Betalok Zok
Monitoring of patients taking beta-blockers includes monitoring heart rate and blood pressure (at the beginning of treatment - daily, then once every 3-4 months), blood glucose concentration in patients with diabetes (once every 4-5 months). The patient should be trained in the method of calculating heart rate and instructed about the need for medical consultation if the heart rate is less than 50/min.
It is possible that the severity of allergic reactions may increase (against the background of a burdened allergic history) and there will be no effect from the administration of usual doses of epinephrine.
In elderly patients, it is recommended to monitor kidney function (once every 4-5 months). May increase symptoms of peripheral arterial circulation disorders. Patients with cardiac arrhythmias whose systolic blood pressure is below 100 mm Hg should be given IV only if special precautions are taken (there is a risk of a further decrease in blood pressure). The drug is discontinued gradually, reducing the dose over 10 days.
In case of arterial hypertension, the effect occurs after 2-5 days, a stable effect is observed after 1-2 months.
For exertional angina, the selected dose of the drug should ensure the heart rate at rest within the range of 55-60 beats/min, and during exercise - no more than 110 beats/min. In smokers, the effectiveness of beta-blockers is lower.
In combination therapy with clonidine, the latter should be discontinued several days after metoprolol is discontinued in order to avoid a hypertensive crisis. At a dose above 200 mg/day, cardioselectivity decreases.
Metoprolol may mask some clinical manifestations of thyrotoxicosis (for example, tachycardia). Abrupt withdrawal in patients with thyrotoxicosis is contraindicated because it can increase symptoms.
In diabetes mellitus, it can mask tachycardia caused by hypoglycemia. Unlike non-selective beta-blockers, it practically does not enhance insulin-induced hypoglycemia and does not delay the restoration of blood glucose concentrations to normal levels.
If necessary, beta2-agonists are used as concomitant therapy for patients with bronchial asthma; for pheochromocytoma - alpha-blockers.
If surgical intervention is necessary, it is necessary to warn the anesthesiologist about the therapy being performed (choosing a drug for general anesthesia with minimal negative inotropic effect); discontinuation of the drug is not recommended.
Reciprocal activation of the n.vagus can be eliminated by intravenous administration of atropine (1-2 mg).
Drugs that reduce catecholamine reserves (for example, reserpine) can enhance the effect of beta-blockers, so patients taking such combinations of drugs should be under constant medical supervision to detect an excessive decrease in blood pressure or bradycardia.
If elderly patients develop increasing bradycardia (less than 50/min), arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg), AV block, bronchospasm, ventricular arrhythmias, severe liver and kidney dysfunction, it is necessary to reduce the dose or stop treatment . It is recommended to discontinue therapy if skin rashes appear and depression develops caused by taking beta-blockers.
The drug is discontinued gradually, reducing the dose over 10 days. If treatment is abruptly stopped, withdrawal syndrome may occur (increased angina attacks, increased blood pressure). When discontinuing the drug, special attention should be paid to patients with angina pectoris.
Patients who use contact lenses should take into account that during treatment with beta-blockers, the production of tear fluid may decrease.
During pregnancy, it is prescribed only for strict indications (due to the possible development of bradycardia, hypotension, hypoglycemia and respiratory paralysis in the newborn). Treatment must be interrupted 48-72 hours before delivery. In cases where this is not possible, it is necessary to ensure strict monitoring of newborns for 48-72 hours after delivery.
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Indications for use
Based on the considered effect of the drug on the body, it is prescribed by cardiologists for use in the following heart rhythm pathologies:
- sinus and supraventricular tachycardia;
- supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias;
- atrial fibrillation;
- ventricular extrasystole;
- atrial flutter;
- arrhythmia caused by mitral valve prolapse.
In addition to cardiac disorders, reviews of which by cardiologists do not raise concerns regarding its effect on the body, it can be prescribed for use in the presence of such problems and diseases as:
- unstable angina;
- hypertensive crisis;
- angina pectoris;
- cardiac ischemia;
- acute phase of myocardial infarction;
- arterial hypertension;
- chronic heart failure;
- functional disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- senile or essential tremor;
- in complex therapy of thyrotoxicosis;
- panic attacks.
The drug "Betalok ZOK" can be used during complex therapy for an unreasonable state of anxiety, in cases of akathisia while taking antipsychotics. The drug can be prescribed to relieve migraines, as well as to reduce symptoms during the onset of withdrawal symptoms.
Known contraindications for use
Like any medicine, this drug has a number of contraindications. Doctors do not recommend its use if the patient has a history of the following diseases:
- decompensated form of chronic heart failure;
- state of cardiogenic shock;
- sinus bradycardia;
- arterial hypotension;
- acute heart failure.
People prone to allergies and hypersensitivity to metoprolol should take this drug under medical supervision. Cardiologists also advise caution in taking this medicine to people with problems such as:
- obstructive bronchitis;
- emphysema;
- bronchial asthma;
- metabolic acidosis;
- diabetes;
- kidney disease;
- psoriasis;
- liver failure;
- peripheral circulatory disorder.
Women during pregnancy are not prescribed this drug, as it can lead to a decrease in the heart rate of the pregnant fetus. It is also undesirable to take this drug during lactation.
pharmachologic effect
Manufacturer: Astra Zeneca, Sweden
Release form: extended-release tablets
Active ingredient: Metoprolol
Synonyms: Egilok Retard, Metoprolol Retard, Metoprolol KRKA
Betaloc ZOK is a selective beta-1 adrenergic blocker, that is, it blocks mainly beta-1 adrenergic receptors, reducing cardiac output, slowing the rhythm, facilitating myocardial stimulation during physical and mental stress, preventing reflex tachycardia. The drug inhibits the activity of the renin-angiotensin system, restores the sensitivity of baroreceptors, which, together with a decrease in cardiac output, causes a rapid hypotensive effect.
By reducing the frequency and strength of myocardial contractions, as well as its need for oxygen, Betaloc ZOK has an antianginal (anti-ischemic) effect.
The drug slows down the sinus rhythm and the rate of propagation of excitation through the atrioventricular node, inhibits the automaticity of the heart, lengthens the refractory period, and reduces the force of heart contractions. Thanks to these effects, the drug has an antiarrhythmic effect.
Since in therapeutic doses the drug does not affect beta-2 adrenergic receptors, bronchospasm, decreased sugar and constriction of peripheral vessels do not occur.
Betaloc lowers blood pressure, but is not a diuretic.
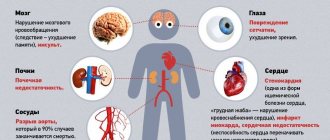
Possible side effects
Before using this medicine, you should carefully study information about all possible side effects using the official instructions in the package. Since the drug directly affects the heart rate, in a short time it can significantly reduce the pulse and lower blood pressure, the side effects of taking it should be taken seriously.
"Betaloc ZOK" can affect various organs and systems of the body, for example:
- from the sensory organs, vision impairment, dry eyes, and tinnitus may occur;
- possible disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system, such as slow motor and mental reactions, headaches;
- when large doses of the drug are prescribed, respiratory dysfunction may occur - bronchospasm, shortness of breath, nasal congestion;
- from the dermatological side, various rashes, skin itching, urticaria, photodermatosis, psoriasis-like reactions are possible.
If any changes in well-being occur or if symptoms similar to those described above occur, cardiologists advise that you must notify your doctor.
Analogs
Each patient has his own individual characteristics of the body, so it is better to find out in advance than to replace Betalok Zok. In almost any pharmacy or pharmaceutical online store you can purchase the following analogues of the drug:
- Metokor;
- Bisoprolol;
- Vasocardin;
- Metoprolol;
- Metoprolol Tartrate;
- Azoprol Retard;
- Egilok Retard;
- Corvitol.
Bisoprolol or Betaloc Zok - which is better?
It is difficult to say which medication is better for therapy. Bisoprolol is also a beta blocker and is often used in the treatment of heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, and for the prevention of angina pectoris. The effectiveness of these two drugs depends on the diagnosed disease, its severity and the individual characteristics of the patient's health.
Overdose
An overdose of the drug is possible if it is not used adequately to achieve the fastest effect. The Betalok treatment regimen must be agreed upon with your doctor! The fact that the drug has been taken in excess becomes clear after 20 minutes - 2 hours. Then, as a result, the following symptoms are observed:
- apnea;
- asystole;
- atrioventricular block;
- bradycardia;
- bronchospasm;
- lowering blood pressure;
- vomit;
- heart failure;
- convulsions;
- nausea;
- tremor;
- respiratory depression;
- fatigue;
- cardiogenic shock;
- esophageal spasm.
In particularly severe cases, hospitalization may be required. There is no antidote to the drug, so treatment is symptomatic.
Release form
"Betalok ZOK", reviews of cardiologists about the action of which confirm its effectiveness, is produced in the form of biconvex white tablets. They have an oval shape and can be engraved or notched. The medicine is available in various dosages: there is “Betaloc ZOK” 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg. Depending on the manufacturer, tablets can be sold to the end consumer either in cardboard packaging or in plastic bottles.
If a doctor has prescribed a dosage of 25 mg for a patient to take, if it is not available, you can safely buy Betaloc ZOK 50 mg or 100 mg. These tablets can be divided in half. In this case, the prolonged effect of the drug is completely preserved. But at the same time, it is strongly recommended not to crumble or chew them.
How does the drug work?
One of the drugs actively used in cardiology is Betaloc ZOK tablets. Reviews from cardiologists about it are based on its functional richness. The active component of the drug, metoprolol succinate, belongs to the pharmaceutical group of beta-blockers. It has antiarrhythmic, antianginal (anti-ischemic), beta1-adrenergic blocking, hypotensive effects.
Adrenergic receptors are widely distributed throughout the human body. They belong to transmembrane cell receptors and respond to neurotransmitter hormones - adrenaline and norepinephrine, which belong to the group of catecholamines.
β1 receptors are localized in the heart and kidneys. Their activation leads to increased strength and heart rate, and the myocardium requires more oxygen. This also leads to increased blood pressure. In the kidneys, β1 receptors are components of the juxtaglomerular apparatus, a component of the endocrine system.
Metoprolol succinate successfully blocks β1 receptors, and the dose of this drug for active functionality is required significantly lower than similar substances.
It suppresses the stimulating effect of catecholamines, which manifests itself during stress and physical activity, significantly reduces myocardial contractility and cardiac output and, as a result, lowers high blood pressure and heart rate. In addition, the active substance of the drug Betaloc ZOK increases the period of diastole and reduces oxygen starvation of the myocardium.
Studies conducted by the developer of the drug have shown that the concentration of the active substance (metoprolol succinate) in the blood plasma during treatment is constant, which ensures a stable therapeutic effect for a day or more. This avoids the peak side effects observed when used in the treatment of drugs with other substances that have beta-blockers as an active component.
Treatment with this drug allows you to obtain a persistent decrease in blood pressure during physical activity, while standing and lying down, as well as at rest.
The drug "Betalok ZOK" has recommendations from cardiologists, since studies conducted on the system for determining survival in chronic heart failure (MERIT-HF) show a significant increase in the survival rate of such patients, as well as a decrease in the number of required hospitalizations according to clinical indicators of threat to life.
Interaction with other drugs
Also, the doctor prescribing Betaloc ZOK should be informed about all the medications that the patient is using at the time of prescription. There are substances the use of which is strictly contraindicated when using Betalok ZOK. When taking it, it is strictly forbidden to inject Verapamil into a person. When using Betalok ZOK, you should be very careful when prescribing drugs similar to Reserpine (which, by their action, reduce the reserves of catecholamines). Such simultaneous administration can provoke an attack of bradycardia and a rapid drop in blood pressure in the patient.