Hemorrhoids are a disease that gives a person a lot of discomfort and occurs due to dilation of the veins of the lower segment of the rectum. Pain, discomfort, difficulty during defecation, bleeding of nodes - all this disrupts the patient’s quality of life, causing suffering both morally and physiologically.
There is a theory that hemorrhoids develop due to the consumption of hot and spicy foods. This theory has not been proven, however, it is difficult to disagree with the fact that the nature of food affects the course of the disease. Following a diet for hemorrhoids is the key to ensuring that an exacerbation of the disease is less likely to occur. Therefore, a proper diet is the prevention of hemorrhoids.
General information
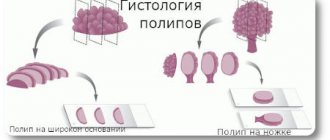
Hemorrhoids are a disease of the rectum, characterized by pathological enlargement of the veins in the anus.
The first signs of the disease are blood during bowel movements, itching in the anus, pain during bowel movements. The main cause of the disorder is an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and in the vessels of the rectum.
Factors contributing to blood stagnation in the veins of the anus:
- straining during bowel movements;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- lifting weights;
- dehydration of the body;
- straining during childbirth;
- acute hypovitaminosis;
- diseases of the pelvic organs (cystitis, prostatitis);
- severe cough syndrome (with bronchial asthma).
- prolonged “standing” on your feet.
- alcohol abuse.
In most cases, this disease develops gradually without the presence of pronounced symptoms. Initially, a person feels slight discomfort in the anus (during bowel movement). At this stage, hemorrhoids occasionally fall out, but are easily reduced (on their own).
As the disease progresses, pain during bowel movements increases, and minor bleeding from the anus occurs. In this case, hemorrhoidal “bumps” fall out not only during emptying, but also with the slightest physical effort. In the absence of proper therapy, the disease is fraught with severe complications (necrosis, thrombosis, paraproctitis, cryptitis).
At the last stage of the disease, it is possible to get rid of the nodes only through surgical intervention, since they are constantly on the outside and cannot be corrected on their own.
Principles of nutrition
The main objectives of the “antihemorrhoidal” diet are to restore impaired intestinal functions (eliminate constipation or diarrhea), normalize blood flow in the pelvic organs, and increase vascular elasticity.
General principles of nutrition:
- Maintain drinking regime. Considering that the density of stool depends on the amount of liquid consumed, it is important to consume at least 2 liters of water per day to thin the stool. With a lack of drinking resources, the transit of chyme through the intestines slows down. This leads to compaction of feces and damage to the veins of the anal canal (from bowel movements).
To combat constipation (especially long-term constipation), drink a third of the daily volume of water on an empty stomach (in 1-1.5 hours). The remaining portion of liquid is consumed throughout the day (in small sips).
- Enrich your daily diet with fiber. Dietary fiber is the basis of dietary nutrition for hemorrhoids. Fiber, by increasing the volume of feces, promotes gentle bowel movements. Along with this, pectins have an astringent, enveloping and protective effect on the digestive tract.
Remember, the diet of people suffering from hemorrhoids should consist of 50% plant fiber.
- Eliminate alcohol from the daily menu. Alcoholic drinks dehydrate the patient's body, promoting dehydration of water from the intestines. In case of hemorrhoidal disease, it is permissible to consume alcohol only during the period of remission (in minimal doses).
- Follow a fractional diet. The optimal frequency of meals is 6 times a day. Preference should be given to liquid crushed foods: pureed soups, fermented milk products, boiled porridges, fruit smoothies. A fractional diet is indicated in the acute and postoperative period (to reduce pressure on the intestinal walls during bowel movements).
- Chew food thoroughly. This will prevent large particles of food from entering the esophagus and further into the stomach and intestines, which can damage the mucous lining of the large intestine. For good digestion, chew solid foods 30-40 times.
- Consume food in small doses. The size of a single serving should not exceed 250 grams. A dosed diet will help relieve the gastrointestinal tract, and, as a result, reduce pressure on the walls of the anal canal.
- Control the temperature of food. For cracks or prolapses of the intestine, it is important to consume warm food (15-60 degrees). Cold or hot foods irritate the walls of the organ, worsening its evacuation function.
Remember, to maintain intestinal tone, it is important to combine a healthy diet with moderate physical activity (excluding heavy lifting).
Among the preferred sports are: swimming, gymnastics, tennis, race walking, jogging, roller skating, skiing, and skating. They improve blood supply in the pelvic area, train the cardiovascular system, and eliminate peripheral edema. In addition, these sports improve the physical performance of the body, strengthen the immune system, and prevent the appearance of hemorrhoids.
What is strictly prohibited
Alcohol is another major culprit. Alcoholic drinks disrupt the functioning of all internal organs and systems. The digestive organs and intestinal microflora are severely affected. A hangover is similar to a serious illness. Intoxication worsens general health, causes fermentation, bloating, provokes diarrhea or constipation, and irritates the anus. Under the influence of alcohol, the functioning of the circulatory system is disrupted. Initially, the vessels greatly expand, increasing blood flow to the pelvic organs, then they narrow, preventing blood from escaping. Stagnation is observed. The main rule for successful treatment is to give up alcoholic beverages.
Gas formation and intestinal bloating are undesirable. Provocateurs are carbonated drinks, coffee, chocolate, marinades, canned food, mayonnaise, spices, sweets with cream, jam, and baked goods. Fermentation is enhanced by cabbage, grapes, plums, cherries, apricots, citrus fruits, legumes, radishes, and turnips. Spicy, salty, fried, fatty foods should be excluded from the diet. They load the intestines, irritate the walls, and compact the stool.
You will have to give up white bread, chips, crackers, hot dogs, pizza, salted nuts, beer, kvass.
List of permitted products
To reduce the risk of developing or exacerbating the disease, the diet should consist of 50% of foods that improve intestinal function.
For rectal pathologies, consume the following foods:
- Vegetables. To improve stool, the daily menu is enriched with products that have a mild laxative effect: beets, cucumbers, carrots, zucchini, cabbage, pumpkin. Intake of starchy vegetables (potatoes, radishes, radishes) is kept to a minimum (as they cause constipation). Plant foods are consumed fresh, boiled or baked.
- Fermented milk drinks. People suffering from hemorrhoids are recommended to enrich their daily diet with the following products: kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk, yogurt. These drinks supply the body with beneficial flora, stimulate the evacuation function, accelerate the movement of the food bolus through the intestines, and promote the healing of anal fissures.
- Cereals. The following porridges will help reduce the load on the digestive system: buckwheat, pearl barley, oatmeal, wheat, barley. It is better to avoid consuming semolina and rice cereals (as they have a fixing effect).
- Fruits. To prevent and treat constipation, patients’ daily diet includes bananas, apricots, apples, plums, pears, peaches, strawberries, oranges, figs, dried apricots, raisins, and prunes. When choosing a fruit, give preference to ripe fruits, since green ones irritate the intestinal walls.
- Bread. Due to the high gluten content, products made from white flour are “banned.” To improve intestinal functions, it is recommended to consume whole grain baked goods and breads.
- Greenery. Plant tops, thanks to the high concentration of vitamin C and rutin, have a venotonic and anti-inflammatory effect on the intestinal walls. In addition, greens supply the body with iron, which is necessary for the synthesis of red blood cells (especially for bleeding from hemorrhoids).
- Vegetable oils. Envelops the intestinal walls, stimulates painless bowel movements, and heals anal fissures. The most useful oils are pumpkin, sea buckthorn, olive, flaxseed, and cedar. For persistent constipation, take the product twice a day (30 minutes before the morning meal and 60 minutes before bedtime). However, for gallstones, oils are used with caution because they stimulate bile secretion.
To improve the patient's condition, anti-inflammatory teas (linden, sage, chamomile) are included in the daily diet.
Include oil in your diet
Take a tablespoon of olive, flaxseed or other vegetable oil on an empty stomach - this will help improve digestion better than many medications. Moreover, if intestinal problems are combined with gastritis or stomach ulcers, then taking the oil will solve several problems at the same time.
You can also mix a portion of butter with a fermented milk product and drink it before bed - this will make morning bowel cleansing easier.
The body will also be grateful if you replace traditional salad dressings like mayonnaise and sour cream with vegetable oil.
Hemorrhoids: what are their causes and how to protect themselves from the disease
More details
Prohibited Products
Diet therapy for hemorrhoids involves excluding from the menu foods that stimulate blood flow to the vessels, irritate the rectal mucosa, and increase gas formation in the digestive tract.
List of prohibited products:
- pastries, puff pastry products, white flour bread;
- white sugar;
- wheat pasta (white);
- fried foods;
- hot spices (mustard, pepper, horseradish);
- semolina and rice porridge;
- fatty meats;
- alcohol;
- coffee, black tea, carbonated drinks;
- potatoes, radishes, radishes, onions, garlic, beans, peas;
- confectionery;
- whole milk, cream;
- animal fats;
- rich broths;
- quince, blueberry, barberry;
- canned food, marinades, pickles, smoked meats.
In addition, when nodes fall out, it is important to monitor the amount of salt consumed, since its excess provokes an exacerbation of the disease. The optimal portion of spice is 7 grams per day.
Remember, consuming prohibited foods is only permissible during the period of remission (in limited quantities). Therapeutic nutrition in the acute phase of the disease should be strict.
More liquid!
We are used to drinking little. One glass of tea at lunch and that’s it. Why? In order to run to the toilet less often and not reduce labor productivity? We don't need this nonsense, we should drink a lot.
At least two liters per day. Water is as beneficial for hemorrhoids as medications and fiber. The food should be liquefied, and then it will pass the intestines more easily. As soon as you got up in the morning, you drank a couple of glasses of cool boiled water and you are guaranteed normal stool.
Nutrition after surgery
Elective surgery is indicated for people with severe forms of the disease when conservative treatment does not produce positive results. After removal of hemorrhoids, the recovery period lasts 1-1.5 months. During this time, it is important to adhere to a gentle diet (so as not to injure the intestinal wall with rough substances). In addition, for successful scar healing, bowel movements should be avoided in the first 24 hours after hemorrhoidectomy (procedures to remove nodes). In view of this, the daily diet consists of only drinking plenty of fluids (water, green tea, herbal decoctions). On the second day, it is permissible to include dietary food in the patient’s menu.
List of products for the “first week” after surgery:
- vegetable puree soups (ground);
- liquid porridge cooked in water (buckwheat or oatmeal);
- steamed meatballs (from lean meats);
- low-fat fermented milk products (ground cottage cheese, kefir).
A week later, baked fruits, stewed vegetables, boiled fish and meat are added to the patients’ menu.
The main principles of postoperative nutrition (in the first month):
- Maintain drinking regime. To avoid the risk of relapse, the daily menu must contain at least 2 liters of water.
- Consume food every 2 hours. Eating six meals a day “facilitates” the process of defecation, “providing” a soft consistency to the stool.
- Take food in small doses. To reduce the load on the intestinal tract, the serving size should not exceed 160 grams.
- Use gentle food processing methods. In the first month after hemorrhoidectomy, food is consumed only in boiled, baked or steamed form (to eliminate the possibility of damage to the intestines by solid particles).
- Balance the daily menu. To normalize stool, the diet includes at least 60% carbohydrates, 30% fats, 15% proteins.
Remember, disorderly eating after surgery can lead to complications: scar infection, rupture of sutures, bleeding from the anus.
What should you not eat for 30 days after surgery?
During the recovery period, foods that cause flatulence and fermentation are “banned.”
List of prohibited products:
- Fresh berries, vegetables, fruits (especially apples, radishes, cabbage, grapes, turnips, garlic, raspberries).
- Legumes (beans, peas, lentils).
- Whole milk.
- Bakery and confectionery products (including those made from whole grain flour).
- Spices, spices.
- Nuts (especially peanuts, almonds, hazelnuts).
- Carbonated drinks (lemonade, kvass, mineral water).
- Alcohol.
- Black tea, coffee.
- Canned food, marinades, smoked meats, pickles.
- Fatty meats (pork, lamb, duck, goose).
- Mushrooms.
If these rules are followed, the wound will heal completely within a month of diet therapy. Along with this, intestinal motility is restored, the tone of the veins in the anus is normalized, and digestion is improved. To speed up the healing of damaged tissue, you can use bactericidal sitz baths (from sage, calendula or chamomile).
Sea buckthorn will restore intestinal health
Sea buckthorn oil is an effective remedy for hemorrhoids, used in both folk and traditional medicine. The usefulness of this product is due to the presence of a large number of venotonic substances in the composition.
The main components of sea buckthorn oil:
- Vitamins (, , ,). They strengthen the capillaries of the anus, stimulate the regeneration of injured areas of the epithelium, accelerate the healing of postoperative scars, improve the tone of the vascular bed, increase the elasticity of the walls of the anus, and prevent the appearance of new hemorrhoids (due to increased collagen synthesis).
- Tannins (phytoncides, pectins, serotonin, alkaloids, coumarins). They reduce swelling of hemorrhoids, relieve pain in the anus, and eliminate bleeding from the anus.
- Unsaturated fatty acids (palmitic, linoleic, oleic, linolenic, palmitoleic). They improve the rheological characteristics of blood and prevent its stagnation in the pelvic veins.
- Organic acids (malic, oxalic, succinic, tartaric). They reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process, accelerate the healing of anal fissures, and eliminate irritation in the anus.
Sea buckthorn oil is used to treat the disease at all stages of the pathology (including the acute phase).
During the period of remission, the product is used internally in its pure form (to prevent the formation of new nodes). Dosage regimen: 15 milliliters 2 times a day: in the morning (after waking up) and in the evening (before bedtime). The duration of oil therapy is 60 days.
In case of exacerbation of hemorrhoidal disease, it is advisable to combine oral and local intake of plant materials. To reduce the inflammatory process, oil is applied to the “bumps” at least 5 times a day (on gauze pads). The treatment dressing exposure time is 1 hour. If necessary (internal hemorrhoids), the composition is injected into the anus using a turunda or microenema.
How to make your own sea buckthorn oil?
To create a healing potion, it is better to use red rather than orange berries (due to their richer ingredient composition).
Cooking diagram:
- Prepare the berries for processing: rinse, remove branches.
- Squeeze juice from fresh fruits.
- Dry the sea buckthorn cake in the oven (at 40 degrees).
- Grind the dry pomace in a coffee grinder.
- Divide the resulting mixture into 3 parts.
- Pour the first portion of the cake with sunflower oil (refined). Ratio 1:5.
- Infuse the resulting composition for three days in a warm place (stirring 2 times a day).
- Strain the three-day oil through a fine sieve and discard the first cake.
- Add the second part of the dry cake to the “primary” oil. Leave for 3 days.
- Repeat the procedure with a third portion of sea buckthorn.
The finished mixture is poured into a glass container and placed in the refrigerator.
Menu for hemorrhoids
Diet therapy for diseases in the anal area is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the digestive tract, in particular preventing constipation and diarrhea.
Monday
After waking up: 300 ml of water.
Breakfast: 100 g oatmeal, 50 g bananas, 20 g walnuts, 10 g rye toast.
Lunch: 150 ml cabbage, 70 g steam cutlets, 10 ml sea buckthorn oil.
Afternoon snack: 100 g of curd mass, 50 g of cranberries, 20 ml of thermostatic sour cream.
Dinner: 100 g barley porridge, 70 g pike perch (boiled), 50 g mixed greens.
An hour before bedtime: 150 ml of 1% fermented baked milk.
Tuesday
An hour before the 1st meal: 700 ml of water (in 3-4 doses).
Breakfast: 100 g of buckwheat (preferably green), 60 g of cucumber salad, 10 g of bran.
Lunch: 100 g apple-banana smoothie.
Lunch: 150 g of vegetable puree (beets, zucchini, broccoli, carrots), 70 g of steamed meatballs, 20 g of whole grain bread.
Afternoon snack: 150 g fruit cocktail (banana, strawberries, prunes), 20 ml honey.
Dinner: 170 g shrimp-avocado salad, 20 ml pumpkin oil.
An hour before bedtime: 170 g of “young” kefir (one or two days old).
Wednesday
After waking up: 300 ml of clean water.
Breakfast: 100 g egg omelet, 50 g fresh tomatoes, 30 g fresh herbs (dill, cilantro, lettuce).
Lunch: 100 ml fruit jelly, 100 g biscuits.
Lunch: 150 ml fish soup, 100 g vegetable stew (carrots, broccoli, zucchini).
Afternoon snack: 150 ml calendula tea, 100 g pumpkin pancakes (steamed), 20 ml honey.
Dinner: 100 g of wheat porridge, 70 g of lemon-beetroot salad, 15 ml of pumpkin oil.
An hour before bedtime: 150 ml of green smoothie (cilantro, yogurt, salad).
Thursday
40 minutes before the morning meal: 800 ml of water (in 3-4 doses).
Breakfast: 150 g of oatmeal, 50 g of seasonal berries (strawberries, blueberries, mulberries), 20 ml of sea buckthorn oil.
Lunch: 200 ml fruit and curd smoothie.
Lunch: 150 ml of green borscht (lean), 70 g of carrot salad, 50 g of turkey (boiled), 15 g of bread.
Afternoon snack: 150 ml knotweed tea, 100 g apple pie.
Dinner: 150 g pumpkin stuffed with buckwheat, 50 g prunes.
An hour before bedtime: 150 ml of yogurt.
Friday
After waking up: 300 ml of water.
Breakfast: 100 g pearl barley porridge, 50 g prunes.
Lunch: 150 ml sage tea, 100 g apple-carrot casserole (with whole grain flour).
Lunch: 150 ml of soup with meatballs, 70 g of stewed cabbage, 10 ml of olive oil.
Afternoon snack: 150 g of sliced fruit (peach, banana, apple), 30 g of whole grain toast.
Dinner: 150 g of Greek salad (tomatoes, cheese, olives, cucumbers, olive oil), 70 g of hake cutlets (boiled).
An hour before bedtime: 200 ml of yoghurt-beetroot mix.
Saturday
After waking up: 300 ml of water.
First meal: 150 ml of knotweed tea, 100 g of Dutch cheese, 30 g of rye bread (dried), 15 g of butter.
Second breakfast: 150 ml apple compote, 70 g pumpkin casserole.
Lunch: 100 g of tomato puree soup (from fresh tomatoes), 100 g of fish steak, 20 ml of sour cream.
Afternoon snack: 150 g of dried fruits (figs, dried apricots, prunes), 50 ml of yogurt.
Dinner: 100 g vegetable stew, 100 g squash caviar (homemade), 15 ml sea buckthorn oil.
An hour before bedtime: 150 ml of low-fat yogurt.
Sunday
After waking up: 350 ml of clean water (passed through a filter).
First meal: 150 ml of herbal tea (sage, dandelion, yarrow), 150 g of oat pancakes (steamed), 20 ml of honey.
Second breakfast: 100 g of apple and Jerusalem artichoke salad.
Lunch: 150 g broccoli puree, 70 g turkey steak (steam), 30 g fresh herbs.
Afternoon snack: 150 g apple cheese salad, 20 ml sea buckthorn oil, 15 g bread (rye).
Dinner: 100 g beet-carrot caviar, 50 g baked potato, 15 ml pumpkin oil.
An hour before bedtime: 200 ml of yoghurt mousse with prunes.
Fruits
Fruits, like vegetables, are a source of plant fiber, as well as many vitamins, microelements and biologically active substances necessary for the body.
For a disease associated with frequent constipation, it is preferable to eat fresh fruits, which have a mild laxative effect. These are apricot, watermelon, plum, melon, peach, nectarine, banana, apples, persimmon. Dried fruits containing soft fiber are also useful - figs, apricots, dried apricots, prunes. They must be consumed up to 10 pieces per day.
But when dealing with fruits, you should be careful, as unripe or overripe fruits can cause severe diarrhea. You should also avoid eating fruits that are too sour or too sweet. Consumption of the following types of fruits and berries should be limited:
- grape,
- gooseberry,
- Red Ribes,
- tangerines and oranges,
- pears.
A combination of berries and fruits with kefir or cottage cheese is useful.