Gastroenterologists often diagnose their patients with reflux esophagitis, in which the contents of the stomach are refluxed into the lower part of the esophagus, causing the thin mucous membrane of the esophageal tube to become inflamed.
With such a disease, you need to follow a diet, giving up foods that negatively affect the sensitive epithelium of the digestive system. The dietary nutrition prescribed by the gastroenterologist should be combined with drug treatment, normalizing work and rest schedules.
Authorized Products
Despite the fact that esophagitis is associated with the stomach, the patient is still allowed quite a lot of food. The diet is based on foods that act as alkali, namely:
- boiled soups with cereals;
- fish and meat soufflé;
- milk and vegetable soups;
- fish, low-fat varieties, for example, carp, pike perch or hake;
- Meats include turkey, chicken and beef;
- White bread;
- apples and pears;
- crackers;
- boiled potatoes cooked in the oven;
- egg omelet, soufflé;
- carrots, beets;
- vegetables in the form of porridge;
- dairy products, but always with low fat content, namely yogurt, milk and kefir.
Any spices and salt are kept to a minimum. Drinks allowed include jelly, tea, always with the addition of milk, rosehip decoction, compotes, and herbal infusions. It is recommended to drink mineral water, which helps reduce stomach acidity.
Folk recipes
Gastroenterologists widely use various herbs in the treatment of GERD. Most often used:
- pine buds;
- flax seed;
- plantain;
- chamomile;
- Melissa;
- wild rose fruits.
Pharmaceutical chamomile has a healing and anti-allergic effect. Chamomile is prescribed in the form of tea or water infusion.
Raw potatoes. Starch together with water forms a colloidal solution that protects the mucous membrane from the action of damaging factors, reducing the painful manifestations of esophagitis. Take on an empty stomach in the form of finely chopped pieces or juice.
Bee Honey. It is better to use local varieties of honey (Maysky, Lugovoy, Lesnoy). Honey goes well with many approved foods for GERD.
Along with medication and physiotherapy, nutritional therapy is certainly used in the treatment of GERD. Neglect of the principles of nutrition worsens the course of the disease and its prognosis.
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the esophagus
Considering the severity and course of the inflammatory process, esophagitis is divided into:
- catarrhal;
- erosive;
- ulcerative;
- phlegmonous;
- necrotic.
The causes of esophagitis can be:
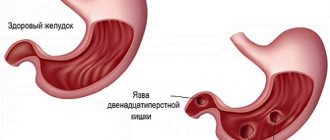
- Reflux esophagitis or GERD is a chronic disease, which is based on a violation of the smooth muscle apparatus of the esophagus and the cardia of the stomach, resulting in frequent entry of stomach contents into the esophagus. The consequence of this is erosive-ulcerative inflammation of the distal esophagus.
Cardia insufficiency can occur as a result of functional disorders (stress, poor nutrition, pregnancy). However, the cause may be organic pathology (gastric ulcers, chronic subatrophic gastritis, gastroduodenitis, chronic gastritis with high acidity, pancreatitis, biliary cirrhosis).
Depending on the level of cardia dysfunction, three degrees of the disease are distinguished. First degree - (the sphincter does not contract completely) frequent belching appears. Second degree - (the sphincter contracts by half) heartburn and pain appear. Third degree - the sphincter does not contract at all.
- Infections (fungi, bacteria, viruses).
Fungi are obligate microorganisms. Candidal esophagitis occurs only when all protective mechanisms are reduced. Mycotic esophagitis can occur with tuberculosis, HIV infection, and cancer.
Bacteria. Inflammation of the esophagus can occur with tuberculosis, syphilis, and diphtheria.
Viruses. Esophagitis can occur when infected with the herpes virus, cytomegalovirus.
- Poisoning (alcohol, acids, alkalis).
- Allergic damage.
- Mechanical damage.
According to the nature of the course, esophagitis is divided into acute (flowing with a violent clinical picture) and chronic (flowing less brightly, characterized by a phase course).
Symptoms in patients with esophagitis:
- pain that occurs immediately after swallowing food is provoked by bending the body; the localization of pain is different, most often it is localized behind the xiphoid process and in the epigastrium, but substernal pain is also possible;
- heartburn, sometimes difficult to tolerate, worsens with errors in diet, after smoking, after active movements;
- belching (air, eaten food, sour);
- increased salivation.
Treatment is often conservative and includes:
- the diet for esophagitis has been developed in detail (meal frequency, possible recipes);
- antacids (Maalox, Gaviscon, Phosphalugel);
- prokinetics (Domperidone, Motilium);
- antibiotics;
- physiotherapeutic treatment (laser therapy, electrophoresis, intraesophageal electrical stimulation of the gastric cardia).
Surgical treatment is indicated:
- if conservative therapy is unsuccessful;
- with repeated aspiration pneumonia;
- for precancerous conditions (Barrett's esophagus);
- with unfavorable outcomes of inflammation of the esophagus (strictures, repeated bleeding).
Summary for parents
Esophagitis is a fairly common disease, including among children. Diet is included in the scope of therapeutic measures and affects their effectiveness. In the acute phase of the disease, the diet is more strict, the duration of its adherence is determined by the doctor.
With chronic esophagitis, the diet must be followed throughout your life.
When organizing a diet for a child, it is important for parents to follow all medical recommendations not only on the list of foods acceptable for consumption, but also on methods of preparing dishes. This will protect the child from developing quite serious complications.
Causes of pathology
To prescribe proper nutrition for reflux esophagitis, a medical examination is carried out to identify the causes of the pathology. There are internal and external factors that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Internal:
- low esophageal sphincter tone;
- pathologies of the stomach, intestines, pancreas, thyroid gland;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- hiatal hernia;
- increased acidity in the body;
- changes in hormonal balance;
- increased pressure in the abdominal area.
External:
- abuse of alcohol and tobacco products;
- improper diet;
- non-compliance with eating rules;
- long course of taking medications;
- stress overexertion.
The nature, regularity, and duration of symptoms depends on the causes of the burning sensation.
Diet during remission
After the phase of exacerbation of the disease (during the period of remission), the patient is transferred to diet No. 1. This is a complete diet that prevents relapse, since it is moderately gentle on the digestive tract.
It contains a reduced amount of animal fats, as they reduce the tone of the sphincter (butter, heavy cream, fatty meat and fish, confectionery). Diet for reflux esophagitis also excludes the consumption of foods that irritate the mucous membrane (coffee, strong tea, mint, onions, garlic, chocolate, tomatoes).
Diet No. 1 for reflux esophagitis allows the use of:
- vegetable soups seasoned with butter or egg-milk mixture. Vegetables cannot be sautéed. Cereals should be well boiled and vegetables pureed;
- dried bread, crackers (no more than 200 g);
- dietary meat (beef, turkey, lamb, chicken). You need to grind it twice in a meat grinder, and then make steamed cutlets, quenelles, and soufflés. You can bake meat without forming a rough crust (in foil);
- lean fish. Can be consumed in pieces or in the form of cutlets;
- porridge (rice, buckwheat, semolina). They are prepared semi-viscous, milk can be added to them;
- milk, kefir, medium-fat cottage cheese;
- butter (up to 20 grams) and vegetable oil. Add to prepared dishes;
- boiled vegetables. It is allowed to eat potatoes, beets, cauliflower, carrots, pumpkin, and zucchini in the form of puree; mashed fruit. Jelly, jelly, compotes, and purees are prepared. Avoid the consumption of citrus fruits and raw fruits;
- weak tea, diluted sweet juices, herbal drinks.
To avoid increased acidity of gastric juice, irritation of the mucous membrane and flatulence, it is recommended to remove from the menu:
- mushrooms;
- pickled, salted, pickled vegetables;
- fatty meat or meat with veins and tendons;
- smoked meats, canned food;
- fried and spicy dishes, stews;
- sauces (mayonnaise, mustard, ketchup);
- sour or fiber-containing vegetables and berries, fruits (tomatoes, onions, garlic, radishes, white cabbage, radishes, cucumbers, asparagus, sorrel, lemon and other citrus fruits, grapes, gooseberries);
- sour cream, yogurt, sour kefir, 35% fat cream, blue cheese;
- puff pastry, butter, yeast dough;
- seasonings, spices;
- pasta;
- millet, corn and pearl barley;
- sour juices (from tomatoes, pomegranates, citrus fruits, currants), carbonated drinks, alcohol, beer, kvass, coffee, strong tea;
- chocolate, halva, ice cream;
- nuts, dates.
With catarrhal esophagitis, the diet may not be so strict, but if pain occurs when passing a bolus of food, then you need to wipe the food to eliminate mechanical irritation of the esophagus. Heartburn is eliminated with the help of milk, so if it is well tolerated, you can drink it for breakfast, dinner and before bed, or add it to milk porridges.
As the mucous membrane recovers and reflux disappears, twisted lean meat or meatballs can be added to soups. Fish and meat cutlets are served with a side dish or vegetable puree. If erosive esophagitis has developed, then dietary nutrition must be adhered to constantly.
This is the only way to avoid relapses of the disease and the occurrence of heartburn, belching, and heaviness in the stomach.
What you can eat with esophageal esophagitis in each specific case will be determined by your doctor, since recommendations should take into account concomitant diseases. Since the diet must be followed constantly, the menu for reflux esophagitis must be drawn up together with a nutritionist.
The specialist will calculate how many calories the patient needs to consume, taking into account his age, gender, body weight and physical activity, and the meals will contain the amount of vitamins and minerals corresponding to age standards. The doctor will also tell you which foods should be present in the diet every day and which ones should not be included every day.
When treating reflux esophagitis, drug therapy is also prescribed, which is designed to eliminate symptoms, reduce the acidity of gastric juice and speed up the recovery of the mucosa. Before using them, you need to read the instructions and follow them strictly so that the medicine does not harm the inflamed tissues.
For example, proton pump inhibitors only work if they are taken half an hour before meals, and if taken incorrectly, they will increase the load on the excretory organs and will not have a therapeutic effect. Reflux esophagitis may require surgical treatment, but it is better not to let it get to that point, but to follow all the doctor’s instructions and strictly follow the diet.
Fully or partially limited products
- Pickled vegetables, mushrooms in any form.
- Fatty and coarse meat, canned food, smoked meats, fatty duck and goose meat, meat and fish broths, pickled fruits and vegetables.
- Fried foods, tomato and mushroom sauces, mushroom decoctions, stewed meat and fish, as they contain a large amount of extractive substances. Broths made from bouillon cubes, dishes with mayonnaise.
- Sour berries and fruits, raw vegetables during an exacerbation period, nuts.
- Puff pastry, yeast and butter dough, fresh bread.
- Tomatoes in any form, onions, garlic, mushrooms, radishes, white cabbage, sorrel, radishes, legumes, cucumbers.
- Condiments, spices, hot sauces, vinegar, horseradish, mustard, mayonnaise, ketchup, tomato paste, lemon juice are not acceptable even as a seasoning for dishes.
- Pasta, millet, pearl barley and barley cereals, as they are coarse and difficult to digest.
- Fermented milk products taste sour.
- Sour juices (citrus, tomato, pomegranate, currant), carbonated drinks, alcohol, coffee, strong tea, mint tea, wine and beer.
- Chocolate and chocolate products, halva.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| corn | 3,5 | 2,8 | 15,6 | 101 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| citrus fruits | 0,9 | 0,2 | 4,4 | 22 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 43 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| vysivkovy bread | 9,0 | 2,2 | 36,0 | 217 |
| oatmeal bread | 10,1 | 5,4 | 49,0 | 289 |
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| carnation | 6,0 | 20,1 | 27,0 | 323 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| cinnamon | 3,9 | 3,2 | 79,8 | 261 |
| Bay leaf | 7,6 | 8,4 | 48,7 | 313 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| fresh mint | 3,7 | 0,4 | 8,0 | 49 |
| dried mint | 19,9 | 6,0 | 22,2 | 285 |
| cayenne pepper | 0,7 | 0,2 | 9,8 | 43 |
| ground red pepper | 0,7 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 21 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
| tomato sauce | 1,7 | 7,8 | 4,5 | 80 |
| spicy tomato sauce | 2,5 | 0,0 | 21,8 | 98 |
| vinegar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 5,0 | 20 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| blue cheese | 20,0 | 29,0 | 0,0 | 340 |
| Chees Feta | 17,0 | 24,0 | 0,0 | 290 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| whiskey | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,4 | 235 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| grapefruit juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 30 |
| lime juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,2 | 25 |
| lemon juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| tangerine juice | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,1 | 36 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet principles
The basic principles of the diet for reflux esophagitis are aimed at mechanical and chemical sparing of the mucous membrane. This can be achieved through the following points:
Avoid fried foods. Patients with reflux esophagitis are recommended to eat exclusively boiled, baked, stewed or steamed foods. Exposure of food to high temperatures combined with the presence of steam or water itself eliminates the possibility of rough and dense pieces being present. The best option would be to eat food immediately after cooking, waiting for it to cool.
- Maintaining temperature conditions. Nutrition for GERD must take into account the fact that cold or hot foods will have an irritating effect on the inflamed mucous membrane. Therefore, the temperature of consumed products should be no lower than 30 and no higher than 40 degrees. The best option would be to eat foods whose temperature corresponds to body temperature.
- High-quality mechanical processing. The diet for esophagitis requires patients to eat food that has undergone mechanical processing. So, porridges and soups should be pureed, and it is recommended to eat meat and vegetables in the form of puree. This feature is due to the fact that mechanical processing completely eliminates the possibility of injury to the mucous membrane from rough or hard pieces. A diet for esophageal esophagitis requires the intake of exclusively liquid foods.
In addition, the diet for GERD with esophagitis should exclude a number of foods that stimulate the production of gastric juice. These include:
Sour. Most fresh vegetables contain a large amount of acids, which can shift the pH of gastric juice to the strongly acidic side. It is worth noting that these acids are deactivated during heat treatment. Based on this, a diet for GERD with high acidity should exclude fresh vegetables and fruits from the diet. The exception is bananas. This fruit is best suited for people with diseases of the digestive tract.
Spicy. One of the reasons for the appearance of acute and chronic diseases of the upper digestive tract is the excessive consumption of spicy and spice-rich foods. In order to prevent esophagitis, such foods should not be eaten during reflux. In addition, reflux will reduce the negative impact on the esophagus.
Alcoholic and carbonated drinks. The diet for reflux esophagitis and GERD should completely exclude such drinks. The fact is that carbon dioxide, which is contained in carbonated drinks, accumulates in the stomach, leading to its distension. As a result of this process, irritation of the mechanoreceptors in the stomach walls is observed, which stimulate the production of gastric juice. In addition, alcohol leads to chemical irritation of the mucous membrane, thereby aggravating the patient's condition.
In order to reduce the load on the digestive system, food should be taken in small portions and often. Meals for reflux and esophagitis should be divided into at least 6 doses, the last of which will be no later than 7 pm.
In addition, you should not take a horizontal position after eating. This is because in this position it will be easier for food to pass back through the cardiac sphincter into the esophagus. Sleep after eating is allowed no earlier than 1.5 hours.
General recommendations
A diet for esophagitis helps reduce the frequency of reflux, which helps eliminate the inflammatory process and heal erosions. Since a person experiences discomfort while eating and nausea afterwards, the diet and volume of food are often disrupted, constipation appears, the therapeutic diet must take these factors into account.
The diet requires compliance with the following rules:
- avoidance of fatty and fried foods;
- you need to eat often, but in small portions;
- do not eat before bedtime;
- provide chemical and mechanical sparing of the digestive system;
- do not drink alcohol;
- remove from the diet all foods that cause increased gas formation;
- drink no more than 1 liter of liquid per day.
How to take it correctly
For weight loss, take it strictly adhering to the regimen, without exceeding the dose. During treatment, the course of weight loss is long - up to 6 months. - 1 year. I recommend monitoring your health, well-being, and listening to your body.
If there are signs of an overdose - diarrhea, heart pain, rare pulse, nausea, headache, blurred vision, you should immediately stop taking the herb.
Plant poisoning occurs when, in an effort to quickly achieve results, women begin to use the drug uncontrollably, without taking into account the condition of the body and contraindications.
Buy ready-made products from trusted manufacturers who produce preparations in the form of powder from roots, oil, tablets for oral use, creams and ointments for external use.
On what principle does it work?
Weight loss occurs for two reasons:
- due to its ability to reduce appetite. According to reviews, cravings for “junk” food are greatly reduced, taste preferences change, and food addiction is reduced. Even those with a sweet tooth note that for dessert they want not tiramisu or cheesecake, but a smoothie or fruit salad;
- laxative and diuretic effect, the ability to cleanse the body of toxins, waste, salt deposits not only from the kidneys and intestines, but also from joints, blood vessels, and bile ducts.
In the first month, those who have a lot of excess fluid in their bodies lose weight quickly. The urine becomes thick and has a pungent odor.
In other cases, weight loss is gradual, peaking 3-4 months after starting treatment. The laxative effect with the correct dosage is mild - the stool is soft, but formed, no more than 1-2 times a day. Gradually, the laxative effect decreases, but cleansing of the body continues. If diarrhea occurs, the amount of the product should be reduced.
What should you not eat during remission?
The following foods are excluded from the menu for reflux esophagitis:
- carbonated drinks;
- fatty foods, remaining in the stomach for a long time, stimulate the production of gastric secretion;
- legume products, causing gas formation, facilitate the release of food into the esophagus;
- pickled, sour, fried foods increase the production of acid in the stomach;
- coffee and strongly brewed tea can increase the acidity of gastric juice;
- Canned food, semi-finished products and sandwiches are excluded.
What foods are prohibited during remission?
The diet for reflux esophagitis contains a list of prohibited foods:
- rich broths from poultry, meat and fish, as well as borscht and okroshka;
- fresh bread, pancakes and pies, rich pastries;
Patients with GERD should not eat baked goods
- oily fish, spicy salted or salted;
- strong spices - hot pepper, horseradish and mustard;
- fatty and spicy cheeses;
- fatty dairy products;
- hard boiled eggs;
- dishes made from vegetables containing coarse fiber - eggplant, cabbage;
- pasta;
- pearl barley, barley, corn.
A proper diet reduces the symptoms of the disease - heartburn, belching, epigastric pain. Against the background of dietary nutrition, medications act more effectively. Once stable remission is achieved, you should not switch to general nutrition on your own. The gastroenterologist will consult the patient on this matter after 3–5 months of therapeutic nutrition.
To summarize, let's highlight the main thoughts. The basis of complex treatment of reflux esophagitis is dietary nutrition. Against the background of a proper diet, medication and physiotherapeutic treatment is effectively carried out. In the acute stage and during exacerbation of reflux esophagitis, treatment table No. 1 b according to Pevzner is prescribed. During the period of remission, gastroenterologists recommend constantly adhering to diet No. 1. Otherwise, a relapse of exacerbation is possible.
Reviews and results
With GERD, the diet must be followed constantly to avoid complications such as esophagitis . In the presence of erosive esophagitis, proper dietary nutrition should become the norm, since relapses of the disease are common. By reviewing your diet, you can avoid exacerbations and feel good for many years. Dietary nutrition helps eliminate heartburn, belching, discomfort in the esophagus and heaviness in the stomach.
- “... Throwbacks into the esophagus caused inflammation, but without erosion (checked by gastroscopy). There was pain behind the sternum, a feeling of squeezing and belching of air. They prescribed treatment and told me to follow a diet until the inflammation goes away. In general, I did it for 1.5 months (mashed dishes), and then I started cooking and chopping, but no longer pureed. I noticed that citrus fruits, tomato paste, pickled and pickled vegetables cause heartburn. After heartburn, pain and heaviness appear, and then constipation. Everything turned out to be connected. I take pills and follow a diet - I felt an improvement, my stomach became lighter, and there was no belching or heartburn. With this diet I lost 4.5 kg. Now I eat everything, but in boiled form and have excluded foods that are potentially dangerous for heartburn”;
- “... I was bothered by heartburn periodically, but for many years (probably 5 or 6). All this time I didn’t attach any importance to it - I prescribed medication for heartburn myself, but didn’t stick to the diet. Over the past month, unpleasant sensations have appeared along the esophagus; it even seemed that the pain intensified when swallowing and passing food. During the examination, erosions were found. I agreed to be hospitalized because at home I wouldn’t be able to take care of my treatment, eat right and take pills by the hour. After 2 weeks, the erosions healed - not even a trace was visible. She continued to follow the diet for up to 4 months. Of course, I ate everything that was not pureed like in the hospital, but boiled or baked in foil (this way a crust does not form and the dishes turn out steamed). I feel good, but apparently I need to follow the diet constantly - after a piece of fried meat, slight heartburn and belching appeared again. I came to the conclusion that you need to follow a diet constantly”;
- “... Esophagitis for many years, it’s good that there are no erosions. In the event of an exacerbation, I immediately take the diet and treatment prescribed by the doctor. I noticed that aggravation is caused by errors in diet (fried fish or cutlets, sour fruits, salads with mayonnaise and pickled cucumbers). It gets worse after eating sweets (jam, honey, candies, halva) - immediately heartburn and belching. You can’t overeat and work in an inclined position, as this worsens the situation, and then even pills don’t help.”
Diet menu for esophageal esophagitis and gastritis
The basis of dietary therapeutic nutrition for reflux esophagitis is made up of important principles:
- food should not have an aggressive effect on the inflamed lining of the esophagus and stomach;
- food products should not increase gas formation or bloating;
- The food consumed should not reduce the acid-base balance of the stomach contents.
A diet for reflux esophagitis must perform a therapeutic function; for this, the patient needs to review his diet, his eating habits and consume exclusively those foods that contribute to a speedy recovery.
When eating and following a diet for reflux esophagitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
you need to eat often, but in small portions - this will prevent stomach overfilling and reduce the production of gastric juice; food should be warm; before meals, you can drink a glass of still mineral water to increase the pH of the stomach contents; It is important to chew food well, since large pieces of food linger longer in the stomach and require more digestive juices; to prevent the appearance of pain during an exacerbation of reflux esophagitis, you need to eat in an upright position, preferably standing, and after eating do not lie down for several hours; Before going to bed, a warm drink is allowed, for example, chamomile tea, it has an anti-inflammatory effect; It is extremely important to refrain from all types of physical activity during the treatment period, especially those associated with abdominal tension and wearing tight clothing around the waist. Warning! Once a diagnosis of reflux esophagitis has been made, you should quit smoking and drinking alcohol forever.
They are traumatic for both the mucous membrane of the esophagus and the stomach.
Warning! Once a diagnosis of reflux esophagitis is made, smoking and drinking alcohol should be stopped forever. They are traumatic for both the mucous membrane of the esophagus and the stomach.
Authorized Products
All dishes during the diet for reflux esophagitis must be stewed, boiled, baked or steamed.
Among the first courses for gastritis and esophagitis, you can eat vegetable and milk soups. They are allowed to diversify with noodles and some types of cereals, but sautéing is prohibited. For second courses for diseases of the digestive tract, nutritionists advise using lean varieties of fish, meat, as well as veal, rabbit, and chicken. While on a diet, it is allowed to eat lean pork in small quantities.
Among the fish that are well suited for dietary nutrition are pollock, hake, perch, bream, cod, and pike. As a side dish during the diet, you can eat stewed or baked vegetables, rice porridge, buckwheat; it is also possible to add a little butter, horns, and durum wheat noodles. Eggs need to be boiled or steamed into an omelet. Dairy products that are acceptable during the diet include low-fat fermented milk products, as well as pureed low-fat cottage cheese.
Desserts and sugar should be excluded, but a small amount of honey, pudding, jelly, and soft cookies during the diet is acceptable for reflux esophagitis. Fruits such as banana, plum, pear will help prevent heartburn.
Advice! Sauces based on yoghurt, milk or sour cream with reduced fat content will help diversify the diet menu for reflux esophagitis.
Prohibited Products
If you have gastrophagial reflux, it is prohibited to consume the following foods during a therapeutic diet:
- bread, fresh pastries, baked goods;
- alcoholic drinks are prohibited even during remission;
- peas and legumes;
- rich broths;
- fatty fish, meat;
- pickles, marinades, preservation;
- strong tea, coffee;
- smoked meats;
- seasonings, mayonnaise, sauces, mustard;
- carbonated drinks, kvass, fruit and berry juices;
- almost all types of sweets, chocolate, halva;
- nuts and seeds;
- raw vegetables, mushrooms, radishes, onions, garlic, ginger;
- fast food.
Attention! Any errors in the therapeutic diet for reflux esophagitis can provoke nausea, vomiting, pain in the iliac region, and heartburn. Therefore, you need to strictly adhere to nutritional rules
Prevention and complications
In order to prevent GERD and its complications, you must follow these rules:
- Unconditional adherence to the rules of healthy eating. In order to prevent GERD, everyone needs to follow a diet. She does not have serious restrictions, but does not recommend consuming large amounts of sour and spicy foods, as well as alcohol. In addition, it is recommended to avoid overeating.
Interesting! Treatment with folk remedies for gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Periodic preventive examinations. Every healthy person should undergo a medical examination at least once a year. Its goal is not only to identify diseases, but also to teach patients the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
If the menu is not followed during reflux, then the risk of complications is high. The most dangerous of them are the appearance of a malignant tumor of the esophagus or Mallory-Weiss syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by the fact that bleeding develops from vessels located extremely close to the cardiac sphincter.
This condition is extremely difficult to treat and can recur. Mallory-Weiss syndrome is highly likely to be fatal.
Cancer of the esophagus and stomach is a common disease today. GERD and esophagitis quite often precede it. This pattern is due to the fact that frequent relapses can provoke the appearance of atypical cells in the tissues of the esophagus or stomach.
Diet for the above pathologies is an important element of their treatment. Compliance with the rules will help significantly improve your well-being, and also reduce the risk of relapses and complications.
Diet for reflux esophagitis and gastritis
With the catarrhal form of esophagitis, the epithelium of the esophageal tube becomes inflamed, and with gastritis, the sensitive lining of the stomach is damaged. To combat these pathologies, the diet should be designed to minimize irritation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. Proper nutrition will help normalize the production of gastric secretions.
You should not drink cow's milk, which only temporarily eliminates the symptoms of heartburn, but the proteins and calcium that enter the body significantly increase gastric secretion. If you have reflux esophagitis, you can drink 1 glass of goat milk every morning. This product can be used as a base for preparing nutritious porridges.
During the treatment period, it is better to avoid confectionery and yeast products, since they contain a large amount of carbohydrates, which contribute to the occurrence of flatulence and prolonged fermentation of food. Otherwise, increased pressure will be applied to the lower digestive tract, increasing the likelihood of stomach contents entering the esophagus.
Rules for eating
For reflux esophagitis, it is recommended to adhere to fractional meals, as this helps improve digestive processes.
It is better not to lie down immediately after eating, since after a person assumes a horizontal position, the likelihood of aggressive hydrochloric acid entering the esophagus from the stomach will increase. It's better to take a little walk and get some fresh air. It is not recommended to engage in heavy physical activity.
If a person feels hungry between main meals, then you should drink a glass of warm water. You can use mineral water, but without gas. In case of exacerbation of the disease, it is forbidden to tighten the belt on your trousers, as this will provoke unwanted acid reflux into the esophagus. Therapeutic diet has been used much longer than drug therapy.
To normalize the functioning of the digestive tract, you need to exclude harmful foods from your diet for at least 4-5 months. You can minimize the likelihood of a relapse of the disease if you avoid foods to which the body reacts most strongly.
Menu for every day
The basic principle of nutrition for reflux esophagitis is the exclusion from the patient’s diet of foods that can excessively irritate the walls of the stomach and cause heartburn.
What should be completely excluded?
The reflux diet involves completely avoiding a number of foods and supplements. These include:
- tomatoes;
- citrus fruit;
- cocoa, chocolate, sweets and confectionery (especially with rich cream);
- alcoholic drinks;
- spicy dishes;
- fried foods;
- fruit juices;
- herbs and spices (cloves, allspice, cinnamon);
- garlic;
- vinegar, citric acid;
- cucumbers;
- radish, turnip, radish;
- strong meat broths;
- Rye bread;
- freshly baked white bread (yesterday’s is ok);
- fatty meat and poultry (pork, lamb, goose, duck);
- lard, butter, margarines;
- fatty fish in any form;
- preserved food (fish, stewed meat, pickled vegetables, canned fruit);
- some cereals: pearl barley, wheat, barley;
- sharp and fatty cheeses;
- some legumes: beans, chickpeas;
- mushrooms, mushroom broth;
- raw onions;
- eggplant;
- ice cream, halva;
- various sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard, curry);
- carbonated drinks;
- kvass.
What can patients eat and drink?
The patient's diet should include the following foods and drinks:
- milk;
- decoction of rose hips (completely without sugar or with a small amount of it);
- dried fruit compotes;
- low-fat fermented milk products: cheeses, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, kefir, sour cream, ayran, tan, yoghurts;
- crumbly porridge with water or milk (millet, oatmeal, buckwheat, rolled oats, rice);
Cooking methods and temperatures
The diet for reflux esophagitis is followed daily, since restoration of the mucous membrane is a long process. Dishes can be cooked in a double boiler, stewed, baked and boiled. Fried foods should be excluded from the diet, as they injure and irritate the walls of the esophagus, and also take a long time to digest in the stomach.
Prepared dishes can only be consumed warm, at a neutral temperature. The ingredients used should be finely chopped or ground through a sieve. Excessively hot and cold foods increase the production of stomach acid.
How to treat the disease
There are therapeutic and surgical methods. First, drugs from different groups are used. This allows you to eliminate or reduce the severity of symptoms. The main principles of drug treatment:
- combination of medications, physiotherapeutic methods, diet;
- depending on the nature of the pathological process, the following drugs are prescribed: antibacterial agents, antacids, prokinetics, proton pump inhibitors - the last 2 types of drugs improve digestion and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Physiotherapy methods: electrical stimulation of the gastric cardia, electrophoresis, laser therapy. If the above methods do not provide the desired result, surgical treatment is resorted to. This method is chosen both when complications develop and in cases where, after eliminating acute symptoms, the process soon worsens again.
How to plan a weekly diet
The diet menu should be thought out in advance in order to purchase permitted products for the week at once and not fill the refrigerator with tempting forbidden delicacies
A diet for esophagitis can be varied and cheerful if you spare no time and imagination. To create an interesting, varied, healthy menu, it is better to consult a nutritionist.
Sample option for a week:
| Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | |
| Monday | Oatmeal with dried apricots, herbal tea, biscuits | Low-fat cottage cheese with fruit, compote | Cauliflower soup with herbs, casserole of vermicelli and minced meat, berry jelly | Baked apples, tea | Steamed fish with mashed potatoes and vegetable salad with vegetable oil |
| Tuesday | Steam omelette, rosehip decoction, dry biscuit | Berry jelly, cookies | Beetroot soup with chicken quenelles, buckwheat porridge with a piece of butter, compote | Lazy dumplings, jelly | Cauliflower casserole, fish soufflé, herbal tea |
| Wednesday | Rice porridge with milk with prunes, sweetened weak tea, a slice of marshmallow | Yogurt with berries, dry biscuit | Vegetable soup with croutons, mashed potatoes, steamed turkey breast, compote | Steam omelette, herbal tea | Liver pancakes, vermicelli, beet salad |
| Thursday | Semolina pudding with raisins, herbal tea, croutons | Boiled egg, crackers, compote | Fish soup with meatballs, rice porridge, boiled carrot salad, tea | Mashed cottage cheese with berries, dry cookies | Steamed chicken cutlet, mashed potatoes, boiled carrot salad |
| Friday | Cottage cheese with berries, rosehip infusion, biscuits | Baked apple, tea | Potato soup with croutons, buckwheat with liver soufflé, compote | Fruit mousse, cookies | Casserole of vermicelli and minced meat, any boiled vegetables, tea |
| Saturday | Soft-boiled egg, slice of dried bread with unleavened homemade cheese, tea | Fruit puree, biscuits | Vermicelli soup with vegetables, steamed cod with potato dumplings, jelly | Steamed cheesecakes with sour cream, sweetened weak tea | Chicken pate with boiled buckwheat, rosehip infusion |
| Sunday | Cheesecakes with dried fruits and sour cream, weak chicory drink, dry biscuit | Fruit mousse | Slimy soup with rice and vegetables, buckwheat with minced meat and sour cream, compote | Semolina casserole with dried fruits, tea | Steamed fish cutlet, mashed potatoes, vegetable salad |
It’s better to avoid snacking, but if you can’t, you should choose sweet fruits, dairy products, and dry biscuits.
Before going to bed, if you have an appetite, you are allowed to drink a glass of milk, kefir, fermented baked milk with crackers, herbal tea, and eat yogurt with fruit.
Sample menu for a week for reflux gastritis and esophagitis
Now that the principles of nutrition for reflux diseases of the stomach and esophagus have become clear, let's move on to specific examples.
To begin with, we will give an example of a weekly diet for a patient with a chronic form of esophagitis or gastritis during a period of remission, without erosions of the mucous membrane. So, a sample menu for reflux gastritis and esophagitis:
Monday:
- breakfast - oatmeal and weak tea;
- second breakfast – low-fat cottage cheese;
- lunch - soup with meatballs, vegetable salad and toasted bread;
- afternoon snack – banana or apple;
- dinner - wheat porridge with steamed cutlet.
Tuesday:
- breakfast – low-fat cottage cheese;
- second breakfast - fruit;
- lunch – mashed potatoes with carrots and boiled chicken breast;
- afternoon snack - compote;
- dinner – rice with boiled chicken.
Wednesday:
- breakfast – cottage cheese casserole with raisins and weak tea;
- second breakfast – cookies with compote;
- lunch – mashed potatoes with carrots and boiled chicken breast;
- afternoon snack - banana, pear or apple;
- dinner - rice porridge with stewed fish or boiled meat.
Thursday:
- breakfast – semolina porridge with jam;
- second breakfast – baked apples;
- lunch - broth and dried bread;
- afternoon snack – cookies with compote;
- dinner – mashed potatoes with boiled beef.
Friday:
- breakfast – low-fat cottage cheese with jam;
- second breakfast – fresh apples;
- lunch – rice porridge with meat;
- afternoon snack - compote;
- dinner - dumplings with cottage cheese.
Saturday
- breakfast - rice pudding with dried apricots;
- second breakfast – dried fruits with tea;
- lunch – milk soup with noodles;
- afternoon snack – cookies with compote;
- dinner – pumpkin porridge and a glass of milk.
Sunday:
- breakfast – rice porridge with milk;
- second breakfast - waffles with coffee;
- lunch - soup with meatballs, vegetable salad, bread;
- afternoon snack – marshmallows and a glass of kefir;
- dinner - pasta with cheese or meat.
Now let's move on to the diet menu for gastritis and reflux esophagitis during an exacerbation. Diet 1a is prescribed for 2-3 days, six meals each, so it would be more relevant to divide it by time:
Day 1
- 7:00 – semolina porridge and tea with milk;
- 11:00 – steamed cheesecake and dried fruit compote;
- 14:00 – pureed meat and rice;
- 17:00 – oatmeal jelly;
- 20:00 – low-fat cottage cheese casserole;
- 22:00 – glass of milk.
Day 2
- 7:00 – grated rice porridge;
- 11:00 – baked apples;
- 14:00 – slimy broth with boiled beef;
- 17:00 – dried fruit compote;
- 20:00 – mashed rice and boiled chicken breast;
- 22:00 – glass of milk.
Although most patients are dissatisfied with the monotony, such a menu for every day for reflux gastritis or esophagitis is balanced in proteins, fats and carbohydrates and has sufficient energy value.
Useful video
We invite you to watch 2 interesting videos about proper dietary nutrition for reflux esophagitis. It's better to see once than to read ten times:
Potato zrazy
Boil the meat and pass through a meat grinder. Finely chop the onion, fry in vegetable oil, add salt. Boil the potatoes and mash them, add salt and mix with a raw egg. Mix meat with onions. Make pancakes from the puree, put minced meat in the middle, form zrazy, roll in white breadcrumbs and bake on a baking sheet in the oven.
Traditional methods of treatment
For reflux esophagitis, aloe, honey and Cahors are used to prepare a tincture, which also helps with gastritis. Crushed half a kilogram of aloe leaves is mixed with a glass of honey, left in the dark for 3 days, a bottle of Cahors is added and kept for another 3 days in a dark place. Drink 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l. 30 minutes before meals for one month.
Is mineral water allowed for reflux esophagitis? Mineral waters “Essentuki 17”, “Essentuki 4”, “Narzan” are used to treat reflux esophagitis, since they contain an alkali that neutralizes the effect of the acidic environment of gastric juice.
You need to take it warmed up to 38-45 * 200 ml before meals.
"Borjomi" for reflux esophagitis is also allowed for use.
Sea buckthorn oil for reflux esophagitis helps relieve inflammation of the esophageal mucosa if taken 1 tbsp. l. three times a day. You cannot drink it on an empty stomach. You can buy oil at a pharmacy.
Flax seeds are allowed for reflux esophagitis, which envelop the mucous membrane of the esophagus and prevent the negative effects of the acidic environment of gastric contents on it. Seeds (70 g), pour 1 liter of water, boil for 2 hours, cool and take 200 ml 1 hour before meals three times a day. Treatment lasts 2 months.
How to gain weight with reflux esophagitis
A strict diet should be followed only during an exacerbation. Next, you need to avoid foods that cause heartburn. To increase weight, you need to eat 5-6 times a day, but do not overeat. Combine pasta and mashed potatoes with protein foods (cutlets, meatballs), combine porridge with nuts, raisins or meat products.
You can eat halva and kozinaki. It's good to drink vitamin cocktails. In the afternoon, drink a mixture of cottage cheese, jam, milk and banana. This diet will help you increase your body weight.
Basic principles of diet for reflux esophagitis
Following a diet for GERD allows you to put the disease into remission and prevent complications. When diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), some of the stomach contents flow into the lower esophagus. The diet does not eliminate the cause of the disease, but improves the patient's condition.
Prohibited foods for esophageal reflux. Its main principles:
- exclude from the diet foods and factors that have an aggressive effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract: carbonated drinks, thermal irritants (hot, cold food), etc.;
- it is necessary to avoid hard foods; with GERD, the patient is recommended to eat foods crushed to a puree state, this allows to reduce the intensity of even greater trauma to damaged areas of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminate additional irritants to the mucous membranes;
- foods containing large amounts of fiber are removed from the diet;
- foods that provoke increased production of gastric juice are prohibited;
- You should not eat fried, fatty foods during the diet, hot sauces and dishes containing a large amount of seasonings;
- food should be boiled, cooked in an oven or double boiler;
- raw foods are poorly tolerated by the digestive system in this disease;
- products containing fruit acids are also prohibited;
- It is recommended to give up alcoholic beverages and smoking - these are additional factors that contribute to irritation of the mucous membranes of the esophagus (upper section);
- exclude from the diet foods that increase gas formation in the intestines, as this increases the pressure in the abdominal cavity;
- recommended daily amount of food: 2300-2800 kcal (for the “table No. 1” diet);
- number of meals per day: 5-7 times, the breaks between them are short, so the patient does not have time to get hungry; if this does happen, you need to drink water;
- the daily volume of water is 1.5 liters, excess fluid is harmful for GERD;
- the recommended amount of calories can be roughly divided into parts, with higher-calorie foods consumed in the first half of the day; the preferred dinner option for GERD is: omelet, fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables approved by the doctor, but they should be steamed.
Allowed foods can be boiled or steamed.
Alcohol
Alcohol irritates the mucous membrane of the esophagus and also provokes reflux.
To avoid the manifestation of negative symptoms, it is better to exclude alcohol from the diet. In rare cases, gastroenterologists allow patients to drink alcohol, but not on an empty stomach.