Write a review
Reviews: 0
Manufacturers: Novartis Pharma SA
Active ingredients
- Not indicated. See instructions
Disease class
- Not indicated. See instructions
Clinical and pharmacological group
- Not indicated. See instructions
Pharmacological action
- Hypoprolactinemic
- Dopaminomimetic
Pharmacological group
- Antiparkinsonian drugs
- Dopaminomimetics
pharmachologic effect
Due to the presence of bromocriptine in its composition, Parlodel tablets form connections with cerebral receptors of the D2 type and combine with them into prolactin molecules.
As a result, lactation and the menstrual cycle are normalized, thanks to the production of prolactin molecules in the ovaries.
The drug Parlodel alleviates the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and eliminates symptoms of depression by reducing the concentration of somatotropin and facilitating dopaminergic processes.
The production of growth hormone is reduced, as a result of which the balance between progesterone and estrogen is restored, which makes it possible to reduce the number of cysts formed in the mammary glands.
Bromocriptine is a chemical formation of an alkaloid group that acts as an antagonist of dopamine receptors.
In higher doses, Parlodel stimulates receptors in the hypothalamus and limbic system.
Medicinal properties
Bromocriptine contained in the drug suppresses the production of prolactin, a pituitary hormone, without affecting other substances if their levels are normal. However, it may reduce elevated levels of growth-regulating hormone in people with acromegaly. The effect is achieved due to the ability of bromocriptine to stimulate dopamine receptors.
Prolactin ensures the occurrence and maintenance of lactation in the neonatal and subsequent periods. At other stages of life not related to childbirth, breastfeeding can provoke milk production, problems with ovulation and menstrual irregularities.
Parlodel, due to its ability to suppress the production of prolactin, can be prescribed to stop the lactation process, as well as to eliminate conditions caused by hypersecretion of the hormone. The advantage of this prescription is that during the course there is no need to follow some traditional methods, such as fluid restriction. In addition, Parlodel does not affect the process of natural contraction of the uterus after childbirth and, what is important, does not allow the development of thromboembolism.
In case of amenorrhea or anovulatory uterine cycle, the drug is prescribed to restore ovulation and normalize menstruation.
Parlodel is known to suppress the growth (or reduce the size) of pituitary adenomas, which depend on prolactin levels.
Prescribing Parlodel to patients suffering from acromegaly helps stop excessive synthesis of growth hormone and prolactin, which reduces the manifestations of the disease and also improves glucose tolerance.
Bromocriptine normalizes the secretion of luteinizing hormone, which significantly reduces the intensity of the manifestation of PJ syndrome.
Prescribing Parlodel to patients with benign breast tumors helps to balance the balance of the hormones progesterone and estrogen, reduce the size and number of cysts and nodes, and relieve the inherent pain of the disease. In patients with high levels of prolactin, the medicine acts differently - it reduces the intensity of synthesis.
The purpose of Parlodel for the treatment of parkinsonism is associated with the ability of the active component to restore normal levels of dopamine by stimulating the receptors responsible for its production. The drug has a beneficial effect on the patient's condition: it eliminates or significantly reduces tremor, restores the speed of reactions, motor reflexes, reduces the intensity of depressive states, etc. The effect of treatment lasts for several years. Parlodel is indicated for both monotherapy and complex measures.
After penetration, bromocriptine is well absorbed. Studies on healthy subjects have shown that the highest plasma levels of drugs are formed after 1-3 hours. A decrease in prolactin occurs 12 hours after administration, reaches peak values within 5-10 hours and persists for half a day.
Removal of the substance in its previous form takes 8-20 hours. Its metabolites and unchanged forms are excreted primarily by the liver (only 6% is excreted in the urine). If the patient has liver problems, the cleansing process is delayed, so a revision of the dosage is required.
Composition and release form
The drug Parlodel is available in the form of round tablets, which are contained in blisters of 10 tablets each.
The drug Parlodel contains the active ingredient bromocriptine mesylate, as well as auxiliary components:
- Trilon B;
- Aerosila hydrate;
- Lactose;
- Maleic acid;
- Regular and modified starch;
- Magnesium stearate.
Indications for use
The drug Parlodel is indicated for patients of both sexes as prescribed by a doctor.
| Indications for women | Indications for men |
| Female infertility. | Decreased libido. |
| Menstrual irregularities. | Prolactinoma. |
| Aminorrhea. | In complex therapy with surgery to remove tumors. |
| Oligomenorrhea. | Acromegaly - together with surgery or radiation therapy. |
| Luteal phase deficiency. | — |
| Hyperprolactinemia due to the use of antihypertensive or sedatives. | — |
| For painful premenstrual syndrome, expressed in swelling, pain in the mammary glands, gas formation, changes in mood. | — |
| To stop lactation due to medical contraindications. | — |
| In complex therapy for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome of anovulatory cycles. | — |
For patients suffering from Parkinson's syndrome, the use of Parlodel can be prescribed at any stage of the treatment of idiopathic conditions.
Oral tablets Parlodel
Instructions for medical use of the drug
Description of pharmacological action
Stimulator of central and peripheral D2-dopamine receptors (ergot alkaloid derivative).
Indications for use
Prolactin-dependent menstrual disorders and female infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome, anovulatory cycles (in addition to antiestrogens), premenstrual syndrome, hyperprolactinemia in men, prolactinomas, acromegaly, suppression of lactation (for medical reasons), postpartum breast engorgement, incipient postpartum mastitis, mastalgia and other forms of benign breast diseases, Parkinson's disease.
Release form
Tablets 2.5 mg; dark glass bottle (bottle) 30 cardboard pack 1; Tablets 2.5 mg; blister 30 cardboard pack 3; Tablets 2.5 mg; dark glass bottle (bottle) 30 cardboard pack 1;
Use during pregnancy
FDA category of effect on the fetus is B.
Contraindications for use
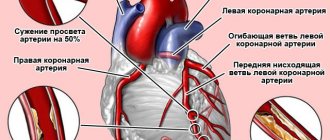
Hypersensitivity, malignant tumors of the mammary glands, hypertension (uncontrolled, during pregnancy, in the postpartum period), coronary heart disease and other severe cardiovascular diseases, mental illness (including a history).
Side effects
Dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, weakness, confusion, psychomotor agitation, hallucinations, dyskinesia, leg muscle cramps, coldness of the upper and lower extremities, orthostatic hypotension, collapse, nasal congestion, hair loss, allergic skin reactions. With long-term treatment of patients with parkinsonism with high doses - exudative pleurisy, pleural, pulmonary or retroperitoneal fibrosis. In rare cases, women in labor have experienced the development of arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, convulsions, stroke, and mental disorders.
Directions for use and doses
Inside, during meals. 1.25–40 mg per day.
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, hallucinations, decreased blood pressure. Treatment: parenteral administration of metoclopramide.
Interactions with other drugs
Macrolides may increase plasma concentrations. Tolerance decreases with alcohol.
Storage conditions
List B.: In a place protected from light, at a temperature below 25 °C.
Best before date
36 months
ATX classification:
N Nervous system
N04 Antiparkinsonian drugs
N04B Dopaminergic drugs
N04BC Dopamine receptor stimulants
N04BC01 Bromocriptine
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated for use if severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system are present.
Parlodel tablets are contraindicated for patients suffering from:
- Endogenous psychosis;
- Gettington's chorea;
- Tremors of a familial nature;
- Intolerance to the main component of the drug bromocriptine;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- Essential tremor;
- Preeclampsia.
Parlodel should be taken with caution in doses strictly prescribed by the doctor to patients taking antihypertensive drugs, pregnant women and Parkinson's disease with dementia.
If the child is breastfed, then the woman should take Parlodel with caution due to the fact that the active substances can affect lactation and the properties of milk.
Caution should be exercised when using the drug Parlodel in patients who have not reached the age of majority, and those under 6 years of age are generally prohibited.
Analogs
Parlodel has been excluded from the State Register of Medicines, but it can be replaced with other medications with the same active substance and effect. Which one is best should only be determined by the attending doctor.
Bromocriptine
"Ozone" (RF)
Average price: (30 tables) – 242 rubles.
A drug based on the active substance of the same name. The content is identical to the concentration in Parlodel. The medicine is intended for the treatment of diseases caused by impaired prolactin secretion.
Pros:
- Stops lactation in a couple of days
- Removes lumps in the breast.
Flaws:
- Lots of side effects.
Side effects
The use of the drug Parlodel can provoke different reactions of the body to the active substance, and also, due to the intake of other drugs, the components can form chemical compounds that act on different organs.
Parlodel may cause:
- Headache;
- Nasal congestion;
- Dermatological reactions;
- Hypersensitivity;
- Asthenic conditions;
- Noise in ears;
- Attacks of tachycardia;
- Confusion;
- Increased libido;
- Alopecia (baldness);
- Constipation;
- Movement disorders;
- Hallucinatory attacks;
- Insomnia;
- Visual impairment;
- Psychomotor agitation;
- Paresthesia;
- Hypotensive effect;
- Shortness of breath;
- Pleural effusion;
- Attacks of vomiting;
- Arrhythmia;
- Bradycardia;
- Pleural fibrosis;
- Dry mouth;
- Changes in the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- Hearing impairment;
- Orthostatic hypotension;
- Leg muscle cramps;
- Sudden falling asleep;
- Diarrhea;
- Nausea;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Peripheral edema;
- Pericardial effusion;
- Epigastric pain;
- Fibrosis of myocardial valves;
- Hypersexuality;
- Myocardial infarction;
- Pulmonary fibrosis;
- Bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Stroke;
- Retroperitoneal fibrosis;
- Mental disorders;
- Pale skin of the hands and feet;
- Pericarditis.
Useful video:
Dosage and overdose
For the treatment of diseases associated with dysfunction of the female and male reproductive systems, the drug Parlodel is taken 1 tablet 1 time per day, recommended at the same time .
The daily dose of the drug can be increased no more than twice to relieve acute inflammatory processes and deviations as prescribed by a doctor for no more than 3 days of use.
For Parkinson's disease, the drug is prescribed as part of complex therapy, 1.25 g. per day (half a tablet).
The dose for patients under puberty is adjusted by the doctor depending on the indications and type of disease.
If the dose recommended for taking Parlodel is exceeded, the following may occur:
- Dizziness;
- Vomit;
- Critical decrease in blood pressure;
- Dyspepsia;
- Tachycardia;
- Fever.
To stop attacks of excess accumulated bromocriptine, it is necessary to take adsorbents to remove its residues from the gastrointestinal tract. Vomiting and hallucinations can be relieved by taking metoclopramide.
Precautionary measures
When prescribing Parlodel, an individual approach to patients is important if they have or have a history of: psychotic disorders, severe cardiovascular pathologies, bleeding or gastrointestinal ulcers.
In people with parkinsonism, in the case of a long course of Parlodel, there is a high probability of developing exudative pleurisy.
If the patient has pleuropulmonary disorders of unexplained origin, he is recommended to undergo a detailed examination - Parlodel therapy may not be suitable.
In case of long-term treatment with doses greater than 30 mg, retroperitoneal fibrosis may develop. To diagnose it early, you should pay attention to the symptoms of the disease: back pain, swelling of the legs, deterioration of kidney function. If the diagnosis is confirmed, Parlodel therapy is canceled.
Instructions for use
Treatment with Parlodel tablets is continued as prescribed by the doctor until the menstrual cycle normalizes and ovulation is restored. If necessary, treatment can be continued for several cycles.
To treat abnormalities of premenstrual syndrome, Parlodel tablets should be taken on the 14th day of the cycle, increasing the dose to 2 tablets per day until the onset of menstruation.
To cancel lactation, as prescribed by a doctor, the drug is taken 2 times a day - morning and evening with meals for 14 days. To prevent lactation after termination of pregnancy, Parlodel tablets are prescribed a few hours after the abortion. 2-3 days after taking the drug, a slight secretion of milk may be observed, which goes away with further use of Parlodel tablets.
For Parkinson's disease, Parlodel tablets are prescribed for use for 6-8 weeks.
If side effects occur when selecting a dose, then the daily dose of tablets must be reduced and maintained for a week.
If side effects disappear, the dose may be increased to the initial level.
special instructions
Treatment with Parlodel can restore impaired fertility function. Therefore, women of childbearing age are advised to pay special attention to reliable contraception.
In patients who are prescribed Parlodel tablets in connection with the treatment of tumors, the presence of malignant tumors should be excluded using sound diagnostic methods.
Women whose treatment is not associated with hyperprolactinemia are advised to take Parlodel in minimal doses to avoid a decrease in plasma Prolactin below normal and the formation of dysfunction of the corpus luteum.
There are reports of isolated cases of the development of stomach ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding, in which the use of Parlodel tablets is excluded.
Patients with a history of gastric dysfunction should take Parlodel only under regular medical supervision.
In the first days of using the drug Parlodel, a decrease in blood pressure is possible, which affects the reaction and general condition of the body, so you should be careful while driving and in patients whose work requires increased concentration.
NEW LEVEL
Quite often, mothers are advised to take bromocriptine or cabergoline to prevent lactation after childbirth or to reduce breast engorgement after milk comes in. Think, look for information about these drugs, look at the contraindications. These drugs pass into breast milk. However, even if you change your mind after taking the drug, you can breastfeed. According to the International Guide to the Compatibility of Drugs with Breastfeeding, no adverse effects were reported among children whose mothers took the drug (or received it in error) and decided to resume breastfeeding.
When taking the drug, engorgement may go away, but along with it, prolactin levels will drop sharply, as a result, breastfeeding may never begin, or the volume of milk produced will be insufficient.
Unfortunately, doctors also recommend stopping lactation when the mother is sick, if it is necessary to take antibiotics, if the child is ill or hospitalized. There are always alternative ways. You can choose medications that are compatible with breastfeeding, or choose the best time to take medications, taking into account the period of their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract and excretion from the body. When the mother is hospitalized, she can express and transfer the milk to the baby. If a child gets sick, breast milk helps him overcome the disease more easily. Advising to stop breastfeeding if a child is ill is simply medical nonsense!
The drug method of stopping lactation uses prolactin inhibitors, which are dopamine D2 receptor agonists. Due to the stimulating effect on dopamine receptors of the hypothalamus, drugs to suppress lactation have a characteristic inhibitory effect on the secretion of hormones of the anterior pituitary gland, especially prolactin and somatotropin.
Most likely, excerpts from medical dictionaries are not entirely clear to you. First, let's try to figure out why the hormones prolactin and somatotropin are needed.
Almost all pregnant and nursing mothers know that prolactin is a hormone necessary for successful lactation; it promotes the production of colostrum and the transformation of colostrum into mature milk. This hormone also affects the growth and development of the mammary glands and an increase in the number of lobules and ducts during pregnancy. But few people know that prolactin receptors are found in almost all organs of our body. Prolactin receptors are found in the mammary glands, heart, lungs, thymus, liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands, uterus, ovaries, testes in men, skeletal muscles, skin and some parts of the central nervous system. However, the effect of prolactin on them has not yet been studied.
Some scientists believe that prolactin is involved in immune responses. During inflammatory processes, infections and other cases when an immune reaction is triggered, the secretion of this hormone by leukocytes increases. Therefore, on the surface of many cells involved in the immune response, there are receptors for prolactin.
As mentioned above, medicinal methods of inhibiting lactation also affect the production of somatotropin.
Somatotropin is a growth hormone. Its functions include stimulation of the synthesis of macrophages, lymphocytes, immunoglobulins and the formation of lymphoid tissue, regulation of fat metabolism, improvement of osteometabolism, kidney and heart function, and rapid wound healing. In short, the hormone somatotropin affects mood, mental abilities, increased immune function, and a person’s energy level.
Somatotropin may affect the function of other hormones. For example, it successfully suppresses the function of insulin, which stimulates the uptake of glucose into tissues, and no less successfully fights the increase in glucose synthesis in the liver. Thus, somatotropin successfully maintains the required level of insulin in the liver.
To suppress lactation, drugs with the active substance bromocriptine or cabergoline are prescribed.
Bromocriptine (brand names Parlodel, Bromolactin, Krypton, Bromocriptine)
Commercial names abroad - Brameston, Broman, Bromergon, Bromocrel, Bromo-Kin, Bromopar, Cycloset, Encript, Pravidel, Provasyn, Umprel.
Bromocriptine is most often used to suppress lactation in the CIS countries. Bromocriptine suppresses the secretion of prolactin. The lower the level of prolactin in the blood, the lower the effectiveness of the drug. That is why drugs with such an active substance are not recommended for use in several European countries.
Even the Pharmacological State Committee of the Russian Ministry of Health recommended the use of bromocriptine to suppress lactation only in severe septic mastitis due to the possible development of serious complications such as pulmonary embolism, stroke, decreased visual acuity and others, including death (“Drug Safety”, Bulletin No. 1, 1998; Bulletin No. 1, 2000). Between 1980 and 1994 There were 531 reports of adverse reactions following the use of bromocriptine in women aged 15–40 years, including 32 deaths due to stroke, myocardial infarction and hypertension.
When using bromocriptine, other side effects are also possible: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, psychomotor agitation, allergic reactions, cramps in the calf muscles.
The use of bromocriptine is contraindicated in severe forms of cardiovascular disease, uncontrolled arterial hypertension, and hypersensitivity to ergot alkaloids. It is necessary to regularly monitor blood pressure (BP), especially in the first week of therapy. In case of development of arterial hypertension, especially when severe headaches occur, the drug is discontinued and an appropriate examination is immediately carried out.
Erythromycin, clarithromycin, troleandomycin increase the bioavailability and concentration of bromocriptine in plasma. The number of side effects may increase. Alcohol intake leads to the development of the following reactions: chest pain, hyperemia, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, reflex cough, throbbing headache, decreased visual acuity, weakness, convulsions.
Cabergoline (trade name Cabergoline, Dostinex, Bergolak, Agalates)
Commercial names abroad - Actualene, Cabaseril, Caberlin, Cabgolin, Lac Stop, Lactamax, Parcar, Sogilen, Sostilar, Triaspar.
Cabergoline is an active substance similar to bromocriptine. It is a powerful inhibitor of prolactin secretion with long-lasting action. Carbegoline stimulates dopamine D2 receptors of lactotropic cells of the pituitary gland and reduces the level of prolactin in the blood, which is observed 3 hours after taking the drug and lasts up to 14–21 days.
Among the side effects that may be observed when using cabergoline are nausea, vomiting, headache, general weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, decreased blood pressure, psychomotor agitation, and cramps in the calf muscles. This drug should not be prescribed for postpartum psychosis or a history of it and postpartum hypertension and with caution for cardiovascular diseases, Raynaud's syndrome, renal or liver failure, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding. Therefore, when prescribing carbegoline, monitoring of blood pressure and gastrointestinal tract functions is necessary. If blood pressure increases, persistent headaches occur, or any signs of neurotoxicity occur, the drug should be discontinued. It is important to remember that the simultaneous use of carbegoline with antibiotics from the macrolide group increases the risk of side effects.
According to the FDA (Food and Drug Administration in the United States), Dostinex is indicated for the treatment of hyperprolactinemic disorders of idiopathic origin or associated with pituitary adenoma. Dostinex is not indicated for the inhibition or suppression of physiological lactation. Cases of high blood pressure, strokes and seizures have been reported as a result of the use of bromocriptine, another dopamine agonist, for this purpose.
Information from the instructions, section “side effects -> inhibition/suppression of lactation”: “On the cardiovascular system: very often - damage to the heart valves (including regurgitation) and similar disorders […]” Very often ≥1/10 ( i.e. one in 10 women or more often).
After such completion of breastfeeding, according to reviews of many women, the development of lactostasis or mastitis is likely. As a result of treatment, subsequent hormonal imbalances are possible, affecting the quality of life. Interfering with the hormonal system is always a risk. Think about how much you need it? Please note that you will have to care for your child while these medications are taken and in effect. You may need help from relatives or friends.
Many methods of suppressing lactation are not effective enough and are currently of mainly historical interest. These include significant restriction of fluid intake, tight bandaging (breast tightening), prescription of saline laxatives, diuretics, and camphor preparations.
Remember that breast milk contains a substance that is a lactation inhibitor.
It is designed to slow down the process of milk production. The more milk remains in the breast and the less often it is emptied, the more inhibitor it has and the less milk it will produce. So if you decide to stop breastfeeding, gradually reduce the number of times you latch or pump. Do not pump your breasts “to the last drop”, only until you feel relief, gradually removing pumping. If you feel fullness in your breasts, but there is no pain, your breasts are soft, and there is no temperature, then you do not need to express. To reduce milk production, you can use infusions of herbs - mint and sage. (You can read more about weaning in this article. - Ed.).
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Parlodel is available with a doctor's prescription.
Recipe in Latin
The prescription is written out by the doctor in two copies in Latin, legibly, clearly, in ink or with a ballpoint pen; corrections are prohibited.
It is allowed to prescribe only one name of the drug on one form, the Latin name of the drug Parlodel is PARLODEL.
The method of application is indicated in Russian or Russian and national languages. The patient's full name, age, and doctor's full name are indicated. The doctor's signature must be certified by his personal seal.
What is better Parlodel, Dostinex or Bromocriptine?
Each of the drugs has its own advantages and disadvantages; their purpose depends on the individual parameters of the body and the characteristics of the disease being transmitted.
The price of Dostinex is significantly higher than that of Parlodel tablets, which is explained by the country of origin. You can learn more about the drug Dostinex in this article.
The drug Bromocriptine and its derivatives are analogues in the pure composition of the active substance, which is suitable for patients with clinical indicators specifically for this alkaloid.
Cross-drug interactions
The active component of Parlodel is a derivative of ergot alkaloid. At the same time it acts as a substrate and inhibitor of the CYP3A4 enzyme. Therefore, during the course, you should take into account the properties of drugs taken in parallel: avoid combining them with drugs with similar characteristics. These medications include azole antimycotics and HIV protease inhibitors. Combination with Erythromycin and Josamycin helps to increase the plasma concentration of bromocriptine.
The effect of Palodel is reduced when combined with antipsychotics (phenothiazine, butyrosphenone, thioxanthin, etc.).
Ethanol impairs the body's tolerance to the drug.
Parlodel tablets are used not only in monotherapy. The drug is allowed to be combined with other antiepileptics. The combination of the drug with Levodopa enhances the antiparkinsonian effect, so it is recommended to reduce the dosage of the latter drug.
Reviews
Vitalina, 24 years old : “Almost always, as far as I can remember, I had terrible pain during my periods. I thought this was normal until my husband actually forcibly sent me to the hospital one time. The doctor discovered some kind of dysfunction and benign formations. The drug Parlodel was prescribed as part of complex therapy. After taking the pills, the discomfort practically disappeared, and I tolerate “these days” much better.”
Galina, 30 years old : “Before the abortion, I was told that I would need to stop lactation after the operation, so immediately after a few hours I took the prescribed Parlodel tablets. After just 2 days the milk completely disappeared. And after the course of treatment, my well-being improved significantly, especially in the premenstrual period.”