that has proven itself in therapy is azithromycin suspension for children. Instructions for use, price, reviews and comparison with analogues will help you better understand the mechanism of action of the drug and estimate the cost of the upcoming treatment.
Instructions for use
Azithromycin is a semisynthetic antibiotic with a bacteriostatic mechanism of action. Accumulating in the human body, it begins to act bactericidal, that is, destroy the cells of bacteria that cause the disease. The drug is available in several forms and in various dosages:
- tablets of 250 and 500 mg;
- capsules of 250 and 500 mg;
- suspension of 100 and 200 mg per 5 ml;
- injection .
for the treatment of children under 12 years of age . It is available in powder form for home preparation. Each package contains a bottle of medicinal powder, a plastic syringe for administering medication to patients with difficulty swallowing and children who cannot drink solid medications, a 5 ml measuring spoon and instructions for using Azithromycin suspension for children.
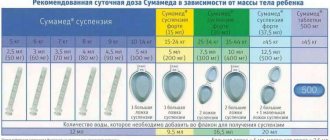
The pediatrician prescribes Azithromycin for children for sore throat, tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia and a number of other common diseases . The dosage is chosen based on the child’s weight. Children weighing over 45 kg are prescribed capsules or tablets with a dosage of 250 mg, and up to 45 kg - syrup.
Dosage of the drug according to the patient's weight.
| Weight (in kg) | Dosage in solution 100 mg per 5 ml (in ml) | Dosage in solution 200 mg per 5 ml (in ml) |
| 5 | 2,5 | – |
| 6 | 3 | – |
| 7 | 3,5 | – |
| 8 | 4 | – |
| 9 | 4,5 | – |
| 10-12 | 10 | – |
| 12-24 | – | 5 |
| 25-34 | – | 7,5 |
| 35-44 | – | 10 |
| 45 or more | – | 12,5 |
In case of a serious illness, the doctor increases the dosage and chooses a different regimen for taking the medicine (stepwise, longer and with larger doses of the medicine). Duration of therapy is from 3 to 5 days.
How to take the drug. The suspension for children, like other forms, is taken once a day 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after. It is better to take the medicine at the same time. If an appointment is missed, doctors recommend resuming the missed appointment and repeating it after 24 hours.
- To prepare the syrup, boiled water at room temperature is poured into a bottle with powder up to the mark indicated on the bottle and the solution is shaken.
- It is recommended to use the suspension within 5 days from the date of preparation.
- prepared preparation before each use .
- After use, the spoon or syringe is washed and wiped dry.
- The drug is washed down with water, rinsing the mouth from any remaining medication.
- For the correct dosage and ease of administration, children under 3 years of age are administered the drug with a special measuring syringe.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Azithromycin, the active substance of Azithromycin Ecomed, is a broad-spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotic belonging to the group of macrolides-azalides. It has a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action, the mechanism of which is based on the suppression of microbial cell protein biosynthesis. When bound to the 50S ribosomal subunit, azithromycin inhibits peptide translocase at the translation stage and suppresses protein synthesis, which slows down the growth and reproduction of bacteria. When used in high concentrations, the substance has a bactericidal effect.
Azithromycin is active against a number of gram-positive and gram-negative anaerobes, intracellular and other microorganisms. They may initially exhibit resistance to the effects of the antibiotic or acquire it.
MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) sensitivity/resistance of microorganisms:
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae: < 0.25 / > 0.5 mg/l;
- Staphylococcus: < 1 / > 2 mg/l;
- Streptococcus pneumonia: <0.25/>0.5 mg/l;
- Streptococcus A, B, C, G: < 0.25 / > 0.5 mg/l;
- Moraxella catarrhalis: < 0.5 / > 0.5 mg/l;
- Haemophilus influenza: <0.12/>4 mg/l.
Microorganisms that in most cases exhibit sensitivity to the effects of azithromycin:
- anaerobes: Fusobacterium spp., Porphyromonas spp., Prevotella spp., Clostridium perfringens;
- gram-negative aerobes: Legionella pneumophila, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Pasteurella multocida, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Haemophilus parainfluenzae;
- gram-positive aerobes: Streptococcus pneumoniae penicillin-sensitive, Staphylococcus aureus methicillin-sensitive, Streptococcus pyogenes;
- other microorganisms: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Borrelia burgdorferi, Mycoplasma hominis, Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, Chlamydia pneumoniae.
Microorganisms that are initially resistant to the drug:
- gram-positive aerobes: Staphylococcus (methicillin-resistant staphylococci have a very high degree of resistance to the action of macrolides), Enterococcus faecalis;
- gram-positive bacteria resistant to erythromycin;
- anaerobes: Bacteroides fragilis.
Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae can develop resistance to the action of azithromycin.
The capsules contain lactulose (as a bifidogenic factor). This is a synthetic disaccharide; its molecule consists of fructose and galactose residues. In the stomach and upper intestines, lactulose is not absorbed and does not undergo hydrolysis. After release from the capsule, it is fermented by the normal microflora of the large intestine (as a substrate), and the growth of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria is stimulated.
Due to the hydrolysis of lactulose in the large intestine, organic acids are formed - lactic, acetic and formic. They inhibit the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, which helps reduce the production of nitrogen-containing toxic substances.
Lactulose thus reduces the damaging effects of the antibiotic on the normal intestinal microflora and the likelihood of developing adverse reactions associated with dysbacteriosis.
Pharmacokinetics
Azithromycin after oral administration is well absorbed and quickly distributed in the body. Bioavailability after a single dose of 500 mg of the substance is 37% (due to the effect of the first pass through the liver). After taking the indicated dose, Cmax (maximum concentration) is 0.4 mg/l, the time to reach it is from 2 to 3 hours. The concentration of azithromycin in cells and tissues is 10–50 times higher than serum concentration. Vd (volume of distribution) is 31.1 l/kg. The rate of binding to plasma proteins is inversely proportional to the concentration of the substance in the blood and ranges from 7 to 50%.
Azithromycin is an acid-stable lipophilic substance. Easily penetrates histohematic barriers. It penetrates well into the respiratory tract, genitourinary tissues and organs (including the prostate gland, soft tissues and skin). Azithromycin is also transported to the site of infection by phagocytes (macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes), where it is released in the presence of bacteria. After the substance penetrates the cell membranes, high concentrations are created in them, which is especially important for the eradication of pathogens located intracellularly.
The concentration of azithromycin in foci of infection is 24–34% higher than in healthy tissues. It correlates with the severity of the inflammatory process. After taking the last dose, it remains in effective concentration for 5–7 days.
In the liver the substance is demethylated. The metabolites that are formed in this case do not have activity. The metabolism of azithromycin involves isoenzymes of which it is an inhibitor - CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP3A7.
Plasma clearance of azithromycin is 630 ml/min. The removal of a substance from blood plasma occurs in two stages:
- first stage: T1/2 (half-life) in the range from 8 to 24 hours after administration is 14–20 hours;
- second stage: T1/2 in the range from 24 to 72 hours after administration is 41 hours.
This allows you to use the drug once a day. More than 50% of the substance is excreted unchanged by the intestines, 6% by the kidneys.
Food intake has a significant impact on pharmacokinetic parameters. The Cmax value increases by 31%, while the AUC value (area under the concentration-time curve) remains unchanged.
In elderly men (from 65 to 85 years), the pharmacokinetic parameters do not change; in women of this age group, an increase in the Cmax value by 30–50% is observed.
Which pharmacies are best to buy from + price
Azithromycin in the form of a suspension is produced in two dosages - 100 and 200 mg per 5 ml of finished syrup. Let's look at the prices for the drug Azithromycin Ecomed, manufactured by ABVA Rus, Russia, in offline and online pharmacies.
| Pharmacy name | Price per package 20 ml, dosage 100 mg/5 ml (in rubles) | Price per package 20 ml, dosage 200 mg/5 ml (in rubles) |
| Vita Central | 175 | 275 |
| Vita-Express | 174 | 274 |
| Apteka.ru | 197 | 274 |
| Piluli.ru | 187 | 391 |
| E Pharmacy | – | 391 |
| Pharmacy chain “Dialogue” | 150 | – |
| Zdravzona.ru | 140 |
Azithromycin suspension
Reviews
Experts and consumers agree that Azithromycin suspension is convenient in treating children, is inexpensive and works effectively.
Reviews from experts
Experts talk about the effectiveness of treatment with a correct diagnosis, the wide distribution of drugs with the active substance Azithromycin, which allows you to choose a drug at a price that suits different groups of the population.
Azithromycin is an antibiotic; all antibiotics are taken as prescribed by a doctor according to strict indications as many times as necessary. Of course, the ideal option is to check whether your microflora is sensitive to it before taking an antibiotic. If you want to treat your throat, you need to take a throat culture; if it’s something else, then you need to take another test.
Azithromycin is the active ingredient in a large number of similar drugs. Depending on the manufacturer of the drug, drugs (Azithromycin) have different half-lives and different toxic effects on the body. For example: Azitrox - side effects develop in 5% of cases, Azithromycin - up to 2%, Sumamed - up to 1%, Zitrocin - up to 3-4%. Sumamed (azithromycin) is an original drug that was developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company Pliva (Croatia). In this example, we see that it is better to use the original drug rather than analogues or generics.
Reviews from parents
Parents note the speed of action of the drug, its affordable price, and ease of use once a day. The disadvantages include the presence of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract.
It treats the disease very well, but it disrupts the intestinal microflora, which is then very difficult to restore. A 2-year-old child had a sore throat; the diagnosis was, as always, a disappointing acute pharyngitis. We first took one antibiotic, then we re-tested, which were very bad, and we were prescribed Azithromycin suspension. The child drank this suspension for five days; there were no side effects or complaints from the child. We retook the tests, they were normal, but diarrhea began, which had to be treated with smecta and normobact.
I buy azithromycin suspension for my child. The course of treatment is three days. An average cold or mild bronchitis will be cured without resorting to injections. Well, of course, like all antibiotics, they cause diarrhea in a weak child’s body.
I have two children, 5 years old and 7 years old. As a rule, if one of them starts to get sick, the other will catch it immediately. So you will have to treat them one by one for months. We tried to treat without antibiotics, but it was crazy. Now, when one gets sick, I immediately treat him with Azithromycin. It helps instantly. However, we must not forget that these are antibiotics and it is better not to use them without a doctor's prescription.
Video
Dr. Komarovsky will remind you how they were discovered, why they are needed and when you really cannot do without antibiotics.
Drug interactions
- antacid drugs: they do not affect the bioavailability of azithromycin, however, when used in combination, the Cmax value in the blood decreases by 30%, therefore Azithromycin Ecomed is taken at least 60 minutes before or 2 hours after meals and taking these drugs;
- P-glycoprotein substrates (digoxin): there is an increase in their concentration in the blood serum;
- zidovudine (with 1000 mg of azithromycin once or repeatedly at a dose of 600 or 1200 mg): azithromycin has little effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of zidovudine, including the renal excretion of the substance or its glucuronide metabolite; at the same time, the concentration of phosphorylated zidovudine and its clinically active metabolite increases in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The clinical significance of this interaction is unclear;
- ergot alkaloids: combined use is not recommended, since there is a theoretical possibility of developing ergotism;
- atorvastatin: during post-registration surveillance, isolated information was obtained about cases of rhabdomyolysis in patients who received azithromycin simultaneously with statins;
- cimetidine: if used 2 hours before taking Azithromycin Ecomed, the pharmacokinetic parameters of these drugs do not change;
- cyclosporine: during combination therapy with azithromycin, caution must be exercised; co-administration of these drugs requires monitoring the plasma concentration of cyclosporine in the blood and, if necessary, dose adjustment (associated with a significant increase in Cmax in the blood plasma and AUC0-5 of cyclosporine);
- terfenadine: no evidence of interaction has been obtained; It has been established that with combined therapy of terfenadine with macrolides, arrhythmia and prolongation of the QT interval may develop.
Indications
Azithromycin suspension is prescribed to children for bacterial infections affecting the upper and lower respiratory tract, ENT organs, gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system, for complications after ARVI, and also in cases where treatment with penicillin derivatives is impossible.
Azithromycin is effective for diseases such as:
- bronchial infections;
- pneumonia caused by mycoplasma and chlamydia;
- complicated pneumonia;
- inflammation of the maxillary sinuses;
- angina;
- sinusitis;
- tonsillitis;
- dermatitis, erysipelas, pustules, impetigo, furunculosis;
- Lyme disease;
- ulcers and gastritis caused by Helicobacter Pylori.
What can be the risk for a child taking the drug?
Practice has shown that allergic reactions to Azithromycin in children are extremely rare. Here are the more common side effects:
- increased anxiety, hyperactivity (or drowsiness), nervousness, mild dizziness;
- loose stools, bloating, nausea;
- cramping abdominal pain;
- slight increase in serum liver enzymes.
Azithromycin (both parents and pediatricians confirm this) works very well, and its cost is quite affordable - 120 rubles. It comes to the rescue of various bacterial infections and helps to survive them without consequences. But it, like other antibiotics, cannot be recommended: it is prescribed strictly according to indications and only by the attending physician!
Contraindications
- Azithromycin is not prescribed to children under 6 months of age and weighing less than 5 kg.
- The drug is contraindicated in patients with liver and kidney disorders.
- Azithromycin is not prescribed to persons with hypersensitivity to macrolides and auxiliary components of the drug.
- Azithromycin is not used in parallel with antacids.
- Use with caution for allergy sufferers and people with diabetes.
Overdose
May manifest as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, reversible hearing loss, and alopecia. If the listed symptoms develop, it is necessary to rinse the child’s stomach and then give him activated carbon (0.5 g per 1 kg of weight), diluted in half a glass of warm water. Coal can be “secured” with Enterosgel or Smecta. Antacids are also indicated for patients over 12 years of age.
Even if you were able to complete these procedures, it would still be a good idea to call an ambulance. Moreover, in advanced cases of overdose, symptomatic treatment will be required, which will either be prescribed by the doctor himself on call, or will be prescribed in the hospital where the small patient will be taken.
Side effects
Side effects of Azithromycin occur due to individual intolerance to individual components of the drug, violation of the dosage regimen and storage conditions of the drug. Taking the drug in 2% of cases causes:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- photosensitivity;
- temporary hearing loss;
- noise in ears;
- increased fatigue;
- excitability;
- aggression;
- anxiety;
- digestive disorders;
- nausea;
- itching;
- skin redness;
- rashes;
- arrhythmia;
- tachycardia;
- liver failure;
- candidiasis;
- swelling;
- nose bleed.
Rarely - anaphylactic shock, liver necrosis (possible death).
The drug accumulates in the body and remains in active doses after the end of administration. This should be taken into account when introducing other drugs into therapy.
Compound
Active substance:
- azithromycin dihydrate 1200 mg.
Excipients:
- xanthan gum (food thickener);
- silicon dioxide (white crystalline powder, when shaken with water it forms a suspension, acts as an enterosorbent);
- calcium stearate (thickener);
- sodium benzoate (preservative);
- sodium carbonate anhydrous (baking powder);
- aspartame (sweetener);
- tartrazine (food coloring);
- ponceau (food coloring);
- flavoring additive “Vanillin”;
- flavoring additive “Apricot”;
- refined sugar to a mass of 3.75 g.
Analogs
| Name of the drug, manufacturer, country of production | Price per package 20 ml, dosage 100 mg/5 ml (in rubles) | Price per package 20 ml, dosage 200 mg/5 ml (in rubles) |
| Sumamed, Pliva, Croatia | 202 | 208 |
| Azitrox for children. Pharmstandard, Russia | 201 | 316 |
| Azithromycin Ecomed, ABVA Rus, Russia | 193 | 391 |
| Hemomycin, Serbia, Hemofarm | 123 | 223 |
| AzitRus, Sintez Acomp, Russia | 44 | 62 |