What is interferon?
Interferons (IFNs) are a group of proteins that are released by cells in response to viral infection. In some cases, interferons begin to be released in response to infection by certain types of bacteria. Interferons were first discovered in 1957, when scientists Alik Isaacs and Jean Lindeman discovered that mice infected with one virus were not infected with other viruses. It was easy for scientists to conclude that in response to a viral infection, cells produce certain universal substances with antiviral activity2.
Currently, more than 20 interferons are known, which are divided into three types3,4:
- Type I – viral interferons. These include interferon alpha (IFN-α), interferon beta (IFN-β), and several other interferons. Interferons alpha and beta are produced in response to viruses, as well as bacterial components that stimulate not only the production of interferon, but also other immune mechanisms.
- Type II – immune interferon, including gamma interferon (IFN-γ). Unlike type 1 interferons, which are the first to respond to a viral infection, gamma interferon is produced at subsequent stages of infection.
- Type III – interferon lambda (IFN-λ). This type of interferon was recently discovered, and its mechanism of action resembles the first type of interferon.
How do human interferons work?
Increased production of interferons begins when a cell is infected with a virus. Note that interferon does not act directly on the virus. First of all, interferon is a signaling molecule that affects neighboring cells, triggering processes in them that interfere with the replication of the virus. Under the influence of interferons, specific enzymes are synthesized in cells that interfere with the assembly of viral particles. Accordingly, the virus cannot further multiply, infecting our body. The second main property of interferons is to stimulate the immune system. In particular, some types of interferons present antigenic (foreign) agents to special T-helper cells of the immune system, which further down the chain pass it on to the next links of the immune pathway, ultimately destroying the pathogen5.
The antiviral properties of interferons have aroused great interest among researchers from the point of view of the treatment of a number of diseases. And over time, thanks to various medical and technological capabilities, it was possible to obtain medications that contain interferon.
General information about the drug
Interferon is a protein that is synthesized by almost all cells of the body. Its three varieties have the following directions:
- α and β – have antiviral activity.
- Γ – takes part in many immune reactions.
Interferon has the following properties:
- Stimulates the production of substances that can suppress the activity of the virus.
- It changes the cellular structure, ultimately creating conditions that are unsuitable for the virus to live in them.
- Stops the proliferation of microorganisms.
After the virus enters the body, the body's cells begin to synthesize interferon. But there are viruses in which cells weakly produce this substance. Such viruses include hepatitis virus, HIV infection, adenovirus, Epstein-Barr virus.
Therefore, there is a need for artificial introduction of protein.
Use of interferon drugs in medicine
Interferon drugs are actively used in the treatment of a wide range of viral diseases. In particular, we are talking about the human papillomavirus, viral hepatitis, herpes infection, as well as influenza and colds. An important factor in the selection of drugs containing interferon for the treatment of a particular disease will be the concentration of interferon in the drug, how it is obtained and what type of interferon (α, β, γ or λ) it contains. Despite the fact that there are interferon preparations that are available without a prescription, it is still better to consult a doctor in advance, since there are a number of contraindications for these drugs. Based on the method of preparation, interferon preparations can be divided into 4 types6,7:
- Leukocyte interferon is obtained from donor blood.
- Lymphoblastic interferon is obtained from a culture of lymphoblastic cells.
- Recombinant interferon is obtained from bacterial or fungal cultures into which the human gene responsible for the production of interferon has previously been inserted. Most often, interferon preparations contain recombinant interferon.
- Pegylated interferons are produced by combining recombinant interferon with polyethylene glycol. This is done to ensure that the drug lasts longer in the body.
Contraindications and possible side effects
The drug may be contraindicated in case of individual intolerance, as well as in severe forms of diseases of the liver, kidneys, cardiac system, central nervous system, thyroid gland.
When the drug is instilled into the nose, children may develop the following side effects:
- The development of muscle pain, hyperthermia and chills, as well as other flu-like manifestations.
- Nausea, upset stool.
- Drowsiness.
- Hives.
- Such reactions occur extremely rarely and most often with long-term use of interferon or increasing its dose.
Advantages and disadvantages of introduced interferons
The advantages of drugs containing interferons include their availability. An important advantage of interferons is their possible use against a wide range of viruses.
The relatively high level of safety of interferon drugs allows them to be used by children, who, as is known, often suffer from influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections.
However, along with the advantages, such drugs also have their disadvantages. Often, excessive amounts of type 1 interferon are associated with suppression of innate antibacterial immunity mechanisms8 and can also provoke a decrease in the production of intrinsic interferon9.
Analogues of the drug
You can buy many drugs at the pharmacy that contain interferon. Among them the most popular:
- Infagel.
- Viferon.
- Laferobion.
- Nazoferon.
- Inferon.
- Roferon.
- Grippferon.
- Lipoferon, etc.
The main active ingredient in all of these medications is interferon; only its dosage and auxiliary components differ. Therefore, you should not replace one remedy with another. Be sure to read the instructions for it and consult a specialist.
Interferon has an immunostimulating effect. It is used to treat many diseases and is also used for preventive purposes. It is acceptable to take interferon from the first days of a child’s life, but you will need to consult a doctor.
Emergency immunoprotection against viruses
The effectiveness of natural interferons (produced in the body) has been proven more than once10. For this reason, given the disadvantages of drugs containing interferons, it is more advisable to stimulate the production of the body’s own interferon. Interferon inducers cope with this task. These are drugs that stimulate the production of one’s own (endogenous) interferon. Interferon inducers, unlike introduced interferons, are slightly allergenic, and most importantly, they cause prolonged production of endogenous IFN in physiological doses sufficient to achieve therapeutic and preventive effects11.
A natural activator of the immune system and, in particular, stimulation of its own interferon are bacterial lysates, which stimulate local immunity without affecting the functioning of the general immune system. One of these is the IRS®19 spray, which contains lysates of 18 bacteria that most often cause respiratory diseases. Unlike systemic immunomodulators, IRS®19 acts locally without interfering with the functioning of the general immune system. It is noteworthy that bacterial lysates are destroyed microorganisms that cannot cause disease, but do induce an immune response14. IRS®19 can be used by both adults and children from 3 months12, which indicates its safety profile. This is especially important because children’s immune systems, which have not yet strengthened, are less able to cope with respiratory infections, which is why children get sick more often13.
The advantage of IRS®19 is that in addition to activating the production of its own interferon, the drug naturally enhances other factors of local immune defense of the nasopharyngeal mucosa: phagocytosis, increases the level of lysozyme and the production of local antibodies, in particular, secretory immunoglobulin A, which makes it possible to cope with both viruses and viruses. and with bacteria. This complex effect on local immunity helps speed up the healing process by 2 times1. IRS®19 acts on the cause of the disease, prevents infection from entering the body and reduces the risk of complications by activating antiviral and antibacterial mechanisms of emergency immunoprotection at the entrance gates of infection13. When IRS®19 is sprayed, a fine aerosol is formed that covers the nasal mucosa, which leads to the rapid mobilization of protective mechanisms12,14.
Another important advantage of IRS®19 is the possibility of using the drug for preventive purposes. Immunological memory after a course of IRS®19 application lasts on average about 4 months13. Such prevention is especially relevant during the season of viral attacks for both adults and children.
Our body, in the process of evolution, has adapted to fight viruses, but if necessary, we can help it without interfering too much with its work.
Interferon and the immune system
During the cold season, the problem of immunity and disease resistance comes to the fore. Everyone now knows the word immunity, but not many know how complex and multi-level the system is included in this concept. In addition, many believe that if a child is sick, it means that his immunity is poor and it urgently needs to be improved. At the same time, they terrorize the doctor, demanding that the child be prescribed a magic pill for all diseases that strengthens the immune system. So, there are no such pills, and in most cases of child illness there is no need for any strengthening - you just need rationality and adequate help in the treatment and follow-up of illnesses. The immune system can be trained and formed just like the muscles of the body, this is what doctors and parents should do, and not look for miracle pills.
What is the immune system?
Immunity is the immunity of the human body to infectious and non-infectious agents. The immune system not only fights viruses and bacteria, but also attacks worms and cancer cells in the body. Unfortunately, most often he can cope with germs and viruses on his own, but worms and tumors are completely beyond his control.
Immunity is usually divided into two large groups. One of them is innate immunity . This is when the body, due to its genetic characteristics, cannot suffer from some diseases - for example, people do not get canine distemper. These features are fixed at the gene level and are inherited from parents to children. The second part of immunity is acquired , which is what most people are talking about when this word is mentioned.
Acquired immunity is divided into two large groups - passive and active .
Passive immunity is the receipt by the body of ready-made antibodies to infections using an injection of special serum or from the mother to the fetus and child through breast milk.
Active immunity is developed during life as a result of illness or vaccination (vaccination). The body produces special substances - antibodies that bind to antigens. An antigen for the body can be a virus, a microbe, a protozoa, and even components of one’s own cells that are sick, damaged, or even healthy ones if there is a breakdown in the immune system. Antigen-antibody complexes are harmless to the body, are usually soluble in blood plasma and are excreted from the body by the kidneys or liver. Due to immunity, the body of an adult and a child resists infection. It is due to the work of the immune system that our temperature rises, inflammation develops, and it is due to the immune system that a rash (allergies) forms. It’s just that the mechanisms of immunity are different in each case.
The main immune cells are white blood cells - leukocytes and lymphocytes. Platelets are also partly involved in the mechanisms of immunity. In addition, many biological fluids and substances are involved in the formation of immunity - saliva, tears, stomach and intestinal mucus, sweat and blood.
Leukocytes work in areas of inflammation. Where the pathogen penetrates and destroys the cells of the body, they absorb (eat) damaged cells, microbes and form pus and inflammation. Lymphocytes synthesize immunoglobulins - special substances that are involved in neutralizing pathogens and remembering them for the future. This allows for the formation of strong immunity in the future - if the pathogen enters again, the disease will no longer develop. The level of these same immunoglobulins today determines the presence of immunity to many diseases and the effectiveness of vaccination.
In addition to immunoglobulins, the body produces a number of biologically active substances that help resist infection. These are interferons, lysozyme, the complement system and others.
We will talk about the interferon system in more detail...
This system is one of the first to be included in the fight against viruses. Interferons are special groups of protein molecules produced by cells of the human immune system. They are designed to combat bacteria, viruses, transformed and non-viable cells of the body. Interferons are a type of weapon with which we can resist pathogenic bacteria, parasites and even cancer cells. Interferon not only independently fights against harmful microorganisms and malignant tumors, but also activates other protective factors - macrophages and natural killer cells.
How does interferon work? Interferon is a product of the body itself. It was found that interferon is produced by any cells of the body as a protective agent in the very first hours of the introduction of any genetically alien agents (antigens), foreign proteins and nucleic acids into the cell. Cells synthesize interferon especially intensively in cases where such antigens are viruses.
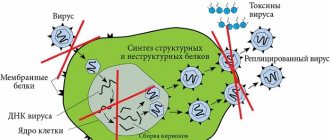
After a cell is infected with a virus, it begins to multiply vigorously, but simultaneously with the virus, the cell begins to produce protection in the form of interferons. A cell affected by a virus dies due to the penetration of the virus into it, but at the same time it enhances the protection of neighboring cells from viruses. Interferon released by a dying cell pursues viruses, protecting neighboring cells. After contact with interferon, each cell dies along with the virus that has penetrated it, but the virus does not leave offspring. Interferon does not penetrate cells, but acts on special receptors on membranes. As a result, it causes the production of special substances in these cells that suppress the proliferation of viruses. And the cells become unfit for the virus to live. The cell affected by the virus dies because it contained the virus, while protecting other cells. The interferon released during this process binds to the virus. And if it penetrates another cell, it will die, preventing the virus from multiplying offspring. In addition, interferon is carried through the bloodstream throughout the body, activating the immune system and the production of antibodies.
That is, interferon itself does not act on viruses, but it helps cells actively protect themselves from infection by viral particles. Even one interferon molecule is enough for each cell for protection, because interferon has high biological activity.
But here it is very important to understand that interferon is nonspecific, it is universal, it does not act selectively against any virus, but protects the body from any viruses (unlike many immunoglobulins, which are strictly specific for a particular virus or bacteria). It is produced in response to any impact, no matter whether it is a virus, microbe or cell damage. But, even despite this, the help of interferons is extremely necessary for the body, since the synthesis of antibodies in response to the introduction of infection is greatly delayed. Antibodies begin to actively develop after a few days, during which time interferons fight the infection. They begin to act from the first hours of illness and their concentration progressively increases.
Interferon can be obtained artificially by culturing it on special blood cells. This made it possible to use it as a medicinal drug. However, it should be remembered that in large doses it inhibits the growth and differentiation of any cells in the body, and not only tumor cells. When interferons are used, they practically do not prevent the development of a viral infection, but significantly reduce the duration of the disease and its severity.
Interferon is obtained by extracting human donor blood from leukocytes. It is purified from ballast and hazardous substances, then concentrated and made highly active. This makes it possible to use it more successfully.
In connection with such difficulties, special substances began to be used - inducers (stimulators) of the production of the body’s own interferon. Some of these drugs are Kagocel, Amixin, Cycloferon, etc...
The most promising and safest today is the use of synthetic ones obtained using special recombinant genetic engineering technologies. They do not even have a purely theoretical chance of transmitting infections through blood.
In our country, two generations of interferon preparations are approved for use in healthcare practice. First-generation drugs include drugs of natural origin obtained from donor raw materials (dry human leukocyte interferon for intranasal use; human leukocyte interferon, suppositories; human leukocyte interferon purified concentrated dry “Lokferon”; leukinferon). Second-generation drugs include drugs of recombinant human interferon alpha-2: Reaferon-EC, Interal, Viferon, Kipferon, Genferon, Reaferon-EC-Lipint, Infagel, etc. Interferons are produced today in various dosage forms - injection solution, nasal drops and eyes, suppositories and ointments, gels, films, tablets, aerosols. Natural interferon is quickly destroyed and removed from the human body. When administered by injection, it loses activity within an hour, so for a pronounced effect it must be administered quite often. It should be noted that recombinant interferons (reaferon, roferon, intron-A, viferon, geneferon and welferon) are more stable than “natural” ones; therefore, they are administered less frequently (2-3 times a day) and can be administered rectally.
You should always remember that these are medications that have side effects and should only be used with a doctor's prescription.
- Author - Polukhina Anastasia Aleksandrovna
- 15.01.2015
- All consultations by the author