- September 7, 2020
- Other drugs
- Suzanna Nyrova
Furosemide in ampoules is a popular diuretic. Used for hypertension and edema. This drug is effective and relatively safe, but proper monitoring, especially of potassium levels, is necessary during treatment. Let's look at detailed instructions for using Furosemide in ampoules.
Composition and pharmacological action
The drug is a diuretic drug and belongs to the group of loop diuretics. Its active substance has a name similar to the commercial one. The drug blocks the excretion of sodium and chlorine, their concentration in the kidney cells increases, as a result of which the amount of excreted fluid increases.
Clinically, this is manifested by the rapid excretion of urine in large volumes, which helps reduce blood pressure, the load on the heart and kidneys, and edema is also effectively eliminated.
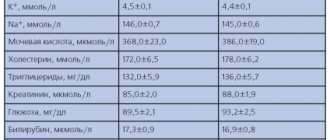
In addition to sodium and chlorine, the secretion of potassium, magnesium and calcium increases, therefore, with long-term use, the patient and the attending physician must simultaneously take vitamin complexes that will help replenish these microelements in the body.
Is it possible to take other drugs at the same time?
Other diuretics (potassium-sparing diuretics, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors), used in parallel with Furosemide, enhance its diuretic effect. If they are used, the doctor should adjust the dosage of the drug.
Potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), used in parallel with the drug, reduce potassium excretion in the urine and prevent hypokalemia.
The diuretic may cause a decrease in potassium levels in the blood and thus increase the toxicity of concomitant cardiac glycosides (for example, Digoxin) and increase the risk of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias.
The drug may interfere with the effects of neuromuscular blocking drugs used in parallel (skeletal muscle relaxants, such as Tubocurarine).
This medication may decrease the effect of catecholamines (eg, epinephrine, norepinephrine) on arterial muscle.
Concomitant use of the drug with corticosteroids may cause sodium retention.
Concomitant use with corticosteroids, corticotropin (ACTH), Carbenoxolone, beta 2-agonists, Reboxetine, Amphotericin B or laxatives increases the risk of hypokalemia.
The drug reduces the excretion of lithium and may increase its toxic effect. Concurrent use with lithium is not recommended. If such combination therapy is necessary, it should be done in a hospital setting where lithium levels will be adequately monitored and doses reduced as needed.
May reduce the effectiveness of oral antidiabetic drugs and insulin, in which case the diuretic dose should be adjusted. It is necessary to monitor blood glucose levels.
If it is used in parallel with antihypertensive or other drugs that can lower blood pressure (some antidepressants, hypnotics, sedatives, antipsychotics, barbiturates, opioids, Baclofen), the antihypertensive effect may increase.
Introducing or increasing the dose of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (angiotensin II receptor antagonists) can significantly reduce blood pressure and reduce kidney function.
Caution should be exercised if diuretics are used in parallel with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen), since these drugs can reduce the diuretic and hypotensive effect of diuretics and cause renal failure.
The drug may enhance the effect of salicylates, which can lead to poisoning by them.
The drug enhances the toxic effect on hearing (ototoxic effect) of aminoglycoside antibiotics (for example, Kanamycin, Neomycin, Vancomycin) and other drugs that can be toxic to hearing. Hearing damage may be permanent.
The use of the drug with Cisplatin can have ototoxic and nephrotoxic (renal toxic) effects.
"Phenytoin" and its derivatives, with long-term use, weaken the diuretic effect of furosemide.
The drug increases the renal toxicity (nephrotoxicity) of cephalosporins and other antibiotics that can be toxic to the kidneys.
The simultaneous use of Risperidone and Furosemide is not recommended. In this case, there was an increased mortality rate in older adults.
Furosemide with Carbamazepine or Aminoglutethimide may increase the risk of hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood).
Probenecid and Methotrexate may reduce the effect of the drug.
Parallel use with Cyclosporine increases the risk of gout.
Indications for use of the injection form
The drug is prescribed for the treatment of chronic kidney disease, nephrotic syndrome, and also to enhance diuresis when the patient is poisoned with chemicals (in cases where they are excreted unchanged by the urinary organs).
Furosemide in injection form is also necessary for the treatment of chronic and acute forms of heart failure, severe arterial hypertension, and also for hypertensive crisis. The drug is used for swelling as a result of dysfunction of the liver and brain.
"Furosemide" in ampoules
The injection solution is administered by drip when rapid effects after administration are required, for example, for ascites, edema due to impaired renal, hepatic or pulmonary function. Sometimes an intravenous injection is given instead of a drip. This treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
After intravenous administration of Furosemide solution, the diuretic effect occurs within 5 minutes and usually lasts about 2 hours. The maximum effect occurs 20-60 minutes after administration. After intramuscular administration, the diuretic effect is somewhat later than after intravenous administration.
Contraindications for use
The medicine is not used if patients have allergic reactions to its active substance and auxiliary components. Other contraindications:
- acute form of glomerulonephritis and renal failure with a complete absence of urine excretion;
- obstruction and narrowing of the lumen of the urinary tract;
- stenosis of large blood vessels and heart valves;
- violation of the water-electrolyte balance of the body;
- gout, increased uric acid levels;
- coma and precoma of various etiologies;
- decreased blood pressure;
- acute period of myocardial infarction.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing Furosemide by injection for prostate adenoma, autoimmune pathologies, diabetes mellitus, cerebral atherosclerosis, decreased protein levels in the body, during pregnancy and lactation.
Careful reception
Caution in use requires prostatic hyperplasia, systemic lupus erythematosus, diabetes mellitus (decreased glucose tolerance), hypoproteinemia (the likelihood of ototoxicity), stenosing atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries, pregnancy (especially in the early stages, can be used for health reasons), during breastfeeding.
How to take Furosemide for swelling?
Course of therapy and dosage
In most cases, the medicine is administered intravenously; it must first be diluted in saline solution. The frequency and dose are determined and adjusted by the doctor; it is forbidden to do this yourself.
These indicators directly depend on the severity of the pathology being treated.
In most situations, 1-2 ampoules of Furosemide are sufficient. If this is not enough, then repeated administration of the medicine is prescribed, the maximum daily amount is 600 mg.
As soon as the patient’s condition has stabilized, they switch to tablet forms. The drug is taken under the supervision of medical personnel, with control of the body’s water and electrolyte balance.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
During this period, it is better not to use Furosemide. The drug is prescribed only when the expected effect exceeds the possible risks to the fetus. During lactation, you should stop breastfeeding. The dose is calculated according to the same principles as for other patients, but it is better to use as much as possible a smaller amount of the drug.
Children and newborns
As for this group of patients, the dose of Furosemide is calculated depending on the weight. The maximum dose that can be used is 0.5-1.5 mg of medication per kilogram of body weight. This applies to those under 15 years of age. For the rest, the dose is calculated in the same way as for adults.
Interaction with other medications
Caution should be exercised when simultaneously prescribing Furosemide injections with other drugs that lower blood pressure, including cardiac glycosides, glucocorticoids, antibacterial agents, and muscle relaxants.
This medicine reduces the effect of hypoglycemic and lithium-containing drugs, Allopurinol. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and pressor amines reduce the effectiveness of Furosemide itself.
When administering this drug, it is important to exercise caution when used concomitantly with radiocontrast and detoxification drugs.
Overdose
Signs of overdose with Furosemide 1% solution: marked decrease in blood pressure, shock, collapse, dehydration, hypovolemia, arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation and AV block), hemoconcentration, dehydration, acute renal failure with anuria, thromboembolism, thrombosis, confusion. , drowsiness, apathy, flaccid paralysis.
Therapy for overdose: correction of the acid-base state and water-salt balance, replenishment of the amount of circulating blood and further symptomatic treatment. There is no specific antidote.
Side effects
Like any drug, Furosemide can cause adverse reactions in patients. The list looks like this:
- decreased blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbance, increased contraction frequency;
- dizziness and headaches, decreased sensitivity, general weakness, apathetic state;
- in rare situations, decreased hearing and vision may occur;
- nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, dry mouth, bowel dysfunction, jaundice;
- allergic reactions of varying severity;
- urinary retention;
- metabolic disorders of uric acid, glucose, cholesterol;
- a general blood test can reveal a decrease in the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells and platelets;
- water-electrolyte imbalance.
In rare cases, patients complain of weakness and muscle cramps, increased blood density, and accumulation of calcium in the kidney tissues.
Reviews from doctors
The drug is used by doctors in a large number of specialties. These are mainly urologists, cardiologists, and resuscitators.
I often use Furosemide by injection. There are a large number of patients with heart failure and arterial hypertension in the hospital. In acute conditions, Furosemide is an indispensable drug. The drug has side effects, but with strict monitoring and dosage they can be easily avoided. It is important to note the fact that Furosemide is affordable.
Lemeshev V.K., cardiologist
This product is always available in our hospital and department as well. Furosemide is highly effective in treating a wide range of diseases, it is easy to dose, and the amount of the drug used is easy to adjust. My clinical practice has only positive results from the use of this drug - Furosemide helps with severe pathologies and acute conditions.
Elenina V.I., resuscitator
When should the drug not be used?
Unfortunately, even if there are indications for use, it cannot always be used. You cannot take this medicine if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to any of the ingredients or other sulfonamides.
You also cannot use the drug if you have:
- anuria or renal failure that does not respond to furosemide injections;
- hypovolemia or dehydration;
- renal failure resulting from intoxication with nephrotoxic or hepatotoxic substances, or renal failure associated with hepatic coma;
- severe hypokalemia or severe hyponatremia;
- pre-coma and coma associated with hepatic encephalopathy.