Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
The drug Levothyroxine is a synthetic levorotatory form of the hormone thyroxine ( T4 ), which is identical to the hormone produced by the thyroid gland. After metabolism in the liver, it is converted into the active form of T3 , which already affects metabolism and tissue development. The mechanisms of effects are due to binding to the genome, changes in metabolism in mitochondria . In small doses it has an anabolic effect. Taking Levothyroxine in medium doses stimulates growth, metabolism, and increases the activity nervous system and cardiovascular system . This increases the need for oxygen. The use of Levothyroxine in high doses reduces the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone . Used to treat hypothyroidism . The effect for hypothyroidism is observed after 3-4 days. With diffuse goiter, the thyroid gland shrinks over 3-6 months.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken on an empty stomach, it is absorbed by 70-80%. Absorption decreases after eating. The maximum concentration is determined after 6 hours. 99% protein bound.
Metabolism with the formation of triiodothyronine occurs in the liver as well as muscles. Triiodothyronine has a more pronounced hormonal effect. The half-life is about 6-8 days. 15% of the dose is excreted in urine and bile.
Levothyroxine, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
Doses of Levothyroxine depend on the clinical picture and severity of hypothyroidism . They are selected individually by a doctor after studying thyroid . Treatment begins with small doses, gradually increasing until effective.
How to take Levothyroxine?
The tablets are taken orally on an empty stomach with a small amount of water. The dose is taken once in the morning. In some cases, on the recommendation of a doctor, the dose is divided into two times and taken until 11-12 noon.
For hypothyroidism, the initial dose is 50-100 mcg, followed by a maintenance dose of 125-250 mcg.
For congenital hypothyroidism - at 6 months - 8-10 mcg per kg of body weight per day, 6-12 months - 6-8 mcg per kg of body weight per day.
For endemic goiter - first 50 mcg per day, increasing to 100-200 mcg.
Euthyroid goiter - 100-200 mcg per day.
TEVA Levotiroxina Sodica Levothyroxine 100 mg 100 tablets
Levothyroxine is a hormonal drug in tablets that replenishes the deficiency of thyroid hormones.
Composition and release form
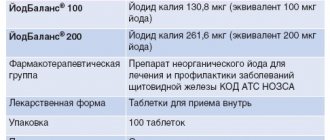
For 1 tablet 25, 50 or 100 mcg:
- Active ingredients: levothyroxine sodium - 25, 50 or 100 mcg;
- Excipients: milk sugar (lactose), talc, Kollidon 25, calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, magnesium stearate.
Tablets of 10 or 25 pcs in blister packs. 1, 2 or 5 packages with instructions for use are placed in a cardboard pack.
Pharmacological group
Thyroid hormones, their analogs and antagonists (including antithyroid drugs).
Pharmacological properties
Replenishes the deficiency of thyroid hormones.
After oral administration, it is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, absorption is 48–79%. Taking on an empty stomach increases the absorption of the active substance. Cmax in plasma is reached after approximately 6 hours. Binding to plasma proteins (thyroxine-binding globulin, thyroxine-binding prealbumin and albumin) is more than 99%. Vd is 0.5 l/kg. Distribution occurs mainly in the liver, brain and muscles.
Approximately 80% of sodium levothyroxine is monodeiodinated in various tissues to form triiodothyronine (T3) and inactive products. A small amount of the active substance undergoes deamination and decarboxylation to form tetraiodothyroacetic acid, as well as conjugation with sulfuric and glucuronic acids (in the liver).
About 15% is excreted by the kidneys and bile unchanged and in the form of conjugates.
Indications for use
- primary and secondary hypothyroidism;
- mixed goiter;
- complex treatment of toxic goiter and autoimmune thyroiditis,
- euthyroid hyperplasia of the thyroid gland;
- prevention of relapses after surgical treatment of nodular and malignant neoplasms of the thyroid gland;
- cretinism.
- as a diagnostic tool for thyroid suppression test.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to the drug and its components,
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland of various origins,
- acute myocardial infarction,
- untreated adrenal insufficiency.
Directions for use and doses
The drug is taken orally on an empty stomach 30 minutes before meals in the morning, without chewing, with a small amount of liquid.
The daily dose of the drug is determined individually based on the indications.
Replacement therapy for hypothyroidism:
- For patients under 55 years of age without cardiovascular diseases, the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 1.6–1.8 mcg/kg body weight;
- Patients over 55 years of age or with cardiovascular disorders - 0.9 mcg/kg body weight. Dose calculations for significant obesity should be done based on the “ideal weight.”
At the initial stage of hypothyroidism replacement therapy:
- For patients under 55 years of age without cardiovascular diseases, the drug is prescribed in the following daily doses: Women: 75–100 mcg; Men: 100–150 mcg.
- For patients over 55 years of age or with cardiovascular disease, Levothyroxine is prescribed at an initial dose of 25 mcg per day. Until the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood normalizes, the dose is increased by 25 mcg once every 2 months. If cardiac symptoms develop or worsen, cardiac treatment must be adjusted.
In the treatment of congenital hypothyroidism, the drug is prescribed depending on age (daily dose/dose based on body weight):
- 0–6 months: 25–50 mcg/10–15 mcg/kg;
- 6–12 months: 50–75 mcg/6–8 mcg/kg;
- 1–5 years: 75–100 mcg/5–6 mcg/kg;
- 6–12 years: 100–150 mcg/4–5 mcg/kg;
- Over 12 years: 100–200 mcg/2–3 mcg/kg.
For other indications, the following dosage regimen is prescribed:
- Euthyroid goiter (treatment and prevention of relapse after surgical treatment): 75–200 mcg per day;
- Thyrotoxicosis (complex therapy): 50–100 mcg per day;
- Thyroid cancer (suppressive therapy): 50–300 mcg per day.
- Before the thyroid suppression test, Levothyroxine is prescribed 75 mcg per day 4 and 3 weeks before the test, 2 and 1 week - 150-200 mcg per day.
The daily dose of Levothyroxine is given to infants 30 minutes before the first feeding in one dose. The tablet should be dissolved in water to form a thin suspension (prepared immediately before administration).
In patients with severe long-term hypothyroidism, therapy should be started with extreme caution with small doses (12.5 mcg per day). The dose is increased to the maintenance dose at longer intervals - every 2 weeks by 12.5 mcg per day. Such patients need to determine the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood more often.
For hypothyroidism, Levothyroxine is usually taken throughout life.
In case of thyrotoxicosis, the drug should be used simultaneously with thyreostatics after achieving a euthyroid state.
In all cases, the duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
Side effect
When used in high doses (including when the dose is increased too quickly at the beginning of the course of treatment), tachycardia, palpitation, arrhythmias, angina attacks, headache, nervousness, tremor, sleep disturbances, feelings of internal restlessness, muscle weakness and convulsions are possible. weight loss, diarrhea, menstrual irregularities and vomiting.
When used in insufficiently effective doses - hypothyroidism (dysmenorrhea, constipation, dryness, puffiness of the skin, headache, lethargy, myalgia, drowsiness, weakness, apathy and weight gain).
Allergic skin reactions are possible.
Overdose
If the dose is exceeded, the following are possible: tachycardia, finger tremor, exophthalmos, weight loss, hyperhidrosis.
Treatment: reducing the dose of the drug. In cases of acute poisoning, gastric lavage or plasmaphoresis are indicated.
Interaction with other drugs
When using the drug together with certain drugs, there is a possibility of the following effects:
- Indirect anticoagulants: strengthening their effect (may require reducing their dose);
- Tricyclic antidepressants: enhancing their effect;
- Estrogen-containing drugs: increased levels of thyroxine-binding globulin (an increase in the dose of levothyroxine sodium may be required);
- Insulin, oral hypoglycemic drugs: increased need for them;
- Cardiac glycosides: decrease in their effect;
- Cholestyramine, colestipol, aluminum hydroxide: decreased plasma concentration of levothyroxine sodium;
- Anabolic steroids, asparaginase, tamoxifen: pharmacokinetic interaction at the level of protein binding;
- Phenytoin, salicylates, clofibrate, furosemide (in high doses): increased levels of levothyroxine sodium not bound to plasma proteins;
- Somatotropin: acceleration of closure of epiphyseal growth zones;
- Phenobarbital, carbamazepine, rifampicin: increased clearance of levothyroxine sodium (increase in dose may be required).
special instructions
The drug reduces the effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy and lactation, Levothyroxine is used only under medical supervision.
The combination of the drug with thyreostatic drugs is contraindicated, as it increases the risk of developing hypothyroidism in the fetus.
The drug should be taken with caution in the presence of cardiovascular diseases: coronary heart disease (atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction), arrhythmias, arterial hypertension.
You should also be careful when using Levothyroxine in patients with diabetes mellitus, long-term severe hypothyroidism, or malabsorption syndrome (dose adjustment may be required).
Note: Not a medicine. There are contraindications. Before use, consult a specialist.
Interaction
Cholestyramine , aluminum preparations and colestipol reduce intestinal absorption and plasma concentrations.
Phenytoin reduces the amount of active substance bound to protein. Estrogens reduce effectiveness.
The metabolism of the drug is affected by amiodarone , PAS , ethionamide , beta-blockers , chloral hydrate , carbamazepine , levodopa , diazepam , dopamine , lovastatin .
The active substance reduces the effect of insulin , cardiac glycosides and enhances the effect of tricyclic antidepressants.
When used with salicylates, furosemide , clofibrate, the plasma concentration of the drug increases.
Reviews of Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine tablets are prescribed for replacement purposes in cases of thyroid . This can happen with the disease hypothyroidism , as well as after operations on this organ. Normalization of hormonal levels is important for these patients, as well as women of childbearing age, since with hypothyroidism pregnancy is unlikely and treatment must be started immediately. During pregnancy, the need for thyroxine by 45% of the initial dose.
Treatment with Levothyroxine is carried out under the control of TSH , an increase in which is a signal of insufficient dose. At the initial stage, the patient’s age and the presence of cardiovascular . In this case, the metabolic status is restored gradually, starting with small doses. Treatment for hypothyroidism is lifelong. In their reviews, patients note that improvement occurs after a few weeks, and the full effect is observed after 2-3 months. The TSH level decreases to normal levels only after 3–6 months from the start of treatment.
According to reviews, the drug was well tolerated and, with the correct dose, did not affect the function of the cardiovascular system . Only some patients complained of tachycardia , arrhythmia , angina pain, tremors and insomnia .
If we compare Levothyroxine - Eutyrox , then it must be said that both drugs have the same active ingredient, so they have the same effect. The drugs differ by manufacturer - Eutirox is produced by Merck KGaA Germany. Its advantage lies in a greater selection of doses (in addition, there are tablets of 75 mcg, 88 mcg, 112 mcg, 125 mcg, 137 mcg and 150 mcg), which is of great importance for the doctor who prescribes treatment depending on the clinical situation.
Levothyroxine for weight loss is also used in bodybuilding, which is associated with the effects it produces: it accelerates metabolism and heat production, burns fat, suppresses appetite, stimulates the central nervous system and increases performance. It is more effective than many fat burners. It is preferred for fat burning compared to triiodothyronine .
In rare cases levothyroxine exhibits low effectiveness in this regard, since against the background of a low-carbohydrate diet, its conversion to triiodothyronine . The duration of the course of taking this drug for the purpose of losing weight is 4-6 weeks. Start by taking 50 mcg per day, divided into 2 doses in the first half of the day. Then gradually increase to 150-300 mcg per day in 2-3 doses. If palpitations and pain in the heart area, excitement and anxiety occur, a beta blocker, asparkam and riboxin . Due to possible side effects, the use of levothyroxine for this purpose has become less common.
Levothyroxine sodium overdose, symptoms and treatment
Accompanied by symptoms of hyperthyroidism (weight loss, palpitations, sinus tachycardia, arrhythmia, angina pectoris, heart failure, tremor, headache, insomnia, heat intolerance, fever, irritability, diarrhea, abdominal pain); increased levels of T3 and T4 in the blood serum and free thyroxine index. Depending on the severity of symptoms, it is recommended to reduce the dose or temporarily discontinue levothyroxine. If clinical symptoms are pronounced, the stomach is washed, cholestyramine, β-adrenergic receptor blockers are prescribed, and oxygen therapy is performed. Thyrostatic drugs are not used. In case of acute poisoning (suicide attempt), plasmapheresis is recommended.
List of pharmacies where you can buy Levothyroxine sodium:
- Moscow
- Saint Petersburg