What's happening? This question is asked by a woman when she sees heavy vaginal discharge, unpleasant odor, itching and burning. Tests for all kinds of sexually transmitted infections are negative. The reasons for this condition can be very different. One of them is gardnerellosis.
Whether Gardnerella vaginalis is an infectious agent or not is an open question, since this rod-shaped bacterium is part of the vaginal microflora in small quantities. In a healthy body, it behaves quietly, does not betray its presence in any way and does not reproduce actively.
About 10 thousand species of microorganisms constantly live in the female body (as well as in the male body). Their total weight is about a kilogram. If we take into account the size of bacteria (there are 10 bacterial cells in every human cell), we can imagine the scale of this neighborhood. Many bacteria do not cause any harm to humans. Moreover, people simply cannot live without them. Each variety of our satellites occupies its own niche and does not leave it quantitatively.
Problems arise when the biological program fails. For some reason (internal or external), the number of some bacteria decreases, while others immediately strive to occupy the vacated space. This also happens in the case of bacterial vaginosis (gardnerellosis): due to a decrease in the number of beneficial lactobacilli in the vagina, opportunistic microorganisms actively multiply . Among them is Gardnerella vaginalis.
What is gardnerellosis in women
The vaginal environment of women includes a certain number of beneficial and opportunistic microorganisms. Normally, the largest number should be lactobacilli; they perform several functions at once:
- Have an antimicrobial effect;
- Activate local immunity;
- Maintains the desired acidity in the vagina.
When their number decreases, the pH of the vagina changes, and the opportunistic flora begins to steadily increase, which causes specific changes to appear. Bacterial vaginosis occurs, the main cause of which may be the rapid proliferation of gardnerella.
Their concentration can increase hundreds of times, and pathology is possible both in women who are sexually active and in virgin girls.
Gardnerellosis is not considered a sexually transmitted disease. However, a woman suffering from bacterial vaginosis can transmit the infection to her sexual partner, resulting in inflammation of the man's urethra or head of the penis.
An infected man or carrier of Gardnerella vaginalis can spread the bacterium to other women during intimate contact. In this regard, gardnerellosis requires a special approach to treatment, after which the doctor must make sure that vaginal dysbiosis is eliminated.
Consequences, prognosis: can it be cured completely and forever?
If treatment is carried out competently, using antimicrobial drugs, restoratives and medications that help restore the “correct” microflora, the risk of negative consequences for the body is minimized.
A common complication is a weakening of the body's defenses . He needs time to get back to normal.
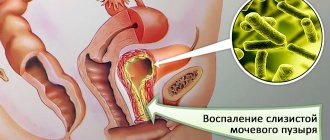
If the disease has been advanced, problems with the urinary tract (cystitis) and reproductive health (failure of the menstrual cycle, inflammation of the ovaries and appendages) may occur.
In general, the prognosis is favorable, and serious complications are rare. The main thing is to recognize the disease at the very beginning.
Classification
There are several forms of bacterial vaginosis:
- COMPENSATED. The analyzes reveal a slight deviation from the norm in the number of opportunistic microorganisms, including gardnerella. There are no obvious symptoms;
- SUBCOMPENSIBLE. The number of lactobacilli is noticeably reduced, the opportunistic flora is increased;
- DECOMPENSED. Beneficial microorganisms are practically not detected in tests; the smear contains only bacteria classified as opportunistic. With this form of the disease, the inflammatory process with corresponding symptoms is highly pronounced; upon examination, atypical changes in the epithelium are revealed.
By identifying a secondary infection during the diagnosis of gardnerellosis in women, there may be:
- Isolated;
- Combined. Often, an increase in gardnerella occurs against the background of syphilis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and thrush.
The classification of vaginosis allows you to choose the most effective course of therapy for each patient individually.
What is the diagnosis of gardnerellosis?
Identification of gardnerella and symptoms typical of gardnerellosis, despite the fact that the bacterium is not the only causative agent/marker of bakvaginosis, is used in the diagnosis of the latter.
A gynecologist can prescribe the necessary tests, including when planning a pregnancy.
Thus, the diagnosis of vaginal gardnerellosis is established subject to the presence of at least three of the four Amsel criteria, which include:
- characteristic vaginal discharge is grayish-white, thick, homogeneous, with a specific odor;
- pH of secretions over 4.5;
- positive amino test result - when mixing equal amounts of the sample and a solution of 10% potassium hydroxide, a “fishy” smell appears;
- Microscopic examination reveals “key” cells.
The 10-point Nugent system is also used for microscopic evaluation of a Gram-stained vaginal discharge sample, scoring:
- lactobacilli (large gram-positive bacteria);
- gardnerella and anaerobic bacteria (small gram-negative/gram-variable bacteria);
- mobiluncus and similar curved gram-negative/gram-variable bacteria.
Each morphotype is awarded points, for the 1st – from 4 to 0, for the 2nd – from 0 to 4, for the 3rd – from 0 to 2.
Moreover, the greater the number of lactobacilli and the fewer other microorganisms, the less points.
For normal flora the sum of points is up to 3, for bakvaginosis - from 7.
In men, diagnosis is carried out in the presence of signs of urethritis, balanitis, prostatitis (it is important to confirm that all these pathologies are caused by gardnerella).
Also to prevent such problems.
In men who are sexual partners of women with bakvaginosis, diagnostic measures and preventive therapy are not carried out.
Since it has been proven that the latter does not affect the number of relapses of vaginal gardnerellosis.
When making a diagnosis, it is important to understand that it is not so much the content of Gardnerella itself that matters, but its quantitative ratio with lactobacilli.
In the absence of symptoms against the background of a sufficient number of representatives of normal microflora, gardnerella can be detected in completely healthy women.
Especially when using high-precision diagnostic methods (PCR, cultural sowing).
Therefore, laboratory testing using the listed methods in the absence of manifestations of the disease in women is considered inappropriate.
And in men, due to the short presence of microorganisms in the urethra, it is usually meaningless.
It is also possible that, against the background of a significant decrease in the number of lactobacilli and pronounced manifestations of vaginal gardnerellosis, the pathogen itself is not detected or its quantity is very small (this may also be the reason for negative tests in the partner).
Therefore, testing for other markers of bacterial vaginosis is recommended.
Thus, gardnerella is not a bacterium for which detection itself is important.
If there are symptoms of the disease, then it is important to determine quantitative indicators.
In general, if PCR, which has a very high sensitivity and is capable of detecting the most minimal microorganism content, turns out to be positive, and bacterial culture is negative, then quantitative assessment is not required at all.
If gardnerella is detected in semen or urine, in the presence of corresponding complaints, a diagnosis of gardnerellosis (cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis) can be made.
In case of frequent relapses of infection, consultations with an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and other specialists are recommended to exclude concomitant diseases.
Routes of infection
As already mentioned, gardnerella occurs in large quantities in women when the natural microflora of the vagina changes. That is, gardnerellosis does not apply to sexually transmitted infections, however, the pathology is directly related to risk factors for the occurrence of major sexually transmitted diseases.
This is a frequent change of sexual partners, lack of barrier contraception. Therefore, a patient with signs of bacterial vaginosis should be examined for all sexually transmitted infections.
A woman who does not have vaginosis could theoretically receive a large amount of gardnerella from an infected man or a carrier of the bacterium.
The risk of infection increases during intimate intimacy in the acute stage, that is, when all the symptoms of infection in a man are pronounced.
The household route of transmission of Gardnerella, that is, through towels, washcloths, underwear, is also possible, but is very rare.
Which doctor should I contact?
If signs of gardnerellosis appear or if this pathogen is detected in a laboratory, it is imperative to contact a specialist. Several doctors are solving this problem at once, everything will depend on what symptoms the patient comes with and to whom. A urologist deals with severe urinary problems.
An obstetrician-gynecologist or dermatovenerologist helps women cope with odor and discharge problems.
Men most often turn to dermatovenerologists.
At-risk groups
Gardnerella is part of the microflora of almost any woman, that is, it cannot be completely removed from the vagina. Increased reproduction of bacteria is possible regardless of age and sexual activity.
According to statistics, gardnerella is detected in higher than normal levels in 28% of women who do not have a sexual partner and in 32% of virgin patients.
However, the risk of bacterial vaginosis caused by Gardnerella is much higher in women at risk. Patients included in this category are:
- Leading an active sex life with frequent changes of partners;
- Not using contraception (condoms);
- Those who have given birth and repeatedly resorted to abortion.
Infection of a newborn girl is also possible if the mother has gardnerellosis at the time of birth.
Causes
The causative agent of many infectious diseases enters the body in the presence of external and internal factors contributing to this.
Gardnerellosis, the symptoms and treatment of which we will discuss below, is no exception. If we consider external factors, then for infection with bacterial vaginosis it is enough:
- stop eating fermented milk products;
- uncontrollably eat sweets and foods rich in carbohydrates;
- abruptly change sexual partner (even if this person is completely healthy, there is a risk of developing the disease);
- have one or more sexually transmitted diseases that negatively affect the vaginal microflora;
- live in a poor environmental environment;
- regularly use antibiotics and corticosteroids;
- constantly use tampons, which deprive the vagina of the necessary air flow;
- wear synthetic, too tight and uncomfortable underwear.
If we talk about the reasons for the development of internal gardnerella, they include:
- hormonal imbalance (often its occurrence is recorded during pregnancy);
- immunodeficiency and general weakness of the body;
- chronic diseases;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- constant stress;
- overwork (physical and psychological).
The presence of gardnerella DNA in the female and male body is not something exceptional. A healthy body is inhabited by many bacteria, and no less than several dozen in the reproductive system. The appearance of any dangerous disease can only be expected when the number of such bacteria exceeds the permissible norm. So, a completely healthy person will not develop gonorrhea only for the reason that gardnerella has entered the body. But the lack of treatment over a long period of time can lead to a phenomenon such as chronic gardnerellosis, which is no less bad.
The danger of gardnerellosis
Vaginal dysbiosis cannot be treated as a disease, the danger of the consequences of which for the body is minimal. If an increased number of gardnerella is not detected in a timely manner and there is no treatment in women, the likelihood of inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes and infertility increases.
For pregnant women, dysbiosis is dangerous due to complications that are possible both during pregnancy and during childbirth.
With a pronounced increase in gardnerella in the vaginal environment, a woman can transmit this bacterium to a man. In most cases, the sexual partner, under the influence of Gardnerella vaginalis, develops urethritis and balanoposthitis; with these diseases, the risk of decreased potency, prostatitis and male infertility increases.
Why is infection dangerous?
This disease is not purely sexually transmitted , but concomitant treatment is necessary. With a long course of gardnerellosis without classic signs - discharge, pain, discomfort in the genital tract - serious complications can develop.
In women, untimely and incorrect treatment can provoke the development of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, including adhesive disease, metroendometritis - inflammation of the muscular layer of the uterus.
Other consequences:
- endometritis;
- damage to the fallopian tubes up to complete obstruction;
- chronic diseases of the urinary system - pyelonephritis;
- infertility.
With timely access to a gynecologist and adequately prescribed therapy, gardnerellosis can be successfully treated.
Even an advanced disease can be cured by completely restoring women’s health.
The main causes of gardnerellosis in women
Any factor, sometimes even the most insignificant, can disrupt the normal balance of vaginal flora. The reasons for the increase in the number of gardnerella in the female body include:
- Infection with microorganisms that cause sexually transmitted diseases. Diseases such as chlamydia, acute trichomoniasis, and gonorrhea lead to inflammation of the mucous walls of the vagina, as a result of which the microflora present changes. This creates the preconditions for the activation of opportunistic microorganisms, including gardnerella;
- Hormonal imbalance. Failure of the endocrine system often occurs during pregnancy and chronic diseases. Stressful situations, antibacterial treatment, and improper use of contraceptives can cause hormone imbalance;
- Severe intoxication. Poisoning with stale and toxic products often leads to intestinal dysbiosis, which can spread to the vagina;
- Endocrine pathologies. Gardnerella levels are often detected at elevated levels in women with diabetes. This disease disrupts the acid-base balance of all mucous membranes, including the vagina;
- Therapeutic gynecological manipulations on the organs of the reproductive system. Dysbiosis can be a consequence of invasive diagnostics (with penetration into the vagina), abortions, and certain procedures;
- Private use of barrier contraception methods. It is certainly necessary to use condoms with untested partners, but sometimes such contraceptives are coated with lubricant, which can negatively affect the microflora;
- Frequent use of drugs intended for vaginal administration and douching. External influences on the vagina can change the ratio of beneficial and harmful microorganisms, which ultimately leads to dysbiosis;
- Decreased functioning of the immune system. Dysbacteriosis of the internal systems of the body often occurs against the background of recurring respiratory infections, blood diseases, helminthiasis, and malignant processes. Immunity is also negatively affected by sudden climate change, long-term drug treatment, strict diets, radiation exposure, chemotherapy;
- Intestinal dysbiosis.
The main reason for the upward deviation of gardnerella must be established during the diagnostic process. This is necessary to choose the correct and effective therapy.
Where does the pathology come from: causes and routes of transmission
Where does Gardnerella come from in women, what are the reasons for its appearance? Gardnerellosis develops for a number of reasons , which gynecologists consider classic:
- the use of potent antibiotics that kill microflora in the intestines and vagina, undermining the optimal ratio of microorganisms;
- douching that women do on their own, as a result, the beneficial flora is simply washed away;
- use of antiseptics with a powerful antibacterial effect for douching;
- the use of contraceptives containing the substance 9-nonoxynol, which can have a detrimental effect on lactobacilli;
- promiscuity, frequent change of sexual partners;
- sexual intercourse without contraception.
For gardnerella to begin to actively multiply, causing bacterial vaginosis, several reasons are needed.
Although in women with a weakened immune system, the disease can start in the presence of one factor.
Infection occurs through sexual contact without barrier contraception.
Is gardnerella transmitted from woman to man and vice versa, can a man infect a woman? The source of infection is a sick woman. The main routes of infection are from women to men and vice versa.
Although doctors say that gardnerella cannot take root in the male body, men act as a carrier of the microorganism.
Some argue that there is an oral method of infection. But it has been proven that gardnerella cannot exist and develop on the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. Therefore, this route of transmission is questioned.
Symptoms
Gardnerellosis in women can occur:
- Asymptomatic. Gardnerella is detected only diagnostically, the patient does not present any obvious complaints;
- With a clear clinical picture. In this case, atypical discharge, discomfort, and pain appear.
From the moment of exposure to a factor that provokes an imbalance of microflora or after transmission of infection during sexual intercourse until the appearance of the main symptoms of the pathology, it can take from 3-4 to 20 days. At this time, the opportunistic flora gradually replaces the healthy one.
The disease can be suspected by a number of signs, these are:
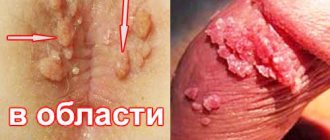
- Vaginal discharge. At the early stage of Gardnerella reproduction, they are slimy and slightly cloudy, then they become viscous grayish or green-yellow;
- The appearance of an unpleasant, fetid odor from the genital tract. Reminds me of a decaying fish. This aroma is due to the rapid decomposition of amines due to the colonization of the vaginal mucosa by gardnerella;
- Discomfort in the vagina. Occurs due to an inflammatory reaction. The mucous membranes are swollen and hyperemic. Itching and burning are not typical for gardnerellosis; their appearance indicates either the neglect of the process or the addition of sexually transmitted infections;
- Pain during intimacy. They occur both during sexual intercourse and after it;
- Cycle failure.
The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen during urine excretion indicates the development of urethritis and cystitis, which is quite possible if gardnerella spreads higher up the urinary system.
In acute cases of bacterial vaginosis, a disturbance in the general condition is also possible. Women report malaise, weakness, and a rise in temperature.
Case from practice
My mother brought her 33-year-old daughter to my appointment, literally by the hand. My mother answered all my questions; the girl seemed to have taken water into her mouth. After asking if the patient herself could talk, I took my mother out into the corridor and asked her to wait. The following picture emerged: the patient was unmarried (which was not surprising given such a feeling of self-doubt), and had no intention of getting married. It turned out that the young woman experienced real horror before intimacy with a man because of an unpleasant odor from the vagina of an incomprehensible nature. No hygiene products helped, and this smell haunted her for 10 years. As a student, my patient had her only attempt at intimacy with a young man. They only met for a month, and then the young man simply disappeared, leaving this terrible smell as a memory. Later, several more times it came to intimacy, but with the same result: the partner disappeared, not hiding his irritation and hostility. The girl withdrew into herself and stopped communicating with members of the opposite sex. Time passed, the smell did not disappear, the prospect of finding a family became more and more elusive. And mom sounded the alarm... The girl really needed to be saved.
Features of the pathology
According to the nature of the pathological process, gardnerellosis can be:
- SHARP. Mostly occurs when infected with a large amount of Gardnerella from a sexual partner. Symptoms increase rapidly over 3-5 days;
- SUBACUTE. Develops gradually, usually over one and a half to two weeks;
- CHRONIC. Erased symptoms of the pathology are recorded for 6 or more months;
- RECURRENT. It is characterized by alternating phases of exacerbations with remission.
According to the nature of the discharge, bacterial vaginosis caused by Gardnerella can be:
- SEROUS. The secretion released from the vagina has a yellowish tint;
- PURPENT. Its occurrence is indicated by a greenish tint of mucus;
- FIBRINOUS. Bloody streaks are noticeable in the discharge.
Fibrinous gardnerellosis indicates the neglect of the process in which a change in the epithelial layer of the vaginal walls occurs.
Venereologist at a private clinic
To ensure that the treatment does not cause discomfort, it is necessary to select a venereologist who has been monitoring you and the results of the therapy throughout the entire period.
Help in selecting specialists is provided by the help desk for private clinics in Moscow “Your Doctor”. You can make an appointment by calling from your home or mobile phone at a time convenient for you.
Useful information on the topic of venereologist:
- Venereologist
- Venereologist consultation
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases
- Treatment of sexually transmitted diseases
- Examination by a venereologist
- Venereology - the science of sexually transmitted infections
- Venereologist appointment
- Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases
- Paid venereologist
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Kasabov Vadim Vladimirovich Dermatovenerologist
Back to section
The danger of gardnerella for pregnant women
A significant excess of gardnerella in pregnant women can cause:
- Intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- Premature birth;
- Transmission of infection to a newborn during natural birth;
- Complications after cesarean section, including endometritis;
- Low body weight of the child;
- Rupture of the fetal membrane, and this complication often occurs in the first trimester and accordingly leads to miscarriage;
- Pneumonia in a child during the perinatal period.
All complications that arise as a result of the colonization of the vagina by Gardnerella are extremely dangerous for the mother and child. Therefore, the pathology cannot be ignored - a woman can receive its full treatment even while waiting for the baby.
Features of the course of the disease in pregnant women
Gardnerellosis in women, if the symptoms and necessary treatment are ignored, can seriously affect the reproductive function of the body. In pregnant women, the disorder is often accompanied by thrush, in which there is a risk of infection of internal organs and the mucous membrane of the developing fetus.
Gardnerellosis has no direct effect on the fetus, but can cause complications:
- birth of a child prematurely;
- low birth weight;
- inflammation of the uterine mucosa;
- rupture of the birth canal, subsequent inflammation;
- the development of a secondary infection and its penetration through the placenta (vaginal candidiasis);
- Chorioamnionitis (premature rupture of the membranes).
To exclude the disease, pregnant women should be periodically checked for the presence of bacteria. The difficulty of treatment is that it is undesirable to use antibiotics during this period. If vaginitis begins, metronidazole vaginal gel should be used during the 1st trimester of pregnancy.
For women who are breastfeeding, drugs are prescribed intravaginally.
Gardnerellosis and bacterial vaginosis - is there a difference?
Bacterial vaginosis is a pathology that occurs as a result of a violation of the vaginal microflora. Accordingly, the reasons for its development may be not only gardnerella, but also other microorganisms related to conditionally pathogenic microflora.
Gardnerellosis usually means changes in tests that only indicate an increase in the number of gardnerella. An isolated microflora disorder is rarely detected, therefore in practical gynecology the term bacterial vaginosis is most often used.
Principles of therapy
There are several principles of therapy that can help cope with the infectious process occurring in the body.
First of all, it is recommended:
- visit a doctor, tell him about the presence of certain symptoms and undergo examination
- start taking antibiotic therapy only after it is recommended by your doctor
- Before starting to use antibiotics, it is recommended to undergo an examination to clarify the nature of the pathogen and its sensitivity to drugs with antimicrobial activity
- If the doctor has prescribed antibiotic therapy, you must carefully follow the recommendations for dosage and duration of treatment
- Once the disease has been controlled, measures must be taken to prevent symptoms from reoccurring
It is important to remember that if the patient does not follow basic recommendations, getting rid of gardnerellosis will not be so easy.
Moreover, in some cases the disease poses a serious danger, as it can lead to the development of infertility.
It is important to remember that the goal of treatment is not only the relief of unpleasant symptoms.
But also the fight against a specific pathogen that is the cause of inconvenience.
Diagnostics
A thorough examination of women during preventive examinations and during initial consultations is necessary to identify all the slightest changes.
To establish the state of the vaginal environment and the ratio of gardnerella and beneficial microorganisms it is necessary:
- Conduct a survey and gynecological examination. The gynecologist must collect information about the nature of sexual activity, previous diseases, and possible causes of dysbiosis. During the examination on the chair, the condition of the vaginal walls is assessed;
- Order a smear examination for the presence of pathogenic bacteria, take material for markers of vaginosis;
- Determine the acidity of the vaginal environment. For this purpose, special test strips are used;
- Conduct PCR diagnostics. Polymer chain reaction tests help identify most types of sexually transmitted infections;
- Carry out the reaction with isonitrile. It is this substance that gives the mucus a specific odor when gardnerella multiplies.
In order to determine whether there are deviations in the number of Gardnerella, the following is carried out:
- Microscopic analysis. The biomaterial (smear) is stained with a reagent, which allows gardnerella to give a special color. Then the smear is examined under a microscope, all cells within the field of view of the laboratory technician are taken into account;
- Bac sowing. The biomaterial is placed in special conditions that are suitable for the propagation of Gardnerella. After reaching a certain number of microorganisms, their resistance to antibacterial agents is checked. The results of bacterial culture become known after 7-10 days;
- PCR. This study allows you to determine the DNA of most pathogenic bacteria. The method is highly accurate and detects Gardnerella in a smear even in small quantities;
- Cytological examination. It is additional, allows you to identify vaginosis, inflammatory changes in the vagina and cervical cancer;
- QACH (Hay-Ison smear analysis). It is used to establish the type of pathogenic flora that causes changes in the microflora.
In order for the tests to be as reliable as possible, a woman should prepare for smear collection:
- There should be no sexual intercourse for at least 24 hours;
- A day before diagnosis, you need to stop douching and using antibacterial agents using the vaginal route;
- Avoid urination 3 hours before the test;
- On the day of taking a smear, wash yourself without soap.
The study should be planned on days 7-10 of the menstrual cycle.
Decoding the results
PCR analysis produces only two conclusions - negative or positive.
If the result is positive, the patient is diagnosed with bacterial vaginosis, and she is sent for further diagnostics in order to detect the specific type of causative agent of inflammation.
If gardnerellosis is suspected, tank culture is important. The analysis shows not only the number of gardnerella, but also their sensitivity to antibiotics.
During the diagnostic process, the following gardnerella values can be established:
- 105-106 in the test smear indicates a variant of the norm;
- 107-109 – this indicator indicates a stable infection.
When conducting a smear examination, the degree of vaginal cleanliness is also assessed:
- Zero degree indicates the absence of infectious microorganisms;
- First degree. The vaginal environment is within normal limits. There may be a small number of gardnerella or other opportunistic microorganisms;
- Second degree. Pathogenic organisms are detected within normal limits, lactobacilli become fewer;
- Third degree. Gardnerella is slightly elevated, lactobacilli are few or not detected at all;
- Fourth degree. Lactobacilli are less than 6%; the main part of the smear is represented by pathogenic bacteria.
A doctor should interpret the tests and prescribe appropriate treatment.
How to cure a disease
Treatment is prescribed only by a gynecologist, taking into account the composition of the vaginal microflora. Therapy is conservative and long-term and includes 2 stages:
- Destruction of pathogenic bacteria. The doctor selects oral antibiotics, as well as vaginal suppositories with an antibacterial composition.
- Restoring normal microflora by increasing the number of beneficial microorganisms.
In parallel, immunotherapy is carried out. To reduce itching and irritation, it is allowed to use herbal infusions (chamomile, celandine, St. John's wort).
It is important to identify the main cause of microflora imbalance. When sexually transmitted infections are detected, therapy is aimed at eliminating them. In case of hormonal disorders, replacement therapy with hormonal drugs is carried out.
During treatment, it is important to use a condom during sexual intercourse. If there is a permanent partner, therapy is prescribed to both.
Principles of treatment
For gardnerellosis, antibiotics are mandatory:
- Nitromidazoles (Tinidazole, Ornidazole, Metronidazole). Can be prescribed orally (tablets and capsules), topically (in the form of ointments), intravaginally;
- Lincosamides (Clindamycin). The most commonly used are clindamycin suppositories, ointment, and gel;
- Macrolides (Azithromycin, Josamycin, Erythromycin). In most cases, they are prescribed for severe forms of vaginosis orally or by injection;
- Tetracyclines (Doxycycline). The drug is effective if gardnerella develops against the background of chlamydia and other sexually transmitted diseases;
- Fluoroquinolones (Ofloxacin - an analogue of Ofloxin). They are used if Gardnerella is combined with an STI.
Gardnerella is not sensitive to aminoglycosides, so it is not advisable to take antibiotics from this group when treating gardnerellosis.
Antibacterial treatment lasts an average of 10 days. After a course of therapy, you should definitely take tests for gardnerella again.
In addition to antibiotics, women with this disease are often prescribed immunostimulants (Immunal, Wobenzym, Genferon) and lactobacilli in tablets or vaginal suppositories (Acilact, Lactobacterin).
The use of lactobacilli has a positive effect on the microflora of the entire body and helps neutralize the negative effects of antibiotics on the digestive tract.
Recommendations for the use of local drugs
Oral antibacterial treatment for bacterial vaginosis is often combined with the use of topical medications. Their use enhances the therapeutic effect of systemic antibiotics and prevents secondary infection.
Vaginal antibacterial agents are often prescribed to pregnant women.
The greatest effectiveness in normalizing the number of gardnerella is manifested when using:
- Terzhinana. Available in the form of vaginal tablets. It contains an antifungal component, an antibiotic and a glucocorticosteroid. Terzhinan relieves inflammation and accompanying discomfort well;
- Kliona – D. The drug is a combination of an antifungal agent and an antibiotic, the release form is tablets for vaginal administration;
- McMiror. Available in the form of candles. Has an antimicrobial and antifungal effect. Promotes the growth of lactobacilli;
- Neo-Penotran. Contains an antibiotic and antifungal component.
Treatment with suppositories and vaginal tablets usually lasts for 5-7 days.
Signs and manifestations of the disease
Very often, infectious diseases of the genitourinary system occur without any symptoms. Even specific vaginal discharge is not observed. The woman is not bothered by abdominal pain, bleeding, or irregular menstruation. However, the consequences of excess gardnerella content will not be long in coming. To prevent complications, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gynecologist at least twice a year.
Untreated gardnerellosis leads to nonspecific vaginitis - an inflammatory disease of the vagina. Its signs:
- Unpleasant odor;
- Discharge;
- Burning;
- Itching;
- Painful sensations.
Any alkali increases symptoms, especially the smell. Ordinary soap and sperm have an alkaline reaction.
In case of nonspecific vaginitis, it is necessary to undergo tests for microflora in order to accurately identify the causative agent of the infection and undergo a course of adequate therapy. In addition to gardnerella, this disease can be caused by:
- Staphylococcus;
- Streptococci;
- Proteas;
- Escherichia coli;
- Candida;
- Enterococci and others.
Along with bacteria, a fungus can be a pathogen for vaginitis. Therefore, gardnerellosis should first of all be differentiated from the equally common candidiasis
Folk recipes
The effectiveness of drug therapy can be enhanced using traditional medicine methods. For gardnerellosis, immunostimulating herbal infusions, agents that improve metabolic processes, and douching with medicinal decoctions are useful.
The following help to normalize the microflora and reduce the number of gardnerella:
- Douching with oak decoction. Pour 10 grams of crushed bark into a glass of boiling water, leave and strain. Douching is carried out with a warm solution before bedtime for a week;
- Douching with an infusion of a mixture of plantain leaves and chamomile flowers. Plant materials are mixed in equal proportions, a tablespoon of the mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water. The procedure is carried out before bedtime;
- Tampons soaked in sea buckthorn oil. Sterile tampons are generously soaked in heated sea buckthorn oil and inserted into the vagina overnight. The course of their use is from 7 to 10 days;
- Walnut infusion. 5 pieces of walnut leaves need to be crushed and poured with a glass of hot water. After cooling, the infusion is filtered and drunk throughout the day. Duration of use is two weeks.
To increase the body's defenses, infusions and decoctions from the roots of marshmallow, echinacea, St. John's wort, and elecampane are well suited.
During treatment, it is advisable to follow diet therapy - avoid fatty and salty foods, and alcohol. The diet should include more vegetable and dairy products, cereals, and vegetable soups.
How to be treated with traditional medicine?
What is good about traditional medicine is its relative safety. Women who fundamentally do not want to use chemicals can try to get rid of the microbe using folk remedies.
This disease is new. Or rather, they began to recognize it not so long ago. Therefore, folk recipes only fight unpleasant discharge and restore vaginal microflora.
Despite the seeming harmlessness of traditional methods, pregnant women should under no circumstances use them without consulting a gynecologist!
Traditional recipes for douching
- Prepare an infusion of chamomile and plantain (a tablespoon of herb per liter jar of boiling water). After straining, you can use it (2 times a day).
- Oak bark helps a lot. 1 tbsp. l. The product is poured with boiling water (200 ml) and heated for 10 minutes in a water bath. After this, it is infused for another three hours in a thermos. Strain, cool and apply every evening for a week.
- Place one tablespoon (tablespoon) of bird cherry in boiling water (2 cups) and keep on low heat for 20 minutes. Use one glass per day daily.
Using tampons with folk remedies
You can make a tampon yourself from rolled up gauze, or you can buy it at a pharmacy. Soak a tampon with sea buckthorn oil or a mixture of aloe juice and olive oil (1:1). Do the procedure in the evening, leaving the tampon on overnight.
For more effective treatment, you can prepare your own immunomodulatory tincture:
- Place a tablespoon (tablespoon) of dry rowan in boiling water (200 ml) and boil for 15 minutes. Then add a spoonful of honey and grated onion to the broth. Take 1 tablespoon 4 times a day.
And the main folk treatment is proper nutrition: fresh vegetables, unsweetened bakery and dairy products, cereals.
Prevention
Gardnerella belongs to the opportunistic flora, so these microorganisms cannot be completely removed from the body. However, you can make sure that their number is always within the normal range.
To do this you need:
- Change sexual partners less often;
- When having intimacy with casual acquaintances, use a condom;
- Strengthen immunity;
- Carry out complete hygiene of the genitals every day;
- Treat sexually transmitted diseases and chronic pathologies in a timely manner;
- Avoid stressful situations.
Preventive measures include periodic visits to the gynecologist. Timely detection of abnormalities in smears will allow treatment to be carried out on time, and gardnerella will not lead to complications.
Preventive recommendations
Considering that the opportunistic bacterium is already present in the female vagina, it cannot become infected. Therefore, there is no 100% guarantee against vaginosis. But you can reduce the risk of its occurrence. To do this you need to follow simple rules:
- Be attentive to your health. If you experience unpleasant symptoms, do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor.
- It is wise to maintain intimate hygiene. Excessive use of detergents, even delicate ones, can lead to disruption of the vaginal microflora.
- Do not get carried away with panty liners or scented products.
- Always use a condom with a new sexual partner.
- Do not prescribe antibiotics or hormonal drugs on your own.
- Do not use antiseptic vaginal suppositories or tablets without a doctor's prescription.
- Try to lead a healthy lifestyle.
- It is important to maintain overall immunity at an optimal level. For this, preventive intake of multivitamins and physical activity are recommended.
Even if there are no problems with women's health, visit a doctor regularly and get tested. The only means of prevention for men is the use of a condom, as well as joint treatment if vaginosis is detected in a partner.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosing the disease is a simple procedure. The material for the study is vaginal discharge or flushing of vaginal contents. Once the microorganisms that cause or are associated with gardenellosis are identified, a diagnosis is made. The presence or absence of lactobacilli and changes in the acidity of the vaginal environment are also checked.
When examined by a doctor or laboratory, the following criteria are used:
- the presence of a white thin coating on the walls of the vagina;
- pH test of vaginal discharge;
- potassium hydroxide secretion test;
- the presence of cells covered with bacteria when analyzed under a microscope.
Additional information that will help clarify the picture of the disease:
- date of last menstruation;
- number of sexual partners;
- previous infections in the genitourinary organs;
- whether there were sexually transmitted diseases;
- contraceptive method;
- pregnancy history;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- use of tampons.