Ataxia is a disease that is a failure in the continuity of motor operations of different muscles in the absence of muscle weakness. Simply put, ataxia is a commonly observed motor dysfunction, a neuromuscular defect that is often genetic. In addition, it can arise as a result of serious interruptions in vitamin B12, leading to cerebral stroke. Motor acts with the disease in question become distorted, clumsy, their consistency and order are disrupted, and an imbalance of balance is observed during motor operations and in a standing position. In the limbs, strength may be maintained or slightly reduced.
Sensitive ataxia
In most cases, this pathology occurs due to damage to the posterior columns, posterior nerves, peripheral nodes, thalamus opticus, and parietal cortex. Signs of sensitive ataxia can be observed in all limbs at once, or in only one of them. Doctors often diagnose signs of ataxia, which occurs due to a disorder of the joint-muscular sensation in the legs.
Characteristic signs of ataxia will be the patient's instability, excessive bending of his legs at the knee and hip joints. Many patients often feel as if they are walking on cotton wool or a carpet. Patients try to compensate for walking impairments with the help of vision, as they begin to constantly look at their feet. Due to severe damage to the posterior columns, patients almost completely stop walking.
Cerebellar ataxia
It occurs due to serious damage to the cerebellar vermis, as well as its legs and hemispheres. However, it is worth noting that cerebellar ataxia can be a symptom of diseases such as multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, or a malignant neoplasm in the cerebellum or brain stem. Patients with this pathology usually fall toward the damaged cerebellar hemisphere when walking. During such episodes, even falls are possible.
The patient usually staggers greatly when walking, and also places his legs too wide, his movements are slow, sweeping and awkward. Impaired coordination remains virtually unchanged even with vision control. Patients may experience serious speech disturbances, which gradually slow down, become scanned and drawn out. There are also problems with handwriting, which becomes uneven and splayed.
Vestibular ataxia
This pathology occurs due to damage to the vestibular nerve, labyrinth, cortical center and nuclei in the brain stem. This type of ataxia is observed in various ear diseases, brainstem encephalitis, Meniere's syndrome, and tumors of the fourth ventricle of the brain. The main sign of the pathology is considered to be regular severe dizziness, as a result of which the patient begins to feel as if all objects are moving in the same direction. Turning his head, the patient feels increased dizziness.
Severe dizziness leads to unsteady gait and falls. It is also noticeable that the patient tries to make very careful head movements. Vestibular ataxia is also characterized by symptoms such as vomiting, nausea and horizontal nystagmus.
The drug "Tagista"
The Russian analogue of Betaserk is the drug Tagista, which differs from the original only in cost. The price of the substitute is 80-90 rubles per package. While an imported product will cost the buyer 640-690 rubles.
The medication is often prescribed for cerebellar ataxia. Treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a specialist. Tablets are available in dosages of 8, 16 and 24 mg of betahistine.
Indications for the appointment of "Tagist" are such pathological conditions as Meniere's syndrome, vestibular vertigo, vestibular neuritis, hydrocele of the inner ear. It is forbidden to use the product if you have pheochromocytoma or hypersensitivity to the components in the composition. The medication is not prescribed to children under 18 years of age.
Depending on the severity of the condition, Tagista tablets may be prescribed in 1-2 pieces. (at a dosage of 8 mg) three times a day. An improvement in the condition is observed after the first dose of the drug.
Cortical ataxia
Cortical ataxia in most cases occurs due to damage to the frontal lobe of the brain. Its most common causes include tumors, circulatory disorders in the brain, and abscesses. In the case of this type of ataxia, symptoms such as unsteadiness when walking, falling over, or bending to the side appear.
Due to severe damage to the frontal lobe, patients may lose the ability to walk and stand. Cortical ataxia is also characterized by other symptoms: mental changes, grasping reflex, impaired sense of smell. In many ways, the clinical picture of cortical ataxia is similar to the symptoms of cerebellar pathology.
Cerebellar Pierre-Marie ataxia
The main manifestation of the disease is cerebellar ataxia. The disease occurs due to hypoplasia of the cerebellum, atrophy of the pons and inferior olives. Typically, the first signs of pathology appear in a patient at the age of 35 years.
The most characteristic symptoms of the disease are considered to be disturbances in gait, speech and facial expressions. In addition, patients usually experience dysmetria, static ataxia, adiadochokinesis, increased tendon reflexes, and decreased strength in the muscles of the limbs. Patients are often diagnosed with oculomotor disorders:
- lack of convergence;
- ptosis;
- paresis of the abducens nerve;
- Argyll-Robertson sign;
- decreased visual acuity;
- narrowing of visual fields;
- atrophy of the optic nerves.
Drug therapy
Treatment of cerebellar ataxia requires the mandatory use of the following categories of medications:
- muscle relaxants (help eliminate muscle spasms);
- nootropics (improves brain activity);
- drugs that help cope with vestibular disorders;
- antidepressants;
- B vitamins, vitamin C and PP;
- anticonvulsant medications.
For cerebellar ataxia, drugs such as Betaserc, Betagistin, Tagista, Betaver, Westinorm, Phenibut, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin, Mexidol, Sermion, Cavinton are used ", "Neurobeks", "Milgamma", "Mydocalm", "Pregabalin".
Familial Friedreich's ataxia
This disease is hereditary and occurs due to damage to the spinal systems. As a result of research, it was found that many patients with this type of ataxia often have consanguineous marriages in their pedigree. The main symptom of ataxia is an unsteady and clumsy gait.
The gradual development of the disease leads to impaired hand movements, problems with facial expressions, slowed speech, and hearing loss. Further development of ataxia leads to changes in the skeleton, heart rhythm disturbances, endocrine disorders, frequent dislocations, and kyphoscoliosis.
Reasons for development
The disease is a symptom complex that consists of disorders of dynamic and static human motor skills. The acquired form of pathology develops in the presence of the following factors:
- head injury;
- multiple sclerosis;
- cerebral stroke (ischemic, hypertensive);
- viral or infectious diseases;
- heavy metal intoxication;
- brain tumors;
- obstructive hydrocephalus;
- Guillain–Barre syndrome;
- acute vitamin B12 deficiency.
The listed syndromes lead to the development of cerebellar ataxia with an acute onset. The disease, the symptoms of which begin to appear within a few weeks, has a subacute onset. The main causes of the development of pathology are endocrine disorders, metabolic disorders, malignant tumors, and toxic poisoning.
Progressive chronic ataxia occurs against the background of chronic alcoholism and atrophic processes affecting the cerebellum.
Diagnosis of ataxia
- Diagnosis of the disease begins with the collection of complaints and anamnesis. Namely, the doctor must ask the patient how long ago he began to have complaints about unsteadiness of gait and poor coordination of movements, and how often and regularly these symptoms appear. It is definitely worth checking with the patient whether his relatives have had this disease. It is also necessary to find out whether the patient has taken any medications such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates.
- Patients suspected of having ataxia require a neurological examination. This examination involves assessing coordination of movements and gait, assessing strength in the limbs and muscle tone, the presence of nystagmus, and strength in the limbs.
- A correct assessment of hearing will also require an examination by an otolaryngologist.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms for various types of ataxia:
- change in gait;
- impaired coordination of movements of the arms and legs.
Based on these signs, a “basic” diagnosis can be made, but each type of disease also has its own specific manifestations.
- The vestibular variety is often accompanied by hearing impairment, since the vestibular apparatus is, strictly speaking, part of the inner ear.
- With the cerebellar variety, speech disturbances occur - it becomes extended, spasmodic, and often resembles chanting; Another sign is a violation of handwriting, it becomes sweeping, uneven, the letters are often enormous in size.
- With cortical ataxia, a weakened sense of smell and mental disturbances are observed. Hereditary varieties of the disease are accompanied by visual impairment, hearing impairment, endocrine disorders, decreased intelligence, and depression. Louis-Bar disease can also be accompanied by rhinitis, bronchitis, pneumonia and some other similar diseases, and the body's immune system is primarily affected.
The types of ataxia themselves are sometimes manifestations of other, more general diseases, so they are accompanied by signs of these ailments.
Additional tests
For a more detailed study of the disease, a consultation with a neurosurgeon will be required, as well as a number of instrumental studies.
- In particular, a lot of information about the disease can be obtained using electroencephalography. This technique evaluates the electrical activity of various parts of the brain, which tends to change in various diseases.
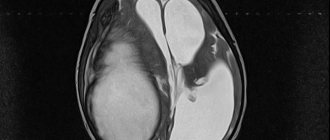
- No less effective techniques are also CT and MRI of the brain. They allow you to study the structure of the brain layer by layer, detect violations of the structure of its tissues, identify ulcers, tumors, and hemorrhages.
- Magnetic resonance angiography will help detect tumors in the brain and assess the integrity of the arteries in the skull.
Complications of ataxia
Treatment of ataxia must be timely, as otherwise serious complications are possible. One of the most dangerous complications of ataxia is heart failure. This is an acute or chronic condition, which is accompanied by shortness of breath, swelling, and frequent fatigue. The danger of the pathology is that it can cause pulmonary edema. Today, heart failure is one of the common causes of death. No less dangerous complications of ataxia are repeated infectious diseases and respiratory failure.
Recommendations
A consultation with a neurologist and DNA diagnostics are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Russian State Medical University, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Gusev E.I. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Treatment of ataxia
Treatment of ataxia is aimed at eliminating the etiological factor that triggered the development. Depending on the specific disease, the following operations may be prescribed:
- tumor removal;
- elimination of hemorrhage;
- removal of the abscess and subsequent antibiotic therapy.
In rare cases, a procedure to relieve pressure in the posterior fossa may be necessary. Namely, this procedure is carried out if a patient has an Arnold-Chiari malformation, which is characterized by a slight descent of part of the cerebellum into the opening of the skull, which ultimately leads to severe compression of the brain stem. Ataxia can also be caused by hydrocephalus, which is characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system of the brain. In this case, doctors create an outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which normalizes metabolism in the brain.
If the cause of this serious disease is high blood pressure, it is imperative to normalize it with the help of drug therapy. In case of circulatory problems in the brain, drugs that improve metabolism and blood flow are also indicated. These primarily include nootropics and angioprotectors.
Ear diseases can also lead to the development of ataxia. In case of infectious brain damage caused by ear pathology, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed. If there is a lack of vitamin B12, it must be compensated. To eliminate poisoning, vitamins A, B, and C are prescribed. For demyelinating diseases, hormonal medications are indicated, as well as plasmapheresis. This procedure involves removing blood plasma, but preserving blood cells.
Ataxia is a dangerous disease because, due to lack of coordination, the patient can experience serious injuries. This can be prevented by following a few rules:
- It is better for all patients, regardless of the stage of their disease, to avoid driving a car and working with power tools. In these situations, poor coordination can cause serious injury.
- Patients with ataxia should always keep the room well-lit to increase depth of perception and avoid injury. Twilight is especially dangerous for patients.
- Many patients experience serious difficulty climbing stairs. To avoid injury, be sure to hold on to the railing or use outside help when climbing stairs.
- If it is very difficult for a patient to move independently due to lack of coordination, he should use a walker or cane while moving.
- If you experience a feeling of nausea or severe dizziness, you should immediately sit down or lie down.
- Doctors also advise listening to your body. Therefore, if the disease worsens, you should make an appointment with a neurologist.