Pain in the left side under the ribs is one of the most common clinical signs that patients complain about when visiting a gastroenterologist. This symptom has several variations and can also occur in both adults and children.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention and prognosis
The most common cause is gastroenterological pathological conditions. However, there are a number of other diseases and physiological sources of such an unpleasant manifestation.
In addition to the pain on the left side under the ribs, the symptoms will include many other clinical manifestations. The most common are:
- nausea and vomiting;
- violation of the act of defecation;
- fluctuations in heart rate and blood pressure.
The diagnostic process is aimed at identifying a predisposing factor, which is why it combines a whole range of laboratory and instrumental measures. In addition, manipulations carried out personally by the clinician are very important.
To get rid of this symptom, conservative therapeutic methods are used. However, it can be completely eliminated only after the underlying disease is cured.
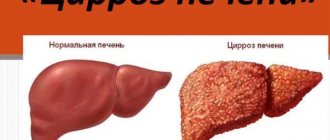
Spleen diseases
Enlargement (splenomegaly)
Pathological conditions characterized by enlargement of this organ (hypertrophy) cause the appearance of pain in the left hypochondrium.
There are few sensitive receptors in the tissue, but the organ capsule responds to stretching processes due to the presence of baroreceptors in it. It is for this reason that dull pain in the left side, localized in front under the left rib, most often occurs with a significant increase in the volume of the spleen. Pathological processes that can cause the spleen to enlarge include:
- blood oncology (leukemia) (determined by an oncologist);
- hereditary diseases associated with pathology of the blood system (sickle cell anemia);
- anemia that occurs with the destruction of blood cells (hemolytic);
- circulatory disorders in the vessels of the spleen (thrombosis of the splenic vein);
- “storage” diseases (amyloidosis, Gaucher disease);
- lymphoma;
- metastases of various tumors;
- some infectious processes (mononucleosis, malaria);
- parasitic diseases (echinococcosis);
- liver pathologies (for example, cirrhosis) – treated by a hepatologist.
Gap
The injury, which results in capsule rupture, is characterized by severe pain, even to the point of fainting, in the left hypochondrium, which intensifies with inhalation and sudden movements. In addition, other symptoms of intra-abdominal bleeding appear: increased heart rate, dizziness, drop in pressure, sharp pain when pressing under the left rib, tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall.
Identification of disorders by type of pain. What to do, what treatment will be needed?
Pain of a pathological nature poses a danger not only to the health of the body, but some are also fatal.
Based on the location of the symptom (left thoracic region, lower abdomen or hypochondrium) and description of the pain characteristics, the specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis and narrow the scope of the examination. It is important that a painful symptom can also be caused by pathologies in the organs of the reproductive system (in women).
Sharp sharp pain
Sharp pain more often signals serious problems in the body or exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Description of possible causes with recommended treatment methods:
| Provoking factors | Treatment nuances | Types of drugs | Folk compositions |
| Open stomach ulcer | It is forbidden to carry out independent treatment, even taking painkillers, as they will worsen the diagnosis. | These drugs are used only in a hospital after identifying the cause of the pain:
| For sharp and acute pain, the use of folk remedies is not recommended. Since it is important to initially identify the cause of the symptom. |
| Acute pancreatitis | |||
| Exacerbation of renal failure | |||
| Rupture of the spleen or left kidney | |||
| Fractured ribs | |||
| Myocardial infarction |
In case of severe pain, you must immediately call emergency help and ensure that the victim remains in a restful and comfortable position. Carrying out self-diagnosis is dangerous due to the development of death.
Dull aching pain
Dull pain is more often caused by chronic diseases.
Description of possible causes with recommended treatment methods:
| Provoking factors | Treatment nuances | Types of drugs | Folk compositions |
| Chronic diseases of the stomach, pancreas and duodenum. | Untreated diseases often become chronic, so when periodic pain appears, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics and a full course of treatment under the supervision of a doctor. | In the presence of chronic pathologies, the following types of medications are recommended (prescribed by a doctor):
|
|
| Cardiac ischemia | |||
| Beginning of the development of a heart attack | |||
| Oncological formations in the liver, pancreas, spleen. | |||
| Joint diseases | |||
| Pneumonia in the left lung |
Chronic diseases are dangerous due to the subsequent complete failure of the organ to function in the absence of therapy.
Nagging pain
Nagging pain mainly signals pathologies of the spleen and liver (pain can radiate to the left side).
To eliminate pain, specialists prescribe:
- painkillers (Panadol, Efferalgan);
- enzymes for liver function (Allohol, Heptral);
- enterosorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb).
Among traditional methods, it is recommended to use honey with cinnamon (the recipe is described above). Since the activity of these organs is impaired, it is important to cleanse the body of waste and toxins through medication. Otherwise, intoxication of the entire body is possible.
Stitching pain
Pain of a stabbing nature often accompanies kidney disease. The pathology is distinguished by the development of swelling and disruption of the urination process. Self-medication is dangerous due to organ failure.
Drug therapy uses:
- diuretics (Bumetanide, Furosemide);
- painkillers (Aspirin, Paracetamol);
- antibiotics (Amoxiclav, Azitrox);
- anti-inflammatory (Indomethacin, Diclofenac).
Traditional recipes:
- steam 10 g of carrot seeds in 200 ml. Leave for an hour. Drink 100 ml 6 times a day;
- grate horseradish, sweeten. Take 10 g before meals. If there are kidney stones, treatment is carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Additionally, the drinking regime and the amount of salt consumed are limited.
Throbbing pain
Pulsating pain occurs with the development or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
The following groups of medications are used for treatment:
- painkillers (Duspatalin, Platyfillin);
- enzymes that normalize the activity of the pancreas (Pancreatin, Creon);
- drugs with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects (Abaktal, Tienam);
- antipyretics (Ibuklin, Maxicold).
Folk compositions:
- steam 20 g of dry wormwood in 500 ml of boiling water. Leave in a thermos for 1 hour. Drink 50 ml 3-5 times a day;
- steam 5 g of dry plantain in 200 ml of boiling water. Leave to drink instead of tea for 20 minutes.
It is also important to follow a strict diet prescribed by your doctor during the period of exacerbation of the disease.
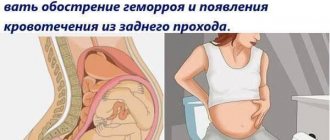
Pain due to “female” reasons
A woman’s left hypochondrium also hurts for natural and pathological reasons that occur in the reproductive organs.
Possible deviations and ways to eliminate them:
| Provoking factors | Features of therapy | Medications | Folk recipes |
| Ectopic pregnancy | In case of ectopic pregnancy and advanced diseases, when there is no effect from taking medications, surgical intervention is required; in other cases, drug therapy is used. |
|
|
| Ovulation, PMS and menstruation | |||
| Pregnancy, the child compresses the organs located on the left side. And also the beginning of contractions | |||
| Pathologies in the left ovary or in the left fallopian tube (inflammation, formations of any nature, ovarian torsion) | |||
| Endometriosis, fibroids, cancer in the uterus | |||
| Threat of miscarriage |
Self-medication of these pathologies is dangerous due to the development of infertility, and ectopic pregnancy can result in death.
When tilted
Pain that occurs or gets worse when bending over may indicate inflammation of the muscle tissue or a pinched nerve.
Anti-inflammatory (Desonide, Clofeson) and painkillers (Omnopon, Promedol) medications are used in treatment.
Also, to reduce pain, you can apply a leaf of cabbage or Kalanchoe (fix with a bandage and leave for 4 to 8 hours) or take baths with the addition of a decoction of pine needles (1.5 kg of pine needles, steamed with 2 liters of boiling water).
When inhaling
Pain that intensifies or appears when you inhale may indicate problems in the diaphragm. These pathologies can be life-threatening, so medication or alternative treatment is contraindicated until an ambulance arrives.
After physical activity
The occurrence of pain after physical activity is mostly natural and does not require drug treatment. To prevent its occurrence, it is necessary to warm up and warm up the muscles.
Pain allows early detection of the onset of the disease. It is important to immediately determine where the symptom is localized (left or right hypochondrium, lower or upper abdomen) and the characteristics of the pain (sharp, dull, throbbing).
This data will allow you to preliminarily determine the cause of the symptom and speed up the diagnostic process. Since in some cases, timely detection of the disease can save life (for example, ectopic pregnancy in women).
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Intestinal diseases
In the abdomen on the left there is a loop of transition of the transverse colon into the descending part of the large intestine. When inflammatory processes occur in the intestinal wall (colitis), pain appears in the left hypochondrium, but the patient in this situation will feel pain in the left hypochondrium.
Expansion of the intestinal wall during flatulence (hyperpneumatization) leads to the patient having severe abdominal pain under the left rib in front. A light touch causes increased pain due to stretching of the intestinal wall. Obstruction of the large intestine is manifested by intense pain, which intensifies when pressing on the abdomen. Characterized by intestinal bloating, as well as the appearance of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation and general symptoms of intoxication of the body. A tumor of the transverse colon is manifested by the fact that the patient has long-term moderate pain on the left under the ribs, accompanied by bloating, nausea, constipation, and the appearance of black stools. Symptoms gradually (over several months) become more pronounced.
Adhesive disease
Any surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity is fraught with the development of adhesions. Moreover, the method of surgical intervention does not always matter (open access or laparoscopic). Therefore, when the adhesive process develops, this becomes the reason for patients complaining after surgery that they have pain on the left side under the ribs.
It has been proven that adhesions develop in cases where inflammatory exudate (fluid) accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
When the adhesions are located between the wall of the colon and the anterior abdominal wall in the area of the left hypochondrium, pain occurs, which intensifies with intestinal peristalsis.
Stomach diseases
Most of the stomach (approximately 80%) is located on the left side of the midline. For this reason, his diseases can lead to pain in the left hypochondrium in front. The following disturbances in the functioning of the stomach can cause pain:
- Inflammation (gastritis) causes subcostal nagging pain in the left side of the abdomen, which intensifies with errors in diet. Effective remedies for stomach pain can be found here.
- A peptic ulcer in the area of the greater curvature of the stomach often causes pain under the ribs on the left. Ulcers are characterized by the appearance of so-called “hunger” pains, which appear 4-5 hours after eating.
- Perforation of the ulcer is manifested by the occurrence of a sharp “dagger” pain in the hypochondrium.
Cause: intercostal neuralgia
Various neurological diseases can cause compression or irritation of the intercostal nerves. Pain caused by intercostal neuralgia has a wide range of manifestations:
- In the area of the ribs, under the ribs - shooting, piercing, sharp or aching, burning or dull pain (see also pain in the heart).
- The pain may intensify with sudden movements, sneezing, inhaling, coughing, even when changing body position.
- Attacks of intercostal neuralgia are accompanied by stabbing pain in the chest, left side, manifested by muscle twitching, pallor or redness of the skin, and increased sweating.
- When pressing on certain points on the back, chest, between the ribs or along the spine, painful sensations also appear.
With neuralgia, pain can be localized not only in the left side, but also in the lower back, under the shoulder blade (as with heart disease). They can occur at night, in the morning, and during the day, for quite a long time; in places where the nerve pathways are damaged, a feeling of numbness sometimes appears.
Rare diaphragmatic hernias
The diaphragm is a muscular organ that has several physiological openings through which vascular bundles, the esophagus, the aorta, etc. pass. In rare cases, hernias of the costosternal triangle of the diaphragm occur, in which the intestinal walls are pinched. When such a hernia appears on the left side, the painful feeling will be localized in the projection of the hypochondrium.
Doctor's advice
In rare cases, such symptoms can be caused by kidney diseases, such as pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, kidney cancer, polycystic disease, nephroptosis, renal artery thrombosis. Other manifestations of the disease may be an increase in temperature up to 40 degrees, a change in the volume of urine excreted, both downward and upward, increased urination, swelling of the face, especially the eyelids, increased blood pressure, redness of urine (the color of meat slop), nausea , vomit. To exclude or confirm kidney disease, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder (it happens that a stone or sand comes out of the kidney and enters the bladder), a general urine test and a general blood test. And, of course, consult a nephrologist, urologist or therapist. The doctor will prescribe further examination and select the necessary treatment.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Irradiation (reflection) of pain from the chest organs
Sometimes certain diseases of the organs located in the chest can cause the patient to experience pain on the left under the ribs in the lateral part. These include: coronary heart disease, left-sided lower lobe pneumonia, left-sided pleurisy, pericarditis. A classic example of irradiation is the abdominal form of infarction. With this pathology, the patient has pain not in the chest, but under the ribs on the left. According to statistics, approximately 5% of cases of myocardial infarction occur with a similar syndrome. If you have heart problems, consult a cardiologist or heart surgeon.
Literature
- Boudina, Sihem; Abel, Evan Dale (1 March 2010). "Diabetic cardiomyopathy, causes and effects." Reviews in endocrine & metabolic disorders. 11 (1): 31–39. ISSN 1389-9155. PMC 2914514 Freely accessible. PMID 20180026. doi:10.1007/s11154-010-9131-7.
- Acton, Q. Ashton (2013). Advances in Heart Research and Application: 2013 Edition. Scholarly Editions. ISBN 978-1-481-68280-0.
- "Definition: neuralgia". International Association for the Study of Pain taxonomy. Archived from the original on|archive-url= requires |archive-date= (help). Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- Diagnostic tactics in patients with pleurisy of unknown etiology: Abstract of the dissertation / Harutyunyan A. V. - 2009.
- Morphogenesis and pathological anatomy of non-tumor exudative pleurisy Abstract of the dissertation / Friss S. A. - 2005.
Abdominal pregnancy
Occurs in no more than 0.5% of all cases of pregnancy outside the uterine cavity. However, during abdominal pregnancy, the fertilized egg is often attached to full-blooded, well-supplied organs, which include the spleen, intestinal mesentery, and liver, which is why women may experience pain under the ribs on the left.
In rare cases, pain in the left hypochondrium may occur due to abdominal pregnancy. Despite the apparent absurdity of this situation, similar cases have been recorded in medicine. You can use an online consultation with a doctor on our website in a paid or free mode to determine the severity of your problem.
The causes of pain in the left hypochondrium can be various pathological processes. Some of them require intensive care or even surgical intervention (rupture of the spleen, perforation of a stomach ulcer, etc.).
Any symptoms should prompt you to see a doctor. Only a competent specialist can correctly determine why pain occurs, comparing it with other manifestations of various pathologies, and prescribe effective treatment.
Learn about the causes of pain under the left rib in the front from the video:
Useful articles on the topic: Kidney disease in women: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Pain in the right side under the ribs in front - what could it be?
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://base.garant.ru/70349708/ https://gpfm.ru/assets/image%20for%20events/bol-v-zhivote.pdf
Rate how useful the article was
4.7 28 people voted, average rating 4.7
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Diagnostics
In order to find out which factor served as the source of pain in a given localization, it is necessary to carry out a wide range of laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Given that the left side most often hurts when coughing due to pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract, it is first worth consulting a gastroenterologist. It is this doctor who will perform the primary diagnostic procedures, including:
- studying the medical history to identify the primary source with a pathological basis;
- collection and analysis of life history, as this may indicate the impact of other causes;
- a thorough physical examination of the patient;
- deep palpation and percussion of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity;
- measuring heart rate, blood tone and body temperature;
- a detailed survey of the patient to obtain information about the symptomatic picture, which can sometimes directly indicate the underlying pathology.
A comprehensive examination begins with laboratory tests, namely:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- coprogram;
- PCR analysis;
- hormonal and immunological studies;
- blood culture;
- general clinical urine analysis.
The following instrumental examinations can help make a correct diagnosis:
- abdominal ultrasonography;
- gastroscopy and colonoscopy;
- ECG and FGDS;
- CT and MRI;
- X-ray of the chest and spinal column;
- endoscopic biopsy.
Gastroscopy
Since pain can occur due to damage to other internal organs, the following specialists can also take part in the diagnostic process:
- endocrinologist and nephrologist;
- pulmonologist and neurologist;
- traumatologist and cardiologist;
- gynecologist and therapist;
- pediatrician and vertebrologist.
Depending on which doctor the patient is referred to for additional examination, he will be prescribed specific laboratory and instrumental procedures.