pharmachologic effect
A combined set containing an antifungal drug, an antibiotic and an antibacterial drug with antiprotozoal activity.
Fluconazole -
an antifungal drug, a triazole derivative, is a powerful selective inhibitor of sterol synthesis in fungal cells.
Effective against opportunistic mycoses
, incl.
caused by Candida spp., Cryptococcus neoformans, Microsporum spp., Trichophyton spp.
Fluconazole
has also been shown to be active in models of endemic mycoses,
including infections caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum.
Azithromycin -
a broad-spectrum antibiotic, a representative of the subgroup of macrolide antibiotics - azalides. When high concentrations are created at the site of inflammation, it has a bactericidal effect.
Active against gram-positive cocci
: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, streptococci of groups C, F and G, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus viridans;
gram-negative bacteria
: Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Legionella pneumophila, Haemophilus ducreyi, Campylobacter jejuni, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Gardnerella vaginalis;
some anaerobic microorganisms
: Bacteroides bivius, Clostridium perfringens, Peptostreptococcus spp., as well as Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Treponema pallidum, Borrelia burgdorferi.
Azithromycin is not active against
gram-positive bacteria resistant to erythromycin.
Secnidazole
- antimicrobial bactericidal drug, a synthetic derivative of nitroimidazole.
Active against obligate anaerobic bacteria
(spore- and non-spore-forming), causative agents of some protozoal infections: Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica.
Secnidazole is not active against
aerobic bacteria.
Increases the sensitivity of tumors to radiation, causes sensitization to ethanol (disulfiram-like effect). Interacts with DNA, causing disruption of the helical structure, strand breakage, suppression of nucleic acid synthesis and cell death.
Pharmacokinetics
Fluconazole
Suction
After oral administration, fluconazole is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, bioavailability is 90%. When taken on an empty stomach at a dose of 150 mg, Cmax in blood plasma is 90% of the content in plasma with intravenous administration - 2.5-3.5 mg/l. Concomitant food intake does not affect the absorption of the drug taken orally. Cmax in plasma reaches its peak 0.5-1.5 hours after administration. Plasma concentration is directly proportional to dose.
Distribution
Administration of a loading dose (on the first day), 2 times higher than the usual daily dose, allows you to achieve a concentration corresponding to 90% Css by day 2. When taking the drug 1 time/day. 90% Css level is achieved by 4-5 days of treatment.
Vd approaches the total water content of the body. Plasma protein binding - 11-12%.
Fluconazole penetrates well into all biological fluids of the body. Concentrations of the drug in saliva and sputum are similar to its levels in plasma. In patients with fungal meningitis, the fluconazole content in the cerebrospinal fluid reaches 80% of its plasma level. In the stratum corneum, epidermis, dermis and sweat fluid, high concentrations are reached that exceed serum concentrations.
Removal
T1/2 of fluconazole is about 30 hours.
Approximately 80% is excreted unchanged in the urine. Fluconazole clearance is proportional to QC. No fluconazole metabolites were detected in peripheral blood.
Azithromycin
Suction
After oral administration, azithromycin is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, due to its stability in an acidic environment and lipophilicity. At a dose of 500 mg, the Cmax of azithromycin in blood plasma is reached after 2.5-2.96 hours and is 0.4 mg/l. Bioavailability is 37%.
Distribution
Azithromycin penetrates well into the respiratory tract, organs and tissues of the urogenital tract (including the prostate gland), skin and soft tissues. The high concentration in tissues (10-15 times higher than in blood plasma) and long T1/2 are due to the low binding of azithromycin to plasma proteins, as well as its ability to penetrate eukaryotic cells and concentrate in the low pH environment surrounding lysosomes. This, in turn, determines the large Vd - 31.1 l/kg and high plasma clearance.
The ability of azithromycin to accumulate predominantly in lysosomes is important for the elimination of intracellular pathogens. It has been proven that phagocytes deliver azithromycin to sites of infection, where it is released during the process of phagocytosis. The concentration of azithromycin in foci of infection is significantly higher than in healthy tissues (on average by 24-34%) and correlates with the degree of inflammatory edema. Despite its high concentration in phagocytes, azithromycin does not have a significant effect on their function. Azithromycin remains in bactericidal concentrations at the site of inflammation for 5-7 days after taking the last dose, which made it possible to develop short (3-day and 5-day) courses of treatment.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver by demethylation, the resulting metabolites are inactive.
Removal
The elimination of azithromycin from blood plasma occurs in 2 stages: T1/2 is 14-20 hours in the range from 8 to 24 hours after taking the drug and 41 hours in the range from 24 to 72 hours, which allows the drug to be used once a day.
Secnidazole
Suction and distribution
Absorption is high, bioavailability is 80%. After a single oral dose of 2 g, Tmax is 4 hours.
Penetrates the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
Metabolism and excretion
Metabolized in the liver.
Excreted in the urine within 72 hours (16% of the dose).
Compound
The medicine is available in the form of a combination course consisting of 1 tablet of fluconazole , 1 tablet of azithromycin and 2 tablets of secnidazole .
Composition of Azithromycin tablets
The tablet contains 1000 mg azithromycin .
Additionally: 2 mg colloidal silicon dioxide, 12 mg sodium lauryl sulfate, 37.24 mg croscarmellose sodium, 40 mg povidone K30, 16 mg magnesium stearate.
Shell: 24.5 mg hypromellose, 6 mg titanium dioxide, 3.8 mg diethyl phthalate, 5.2 mg talc, 4.2 mg macrogol 4000, 1.06 mg crimson dye (Ponceau 4R).
Composition of Fluconazole tablets
The tablet contains 150 mg of fluconazole .
Additionally: 153 mg microcrystalline cellulose, 14.5 mg calcium hydrogen phosphate, 5 mg croscarmellose sodium, 4 mg magnesium stearate, 1 mg colloidal silicon dioxide, 2.5 mg crimson dye (Ponceau 4R).
Composition of Secnidazole tablets
The tablet contains 1000 mg secnidazole .
Additionally: 6 mg colloidal silica, 95 mg corn starch, 130 mg microcrystalline cellulose, 20 mg sodium carboxymethyl starch, 2.5 mg povidone (PVPK-30), 10 mg magnesium stearate, 11.5 mg talc.
Shell: 27.1 mg hypromellose, 5.7 mg talc, 4 mg diethyl phthalate, 11.2 mg titanium dioxide, 4.6 mg macrogol 4000.
Side effect
From the cardiovascular system:
very rarely - heart rhythm disturbances.
From the digestive system:
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, digestive disorders, abdominal pain, flatulence, lack of appetite.
From the senses:
rarely - taste disturbances.
From the hematopoietic system:
leukopenia.
Allergic reactions:
skin rashes, itching, anaphylactic reactions.
Other:
very rarely - headache, dizziness, stomatitis.
Reviews
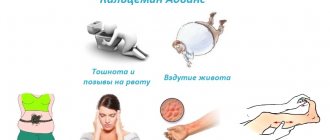
Patients who took Safocid note its effectiveness. Symptoms of the disease disappear after the first or second day of taking the drug . But they also mention
severe side effects from the pills taken, which appear an hour or two after taking and last up to five days.
About 80% of patients experienced indigestion, nausea (sometimes to the point of vomiting), loss of appetite, weakness, apathy, headache.
Cases of an allergic reaction to drugs in the form of red rashes on the skin, accompanied by itching, have been described. After taking antihistamines, the itching goes away, but the rash persists for up to a week.
In general, patients recommend using Safocid only when absolutely necessary and as prescribed by a doctor.
The high cost of Safocid is also noted . But the drugs included in the kit can be purchased separately.
If you have experience using the drug, please share your opinion at the end of the article.
Contraindications to the use of the drug SAFOTSID
— organic diseases of the central nervous system;
- simultaneous use of terfenadine, astemizole or other drugs that prolong the QT interval;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- childhood;
- hypersensitivity to fluconazole and other azole compounds;
- hypersensitivity to azithromycin and other macrolides;
- hypersensitivity to secnidazole and other nitroimidazoles.
Carefully _
the drug should be used simultaneously with cisapride, rifabutin or other drugs metabolized by isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
Drug interactions
Fluconazole
With the simultaneous use of fluconazole and warfarin, prothrombin time increases by an average of 12%. In this regard, it is recommended to carefully monitor prothrombin time in patients receiving the drug in combination with coumarin anticoagulants.
Fluconazole increases plasma T1/2 of oral hypoglycemic agents - sulfonylurea derivatives (including chlorpropamide, glibenclamide, glipizide, tolbutamide) in healthy people. The simultaneous use of fluconazole and oral hypoglycemic agents is allowed, but the doctor should keep in mind the possibility of developing hypoglycemia.
Patients receiving high doses of theophylline or who are at risk of developing theophylline toxicity should be monitored for early detection of symptoms of theophylline overdose, as taking fluconazole leads to a decrease in the average rate of clearance of theophylline from plasma.
The simultaneous use of fluconazole with terfenadine, astemizole or other drugs that prolong the QT interval is contraindicated.
When using fluconazole simultaneously with cisapride, rifabutin or other drugs metabolized by P450 isoenzymes, caution should be exercised.
Azithromycin
Antacids (aluminum and magnesium-containing), ethanol and food slow down and reduce the absorption of azithromycin.
With the simultaneous use of warfarin and azithromycin (in usual doses), no changes in prothrombin time were detected, however, with the interaction of macrolides and warfarin, an increase in the anticoagulant effect is possible. Patients' prothrombin time should be carefully monitored.
With simultaneous use of azithromycin with digoxin, the concentration of the latter in the blood plasma increases.
When azithromycin is used simultaneously with ergotamine or dihydroergotamine, the toxic effect (vasospasm, dysesthesia) increases.
Azithromycin slows the elimination and increases the plasma concentration and toxicity of cycloserine, indirect anticoagulants, methylprednisolone, felodipine, as well as drugs subject to microsomal oxidation (including carbamazepine, terfenadine, cyclosporine, hexobarbital, ergot alkaloids, valproic acid, disopyramide, bromocriptine , phenytoin, oral hypoglycemic agents, theophylline and other xanthine derivatives), due to the inhibition of microsomal oxidation in hepatocytes by azithromycin.
Lincosamides weaken, tetracycline and chloramphenicol enhance the effectiveness of azithromycin.
Secnidazole
Enhances the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents. When used together with ethanol, a disulfiram-like reaction may develop (including abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headache, flushing of the face).
Overdose
Episodes of overdose during treatment using the Safocid tablet kit have not been described. If you accidentally take dosages of the drug that exceed those recommended, the patient should immediately seek qualified help.
Azithromycin
Negative symptoms of an azithromycin overdose are: nausea, vomiting, transient hearing loss , diarrhea .
These manifestations are subject to symptomatic treatment, including the intake of sorbents and control over the vital functions of the body.
Fluconazole
Characteristic symptoms of taking excessive doses of fluconazole are: paranoid behavior and hallucinations .
In this case, symptomatic therapy with cleansing of the gastrointestinal tract and forced diuresis . A 3-hour hemodialysis reduces the plasma concentration of fluconazole by approximately half.
Secnidazole
If an overdose of secnidazole is suspected, in turn, it is recommended to carry out symptomatic and supportive treatment with cleansing of the gastrointestinal tract and taking sorbents.