General information
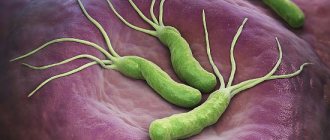
Just a few decades ago, medicine did not know the true cause of ulcerative defects in the digestive tract. About half a century ago, scientists were able to prove the negative impact of a microorganism such as Helycobacter pylori , which lives in the human digestive tract.
In a normal state, the immune system is able to maintain the concentration of microorganisms at a safe level, but when certain conditions are created, harmful bacteria rapidly multiply, which damage the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. Helicobacter pylori contributes to the development of helicobacteriosis , which affects not only the stomach, but also the duodenum. Its usual habitat is the pyloric section of the stomach, which is what gave it its name. It has already been proven that the microorganism can easily withstand the aggressive effects of the acidic environment of the stomach. With the help of special flagella, harmful bacteria move and attach to the gastrointestinal tract.
It is Helicobacter pylori that provokes most diseases of the digestive tract (source Wikipedia). An increase in the number of pathogenic microorganisms leads to the launch of inflammatory processes ( gastritis , peptic ulcer , cancer ).
Suppressing the activity of h.pylori allows you to avoid the development of many gastrointestinal diseases. Even the most specialized forum will not give you answers to all your questions; you need to be examined and treated only by a qualified specialist.
What happens in the body
As soon as Helicobacter enters the human body, it immediately descends into the stomach, where it lives for the rest of the time. In order not to die from gastric juice, the composition of which is quite aggressive, Helicobacter secretes special enzymes that surround it with a shell and neutralize the acid. The spiral-shaped antennae that Helicobacter has allow it to drill through the mucous layer and get to the cells of the parietal tissues, which are usually hidden from acid.
It is the parietal cells of tissues that become the main food for Helicobacter. The pathogenic microorganism eats them and poisons the environment with the products of its vital activity. At the same time, those blood cells that react to Helicobacter and strive to destroy them (neutrophils) wake up in the body. However, by destroying the pathogenic microorganism, neutrophils also destroy mucosal cells that have already been touched by Helicobacter.
After the layer of the mucous membrane is damaged, hydrochloric acid begins to actively affect the tissue. This is how the inflammatory process develops and an ulcer occurs. The localization of ulcers is most often similar. This is explained by the fact that Helicobacter itself is very fond of two parts of the stomach - the bulb and the pylorus.
Pathogenesis
Not all patients infected with Helicobacter subsequently develop a bacteria-dependent pathology. Colonization of microorganisms on the gastric mucosa occurs through the adhesion of bacteria to epithelial cells. The attachment process occurs due to specific receptor interactions.
Patients with blood type O (one) express adhesion membrane receptors in much greater quantities than those with blood type AB (blood group four). This explains the greatest predisposition to the formation of ulcers in people with the first blood group.
One of the risk factors for the development of duodenal ulcers is gastric metaplasia of the duodenal mucosa, which over time becomes colonized by Helicobacter pylori. The above-described gastric ectopic epithelium occurs in 30% of people. Gastric metaplasia is formed as a result of excessive secretion of hydrochloric acid with the reflux of contents into the duodenum and the subsequent development of nonspecific duodenitis . Predisposing factors include genetic predisposition and the use of drugs from the NSAID group.
Disruption of the structure of the gastroduodenal mucosa can be the result of exposure to several bacterial factors. Almost all strains of Helicobacter produce a huge amount of urease , under the influence of which urea is hydrolyzed to carbon dioxide and ammonia. Ammonia in large quantities has a damaging effect on epithelial cells. Under the influence of other bacterial enzymes, the protective layer of the mucous wall is destroyed.
Misconceptions about Helicobacter pylori
Many people think that Helicobacter pylori is a pathogenic microorganism and treatment must be carried out. This is a false statement because 70% of the population has these bacteria in their bodies.
A person needs therapy if, under the influence of certain factors, Helicobacter pylori is activated. An increase in pathogenic flora provokes various diseases that are accompanied by an inflammatory process.
Treatment is not recommended for children under 8 years of age, since at this age the immune system is not fully formed . It does not produce antibodies. And the use of antibiotics in such a situation can cause serious harm to a small organism.
Helicobacteriosis should be treated if accompanying symptoms appear that indicate the development of an inflammatory process. When the infection is dormant and the results show a small concentration of bacteria, therapy is not necessary.
In this situation, the gastroenterologist will monitor the patient’s condition in order to quickly respond in case of illness by prescribing examination and treatment.
Reasons for how Helicobacter pylori is transmitted
Where does the infection come from: infection occurs by transmission of the microorganism from one person to another through the oral-oral or fecal-oral route. There is also a hypothesis according to which Helicobacter can be infected from cats or mechanically through flies.
In most cases, infection occurs in childhood, most often from person to person. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is transmitted through several routes:
- Fecal-oral route . The microorganism is excreted in the stool of an infected person. The source of infection is food or water contaminated with feces.
- Oral-oral route . There is a hypothesis that the Helicobacter bacterium may be present in the oral cavity, which increases the risk of infection when sharing toothbrushes and cutlery, and patients also become infected through kissing.
- Iatrogenic way . Caused by medical procedures, such as endoscopic examination.
Transfer methods
The exact mechanism of transmission and the causes of helicobacteriosis are not known today, but a list of possible modes of infection has been compiled.
These include:
- use of non-sterile medical instruments;
- the presence of common objects with a person who suffers from helicobacteriosis;
- quenching thirst with tap water;
- eating unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene standards;
- transmission of bacteria through the air.
The source of an infection called “helicobacter pylori” can be a sick person or a carrier of the bacterium. The latter is often unaware of his “mission” until one day the presence of “colonies” built by Helicobacter pylori is detected in his body.
If at least one member of the household is sick, then everyone else will acquire helicobacteriosis in the near future, becoming infected from each other.
Symptoms of Helicobacter pylori
For a long time, the pathology may not manifest itself clinically. First, the Helicorbacter bacterium attaches to the mucous membrane of the duodenum and small intestine, producing enzymes with toxic effects, which subsequently gradually corrode the epithelial cells. Symptoms of Helicobacter pylori in adults increase as the disease progresses.
The first symptoms of helicobacteriosis appear only with the formation of erosions and ulcerative lesions on the mucous membranes. Patients complain of symptoms such as:
- constant pain in the epigastric region;
- a feeling of fullness in the stomach and a feeling of bloating after eating;
- the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth;
- vomiting, attacks of nausea;
- frequent belching with an acidic taste in the mouth;
- burning in the esophagus;
- increased gas formation, flatulence with discomfort and colic in the epigastrium.
Discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the epigastrium appear mainly immediately after eating and do not disappear even after defecation or bowel movement. Patients complain of severe weakness, apathy, excessive fatigue , drowsiness and irritability.
Often small rashes appear on the skin, including on the face. Photo of Helicobacter pylori symptoms on the face: Symptoms on the face do not disappear when using external cosmetics and cleansers; complete, comprehensive treatment is required. When gastritis and peptic ulcer of the digestive tract are combined, bad breath appears, stools are disrupted (loose or constipated), and the nail plates become brittle.
Symptoms of manifestation
Often the initial stage of the disease does not manifest itself in any way, which prevents it from being diagnosed in the early stages of development, since the person has absolutely no idea that he is a carrier of such a serious illness. The main signs that the Helicobacter bacterium has settled in the stomach is the appearance of gastritis or ulcers, since, first of all, it is this virus that causes their appearance. This symptom requires urgent intervention.
You should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Unstable stool (constipation alternates with diarrhea and vice versa)
- Having allergies;
- Problems with odor in the mouth, especially with healthy teeth;
- Nails break;
- Hair fall out;
- Soreness in the stomach area, which appears periodically, disappears after a person eats;
- Attacks of nausea, vomiting of unknown etiology;
- Severe attacks of heartburn;
- Meat is not digestible;
- Heaviness appears in the stomach.
There are several forms in which the bacterium can appear. For example, if a person has a strong, strong immune system, then the disease may not manifest itself for a fairly long period of time. This is considered a latent form of the disease. May manifest as symptoms of acute gastritis. This malaise manifests itself with severe pain and vomiting.
In 50% of cases, patients are diagnosed with gastritis, which has a chronic form. The pain appears intermittently and the gums bleed. The above symptoms are reinforced by heartburn, nausea, and vomiting attacks. Sometimes a person belches with an unpleasant odor or has a bad taste in the mouth.
It is not uncommon for a patient to develop gastroduodenitis. This pathology has several degrees of manifestation (weak, moderate, or severe). This process is characterized by pathologies in which the duodenum is involved. A person loses his appetite, problems with stool are less likely to occur; this pathology is similar in its manifestations to gastritis.
The appearance of an ulcer in the stomach or the appearance of erosion is no less informative about the presence of Helicobacter pillory. For this case, the symptoms are similar to those characteristic of gastritis. But with an ulcer, they become significantly worse and have a more pronounced character.
If the bacterium enters the body outside the stomach, a person develops skin problems. Acne rashes appear on the face, which do not go away with the use of cosmetics. Over time they will only get worse. There is an opinion about the connection of the bacterium with the development of skin diseases such as dermatitis, lichen, psoriasis, etc.
Analysis for Helicobacter pylori
To identify Helicobacter pylori, you need to undergo a series of tests. Diagnosis is quite simple and includes several methods.
ELISA for bacteria
The research method is used to assess the level of concentration of existing antibodies to H. pylori in the patient’s blood. The immune response is formed 1-2 weeks after the microorganism enters the human body. In some cases, a false negative response is recorded, which may be due to the specifics of the immune system.
A positive test indicates the need to undergo a full examination. Your doctor will tell you how to treat the disease.
Immunological blood test for Helicobacter pylori for IgG, IgM, IgA
In response to infections entering the body, special proteins are produced - immunoglobulins igg, which try to resist the foreign agent. Detection of immunoglobulins IgG, IgM, IgA indicates infection with H. Pylori.
The main feature of immunoglobulins is that they are able to overtake pathogenic cells anywhere in a person. Proteins appear in the blood after damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
Blood test interpretation:
- A negative result or low IgG content indicates the absence of bacteria in the body and a low risk of developing gastritis associated with H. pylori and gastrointestinal ulcers. This is the norm for Helicobacter pylori in a blood test. If 3-4 weeks have passed since the infection, the result may also be negative. For epigastric pain, it is recommended to donate blood again. The price of the analysis is 700 rubles for each immunoglobulin.
- A positive result or an increased level of IgG may indicate the presence of infection in the body and a high risk of developing gastrointestinal ulcers or cancer. A positive result can also be recorded in patients who have recently recovered from pathology; a reduced IgM content is recorded immediately after infection.
- Elevated IgM levels indicate an early stage of infection.
Urease test
The analysis is carried out after taking a biopsy of the mucous membrane during an endoscopic examination. The resulting material is placed in a carrier gel that contains urea, a bacteriostatic agent and a pH indicator. Depending on the change in color of the biopsy sample, a conclusion is drawn.
Breath test for Helicobacter pylori
The examination requires the collection of a fasting background sample of exhaled air. Preparation consists of drinking an aqueous solution of urea labeled with 13C (test solution) after a light breakfast. The final 4 samples are taken every 15 minutes.
A normal breath test for Helicobacter pylori is 1%. The price of the test depends on the region. You can take an in vitro breathing test in Moscow and St. Petersburg for 2,250 rubles.
Hemotest
The study is based on determining the amount of antibody titer - IgG. Immunoglobulins are able to bind pathogens, blocking their negative effects. How to get tested for Helicobacter pylori: on the eve of the test, you should not drink alcoholic beverages or coffee, and smoking is prohibited. You need to take the test on an empty stomach - the fasting period is 8 hours. The study is an enzyme immunoassay of blood taken from a vein into a sterile tube. The analysis is repeated several times throughout the entire period of therapy. The price of in vitro analysis is 800 rubles.
Stool analysis
Today, there are 3 special research methods that can detect Helicobacter pylori:
- Cultural Research . The resulting biomaterial is placed in a nutrient medium, which creates favorable conditions for the growth and reproduction of colonial organisms. Additionally, chemical dyes or medications can be used to assess the degree of sensitivity of microorganisms to various drugs.
- Stool PCR . Due to special enzymes, “enemy” DNA is isolated with further doubling of its particle. Activities for artificial DNA replication are carried out until a complete genetic code is created, which is subsequently compared with an existing Helicobacter pylori sample.
- Immunological method . A solution with antibodies that react violently to the presence of Helicobacter pylori antigens is added to the resulting biological material. An active reaction reaction indicates contamination of the sample with pathogenic microorganisms.
Express test
This test allows you to detect antibodies to infection in whole blood. You can do the test at home, provided you follow all the rules.
The test system includes:
- indicator tablet packed in a special vacuum bag;
- pipette for applying a drop of blood to the tablet;
- a reagent used to dilute the resulting blood sample;
- antiseptic wipe;
- scarifier;
- instructions.
Preparing for the test
It is proper preparation that affects the accuracy of the result, so it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations:
- refuse antibiotic treatment a month before the procedure;
- do not drink alcohol for three days;
- do not eat anything, do not smoke, do not chew gum 6 hours before the examination;
- an hour before the test you are allowed to drink no more than 10 ml of water;
- Immediately before the test, brush your teeth and use mouthwash.
- It is also undesirable to eat legumes - soy, beans, peas and corn.
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori with folk remedies
Basic drug treatment can be supplemented with folk remedies. The most effective methods include propolis, which has several beneficial properties:
- antibacterial;
- antiseptic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antioxidant;
- immunomodulatory;
- vasoconstrictor.
Propolis can cleanse the body of waste and toxins that are released during the life of pathogenic microorganisms. Propolis can also be used in pediatric practice, provided that an allergic reaction .
Most often, it is the alcohol tincture of propolis that is used, which can be easily found at any pharmacy. To obtain a solution of the required concentration, add 10 drops of tincture to 100 ml of plain water. The course of treatment is 1 month, the solution must be taken before meals. The reviews are positive, the effect is observed already in the first week of treatment.
Etiology
Today in official medicine there is no exact etiological picture. Helicobacter pylori infection is most often transmitted orally. In addition, the following routes of transmission of Helicobacter infection should be highlighted:
- with close physical contact;
- with poor-quality processing of medical equipment and instruments (endoscope, enema);
- using shared utensils;
- when coughing, sneezing;
- failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene.
The cause of the development of the infectious process can also be the consumption of poorly peeled vegetables and fruits. As medical practice shows, the most common cause of the development of helicobacteriosis is failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene.
Prevention of Helicobacter pylori
If one of your family members is being treated for helicobacteriosis, then you should definitely undergo a screening examination to detect the infection.
It has already been proven that if at least one family member is infected, the risk of infecting the rest reaches 95%. Helicobacteriosis is considered a social disease and requires compliance with very strict rules of personal hygiene. Prevention also involves increasing immunity and improving the diet.
Control tests are performed 2-6 weeks after completion of the course of therapy. Patients who have been diagnosed with complications such as perforation of the gastric mucosa or bleeding should be under special supervision. Patients from this risk group have a very high risk of death if the disease relapses.
Diagnosis of the disease
The presence of a microorganism is diagnosed through specific laboratory tests, due to the absence of characteristic signs unique to this disease. But before they are prescribed, the patient is interviewed, examined, and physically and endoscopically examined.
Fibrogastroscopy is also performed, that is, a sample of atrophied stomach tissue (biopsy) is obtained using special equipment.
Tests are taken both for diagnosis and to monitor the progress of treatment. Identification of the exact cause is possible only after receiving the results of the study:
- blood and saliva taken in case of bleeding gums;
- feces for the presence of microbial waste;
- blood to determine antibodies.
Diagnostic measures are also carried out a month or a month and a half after the end of the course of antibiotics. To be sure, two methods are used. This step allows you to more accurately determine the result of the therapy.
Diet for Helicobacter pylori
Diet for Helicobacter pylori
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 14-21 days
- Terms: 1-3 months
- Cost of food: 1620-1700 rubles per week
General diet rules:
- exclude foods that irritate the mucous walls of the digestive tract and create additional stress on the gastrointestinal tract;
- the diet should be as balanced as possible;
- food products should promote accelerated healing of ulcerative defects and erosions on the mucous membranes;
- Eating too cold or hot foods is unacceptable;
- you need to eat fractionally, preferably 5-6 times a day;
- observe drinking regime;
- products should be steamed or boiled;
- all ingredients of the dish must be crushed as much as possible;
- Fermented milk products must be present in the diet.
How to get rid of Helicobacter pylori in adults
Helicobacteriosis is treated comprehensively; long-term therapy is selected for patients, taking into account the presenting symptoms and the results of the diagnosis. It is necessary to completely destroy harmful bacteria in the human stomach.
Medicines
It is important to take medications strictly as prescribed by a gastroenterologist. Failure to comply with the treatment regimen will lead to ineffective results, or even cause serious complications.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Antibiotics | Azithromycin, Amoxiclav | The medicine should be taken 1 time per day before or after meals. The adult dosage is 250-500 mg. The course of treatment lasts 3 days. |
| Preparations of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate | De-Nol, Ranitidine | The drugs form protection for damaged cells. Patients are prescribed 1-2 tablets 2-4 times a day. The course of therapy lasts 4-8 weeks. The tablets should not be chewed, but swallowed whole and washed down with a small amount of water. |
| Proton pump blockers | Omeprazole, Nolpaza | Medicines reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Taking into account the diagnosis and condition of the person, the doctor prescribes 0.02-0.04 g once a day. It is preferable to take the medicine in the morning before breakfast. Swallow the capsules and wash down with water. |
| Gastrocytoprotectors | Bismol, Bismofalk | It is recommended to take the drug orally 30 minutes before meals. The dosage for an adult patient is 1 tablet 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 4-8 weeks. |
| Probiotics | Acipol, Linex | Medicines restore beneficial microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Adults need to take 1 capsule 3-4 times a day for 10-15 days. After completing therapy, you can take a break of 30 days and continue treatment. |
If severe pain occurs, the specialist prescribes antispasmodics or painkillers (No-Shpa, Analgin) to patients.
Vitamin and mineral complexes, which are also prescribed by a specialized doctor, will help increase the defenses and resistance of the human body. It is important not to engage in therapy on your own, as this can worsen your health condition.
ethnoscience
Non-traditional methods of treatment for helicobacteriosis require consultation with a specialized gastroenterologist. It is necessary to select safe and effective recipes that will not cause an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Chicken eggs | Treatment is carried out with fresh eggs. Every morning the patient is advised to wipe the shell well and wash with soap. Punch and drink on an empty stomach. | If desired, a raw egg can be eaten with a small amount of natural honey. Therapy lasts 30 days, then you need to take a break and you can continue treatment. |
| Decoctions | Mix celandine, St. John's wort, yarrow and chamomile in equal parts. Pour 4 tbsp. herbal mixture with hot water (0.5 l). Leave and strain. | It is recommended to drink the decoction in small sips before each meal. |
| Syrup | The medicine is prepared on the basis of rose hips. You can buy pharmacy syrup. | The product is taken orally, 1 tsp. before eating. The course of treatment lasts 30 days. Then it is recommended to take a break for 2 weeks and continue therapy. |
| Propolis | Mix 100 ml of water and 10 drops of propolis alcohol tincture. | It is recommended to take the medicine orally before meals for 30 days. |
| Cabbage juice | You can drink fresh cabbage juice if you do not have chronic gastritis. | The recommended dosage for an adult patient is 100 ml. It is preferable to drink cabbage juice 20-30 minutes before meals. |
| Air | Pour the dry root of the plant (4 tbsp) with hot water (500 ml). Leave for 3-4 hours and strain. | It is recommended to take the finished medicine 50 ml each time before meals 30 minutes. |
Folk remedies have a bactericidal and immunostimulating effect. They help improve blood circulation, reduce inflammation and remove toxins from the human body. Propolis can be given even to children if there is no tendency to allergic reactions.
Nutrition and diet
Helicobacteriosis (symptoms and treatment require a comprehensive examination) requires adherence to dietary nutrition in order to reduce the load on the damaged mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
| Recommended dishes | Prohibited Products |
|
|
You should eat in fractional portions, giving preference to pureed and warm dishes.
Food must be chewed thoroughly. The drinking regime includes at least 2 liters of clean still water per day. Dietary nutrition should be followed for at least 1-2 months.
Consequences and complications
The presence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach is not an independent disease. Against the background of infection, the risk of developing various diseases of the digestive tract increases significantly. Despite the fact that histological gastritis is recorded in all patients infected with Helicobacter pylori, the clinical picture develops only in some. 10-20% of patients develop ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, and 1-2% develop stomach cancer.
Diseases and conditions that can develop as a result of Helicobacter infection:
- Gastritis . It is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa. After infection, an acute form of gastritis gradually develops, accompanied by nausea and dyspepsia. Against the background of an acute inflammatory process, the production of gastric juice decreases. Subsequently, the disease becomes chronic.
- Ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract . 90-95% of duodenal ulcers are associated with Helicobacter pylori (the figure for the stomach is 70-85%).
- Functional dyspepsia . It is characterized by severe pain in the upper quadrant of the epigastrium. The sensations are not associated with stomach lesions and peptic ulcers. Therapy is based on eradicating the infection to reduce the severity of symptoms and reduce the risk of developing stomach cancer in the future.
- Stomach cancer . Helicobacter is the leading etiological factor in the development of cancer in the stomach. Against the background of infection, the production of free radicals increases and the risk of mutations in stomach cells increases.
Preventive measures
Despite the difficulties associated with helicobacteriosis, prevention does not require much effort and time. Its rules are quite simple and familiar to everyone.
To avoid this disease you need to:
- To perform personal hygiene, use only your own equipment;
- wash fruits and vegetables before eating;
- avoid touching and sharing objects with unfamiliar people;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- give up all harmful addictions;
- be more careful when choosing a sexual partner;
- contact a medical facility in a timely manner if you have any doubts about your health.
Immunity to this pathology is not developed, so the only way out of the situation is to prevent health problems by improving the quality of life. You can do this by taking care of yourself.
Denial of alcohol and cigarettes, regular exercise, proper rest - all this will help improve your body’s health, strengthen your immune system and look at the world with different eyes.
List of sources
- Hulst RWM, Keller JJ, Rauws EAJ, Tytgat GNJ Regular issues of “Breast Cancer” No. 5 dated 03/03/1997, Gastroenterology, “Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection”
- Loranskaya I.D., Stepanova E.V., Rakitskaya L.G., Mamedova L.D. Regular issues of “Breast Cancer” No. 13 dated July 13, 2015, Gastroenterology “Helicobacter pylori eradication - ways to achieve effectiveness”
- Ivashkin V.T., Maev I.V., Lapina T.L., Sheptulin A.A. Recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in adults // RZHGGK. 2012. No. 1
Therapeutic measures
You can get rid of the disease only by using a set of therapeutic measures. There are a number of indications for treatment that are mandatory. First of all, compulsory treatment should be given to people who are related (live in the same room), who suffer from ulcers of any degree or form, who have undergone gastrectomy as a consequence of cancer, and who suffer from maltoma.
Several effective methods of therapy are known:
- Triple scheme, carried out over the course of a week (use of Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin, Pariet);
- Quadruple therapy is carried out for at least 7 days. Preparations of bismuth salts, Clarithromycin (Tetracycline), Pariet, Metronidazole are used. The four-part treatment is believed to be more effective in combating the bacteria.
An antibiotic is a necessary remedy; without it, therapy will not be effective.
It should be borne in mind that Metronidazole is used only if the patient is prescribed a four-component treatment, this is due to the high resistance of the bacteria to this type of drug. Therefore, for a triple regimen, this medication will be completely useless.
A third method of treatment is known; it is used as a last resort, if the therapeutic measures carried out previously did not produce any effect. The doctor takes tests through a biopsy. After which they are sent to the laboratory, where a series of tests are performed, after which the attending physician examines the results and prescribes an effective, but individual regimen of therapeutic measures.
It is important to remember that this method is extremely unique, which does not allow it to be used for other patients with the same disease
General recommendations
Medicines for Helicobacter pylori involve the use of specific antibiotics, nitromidazoles (their derivatives), colloidal bismuth salts, proton pump inhibitors, probiotics, which can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Self-medication is not only unsafe for your health and the health of your child, but it is also fraught with subsequent peak situations in which any doctor’s prescription will not have the desired effect due to the acquired resistance of the bacteria to many drugs.
Therefore, only a doctor can decide how to treat Helicobacter pylori. And in order to stay healthy longer, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, quit bad habits, balance and enrich your diet with healthy vitamins and microelements, promptly sanitize nasopharyngeal infections and prevent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of the body, and, most importantly, adhere to personal hygiene. In addition, a positive attitude in life will help avoid many diseases.
Video on how to treat Helicobacter pylori:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ciFqLo4cSyU