Levomycetin is an antibacterial antimicrobial agent with a broad spectrum of action. The drug is very quickly absorbed in the stomach and penetrates the systemic bloodstream.
This allows you to cope with various pathologies in a short time. Levomycetin is often prescribed to children for poisoning, stool disorders, and infectious and inflammatory pathologies.
Release form and composition
The drug in question has several dosage forms:
- pills;
- capsules;
- ointment;
- powder for the preparation of injection solution;
- alcohol solution for external use;
- eye drops.
The active ingredient is chloramphenicol.
The composition of chloramphenicol ointment includes such additional components as propylene glycol, liquid paraffin, polyethylene glycol, cetostearyl ether, cetylstearyl alcohol, water. The concentration of the main component is 1% or 5%. The drug is produced in tubes of 20 and 30 g, packed in cardboard boxes. Levomekol is the trade name of the ointment preparation.
The substance intended for the preparation of injection solutions is chloramphenicol sodium succinate. It is a white or yellowish powder that is sterile and hygroscopic. It is available in glass bottles of 0.5 and 1 g, closed with rubber stoppers with aluminum fixation.
Eye drops
The ophthalmic version of the drug is available in the form of drops with a concentration of 0.25%.
The liquid is sold in darkened glass bottles or polymer droppers with a volume of 1, 2, 5 or 10 ml.
Double-distilled water is used as a solvent, and boric acid is an additional substance.
Pills
The tableted drug has a bitter taste and a white or slightly yellowish color; there may be small inclusions. The shape of the tablets is flat, round, with a chamfer at the ends and a central groove on one side. The content of chloramphenicol is 0.25 or 0.5 g. Excipients are stearic acid, potato starch and hydroxypropylcellulose.
Blisters with medicine can be placed in cardboard packs of 1 or 2.
Tablets are packaged in 10 pcs. in contour cellless packaging or blisters, which can be placed in cardboard packs of 1 or 2.
Often strips and blister sheets are sold without a box.
Sometimes medicine is sold in jars (10, 20, 30 tablets each), the outer packaging of which is cardboard.
Capsules
These are 250 or 500 mg tablets with a film coating containing powdered sugar. They are packaged in 10 pieces. in blisters, arranged in 1-6 pcs. in cardboard boxes.
Solution
A liquid product for external use is prepared by dissolving powdered chloramphenicol in 70% ethanol. The liquid has a concentration of the main component of 0.25%, 1% or 3%. The drug is poured into darkened glass containers with a volume of 50, 40, 30 or 25 ml. The bottle is placed in a cardboard box along with instructions.
Levomycetin is poured into darkened glass containers of 50, 40, 30 or 25 ml.
Analogs
Analogues of Levomycetin in the form of tablets and capsules are the following drugs:
- According to the active ingredient: Levomycetin Aktitab, Levomycetin-UBF, Levomycetin-KMP, Levomycetin sodium succinate, Levomycetin-LekT,
- By purpose and mechanism of action: Fluimucil-antibiotic IT,
Analogs of Levomycetin in the form of an alcohol solution are:
- Ingredients: Levovinisol, Levomycetin;
- By mechanism of action: Altargo, Bactroban, Baneocin, Bonderm, Heliomycin, Gentamicin, Linkomycin, Neomycin, Syntomycin, Supirocin, Fuzidin, Fuzimet, Fucidin, Fusiderm.
Analogs of Levomycetin in the form of eye drops are:
- According to the active ingredient: Levomycetin-AKOS, Levomycetin-Akri, Levomycetin-DIA, Levomycetin-Ferein;
- According to belonging to the same pharmacological group: Azidrop, Gentamicin, Dilaterol, Colbiocin, Nettavisc, Nettacin, Eye films with kanamycin, Tetracycline, Tobrex, Tobropt, Fucithalmic, Erythromycin, Tobrosopt.
pharmachologic effect
The active substance of the drug in question, chloramphenicol, has a pronounced antimicrobial effect. It exhibits bacteriostatic properties, blocking the peptidyl transferase activity of bacteria, which leads to disruption of the protein biosynthesis chain. Effective against staphylo- and streptococcal organisms, a variety of gram-negative bacteria, including salmonella, chlamydia, spirochetes, rickettsia, and also against some viruses.
Chloramphenicol effectively fights bacterial strains resistant to streptomycin, penicillin and sulfonamide drugs. However, it is not capable of destroying tuberculosis pathogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, fungal organisms and protozoa.
This compound is highly toxic, so it is used when less aggressive antibiotics fail
Resistance of microorganisms to this antibiotic develops slowly. At the same time, resistance to the action of other chemotherapeutic agents does not develop.
1-3 hours after oral administration, the drug is almost completely absorbed into the blood.
1-3 hours after oral administration, the drug is almost completely absorbed into the blood.
Chloramphenicol easily penetrates tissues and liquid substances, including cerebrospinal fluid and breast milk, overcomes the placental barrier, and is characterized by high bioavailability (up to 80%). It is concentrated in large quantities in the kidneys and liver. The duration of action of the antibiotic is 4-5 hours.
The main volume of the drug is metabolized by the liver, the rest is hydrolyzed in the intestine. Metabolites do not show activity. Excretion is carried out mainly by the kidneys.
What is levomycetin and what is it used for?
One of the dosage forms that are included in the group of antibiotics is Levomycetin. Its spectrum of action is wide and is considered an excellent assistant in the fight against many diseases. Due to the presence of chloramphenicol, this medicine has an effect in the treatment of serious diseases, both infectious and non-infectious:
- eye diseases,
- venereal diseases,
- psittacosis,
- acute infectious diseases, etc.
Treats diseases associated with bacteria that are resistant to drugs of the penicillin group, as well as sulfonamides and streptomycin.
Levomycetin is a drug that is well and quickly absorbed, and within 3-4 hours it can have a therapeutic effect on the concentration of bacteria and microorganisms. Absorption of the drug occurs directly in the gastrointestinal tract (when administered rectally).
It then continues to penetrate the fluid structure of the body, the brain or the placenta (if prescribed during pregnancy). If the medicine is used to treat eye diseases - cornea, iris. In this case, penetration into the lens itself is not observed.
As a dosage form, it is prescribed for the treatment of serious diseases that significantly affect human health:
- chlamydia,
- rickettsiosis,
- tularemia,
- salmonellosis (generalized forms),
- paratyphoid and typhoid fever.
Most often, Levomycetin is used for treatment and prevention. It is believed that if other chemotherapy drugs are powerless, then salvation lies only in it.
What does Levomycetin help with?
The drug is prescribed for such inflammatory and infectious lesions provoked by microorganisms susceptible to its action, such as:
- dysentery;
- typhoid or typhus;
- brucellosis;
- salmonellosis;
- chlamydia;
- paratyphoid;
- tularemia;
- purulent peritonitis;
- meningitis of bacterial origin;
- cerebral abscess;
- respiratory diseases, including pneumonia;
- cystitis, biliary and urinary tract infections;
- urogenital inflammation;
- psittacosis;
- purulent otitis;
- wound infection with suppuration;
- burns;
- purulent-inflammatory dermatological diseases, eczema of bacterial origin, inflammation of the skin at the injection site;
- bedsores, trophic ulcerations, post-traumatic sepsis;
- abscess in soft tissues;
- digestive tract infection, intestinal disorders;
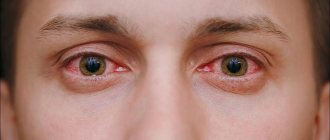
- conjunctivitis, stye, keratitis.
The drug is prescribed for the treatment of cystitis.
Crushed tablets together with boric and salicylic acid are used to prepare a suspension for pimples and acne. Another composition of the acne remedy includes chloramphenicol powder, calendula decoction/tincture and aspirin. There are similar recipes with streptocide. Such talkers are effective and very popular.
Many people are accustomed to considering the drug in question an effective way to treat diarrhea, forgetting that it is an antibiotic. All over the world it is considered as an outdated medicine, which should be used in special cases for severe forms of infectious lesions.
Indications for use
As indicated in the instructions for Levomycetin, in the form of capsules and tablets, this drug is indicated for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms that are sensitive to chloramphenicol. In particular, it is prescribed for therapy:
- Typhoid fever;
- Dysentery;
- Paratyphoid;
- Tularemia;
- Brucellosis;
- Typhus and other rickettsioses (infectious diseases caused by rickettsia - intracellular microorganisms);
- Whooping cough;
- Trachomas;
- Pneumonia;
- Sepsis;
- Meningitis;
- Osteomyelitis.
Externally, Levomycetin, according to the instructions, is used to treat:
- Boils;
- Second and third degree burns;
- Purulent skin lesions;
- Long-term non-healing trophic ulcers;
- Cracked nipples in breastfeeding women.
In ophthalmology, Levomycetin is used for the treatment of inflammatory eye diseases, including keratitis, blepharitis, and conjunctivitis.
How to take Levomycetin
Taking into account the high probability of adverse reactions, the drug is taken only as prescribed by a doctor and the dosage is strictly observed.
The tablets should be taken 30 minutes before meals.
If you have nausea and vomiting, you can take the medicine 1 hour after eating. The adult daily dose for oral administration in case of severe lesions can be increased by 1.5-2 times. Children's dosage is prescribed taking into account body weight. The course of treatment is determined according to individual indicators and averages 1-1.5 weeks.
When treating skin diseases, apply an ointment to the problem area and rub in lightly.
The ointment is applied topically in a thin layer under the bandage. You can soak a gauze pad with it and apply it to the wound or burn surface after the stage of cleansing and antiseptic treatment.
Local therapy should be combined with appropriate oral medications.
When treating acne and other skin diseases, apply an ointment to the problem area and rub in lightly (if possible). The dosage depends on the size of the treated area and the observed dynamics, taking into account the doses recommended by the doctor and the age of the patient. It is not advisable to use the drug for longer than 2 weeks.
An alcohol solution is used externally to treat burns, scratches, and cracks. Can be applied under an occlusive dressing. For otitis media, liquid should be dripped into the ears.
How to divorce
The sterile powder should be diluted extemporaneously. The concentration of the solution, as well as the dose used, depends on the severity of the disease. For intramuscular administration, water for preparing injections or novocaine solution 0.5 or 0.25% is used as a solvent. You need to inject deeply into the muscle.
For children, Levomycetin injections are given only intramuscularly.
To inject the drug into a vein, the powder is diluted with injection water or a 40% or 5% glucose solution. For patients with diabetes mellitus, saline solution is used as a solvent. The antibiotic should be administered intravenously gradually, the procedure should take at least 3 minutes. For children, injections are given only intramuscularly.
In ophthalmology, the powder is diluted with sterile water for preparing injections or saline solution. To perform a parabulbar injection, the concentration of chloramphenicol should be 20%, and a 5% solution is required for instillation.
How many days to drip
The duration of ophthalmic use of the drug is determined individually. The course of treatment can take from 5 to 15 days.
Antibiotics of the chloramphenicol group
Home Medical encyclopedia Medicines Antimicrobial and antiparasitic medicines
ANTIBIOTICS OF THE LEVOMYCETIN GROUP
LEVOMYCETIN (Laevomycetinum)
Synonyms: Chloramphenicol, Chloroid, Alphycetin, Berlitsetin, Biofenicol, Hemycetin, Chlornitromycin, Chlorocycline, Chloromycetin, Chloronitrin, Chloroptik, Klobinekol, Detreomycin, Galomycetin, Leukomyin, Paraxin, Syntomycetin, Typhomycetin, Typhomyin, etc.
A synthetic substance identical to the natural antibiotic chloramphenicol, which is a waste product of the microorganism Streptomycesvenezuelae.
Pharmachologic effect. Levomyietin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic; effective against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, rickettsia, spirochetes and some large viruses (the causative agents of trachoma /an infectious eye disease that can lead to blindness/, psittacosis /an acute infectious disease transmitted to humans from birds/, inguinal lymphogranulomatosis /IV venereal disease - disease sexually transmitted; characterized by inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes followed by the formation of bleeding ulcers/etc.); acts on bacterial strains resistant to penicillin, streptomycin, and sulfonamides. In normal doses it acts bacteriostatically (prevents the growth of bacteria). Weakly active against acid-fast bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, clostridia and protozoa.
The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of levomyetin is associated with a violation of the synthesis of microbial proteins.
Drug resistance to the drug develops relatively slowly, and, as a rule, cross-resistance to other chemotherapeutic agents does not occur.
Levomycetin is easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration, the maximum concentration in the blood is created after 2-3 hours; Within 4-5 hours after a single dose of treatment, a therapeutically active concentration remains in the blood, then a significant decrease in concentration occurs. The drug penetrates well into organs and body fluids, through the blood-brain barrier (the barrier between blood and brain tissue), through the placenta, and is found in breast milk. Therapeutic concentrations of chloramphenicol, when administered orally or topically, are created in the vitreous body (the transparent mass that fills the cavity of the eyeball), the cornea (the transparent membrane of the eye), the iris, and the aqueous humor of the eye; The drug does not penetrate into the lens. Levomycetin is well absorbed when administered rectally (through the rectum). It is excreted mainly in the urine mainly in the form of inactive metabolites (metabolic products); partially - with bile and feces. In the intestine, under the influence of intestinal bacteria, hydrolysis (decomposition with the participation of water) of chloramphenicol occurs with the formation of inactive metabolites.
Indications for use. Lsvomiietin is used for typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, generalized forms of salmonellosis, brucellosis, tularemia, meningitis, rickettsinosis, and chlamydiasis.
For infectious processes of other etiology (Causes) caused by pathogens sensitive to the action of chloramphenicol, the drug is indicated in case of ineffectiveness of other chemotherapeutic drugs.
Levomycetin is also used topically for the prevention and treatment of eye infectious diseases (conjunctivitis - inflammation of the outer membrane of the eye, blepharitis - inflammation of the edges of the eyelids, etc.).
Method of administration and dose. Before prescribing a drug to a patient, it is advisable to determine the sensitivity to it of the microflora that caused the disease in this patient. Levomycetin is used orally in tablets and capsules, topically in the form of aqueous solutions and ointments.
Orally in the form of tablets or capsules, usually taken 30 minutes before meals (in case of nausea or vomiting, an hour after meals). Single dose for adults - 0.25-0.5 g; daily dose - 2 g. In especially severe cases (typhoid fever, peritonitis / inflammation of the peritoneum / etc.), you can prescribe the drug in a dose of up to 4 g per day (under the strict supervision of a doctor and control over blood condition and kidney function). The daily dose of tablets and capsules is taken in 3-4 doses. Long-acting tablets are prescribed only to adults: in the first days of illness, 1.3 g (2 tablets) 2 times a day; after normalization of body temperature, 0.65 g (one tablet) 2 times a day. For children, chloramphenicol is prescribed in the form of tablets or capsules. A single dose of the drug for children under 3 years of age is 10-15 mg/kg, from 3 to 8 years - 0.15-0.2 g; over 8 years - 0.2-0.3 g; taken 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment with chloramphenicol is 7-10 days. According to indications, if it is well tolerated and there are no changes in the hematopoietic system, treatment can be extended to 2 weeks. If nausea and vomiting develop while taking the drug, take it 1 hour after eating.
Locally, chloramphenicol can be used in the form of liniment (1-10%) for the treatment of trachoma (an infectious eye disease that can lead to blindness), pustular skin lesions, furunculosis (multiple purulent inflammation of the skin), burns, cracks, etc.
In the treatment of conjunctivitis, keratitis (inflammation of the cornea), blepharitis, 1% liniment or 0.25% aqueous solution (eye drops) can be used. Dressings with levomyetin liniment are used for purulent wound infections.
Side effect. When treated with chloramphenicol, dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting, loose stools), irritation of the mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx, skin rash, dermatitis (skin inflammation), rash and irritation around the anus, etc. may be observed.
It should be taken into account that chloramphenicol can have a toxic (damaging) effect on the hematopoietic system (causes reticulocytopenia /a decrease in the number of reticulocytes - blood cells in the blood/, granulocytopenia /a decrease in the content of granulocytes in the blood/, sometimes a decrease in the number of erythrocytes /blood cells that carry oxygen/ ). In severe cases, aplastic anemia is possible (a decrease in hemoglobin content in the blood due to inhibition of the hematopoietic function of the bone marrow). Severe complications from the hematopoietic system are often associated with the use of large doses of chloramphenicol. Young children are most sensitive to the drug.
Large doses of chloramphenicol can cause psychomotor disorders (psychomotor agitation - increased motor and speech activity, usually followed by a reverse reaction), confusion, visual and auditory hallucinations (delusions, visions that acquire the character of reality), decreased hearing and vision acuity.
The use of chloramphenicol is sometimes accompanied by suppression of intestinal microflora, the development of dysbiosis (disturbances in the composition of the body's normal microflora), and secondary fungal infection.
When using chloramphenicol in the form of eye drops and ointments, local allergic reactions are possible.
Treatment with chloramphenicol should be carried out under the control of the blood picture and the functional state of the patient’s liver and kidneys.
Contraindications. Uncontrolled prescription of chloramphenicol and its use in mild forms of infectious processes, especially in pediatric practice, should not be allowed.
Levomycetin should not be prescribed for acute respiratory (breathing) diseases, sore throat and for prophylactic purposes.
Levomycetin is not prescribed together with drugs that inhibit hematopoiesis (sulfonamides, pyrazodone derivatives, cytostatics). Due to possible changes in the metabolism of a number of drugs, chloramphenicol is not recommended for use in combination with diphenin, neodicoumarin, butamide, and barbiturates.
Levomycetin is contraindicated in case of inhibition of hematopoiesis, individual intolerance to the drug, skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, fungal infections), during pregnancy and in newborns.
The drug should be prescribed with caution to patients with a history of allergic reactions.
Release form. Tablets of 0.25 and 0.5 g; film-coated tablets, 0.25 g; chloramphenicol tablets of prolonged (long-term) action, containing 0.65 g of the drug (two-layer tablets, the outer layer contains 0.25 g of chloramphenicol, the inner layer - 0.4 g) in a package of 10 pieces; in capsules containing 0.1; 0.25 and 0.5 g of chloramphenicol, in a package of 10 or 16 capsules; 0.25% solution (eye drops) in 10 ml bottles. For external use as an antiseptic (disinfectant), a ready-made solution containing chloramphenicol 2.5 g, boric acid 1 g, ethyl alcohol 70% up to 100 ml is also used; chloramphenicol alcohol solution 0.25%; 1%; 3% and 5%.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
IRUXOL (Iruxol)
Pharmachologic effect. Justridyl peptidase, which is part of the drug, is a proteolytic (protein-breaking) enzyme isolated from Clostridiumhistolyticum.
The ointment promotes enzymatic cleansing of wounds, prevents the development of infection, and accelerates regeneration (recovery).
Indications for use. Used for varicose ulcers (ulcerations at the site of dilated veins of the extremities), burns, frostbite, long-term non-healing ulcers, etc.
Method of administration and dose. Apply a thin layer 2 times a day. Exfoliated necrotic masses (dead tissue) are first removed.
Side effect. Possible side effects (burning, pain) are rare and go away on their own.
Release form. An ointment containing 10 mg of chloramphenicol per 1 g and 0.6 units of clostridyl peptidase A, in tubes of 10 and 30 g.
Storage conditions. In a cool place.
LEVOVINIZOL (Laevovinisolum)
Combined drug in aerosol packaging.
Pharmachologic effect. Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Indications for use. Used to treat superficial and limited deep burns, bedsores (tissue necrosis caused by prolonged pressure on them due to lying), trophic ulcers (slow-healing skin defects), infected wounds (with an area of no more than 20 cm2).
Method of administration and dose. Press the valve of the cylinder and spray the drug in the affected area from a distance of 20-30 cm for 1-3 seconds.
Usually the aerosol is applied 2-3 times a week; for severe lesions, the drug can be used daily or 2 times a day.
Side effect. When the drug is applied to the wounds, a transient burning sensation is noted.
Contraindications. Levovinisol should not be used for extensive granulating (healing) wounds, if the patient is individually hypersensitive to chloramphenicol, or if the microflora is resistant to chloramphenicol.
When spraying, be careful not to get the drug into your eyes.
Release form. Aerosol cans. Composition: chloramphenicol - 0.136 g, vinylin - 13.5 g, linetol - 13.4 g, ethyl alcohol 95% - 2.9 g, citral - 0.1 g and propellant (freon) - up to 60 g.
Storage conditions. At temperatures from +5 to +20 °C.
"LEVOMEKOL" OINTMENT (Unguentum "Laevomecol")
Pharmachologic effect. Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Indications for use. Used to treat purulent wounds.
Method of administration and dose. Before prescribing a drug to a patient, it is advisable to determine the sensitivity to it of the microflora that caused the disease in this patient. Sterile gauze pads are soaked in the ointment and loosely filled into the wound. Dressings are performed daily until the wound is completely cleansed of purulent-necrotic masses (inflamed necrotic / dead / tissue).
It is possible to introduce the ointment (warmed to +35-+36 °C) into the purulent cavities (through a drainage tube using a syringe).
Side effect. When the drug is applied to the wounds, a transient burning sensation is noted.
Contraindications. The ointment is contraindicated in case of individual hypersensitivity to chloramphenicol.
Release form. In jars of 100 g. Contains: chloramphenicol - 0.75 g, methyluracil - 4 g, polyethylene oxide - 95.25 g (per 100 g).
Storage conditions. In a dry, cool place, protected from light.
"LEVOSIN" OINTMENT (Unguentum "Laevosin")
Pharmachologic effect. Has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Indications for use. Used for the treatment of purulent wounds in the first phase of the wound process.
Method of administration and dose. Before prescribing a drug to a patient, it is advisable to determine the sensitivity to it of the microflora that caused the disease in this patient. Sterile gauze pads are soaked in the ointment and loosely filled into the wound. Dressings are performed daily until the wound is completely cleansed of purulent-necrotic masses (inflamed necrotic/dead/ tissue).
It is possible to introduce the ointment (warmed to +35-+36 °C) into the purulent cavities (through a drainage tube using a syringe).
Contraindications. The ointment is contraindicated in case of individual hypersensitivity to chloramphenicol.
Release form. In cans of 50 g. Contains: chloramphenicol - 1 g, sulfadimethoxine - 4 g, methyluracil - 4 g, trimecaine - 3 g, polyethylene oxide - up to 100 g.
Storage conditions. In a dry, cool place, protected from light.
"FULEVIL" OINTMENT (Unguentum "Fulevil")
Indications for use. Used to treat dermatitis (inflammation of the skin), long-term non-healing wounds, rectal fissures, bedsores (tissue necrosis caused by prolonged pressure on them due to lying down), I-II degree burns.
Method of administration and dose. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to a sterile napkin, which is applied to the treated wound surface. The dressing is left for 24 hours, changed daily or 2-3 times a week, depending on the amount of purulent discharge from the wound. Duration of treatment is 1-4 weeks.
Release form. Ointment containing chloramphenicol (2%), furatsilin (0.1%), solution (oil) of retinol acetate (vit. A), anhydrous lanolin, in orange glass jars of 25 g.
Side effect. When the drug is applied to the wounds, a transient burning sensation is noted.
Contraindications. Individual hypersensitivity to chloramphenicol.
Storage conditions. In a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding +10 °C.
Levomycetin is also included in the composition of the drug “corticomycetin” ointment.
LEVOMYCETIN STEARATE (Laevomycetinistearas)
Synonyms: Eulevomycetin.
Pharmachologic effect. Invitro (“in vitro”) does not have an antimicrobial effect; its activity appears only invivo (in the body) after the breakdown and release of chloramphenicol. In the gastrointestinal tract it is saponified (decomposed) to form chloramphenicol, which is the active ingredient of the drug. Its concentration in the blood increases more slowly than with the administration of the drug chloramphenicol.
Indications for use. In the same cases as chloramphenicol, in pediatric practice, when the administration of chloramphenicol is difficult due to the bitter taste.
Method of administration and dose. Before prescribing a drug to a patient, it is advisable to determine the sensitivity to it of the microflora that caused the disease in this patient. Orally 3-4 times a day: adults usually 1 g per dose; children under 3 years old - at the rate of 0.02 g/kg, from 3 to 8 years old - 0.3-0.4 g per dose, from 8 years and older - 0.4-0.6 g per dose.
A suspension (5%) is prescribed to children under one month of age, 25-40 drops per dose, from 2 to 6 months. - 1/2 teaspoon, from 7 months. up to 1 year - 1/2-1 teaspoon, from 1 year to 2 years - 1 teaspoon, from 3 to 8 years - 1-2 teaspoons per dose.
Side effects and contraindications. The same as for chloramphenicol.
Release form. Powder; tablets 0.25 g in a package of 10 pieces. Suspension 5%, 50 ml.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
LEVOMYCETIN SUCCINATE SOLUBLE (Laevomycetinisuccinassolubile)
Pharmachologic effect. According to the antibacterial spectrum of action of chloramphenicol, succinate does not differ from chloramphenicol, but as a drug soluble in water, it can be used for injection.
Indications for use. Used for typhoid and paratyphoid fever, dysentery, brucellosis (an infectious disease transmitted to humans, usually from farm animals), whooping cough, pneumonia (pneumonia) of various etiologies (causes), purulent infections and other infectious diseases. It is also used for the prevention and relief (removal) of infections in wound injuries of the eye.
Method of administration and dose. Before prescribing a drug to a patient, it is advisable to determine the sensitivity to it of the microflora that caused the disease in this patient. Administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously. Dose for adults: 0.5-1.0 g (as a 20% solution) per injection 2-3 times a day (at intervals of 8-12 hours). If necessary, the daily dose is increased to 4 g.
Children are recommended to administer intramuscularly: daily dose for children 1 year of age is 25-30 mg/kg, over 1 year of age - 50 mg/kg (in 2 injections with an interval of 12 hours).
In ophthalmological (eye) practice, it is used in the form of parabulbar injections (introductions into the cavity surrounding the eyeball) and installations (instillations). 0.2-0.3 ml of a 20% solution is administered parabulbarly 1-2 times a day. A 5% solution is instilled into the conjunctival sac (the cavity between the back surface of the eyelids and the front surface of the eyeball), 1-2 drops 3-5 times a day.
Solutions for injections are prepared with a 0.25-0.5% solution of novocaine, for installations - with sterile water for injection.
Side effects and contraindications. The same as for chloramphenicol.
Release form. Bottles of 1 g.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
SINTHOMYCIN (Svnthomycinum)
Pharmachologic effect. It is a mixture of right- and left-handed isomers of chloramphenicol.
The use of syntomycin may be accompanied by the same complications that are observed during treatment with chloramphenicol; in addition, changes in the nervous system were noted in the form of excitement, feelings of fear and others
violations. In this regard, the drug is not prescribed orally, but is used only externally in the form of liniments and other dosage forms.
SINTOMYCIN Liniment (LinimentuinSynthomycini)
Synonyms: Synthomycin emulsion.
Indications for use. It is used to treat purulent wounds, purulent-inflammatory diseases of the skin and mucous membranes, trachoma (an infectious eye disease that can lead to blindness), sycosis (purulent inflammation of the hair follicles, most often in the mustache and beard area).
Method of administration and dose. Before prescribing a drug to a patient, it is advisable to determine the sensitivity to it of the microflora that caused the disease in this patient. For pustular skin lesions, furunculosis (multiple purulent inflammation of the skin), carbuncles (acute diffuse purulent-necrotic inflammation of several nearby sebaceous glands and hair follicles), purulent wounds, burns, for the treatment of long-term non-healing ulcers, II and III degree burns, cracked nipples in women in labor, etc. apply liniment to the affected area. Apply a regular bandage on top, possibly with parchment or compress paper.
For the treatment of trachoma, 10% (5% or 1%) liniment (emulsion) of synthomycin is used.
Side effect. There may be a burning sensation at the site of application of the drug.
Contraindications. Individual hypersensitivity to the drug.
Release form. In glass jars of 25 g. Composition: 1%, 5% or 10% synthomycin, castor oil, special emulsifier, distilled water, preservative.
Storage conditions. In a dry, cool place, protected from light.
SINTOMYCIN (1%) Linimentum WITH NOVOCAINE (0.5%) (LinimentumSynthomycini1% cumNovocaino1%)
Indications for use. Used for local treatment of infected burn surfaces and purulent wounds accompanied by severe pain.
Method of administration and dose. Liniment is applied to the wound or burn surface. Dressings are done daily or every other day. Local treatment can be combined with oral chloramphenicol.
Side effect. There may be a burning sensation at the site of application of the drug.
Contraindications. Individual hypersensitivity to the drug.
Release form. In glass jars of 25 g.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry, cool place, protected from light.
VAGINAL SUPPOSITORIES WITH SYNTHRMYCIN 0.25 g (Suppositoria vaginaliacum Synthomicino 0.25)
Indications for use. Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs (vaginitis/inflammation of the vagina).
Method of administration and dose. If there are no other prescriptions, 1 suppository (suppository) deep into the vagina at night for 4-6 days.
Side effect. There may be a burning sensation at the site of application of the drug.
Contraindications, Individual hypersensitivity to the drug.
Release form. Vaginal suppositories containing 0.25 g of syntomycin, in a package of 5 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B, In a dry, cool, dark place.
Synthomycin is also included in the fastin ointment preparation.
| print version | This information is not a guide to self-treatment. A doctor's consultation is required. |
special instructions
Due to the high toxicity of chloramphenicol, the following are unacceptable for systemic drugs:
- uncontrolled intake;
- use for preventive purposes;
- treatment of mild forms of bacterial infections.
An alcohol solution of Levomycetin should not be used for ophthalmic purposes.
With prolonged chloramphenicol therapy, severe disorders in the hematopoietic system can develop, so constant monitoring of the state of peripheral blood flow is required.
An alcohol solution should not be used for ophthalmic purposes. It is prohibited to put eye drops or alcohol solution in your nose.
The antibiotic can cause disturbances in nervous regulation.
Therefore, one should refrain from manipulating complex mechanisms until the patient's individual response to such treatment has been established. The duration of use of the product should be as short as possible. It is not advisable to repeat the course of treatment with the drug.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
Chloramphenicol crosses the placenta and enters breast milk. At the stage of bearing a child, taking chloramphenicol drugs is contraindicated. During the treatment period, the mother should stop natural feeding of the baby.
During the period of mother's treatment with Levomycetin, natural feeding of the baby should be suspended.
In children
Prescribe the drug to children with caution. For newborns and infants in the first months of life, due to the insufficient formation of their liver structures, it is used only when absolutely necessary. Tablets should not be given to children under 3 years of age.
For liver dysfunction
The metabolism of chloramphenicol in this case slows down, which can lead to its accumulation in the body and intoxication.
Therefore, dosages should be reduced and the condition of the liver should be monitored during treatment.
For severe liver failure, this antibiotic is not used.
For impaired renal function
Renal pathologies cause a delay in excretion of the drug from the body. In this case, the risk of developing adverse reactions increases. It should be used with caution in the absence of severe complications.
Renal pathologies cause a delay in excretion of the drug from the body.
Use of Levomycetin for children
Use of Levomycetin tablets in pediatrics
Tablet forms of the drug are used in pediatrics under constant monitoring of serum concentrations of chloramphenicol . Depending on age, the dose of Levomycetin tablets for children ranges from 25 to 100 mg/kg/day.
For newborn infants under 2 weeks of age (including premature infants), the formula for calculating the daily dose is as follows: 6.25 mg/kg per dose with a frequency of applications up to 4 times per day.
For infants over 14 days old, 12.5 mg/kg is prescribed per dose every 6 hours or 25 mg/kg every 12 hours.
For severe infections (for example, meningitis ), the dose is increased to 75-100 mg/kg/day.
How to take Levomycetin for diarrhea?
The drug is a fairly serious drug and therefore must be prescribed by a doctor. However, it is often given to children when it is necessary to relieve an intestinal disorder.
As a rule, the dose for children 3-8 years old is from 375 to 500 mg/day. (125 mg per 1 dose), for children 8-16 years old - 750-1000 mg (250 mg per 1 dose).
For diarrhea, a single use of the medicine is allowed. If the child’s condition does not improve, and symptoms persist 4-5 hours after taking the pill, you should consult a physician.
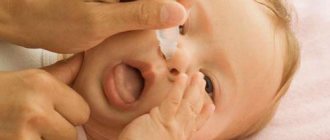
Levomycetin eye drops for children
Eye drops for newborns (in the first 4 weeks after birth) are used only for health reasons.
Levomycetin eye drops for infants are also used with caution. As a rule, 1 drop of antibiotic the conjunctival sac of each eye every 6-8 hours.
For barley , eye drops are not recommended for use in children under 10 years of age.
The use of external therapy in children
The solution is not intended for the treatment of children under 1 year of age; liniment is not used for the treatment of premature and newborn infants.
Side effects of Levomycetin
The drug can cause various side effects:
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- irritation of the oral mucosa;
- dysbacteriosis;
- anemia and other changes in blood composition;
- depressed mood;
- impairment of auditory and visual perception;
- headache;
- psychomotor reactions;
- body rashes, itching;
- allergic swelling;
- hyperthermia;
- superinfection;
- local reactions during external application, instillation, ear instillation;
- gray syndrome;
- collapse.
The drug may cause headaches.
The use of an alcohol solution or ointment may cause a sensitization reaction and lead to increased susceptibility during subsequent treatment.
Reviews of Levomycetin
Reviews found on the Internet about tablets and solution in most cases concern the use of the drug for acne.
When used externally - either in its pure form (if we are talking about a solution) or as part of a mash (for example, a mash containing Aspirin , Levomycetin and calendula tincture) - the product copes with acne within a couple of days.
There are no less good reviews about Levomycetin eye drops. Despite its low cost, the drug gives quick and in the vast majority of cases 100% results.
Contraindications
The medicine should not be taken if you are intolerant to amphenicol or the auxiliary components contained in the composition. Other contraindications:
- hematopoietic disorder;
- blood diseases;
- porphyria;
- lack of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- severe hepatic-renal pathologies;
- skin lesions (mycoses, eczema, psoriasis);
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- children up to 3 years of age (oral administration), newborns (intramuscular and external use).
Overdose
Long-term treatment with high doses leads to the development of severe hematopoietic disorders. This manifests itself in weakness, pallor, hemorrhages and bleeding, and sore throat. Dialysis required.
Long-term treatment with high doses of Levomycetin can cause a sore throat.
Gray syndrome also indicates an overdose - the skin and mucous membranes turn gray, blood pressure and body temperature drop, breathing is impaired, reactions and muscle tone are weakened, and collapse develops. This condition is typical for newborns and small children; it can lead to the patient falling into a coma and possibly death.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
The reason for contacting a doctor is prolonged persistent diarrhea with traces of blood or mucus in the stool, accompanied by severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting and general weakness. Another reason to visit the doctor is the lack of positive results after taking medications for 1-3 days.
Levomycetin is an effective and inexpensive remedy for infectious diarrhea. But to achieve positive results, it is necessary to correctly calculate the dosage and maintain regular therapy. And, since the drug belongs to the group of antibiotics, self-medication is unacceptable (as it can cause complications). Before using the medication, you should read the instructions and do not use the product if there are any contraindications. If for some reason Levomycetin is rejected by the body and does not have a therapeutic effect, under the guidance of a specialist, the antibiotic can be replaced with one of the known analogues.
Drug interactions and compatibility
Drinking alcohol during treatment may cause a disulfiram reaction.
Taking the drug with sulfonamides and cytostatics or during radiation therapy leads to increased adverse reactions. The combination of the drug with hypoglycemic drugs enhances the effect of the latter. Chloramphenicol weakens the effect of the following drugs:
- Erythromycin;
- Penicillin and its derivatives;
- Lincomycin;
- cyclosporine antibiotics;
- Clindamycin.
Phenytoin, barbiturates and indirect anticoagulants remain in the body longer under the influence of this drug.
Chloramphenicol weakens the effect of Erythromycin.
Read also[edit | edit code]
- Antibiotics (antimicrobial agents) Choice of antibiotic
- Combination antibiotic therapy
- Prophylactic antibiotic therapy
- Mechanisms of action of antibiotics
- Sulfonamides, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
- Quinolones and urinary antiseptics
- Beta-lactam antibiotics Penicillins
- Cephalosporins
- Carbapenems
- Beta-lactamase inhibitors
- Tetracyclines
- Antituberculosis drugs (antimycobacterial) Isoniazid
- Rifampicin
- Ethambutol
- Streptomycin
- Pyrazinamide
- Other anti-tuberculosis drugs
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
The drug is available for injection and in tablets with a prescription. Its remaining forms are freely available.
The drug is available for injection and in tablets with a prescription.
Price
Cost of antibiotic:
- Actitab tablets 0.5 g 10 pcs. — from 113 rub.;
- solution 3% 25 ml - from 32 rubles;
- drops 0.25% 1 ml - from 7 rubles;
- ointment - from 128 rub.