Biliary dyskinesia in itself does not threaten human life. However, this does not mean that you should not pay attention to it. Stagnation of bile often leads to the development of other digestive diseases. These include cholelithiasis and cholecystitis.
A gentle diet will help to avoid complications. The patient's rational diet consists of fractional meals. In addition, it is important to know what you can and cannot eat if you have biliary dyskinesia.
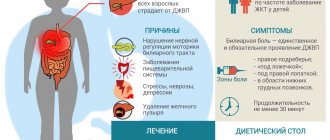
Biliary dyskinesia (BD) occurs in 30% of people, most of whom have no idea what kind of disease it is. Although the disease is not life-threatening, it is important to properly diagnose the symptoms. JVP is dangerous due to complications that will certainly arise if it is not treated.
The essence of the disease lies in the improper outflow of bile through special ducts. Its main function is the breakdown of fats. If this process is disrupted, the body lacks carbohydrates and fatty acids. Depending on the speed of entry into the intestines, hypo- and hyperkinetic dyskinesia are distinguished.
Attention! Both adults and children are at risk. More often women suffer from stagnation of bile.
Characteristics of diet for dyskinesia
The JVP diet is aimed at improving the character and diet, restoring the tone of the bile ducts. Diet therapy plays a major role in the treatment of dyskinesia. To reduce the load on the pipes, sphincters and the gallbladder itself, exclude from the diet:
- cold dishes;
- difficult to digest fats;
- extractive dishes (rich broths);
- coarse fiber vegetables.
The diet reduces the severity of gastrointestinal dyskinesia, increases bile secretion and secretory activity of the liver. Proper nutrition solves several problems at once:
- reduces body weight;
- restores metabolism;
- prevents gas formation;
- normalizes stool;
- serum cholesterol levels decrease.
Failure to comply with the diet for intestinal dyskinesia is fraught with uncertain consequences - cholangitis, estimated cholecystitis, pancreatitis, atypical eczema.
Diet features
The main goal of a therapeutic diet for such disorders is to restore and improve patency (to ensure the passage of bile through the ducts), reduce the impact on the liver, reduce the load on the bile ducts, gallbladder, liver and other organs of the digestive system.
The diet should be varied, despite all dietary restrictions - the body must receive the right amount of carbohydrates, proteins, a minimum of fats and a maximum of vitamins, as well as beneficial microelements.
The optimal content of all the necessary nutrients in the treatment menu looks like this:
- carbohydrates – 300–325 grams;
- proteins 80–90 grams and only half animal origin;
- fats – 75–80 grams, a third – vegetable origin.
The calorie content of the daily menu is 2200–2400 kcal.
For people suffering from biliary dyskinesia, a special diet approved by the Ministry of Health has been approved, and it is prescribed in the complex treatment of these disorders. It should remove secretions and relax the muscle walls of the bile ducts as much as possible.
Basic nutrition for dyskinesia
When studying the principles of nutrition for gallbladder dyskinesia, it is, in principle, important to distinguish between very difficult and least necessary rules. In life, we love ourselves, situations arise when we are forced, at least unusually, to violate the proclaimed diet. If you follow this measure without overeating, consuming prohibited items will not lead to a significant deterioration in well-being or increase pain.
But with exacerbation of biliary dyskinesia, the diet should be very strict. The main prohibited items and drinks are fatty foods, fried foods, spicy foods, alcohol and smoked meats.
You must learn the basic principles of therapeutic nutrition in the JVP:
- Fractional nutrition for biliary dyskinesia prevents bile stagnation. The breaks between meals are about 2-3 hours. The principle is to eat a little, but a lot.
- Gentle cooking. All dishes are boiled or baked, stewing is allowed. Frying is strictly prohibited because trans fats are formed during frying, polyunsaturated fatty acids are destroyed to form toxic substances that overload the digestive tract.
- Maintaining a certain temperature regime. Extremely hot, cold food and drinks are prohibited. Cold temperatures are especially scary. Cold foods cause spasms of the bile ducts. Therefore, the diet of adults and children with biliary dyskinesia excludes the consumption of ice cream (possible only when heated), fruit drinks and ice drinks.
- Quitting alcohol. Alcohol is the main irritant in biliary diseases. Alcohol causes spasm of the muscles and ducts of the gallbladder, disrupting the process of releasing bile from the organ. With the breakdown of ethyl alcohol, the load on the liver increases sharply, which directly affects the functioning of the entire biliary system.
Reviews and results
For dyskinesias of the biliary system, special attention is paid to therapeutic nutrition, since its observance prevents the progression of symptoms, deterioration of the condition and the transition of functional disorders to organic pathology. Judging by the reviews, the diet was prescribed to adults and children, and within a week their condition improved significantly. The important thing is that the diet is easy to tolerate and feasible for a long time.
- “... Two months ago, the child began to complain of nausea and sharp pain under the rib on the right. We were examined and even had to be sounded. A hypertonic type of diarrhea was diagnosed. The doctor warned that nutrition is very important and you need to follow a diet so that there is no deterioration. They also prescribed pills. In 2 weeks, the child became significantly better, but for this we had to force feed him in the morning before school, give him yogurt and cookies with him, and at lunchtime control whether he ate at home or not. It turned out that it is difficult to maintain a regimen not only of nutrition, but also of sleep and rest”;
- “... For dyskinesia, the child was prescribed this diet, and also a sedative - he became nervous, irritable, and screamed all the time. Involuntarily, the whole family (for support and for health) had to eat this way. Everyone is very pleased with the results. After 3 weeks, everything returned to normal for my son, my husband’s heartburn and belching disappeared, and my bloating disappeared. This is what it means to eat right. I can say that the diet is complete, healthy and not difficult to follow. A month later, the weight was reduced by 3.5 kg. Great too! We decided to eat like this all the time, at least until we get tired of it”;
- “... I suffer from hypotonic dyskinesia. Constant heaviness under the rib and bitterness. I know about the diet, but I didn’t attach any importance to it. I noticed that every year it was getting worse and now an ultrasound revealed cholecystitis. Now I have already changed my diet and introduced everyone at home to this. We eat steamed cutlets, boiled chicken and fish. Everyone supported me and didn’t resist me much. I feel great because the food is healthy and nutritious. My husband lost 4 kg in a month.”
Diet for children
Unfortunately, this diagnosis is also found in young patients. Moreover, for example, Dr. Komarovsky is convinced that such a disease in children is not uncommon.
Symptoms of biliary dyskinesia in children are somewhat more pronounced than in adult patients. For example, headaches, severe and rapid fatigue are added to all the signs of pathology listed above. There may also be very strong sweating and tachycardia.
The diet for biliary dyskinesia in children is not much different from the diet with a similar pathology in adults. The basic rule with such a diagnosis in a child is that the caloric content cannot be strictly determined. It is necessary to calculate the energy expenditure of a small patient. For this purpose, a table with the calorie content of different dishes is always available.
It is advisable to accompany a diet for stagnation of bile by introducing certain products or goods into the menu that help dilute and disperse this fluid.
Prohibited goods
Products prohibited during an exacerbation of the disease, which are not included in the dietary menu, unnecessarily burden the patient’s body. Stimulates exacerbation, causing unpleasant symptoms. People who are tormented by this feature should know that they cannot eat with biliary dyskinesia:
- Fast food: dry food, chips, spicy cookies, salted walnuts;
- Desserts high in sugar: cakes, ice cream, sweet filled pastries;
- Carbonated drinks, especially those with colorings and preservatives (mineral water with medium carbonation is allowed);
- Cocoa and coffee
- Fatty primary broths from any meat, “hot” chilled foods;
- Pure fats: lard, bacon;
- Smoked sausage, fatty fish;
- Pickles, spices;
- Legumes (cause gas, bloating);
- Mushrooms (difficult to digest), fresh onions and garlic;
- Dark bread (allowed to be consumed dry);
- Ground spices, mustard, pepper;
- Alcoholic drinks of any resistance (the load on the liver increases greatly, spasms of the smooth muscles of the gallbladder appear).
By completely eliminating these foods, healing improves and symptoms disappear in a short time.
Authorized Products
Having read the list of prohibited foods, people mistakenly believe that the diet practically prohibits everything. But from the goods that are allowed, you can make a tasty, and most importantly, correct menu.
A proper diet should include proteins, carbohydrates and even fats in the right quantities. The diet contains large quantities of fiber, which has a choleretic effect, as well as lyotropic substances that can dilute bile.
Along with food, all necessary vitamins and minerals must be introduced into the human body, so it is advisable to monitor their sufficient quantity in food. Any recipe or food must be checked by a nutritionist to avoid lack of necessary substances.
The list of recommended products includes:
- rye bread, biscuits, crackers;
- low-fat vegetable broths and soups;
- lean meat;
- snow-white fish;
- chicken or turkey without skin;
- low-fat dairy products;
- vegetables;
- vegetable oils;
- not very sweet marmalade, jam.
Drinks include fresh fruit and vegetable juices, rosehip decoction and table mineral water such as Borjomi, you can drink tea, preferably green.
Authorized Products
- Butter. Vegetable fats (olive, corn, flaxseed, sunflower) are included in case of hypotension of the gallbladder and the ratio with animals should be 1:1. Vegetable oils that have not undergone heat treatment cause the production of cholecystokinin , which stimulates the formation of bile. A prerequisite is that all oils are introduced into the finished dish in their natural form.
- Dried wheat bread. For hypotension - wheat bread with bran and rye. Only stale bread is allowed; biscuits, whole grain bread and bran bread are allowed. For the whole day: 150 g of wheat bread and 100 g of rye bread are allowed.
- Soups with vegetable broths (from cereals, vegetables or noodles). You can eat borscht and cabbage soup, beetroot soup, and fruit soups.
- Lean beef, rabbit, chicken, veal. You can boil them and make beef stroganoff from boiled meat; you can bake them after boiling. Chopped products (steamed or baked meatballs, cutlets, meatballs and dumplings) are preferable for bladder hypertonicity.
- Baked lean fish, fish stuffed with vegetables, steamed and baked fish cutlets, soufflés and quenelles.
- Cereal dishes include crumbly porridges made from rice, buckwheat and oatmeal, viscous semolina, and pasta.
- Fermented milk products should be chosen as low-fat. It is recommended to consume low-fat cottage cheese daily (in its natural form and as part of dishes). Milk and sour cream are added only to dishes.
- Eggs are allowed to be eaten as an omelet or soft-boiled. The number of eggs (up to one per day and without yolk) is limited in case of hypertension.
- Various boiled/stewed vegetables, vegetable caviar, carrot, pumpkin, green pea puree. For hypotension - vegetable salads with oil. Mainly the diet should contain cabbage of all varieties, beets and carrots, pumpkin, dill, parsley.
- Fruits and berries should be chosen non-acidic and consumed in the form of compotes, jelly, fruit drinks, infusions (fresh only for hypotension of the gallbladder).
- Sweets (marmalade, honey, jam, sugar 30 g per day are limited in case of hypotonicity of the gallbladder.
- Drinks: rosehip infusion, vegetable juices, weak tea (preferably with milk), bran decoction, still mineral water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| Ryazhenka | 2,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 67 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Nutrition for hypotonic dyskinesia
In the case of hypotonic biliary dyskinesia, bile stagnation is observed. It should be driven away with choleretic products and special plant mixtures, but only in the absence of stones. You can check this during an ultrasound scan.
For better bile circulation and maintaining bladder functionality, it is recommended to include vegetable fats and fiber in your daily diet. This combination provides the desired choleretic effect.
Recommended foods and drinks:
- Vegetable oils, which account for up to 50% of all fats. They play an active role in the production of prostaglandins, which can lead to gallbladder secretion and dilution of bile. Vegetable oil is used without preliminary heat treatment.
- Vegetables, non-acidic berries and fruits. They keep the entire digestive tract active and harmlessly stimulate the flow of bile. The absence of constipation has a positive effect not only on the intestinal tract, but also on the biliary system.
- Natural juices with pulp. They also have a choleretic effect and enrich the body with plant fiber.
- Boiled and steamed eggs. Egg yolks support the multifunctionality of the gallbladder and enrich the body with vitamins and minerals. Egg white is also very healthy.
The products listed above are recommended to be included in your daily diet. But at the same time, it is important to show a sense of proportion and not limit yourself to the same type of dishes. The diet should be very varied. It is important to eat frequently, so that bile does not stagnate in the bladder for a long time and does not even stimulate huge disruptions in the functionality of the biliary system. It is also recommended to limit your intake of total carbohydrates.
What is biliary dyskinesia: what are the causes?
So, there are three types of violations:
1. Hypomotor, in which bile slows down its movement. 2. Hypermotor, when bile, on the contrary, comes out too quickly. 3. Hypotonic-hyperkinetic, if symptoms of both the first and second are present.
And if the first causes constipation, attacks of nausea and nagging pain on the right under the ribs, then the second is accompanied by diarrhea, a bitter taste in the mouth and acute pain on the right. Doctors are categorical in their judgments on this matter and claim that people themselves are to blame for the appearance of this disease. More precisely, the main cause of the disease is an unhealthy lifestyle and poor nutrition. In addition, the following can cause such a failure:
• fast food products, fast food; • daily excess of caffeine; • abuse of fatty, fried, smoked and spicy foods; • drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking; • sedentary lifestyle and excess weight.
Hypertensive nutrition
You have hypertensive biliary dyskinesia, you must also follow diet no. 5, but with its own characteristics. The amount of vegetable fat (animals are prohibited in large quantities) is reduced to 60-70 g per day.
It is necessary to exclude products that contain cholesterol and extractives (broths). Fiber should also be limited, especially for vegetables such as onions, radishes and garlic. They should be completely excluded.
Raw vegetables and fruits should not be consumed with hypertensive dyskinesia. They are pre-cooked, steamed or stewed.
Recommended foods and drinks:
- vegetable puree soups;
- types of meat and fish with low fat content in the form of minced meat;
- egg whites (1-2 pieces per day);
- low-fat cottage cheese, skim milk;
- processed vegetables, especially pumpkin, carrots, potatoes and cauliflower;
- baked sweet fruit purees and berries, from which you can make jelly, homemade jam, compotes.
For all types of dyskinesia, it is necessary to consume cereals. They provide magnesium, which reduces muscle spasms and has a calming effect on the nervous system. It is recommended to eat bran, dried fruits, and hard bread.
Fully or partially limited products
- Extractive dishes (broths), spicy vegetables and herbs with a high content of essential oils: horseradish, parsnips, celery, onions, garlic, shallots, katran, oregano, marjoram, savory, rosemary, basil, radishes, turnips, radish.
- Fatty meat and fish, goose and duck, salted fish, smoked meats, refractory fats, fish caviar, lard, sausages, all types of canned food.
- By-products (internal organs of animals due to their high cholesterol content).
- Eggs are fried and hard-boiled, which are difficult to digest.
- Fresh bread, pastry, fried pastries (pies, pancakes, pancakes), cakes, pastries, puff pastry.
- Cream, whole milk.
- Hot sauces.
- Carbonated and alcoholic drinks, coffee, chocolate, cocoa.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Eggs | ||||
| hard-boiled chicken eggs | 12,9 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 160 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| whiskey | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,4 | 235 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Sample menu for the week
For dyskinesia, it is recommended to constantly follow a diet. Proper nutrition prevents thickening of liver secretions and the formation of stones. Trial menu for the treatment of dyskinesia
Monday
- 1 breakfast muesli with dried fruits, cottage cheese with sour cream, tea with sorbitol
- 2 breakfast baked pear with honey, peach juice
- Lunch: cream soup with vegetables, vermicelli with meatloaf, chamomile infusion
- Afternoon snack cottage cheese casserole, compote
- Dinner baked potatoes with meat soufflé, vinaigrette, tea
Tuesday
- 1 breakfast buckwheat porridge, cookies, tea
- 2 breakfast cottage cheese casserole, carrot juice
- Lunch: puree soup with carrots and broccoli, steamed chicken cutlets, sliced vegetables, compote
- Afternoon snack cheesecakes with sour cream, rosehip decoction
- Dinner vegetable stew, meat soufflé, broccoli salad, tea
Wednesday
- 1 breakfast: semolina porridge with dried apricots, bread, beet juice
- 2 breakfast banana, carrot juice
- Lunch: vegetarian borscht, steamed meat cutlets, lettuce, chamomile infusion
- Afternoon snack cottage cheese casserole, tea
- Dinner baked pollock with mashed potatoes, sliced vegetables, compote
Thursday
- 1 breakfast 2 sandwiches with hard cheese, weak coffee
- 2 breakfast applesauce, vegetable juice
- Lunch: vegetarian soup, baked fish with noodles, compote
- Afternoon snack cottage cheese with prunes, jelly
- Dinner pilaf with vegetables and chicken, tomato and cucumber salad, tea
Friday
- 1 breakfast carrot pancakes, dried fruits, weak tea
- 2 breakfast casserole with apples and pears, rosehip infusion
- Lunch: Lenten borscht, pilaf with veal, lettuce, jelly
- Afternoon snack casserole with pumpkin, vegetable juice
- Dinner fish casserole with boiled potatoes, tea
Saturday
- 1 breakfast toast with squash caviar, homemade yogurt
- 2 breakfast baked pear with honey, herbal infusion
- Lunch slimy oatmeal soup, mashed potatoes with boiled chicken, coffee
- Afternoon snack 100 g dried apricots, low-fat kefir
- Dinner baked hake with carrots, vegetable salad, chamomile infusion
Sunday
- 1 breakfast: muesli with milk, protein omelette, coffee
- 2 breakfast 100 g dried apricots or prunes, compote
- Lunch pureed vegetable soup, boiled veal, vegetables, juice
- Afternoon snack baked fruits with honey, rosehip decoction
- Dinner vegetable stew, meatloaf, weak tea
The diet should be balanced and varied. Consumption of the same products is unsafe, hypovitaminosis, exacerbation of dyskinesia.
How to eat as an adult
Proper nutrition is an important aspect of the treatment of dyskinesia, especially if it is caused by poor diet. A diet for an adult involves limiting fatty foods, as well as spicy, salty and too fatty foods.
Limiting the usual menu and lowering cholesterol will help reduce the viscosity of bile and prevent cholelithiasis, the main complication of dyskinesia.
Proper nutrition for gallbladder disorders in adults involves avoiding alcohol, spicy and smoked foods, and the menu includes as many vegetables and fruits as possible, with the exception of foods that irritate the stomach, which negate treatment.
This is what the diet menu for an adult looks like:
- For breakfast, eat oatmeal or wheat porridge without oil and salt, you can add fruit;
- for lunch, drink fresh carrots and apples or snack on bananas;
- for lunch it is better to eat vegetable broth, rice porridge with boiled fish, drink a glass of dried fruit compote, eat non-acidic fruit;
- for an afternoon snack, you can treat yourself to biscuits with tea or unsweetened marshmallows;
- For dinner, prepare steamed white fish cutlets, pumpkin puree and a mixture of vegetables, tea with honey and milk.
Before going to bed, it is recommended to drink a glass of kefir to improve peristalsis.
Dietary table recipes 5
A tasty and nutritious breakfast is the key to a successful day. Here is an omelet recipe for those who suffer from biliary dyskinesia. You will need:
- protein - 4 pcs.;
- milk - 50 g;
- butter - 5 g;
- sour cream - 10 g;
- greenery.
How to cook:
- Beat milk, cream, whites until smooth.
- Grease the tray with oil and pour out the mixture.
- Bake for 5-7 minutes.
- Sprinkle with herbs.
Roasted vegetables are a good choice for lunch or dinner. To make a delicious dish, you will need:
- cod fillet - 200 g;
- carrots - 1 pc.;
- onion - 1 pc.;
- zucchini - 1 pc.
How to cook:
- Thaw the fish and wash it.
- Cut vegetables into slices or circles.
- Place the onion in the bottom of the pan and place the fish on top.
- Scatter the remaining vegetables on top.
- Bake at 170°C for 30 minutes.
Consequences of non-compliance
Gallbladder dyskinesia is not a dangerous disease, but serves as a predisposing factor for the formation of more serious diseases. The organs of the gastrointestinal tract are vulnerable, intestinal microflora and metabolic processes are disrupted. This leads to the development of the following conditions:
- Gastritis, ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum;
- Pancreatitis and other pancreatic disorders, enzyme deficiency;
- Cholecystitis;
- Formation of gallstones;
- Atopic dermatitis and other skin manifestations (the condition of the digestive system is reflected on the skin).
Manifestations of JVP
Symptoms of hypotonic type DVT are:
- constant, aching pain of varying intensity in the hypochondrium on the right;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea (possible vomiting);
- constipation;
- increased fatigue;
- weakness.
For hypertonic type DVT, the characteristic manifestations are:
- attacks of acute pain in the hypochondrium on the right after physical activity;
- periodic diarrhea;
- nausea;
- headache;
- poor appetite;
- vomiting with bile;
- increased fatigue;
- severe sweating;
- increased heart rate;
- irritability.
This functional pathology can be recognized, in addition to identifying clinical manifestations, using x-ray and ultrasound examination. For children, ultrasound diagnostics is more acceptable due to the lack of radiation exposure during the study.
Supporting actions
For effective treatment, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Compliance with sleep, rest and nutrition. The body must get used to the constant rhythm of life;
- Limiting stressful situations. Nervous overexcitation negatively affects the treatment of dyskinesia;
- Elimination of moral and physical overload. Rest promotes recovery;
- Walking in the fresh air will benefit the recovering body;
- Light physical activity, regular water procedures. The cause of the disease may be excess weight;
- It is advisable to get rid of it;
- Strict adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician. Self-medication is unacceptable.
When treating biliary dyskinesia, the patient’s nutrition is of key importance. To create a menu, you should take into account the patient’s age, type of disease, course, medications taken, lifestyle and general health.
Particular attention should be paid to possible allergic reactions to food. If side effects occur, you should consult a physician. The diet will be reviewed and the allergen will be excluded.
Biliary dyskinesia (BDSD) is said to occur when the tone of the bile ducts decreases, resulting in disruption of the outflow and circulation of bile.
A distinction is made between dyskinesia of the hyperkinetic type (increased tone of the gallbladder) and dyskinesia of the hypotonic type (weakened tone of the gallbladder).
The causes of JVP are:
- poor nutrition with irregular eating patterns;
- liver and gallbladder diseases;
- alcohol abuse.
The essence of the problem
The structure of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
The liver constantly produces bile. It enters the gallbladder through ducts, which is just a reservoir for its accumulation. And only when food from the stomach enters the duodenum in portions, bile is released there through the bile ducts. It is necessary for digesting food (most fatty acids).
The common bile duct carries bile into the duodenum. The duct opens in the area of the Vater nipple, which contains the sphincter of Oddi (a special sphincter that allows bile to pass into the intestine). The secretion of bile is ensured by the contractile function of the gallbladder.
It is the coordinated functioning of the entire biliary system that ensures the normal flow of bile into the duodenum. Spasm or blockage of the ducts, impaired contractility of the sphincter or gallbladder lead to impaired bile secretion.
The duration of contraction of the gallbladder depends on the nature and volume of food entering the stomach. When eating fatty foods, the gallbladder will contract longer until the stomach is completely empty of food. A small amount of low-fat food will cause a short-term contraction of it, then the tone of the gallbladder decreases, and bile accumulates in it again.
There are the following types of JVP:
- hypertensive dyskinesia, in which the tone of the gallbladder (or sphincter) is increased, which leads to a sharp release of bile;
- hypotonic dyskinesia (more severe), caused by decreased tone of the sphincter and bladder, as well as sluggish, insufficient outflow of bile;
- mixed dyskinesia associated with serious changes in the biliary tract.