Flatulence is the increased formation of gas in the intestines. Flatulence is not a disease, it is a dual symptom: it can be either a consequence of eating rough and unsuitable food, or a sign of many diseases of the digestive system. Flatulence in adults is not life-threatening, but it does bring a lot of trouble.
What it is
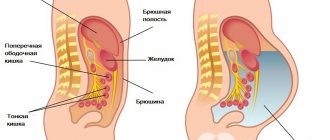
The human intestine contains more than 180 ml of gaseous substances. They are formed when food breaks down. Sulfur, nitrogen, carbon, methane are released. When stomach acid and pancreatic juice of the pancreas begin to interact, carbon monoxide is produced. Air masses also enter the body during swallowing.
Air enters through the rectum during belching. Gas exchange depends on the tone of the abdominal muscles and diaphragm, and intestinal motility. With excessive density of feces, metabolic processes are disrupted, and increased gas formation in the intestines is observed. The release of gas is a natural process that normally occurs in a healthy person up to 20 times during the day and night.
How to quickly remove accumulated gases from the intestines?
You can fight gas formation on your own only in cases with a simple situation. Here are some actionable tips:
- Drink a glass of water 15-20 minutes before eating and two hours later.
- Exercise.
- Eat herbs and seasonings that reduce gas formation.
- Pour boiling water over a teaspoon of chopped plantain and eat the swollen mixture.
- The use of activated carbon quickly relieves an attack, crush 5 tablets, wash down with water.
- Ginger tea will relieve spasms and strengthen the immune system.
- A teaspoon of mustard will cope with bloating, increase the secretion of saliva, promoting digestion.
- A mixture of pine and walnuts with the addition of lemon and purified clay. 100 grams of nuts, chop, grate lemon and 25 grams of clay, mix. Take a tablespoon twice a day.
Symptoms
Flatulence can be fermentative and putrefactive. Both forms manifest themselves in the form of diarrhea, which alternates with constipation, gases with an sour or hydrogen sulfide odor. Symptoms intensify after consuming carbohydrates, dairy products, fiber, and foods rich in protein. Increased gas formation is accompanied by belching, pain in the abdominal area, excessive discharge of gases, bloating, and hiccups.
There are complaints of nausea, disturbances in stool and appetite, difficulty defecating, and bad breath.
- Patients describe a feeling of fullness and discomfort in the abdominal cavity, an enlargement of the abdomen.
- The pain is dull, aching, radiating to different parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gas colic is accompanied by painful, cramping attacks.
Flatulence develops - excessive release of a large amount of digestive gases, after which the patient feels relief.
Choose a specialist and make an appointment with a gastroenterologist online
Increased gas production - normal or pathological?
Increased gas formation, also known as flatulence, is a common phenomenon in men and women, causing a lot of inconvenience. The formation of gases in the intestines is considered a normal physiological process. Most of the gases enter the digestive tract along with ingested food (about 70%), and the remaining 30% are produced by bacteria. They may have a strong odor or no odor at all.
Gases in the intestines are a mixture of oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and methane. The presence of about 200 ml of gas in the intestines is considered normal. Every day, during the act of defecation and outside it, approximately 1 liter of gases is removed from the body, some of them are absorbed into the blood. The presence of certain pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and poor nutrition lead to the formation of 2-3 liters of gas in the stomach.
Types of flatulence
Flatulence can be acute or chronic. Acute forms may indicate peritonitis, dynamic, paralytic and mechanical intestinal obstruction. The chronic course is promoted by aerophagia, neuroses, impaired salivation, and the use of chewing gum. Depending on the cause that provoked the symptom, flatulence can be:
- Nutritional – occurs when consuming foods that produce a large volume of gases. These include cellulose, hemocellulose, pectin, and coarse fiber.
- Psychogenic – observed in patients with stress and psychological disorders.
- Dynamic – occurs when there are disturbances in the transit functions of the gastrointestinal tract. The free movement of gas slows down significantly.
- Digestive – caused by digestive disorders: absorption and circulation of bile, food intolerance.
- High altitude - develops when rising to a high altitude, when the gas expands and pressure increases.
- Dysbiotic – progresses in patients with intestinal microflora disorders.
- Mechanical – observed in patients with evacuation disorders of the gastrointestinal tract that impede motor activity: the formation of adhesions, neoplasms, strictures.
- Circulatory – caused by blood circulation disorders: high blood pressure, congestion, ischemic lesions affecting the large intestine.
Taking into account the type of disorder, the doctor selects an appropriate treatment regimen.
Possible complications
If bloating and belching occur frequently for a long time, then the use of symptomatic therapy must be stopped, as this can lead to a worsening of the condition or the transition of a latent disease to the chronic stage.
In severe cases, advanced disease can lead to serious digestive disorders, gas colic and spastic pain, and intoxication. Pregnant women may be at risk of miscarriage.
In addition, the disease can be accompanied by psychological problems, which leads to nervous disorders, insomnia, loss of appetite, physical and emotional exhaustion.
Only a specialist can determine the exact cause of the disease and possible methods of effective treatment, so if there is no improvement, you should not delay your visit to the doctor.
You can quickly get rid of flatulence and its unpleasant symptoms only through comprehensive measures aimed at improving the quality of nutrition and proper lifestyle, including moderate physical activity and preventive measures in your daily routine.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Causes
Impaired intestinal motility caused by swallowing a large portion of air, intoxication, scleroderma, connective tissue pathologies, and surgical interventions. Increased gas formation is often observed with intestinal dysbiosis. Among the predisposing factors causing excess gas production are:
- anxiety states, nervous tics, stressful situations
- violations of rules and diet
- impaired intestinal motility
- overgrowth of bacterial microorganisms that produce gases
- increased pressure in the gastrointestinal tract during ascent to high altitudes
- production of excess gases: malabsorption syndrome, maldigestion, food abuse
- mechanical damage that disrupts the excretory function of the intestine
- insufficient activity of carbon dioxide transport, which occurs with right ventricular failure
- helminthic infestation followed by a decrease in the absorption area
Airbrushing occurs when you are in a hurry while eating, smoking, talking while eating, drinking carbonated drinks, eating caramels, chewing gum, or using unsuitable dentures. Products with increased gas-forming potential include dried fruits and beer. Flatulence is observed with increased consumption of onions, mushrooms, celery, cruciferous vegetables (various types of cabbage, radishes), cucumbers, carrots, fruits, yeast baked goods, legumes, and grain crops.
Flatulence occurs in people who abuse fatty foods. Eating up to 2 times a day, in large portions, causes increased stress on the colon and gastrointestinal tract. Digestive disorders are often observed in people with a history of enzyme deficiency, dysfunction of the enterohepatic bile circulation, and dysbiosis.
Poor blood circulation in the intestinal area
In case of digestive disorders in the gastrointestinal tract, the large and part of the small intestine suffers from limited blood circulation. The esophagus, rectum and stomach are less susceptible to this disorder. Ischemia develops in the colon, symptoms decrease within 24-72 hours, and after a few weeks the patient recovers completely. The development of acute mesenteric anemia is observed with insufficient blood circulation in the small intestine.
The disease develops due to embolism or thrombosis of the intestinal arteries and progresses in patients with atherosclerosis. In rare cases, the disorder is accompanied by endocarditis, intestinal obstruction, and inflammatory processes in the blood vessels. Circulatory disorders in the intestines manifest themselves:
- vomiting
- sudden severe pain in the abdominal area
- colic in the stomach
- flatulence
- weight disorders
- loose stools
- increased anxiety
Treatment is surgical. In case of intestinal infarction, immediate emergency medical care is required.
Some medications
Increased gas formation is observed in patients who are recommended to take:
- narcotic analgesics
- medications for diarrhea: Immodium, Loperamide
- additives containing psyllium husk or coarse plant fiber
- iron preparations. Bivalent iron acts faster, but is poorly absorbed by the body, and most often there are adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract. Ferric iron acts more slowly but is better tolerated. It is recommended to use modern, chelated formulas. For better absorption, be sure to additionally take co-factors: B vitamins, copper, manganese, silicon, chromium.
Before starting to use the medicine, carefully study the instructions, paying attention to possible side effects. If there are objective indications for taking a medication that causes bloating, discuss with your doctor the possibility of using corrective agents to reduce adverse reactions: Espumisan, Simethicone.
Dysbacteriosis and biocenosis
Dysbacteriosis and biocenosis cause flatulence in more than 50% of patients. Such a disorder occurs as a result of enzymatic, lactase deficiency, due to the use of antibiotics, and food intolerance. Dysbiosis is one of the links that occurs in people with food allergies, inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
With normal microflora the following is observed:
- stimulation of immune status
- regulation of lipid metabolism
- support of metabolic and enzymatic processes
- providing antitoxic, antimutagenic, anticarcinogenic effects
Treatment of dysbacteriosis and biocenosis is complex. Includes diet, taking probiotic drugs: probiotics, prebiotics, syn-biotics.
Adhesions in the gastrointestinal tract
Adhesive processes form in the gastrointestinal tract after surgery, against the background of inflammatory processes. Accompanied by gluing of intestinal loops, disturbances of peristalsis, a feeling of discomfort, and flatulence. A similar complication can accompany childbirth and infectious diseases. It occurs due to violations of the integrity of the peritoneum and manifests itself in the form of:
- nagging pain in the abdominal area, which intensifies after physical activity
- dyspeptic disorders: bloating, diarrhea, increased gas formation;
- prolonged constipation
- intestinal obstruction
To confirm the diagnosis, a blood test is performed, contrast radiography is performed, and ultrasound diagnostics are performed. Additionally, diagnostic laparoscopy of the intestine is indicated. During therapy, conservative and radical methods are used. Conservative treatment is aimed at reducing the inflammatory reaction and restoring the functional state of the affected organs. They follow a diet and fasting is prohibited. If ineffective, surgery is indicated.
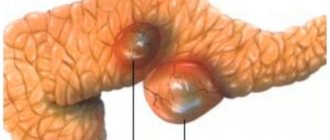
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process that affects the pancreas. It is observed in patients with diabetes mellitus and is accompanied by complaints of constant, paroxysmal pain and flatulence. The absorption of food from the intestines is disrupted, and deficiency conditions develop that need to be corrected in a timely manner. In the chronic form of the disease, exacerbations alternate with remissions.
Mild to moderate course of the disease is accompanied by regular pain; progression leads to diarrhea and the release of excess fat in the feces. Body weight decreases, pain radiates to the left and right hypochondrium. Nausea, flatulence and vomiting worsen after the use of medications that inhibit the functioning of the pancreas (for example, narcotic analgesics).
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome develops against the background of dysbiosis, irregular and balanced nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, and sedentary work. The risk group consists of people with a genetic predisposition and hormonal imbalances. IBS occurs in people who abuse alcohol, carbonated drinks, fast food, chocolate, caffeine-containing foods, cookies, refined foods, and fatty foods.
Irritable bowel syndrome causes complaints of bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Discomfort occurs after eating food and is eliminated after bowel movement. The pain is cramping, spastic, alternates with aching and stabbing.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer, colitis
Gastritis, gastric ulcer and colitis are accompanied by frequent bowel movements, flatulence, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Treatment is selected depending on the degree of progression of the pathological process and the presence of associated complications. Diet is an important element of therapy. Avoid fatty, fried, spicy, heavy foods, spices, refined foods, and simple carbohydrates.
Nervous overstrain
Nervous tension is a manifestation of stress, which manifests itself in the form of disturbances in the regulation of digestion. There are complaints about the development of flatulence, bloating, belching, nausea, and cramps. The stool and reflux are disrupted - the reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus. The intestines are irritated, and gastrointestinal dysfunction is observed.
In addition to digestive disorders, there are complaints of increased sweating, rapid heartbeat, internal trembling, increased irritability, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. To reduce nervous tension, physical activity, breathing exercises, and the use of sedatives are indicated. The lack of timely treatment is fraught with dysfunction of the immune system and cardiovascular disorders.
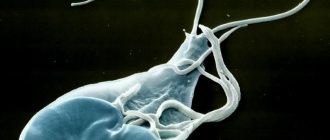
Helminthiasis
Helminthiasis is a parasitic disease that is accompanied by a protracted, long-lasting course and a wide range of clinical manifestations. Occurs under the influence of round and tapeworms, flukes. Ascariasis is accompanied by dyspeptic syndrome: flatulence, nausea, vomiting, weight problems, unstable stools, and a tendency to constipation. The skin around the anus becomes red and swollen, allergies and bronchopulmonary syndrome occur. Treatment is carried out with the help of anthelmintic drugs and liver cleansing drugs.
Polyps and tumors in the intestines
Polyps and tumors are asymptomatic and affect the inner mucous membrane of the intestine. Most often they affect the large intestine, occurring in 14-17% of patients. The dimensions do not exceed 1 cm. Single formations are observed, more often the formation of small groups. The disease is often detected accidentally during a routine examination.
Sometimes polyps and tumor formations appear:
- rectal bleeding
- flatulence
- long-term constipation and diarrhea
- pain in the abdominal area, nausea, vomiting
Laboratory tests indicate iron deficiency anemia, which occurs due to internal bleeding and impaired absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract. The only treatment option is surgery. A polypectomy is required, which is performed during examination of the large intestine.
Possible diseases
Often, bloating is a symptom of other more serious disorders and diseases:
- Dysbacteriosis, when the body lacks special types of beneficial bacteria.
Causes of dysbiosis - Gastritis with low acidity, which leads to decreased digestive function.
- Inflammatory processes of the digestive organs.
- Irritable bowel.
- Pancreatitis associated with insufficient production of enzymes by the pancreas.
- The presence of helminths that release toxic substances and gases during their life.
- Infectious diseases.
- Pathological condition of the liver or gall bladder, leading to stagnant processes.
- Lactose or gluten intolerance.
- The presence of constipation, leading to rotting or fermentation of food.
- Adhesions, polyps and various neoplasms in the intestines.
- Peristalsis or circulatory disorders.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy or PMS.
Foods that cause bloating
If you are intolerant to certain foods or improperly prepared, flatulence may develop. Most often, bloating is preceded by the use of:
- legumes: chickpeas, lentils
- cruciferous: cauliflower and white cabbage, radish, radish, arugula, broccoli
- fermented milk products, cow's milk
- cereals high in gluten
- fresh yeast baked goods
Plant products: cereals, legumes, seeds contain phytic acid, which slows down the absorption of beneficial micronutrients and can cause flatulence. To prevent its development, it is recommended to soak bobos overnight with ½-1 teaspoon of soda. The next morning, drain the water and cook the product until done.
Bloating when eating different types of cabbage is often observed in the absence of enzymes to digest fiber. It may take from 2-3 months to six months for the microflora to form. If you are intolerant to a product, for example, cow protein or gluten, in addition to flatulence, there are complaints of deterioration in general health, weakness, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. To determine food tolerance, it is recommended to take a blood test and eliminate inappropriate foods from the diet.
Farts without smell, how to farts without smell
Sometimes you really want to release gas, but you are afraid of the judgment of others, because a strong stench will arise in the room. How to be? How to prevent yourself from dying from shame? It turns out that there has been an answer to this question for a long time, and sometimes you yourself have noticed when there is a smell and when there is not. First you need to understand what the gas mixture consists of. It contains many different gases, where more than 50% is nitrogen. But let’s divide them according to a different principle: ordinary and caustic. The more dairy, legumes and meat products, as well as bread, in your food, the stronger the gas formation and the more vigorous.
So, caustic gases have the ability to be absorbed into the intestinal walls. Therefore, we must try to endure the acute phases of the desire to fart, so that gases could be absorbed. And then all that remains is to release ordinary gases without harming anyone.
But here you need another skill - to do it silently. One effective way is to produce in small batches. Also, the sound is muffled by soft surfaces: sofas and armchairs.
If you have problems with gas formation and weak sphincter muscles, then you can use aromatic underwear and pads that will neutralize the odor. However, you will still need to master the art of whisperers. But first of all, if you are having such uncontrollable problems, then it is better to adjust your diet.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, an objective medical examination is performed and radiography is used. Tapping the abdominal area is accompanied by tympanic sounds. Additionally, it is recommended to:
- General analysis of urine, blood
- examination of stool, which reveals iodophilic flora, starch grains, connective tissue, muscle fibers
- N-2 breath test to determine hypolactasia, bacterial overgrowth
- ultrasound diagnostics
- magnetic resonance imaging
The absorption function is checked: fatty formations in the stool are determined, tests are carried out with D-xylose.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause causing bloating. In case of eating disorders, a diet is recommended. Products that have a low gas-forming potential are introduced into the diet. It is recommended to consume citrus fruits, hard cheeses, bananas, non-carbonated drinks, and dietary meat. Leave fermented milk products with bacterial (not yeast) leaven and cereals. To determine the tolerability of a particular product, you can take a blood test in the laboratory. Potential triggers of flatulence are also removed from the diet one by one and the body’s reaction is observed. Avoid the use of:
- dairy products
- yeast
- legumes
- soda
- refined sugar
If the cause of bloating is swallowing excess air, it is recommended:
- eat food slowly
- refrain from talking during meals
- do not consume chewing gum, caramels
- do not use a straw when drinking liquid, avoid beer, soda
- quit smoking
- consume sweet fruits and berries, dessert, observing the interval: at least 60-120 after the main meal
If flatulence is not caused by a pathological condition, moderate physical activity is indicated: walking in the fresh air, strengthening the abdominal muscles, yoga, gymnastics, self-massage. In other cases, the gastroenterologist selects a treatment protocol, taking into account the underlying factor of flatulence, accompanying symptoms, and individual characteristics of the body.
The general scheme of drug therapy involves the use of:
- Enterosorbents: Enterosgel, Diosmectite, Activated carbon, Plifepan. Active substances bind and remove toxic substances that produce increased gas formation.
- Defoamers are drugs based on simethicone, which convert gaseous substances into foam and reduce the surface tension of gas bubbles. The drugs of choice are Espumisan, Espusin, which prevent the formation of gas bubbles, eliminate the feeling of heaviness and bloating. Suitable for adults and children, patients with metabolic and hormonal disorders.
- Non-pancreatic enzymes that help digest carbohydrates.
- Carminatives: fennel fruits, dill, caraway seeds, valerian rhizomes, mint.
Diet, physical activity, and treatment of the psycho-emotional state are mandatory elements of complex therapy.
Question answer
Can gas formation affect constipation? Yes maybe. This problem can be combated with a cleansing enema, which only needs to be done once. Several procedures can seriously damage the microflora. Laxative teas based on Alexandria leaf are not recommended for use.
Is burping a sign of flatulence? Not always, because belching can be a symptom of some disease, and bloating does not occur. When sour belching occurs, this indicates the presence of gastritis; bitter - that there is a reflux of bile into the stomach; Putrefactive is a signal that food is retained (in the stomach or intestines).
Could bloating be due to worms? As a rule, this process occurs in the initial stages of helminth infection. If you have any doubts about this, it is better to get tested.
Prevention
To prevent increased gas formation, it is recommended to review your diet and maintain a drinking regime. Treat chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and inflammatory processes in a timely manner. Restore intestinal microflora: eliminate candidiasis, use suitable probiotics to populate beneficial microflora.
At the first signs of gas formation, exacerbation of chronic diseases, inflammatory processes and changes in microflora in the gastrointestinal tract are excluded. Next, adjust the diet, maintain a drinking regime, and follow the recommendations of the attending physician.