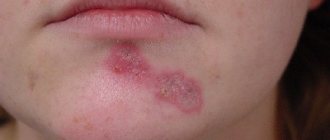
Causes of allergic contact dermatitis
Various factors can trigger the development of allergic contact dermatitis. The first reason is the modern chemical industry with the production of a huge number of chemicals that can cause various types of allergic reactions, including allergic contact dermatitis. These can be paints, varnishes, various household chemicals, some components of cosmetics and perfumes. Synthetic materials used to make clothing and paints can be distinguished. If a person often comes into contact with chemicals at work, then he is susceptible to occupational dermatitis.
Also, one of the main causes of allergic contact dermatitis is taking medications.
Plants can also provoke the occurrence of this unpleasant disease: white ash, hogweed, primrose and others. In such cases they talk about phytodermatitis.
The allergen acts directly on the skin, but the disease process provokes allergic changes that affect the entire body. After an allergen interacts with human skin, the first symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis begin to appear within two weeks. Sensitization of the body and an allergic reaction may appear earlier, it all depends on the strength of the allergen’s effect on the body, which can be weakened as a result of:
- immunity disorders in chronic inflammatory processes;
- predisposition to allergic reactions;
- thinning of the stratum corneum of the skin, etc.
Allergic contact dermatitis with excessive sweating can often be triggered by wearing clothes made from dyed fabrics. It is also possible to identify internal factors that contribute to the disease: a serious malfunction in the functioning of the endocrine system, a metabolic disorder or vitamin deficiencies.
Specifics of dermatitis in children and newborns
Allergic dermatitis is a common disease in children. It is characterized by a chronic course, as well as periods of exacerbations and remissions. At the time of puberty, in many adolescents the pathology disappears completely.
Dermatitis occurs in children for genetic reasons. When a father or mother has an allergy, the baby’s chance of developing it is 50%, if both parents have the disease – 80%. But, the disease develops in a baby only in a situation where the influence of a certain pathogen is added to the genetic factor.
| Manifestations of dermatitis in children |
Dermatitis in infants initially manifests itself as a result of food allergies, created due to a nursing woman’s failure to comply with dietary requirements or the early start of complementary feeding (milk, cereals). Subsequently, the allergic disease is worsened not only by provoking products, but also by other pathogens (dust, fungi, animal hair, various plants). In most babies, the cause of the disease is infection with a certain type of staphylococcus, leading to chronic inflammation of the skin.
The main signs of dermatitis in children:
- itching, burning of the skin;
- sleep disorder;
- gastrointestinal tract disorders;
- hyperemia (redness of the skin);
- anxiety, tearfulness;
- peeling, skin irritation.
With inflammation of the skin and severe itching, the child behaves anxiously, constantly cries, and sleeps poorly. At this point, all possible measures should be taken to relieve symptoms.
Pensioners and young people, do not ruin your skin with pharmaceutical chemicals! Dermatitis can be treated with a natural remedy called...
In children, allergic dermatitis is divided into 3 age categories:
- Infantile - formed in the first or second month of life and lasts up to 2 years. A characteristic rash is localized on the skin folds of the baby, under the knees or in the crook of the arms. Numerous small rashes appear on the face in the cheek area, causing the cheeks to acquire a pathologically crimson tint. The affected areas become wet and crusty.
- Children's dermatitis is observed from 2-12 years. The disease is characterized by redness, itching, with the presence of cracks and erosions. Symptoms often settle on the neck and elbow creases.
- Adolescent – found in girls and boys aged 12-18 years. Most often, the signs of allergic pathology disappear spontaneously, however, on the contrary, it happens that the manifestations intensify significantly. Contact with the irritant causes a rash on the face, arms, legs, and skin folds.
Many young parents do not immediately react to allergic manifestations, thereby worsening the baby’s well-being. In order not to start the disease, you need to seek help from a doctor at the initial signs of a rash or agitation of the baby.
Symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis
Depending on the course of the disease itself, acute and chronic dermatitis are distinguished, which is determined by the frequency of contact with the allergen. In acute allergic contact dermatitis, the site of contact of the allergen with the skin causes skin changes. Sometimes these changes can extend beyond contact. Another feature is the presence of clear boundaries of the lesion. The first symptoms of acute allergic contact dermatitis are redness of the skin and swelling of the tissues. After some time, papules appear and fill with liquid quite quickly. Then they degenerate into bubbles. After healing, crusts form on them, causing severe itching. This process ends with peeling.
The chronic form of allergic contact dermatitis develops against the background of continued exposure to an allergen when an allergic reaction has already occurred. This type of disease is characterized by the spread of inflammatory changes to areas of the skin that are not in contact with the allergen.
As for the lesions on the skin, they have blurred boundaries. Generalization of the process is observed with strong sensitization of the body. The skin becomes covered with formations, papules and lumps appear on the surface. It becomes dry, the skin pattern changes (lichenization). Constant itching provokes the appearance of secondary damage to the skin, as it is scratched (excoriation).
Classification
The classification is based on the clinical symptoms (course) of the skin process, according to which the following are distinguished:
- An acute course, manifested by pronounced bright red hyperemia with predominantly exudative morphological elements (spots, papules, blisters, erosions, weeping). Dermographism (local change in skin color due to mechanical irritation) is persistent, red.
- Subacute course. Hyperemia is less pronounced, pinkish-red in color. In addition to exudative elements, scales, crusts, and infiltration may be present on the skin, mainly at the base of the morphological elements. There is no weeping. Dermographism is not persistent, red.
- Chronic course. Hyperemia of a bluish-reddish color. Exudative elements are practically absent, in places there are scales, crusts, and lichenification. There is no weeping. Dermographism is mixed - red with a transition to white.
Diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis
This allergic disease can be easily diagnosed by its characteristic symptoms. Skin testing can help determine the exact cause of allergic contact dermatitis. To conduct research, special test strips with allergens applied to them are used. The skin is pre-cleaned, after which the strips are glued. An allergic reaction is determined by the appearance of swelling and redness at the site of application. Doctors diagnose and prescribe a course of treatment for allergic dermatitis for each specific case.
For differential diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis and identification of concomitant diseases, the following additional examinations are carried out:
- biochemical and clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- stool analysis for dysbacteriosis;
- blood sugar test.
If necessary, thyroid function tests are performed and the gastrointestinal tract is examined.
Clinical guidelines
Comprehensive treatment of dermatitis begins first of all with the exclusion of the main provocateur (allergen). Therapy involves strict adherence to hygiene rules, the use of only high-quality cosmetics and care products, and restriction from pets. When the pathogens are accurately identified based on the results of the tests, the person should be prevented from coming into contact with this irritant.
If allergic dermatitis occurs in your baby, you must:
- add decoctions of medicinal herbs to bathing water;
- exclude synthetic clothing, fabrics should be hypoallergenic;
- Do not rub the affected skin with a towel;
- wear only comfortable, loose, loose clothing;
- Putting the baby to bed on time is important to follow a daily routine.
If a child with allergic dermatitis is given proper care, the disease can be dealt with faster.
Treatment of allergic contact dermatitis
For treatment of allergic contact dermatitis to be successful, it is necessary to completely eliminate the allergen that caused the disease. If you are allergic to household chemicals, it is recommended to use protective gloves. If you are allergic to synthetic materials, when purchasing clothes, you must carefully study the fabric and its composition; it is recommended to wear only cotton underwear. If you are allergic to metal or metal parts (buttons, zippers, snaps and hooks), you should avoid contact with your skin.
In the treatment of allergic contact dermatitis, the use of corticosteroid ointments is effective: Lokoid, Advantan, Elokom, etc. If large bubbles appear, they need to be punctured. To relieve swelling and itching, modern antihistamines are prescribed: Claritin, Zyrtec, Erius, Zodak, Cetrin, etc.
Treatment methods
There are several treatment options for dermatitis in adult patients. Comprehensive treatment will help get rid of symptoms. But, you should first identify the allergen and try to completely limit contact with it.
Generally accepted rules will help eliminate allergic dermatitis:
- conducting research to determine the type of allergen;
- consumption of vitamin complexes;
- mandatory intake of the required amount of fluid per day (at least 2 l);
- taking antihistamines, sedatives;
- the patient's compliance with the diet and regimen.
Such actions guarantee a favorable outcome from the therapy performed. If rashes have formed on the body and on the face, use internal and external medications.
Systemic treatment
Systematic therapy of allergic dermatitis consists of taking antihistamines. Doctors often prescribe Suprastin, Zyrtec, Claritin, Diazolin, Loratadine. These drugs help relieve symptoms of the disease. Antihistamines relieve itching, redness of the skin, swelling of soft tissues, and reduce the appearance of rashes.
Additional drugs may be:
- sedatives (Persen, Novo-Passit) – eliminate nervous conditions;
- vitamins – make therapy more effective, strengthening the body, increasing regeneration processes;
- enzymes (Linex, Festal, Mezim) - accelerate any chemical processes occurring in cells; products facilitate digestion and increase metabolism;
- sorbents (Polysorb, Enterosgel) – cleanse the body of harmful substances and poisons.
The duration of treatment will depend on the nature of the dermatitis and the timely initiation of action.
Local treatment
Topical preparations will help speed up the elimination of allergic dermatitis. The most effective means are:
- Antihistamines (Zodak, Gistan, Claritin) - medications effectively relieve itching, redness, swelling, and rash. The drug is used to treat the pathological area of the dermis 2 times a day. These products are suitable for treating any type of allergic dermatitis so that it is not caused by chemicals, cosmetics or food allergens.
- Glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone) – hormonal ointments. The substances have a huge number of contraindications and negative effects. As a result, they are prescribed only in situations where the use of antihistamines has not had the desired effect. It should be used strictly as directed and following clear recommendations. Hormonal ointments relieve itching, rashes, urticaria and other manifestations of dermatosis. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin, Tetracycline ointment, Levomekol) are indicated for the infectious nature of allergic dermatitis. Medicines are necessary to prevent formation and in the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
It is important to know! It is not advisable to use ointments for more than a month; addiction to the drugs and their inaction are possible.
Patients with allergic dermatitis are often prescribed calcium gluconate. It turned out that the lack of this component in the body is aggravated by the fact that the symptoms of the skin disease intensify, and along with it the person’s well-being deteriorates.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies provide excellent results, however, these methods must be used after an allergen test, since medicinal herbs themselves can cause allergies. Soothing, anti-inflammatory decoctions prepared from chamomile, string, and calendula are suitable for treating pathological lesions.
Proper nutrition
Diet therapy is not the least important in eliminating allergic dermatosis. It helps speed up the healing process and ensure stable remission. From the menu you need to remove foods that increase sensitization of the body.
Prohibited allergic foods:
- chocolate, candy, honey;
- citruses, strawberries;
- cocoa, coffee;
- eggs;
- tomatoes;
- seafood, fish;
- smoked meats, mayonnaise, spices, marinades;
- nuts.
It is dangerous to eat food that contains preservatives and dyes; these are the strongest allergens. Avoid fried and fatty foods. They increase the absorption of irritating components of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Also reduce, or better yet avoid, sugar and salt.
Pensioners and young people, do not ruin your skin with pharmaceutical chemicals! Dermatitis can be treated with a natural remedy called...
For allergic dermatitis, doctors advise eating black bread, natural apple juice, olive oil, green vegetables, dairy products, herbs, and cereals.
Dermatitis on the skin of the body
A dermatologist can diagnose the disease. Contact him if you notice the first symptoms.
Symptoms
Typical manifestations of skin disease:
- redness
- itching
- combs
- pustules
- peeling skin
Allergic dermatitis can be accompanied by a prolonged runny nose, paroxysmal cough, nasal congestion and sneezing. Acute dermatitis is usually characterized by the formation of subcutaneous blisters filled with colorless liquid. With wet dermatitis, redness and deep cracks form on the skin, from which pus or lymph oozes. Dry dermatitis is characterized by flaking and a feeling of tightness of the skin. Since it is possible to cure your skin, you should never give up, no matter what the symptoms of the disease are!
Atopic dermatitis
Serious chronic disease. It is of an allergic nature: irritation occurs to substances that can penetrate both through contact and through the lungs and stomach. The atopic type often develops in childhood and often remains with a person for life, turning into a chronic form.
Due to the fact that dermatitis is a general name for skin diseases, symptoms and external manifestations of the disease are of great importance in diagnosis.
How to care for skin with dermatitis?
Helping herbs
Many plants have an amazing property - when absorbed into the skin, they reduce inflammation and normalize its structure. Therefore, a common remedy for the treatment of dermatitis is herbal compresses, wraps, and herbal ointments for dermatitis.
You can use a single plant or herbal mixtures that contain several herbs.
- Grind the celandine and squeeze the juice out of the resulting mass. Dilute the juice with boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 2. Use the solution for compresses: soak gauze in it and apply to the affected skin for 10-15 minutes.
- 1 tbsp. Pour 100 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of dry crushed string and leave until a dark brown solution is obtained. Moisten gauze or bandage in the prepared concentrate and apply it to the irritated skin until completely dry (not with weeping dermatitis, otherwise the bandage may dry to the skin). The procedure can be carried out 3 times a day.
Recipe with tar soap
The healing properties of tar have been known for a very long time. This thick oily liquid has a positive effect on the condition of the skin. Birch tar has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, improves blood circulation and stimulates skin regeneration.
You can find tar soap on sale and use it to wash skin affected by dermatitis, or prepare soap according to a folk recipe.
- Mix 100 g of crushed and melted baby soap with 2 tbsp. spoons of any oil, add 2 tbsp. fly in the ointment and 100 ml of water. Mix the resulting mixture until smooth.
Prevention
To prevent the development of allergic dermatitis, you should follow simple preventive rules:
- when working with household chemicals and other products, you should wear protective gloves, and, if necessary, masks;
- strengthen the immune system;
- use natural cosmetics;
- perform personal hygiene measures;
- eat healthy and healthy.
Such simple actions will reduce the likelihood of allergic dermatitis, which will contribute to overall health improvement. In particular, it is necessary to observe preventive measures for women who soon want to become mothers.
Attention! There is no need to be afraid of people with dermatitis. The pathology is not at all contagious; it is not transmitted either by airborne droplets or by shaking hands.
Allergic dermatitis is a disease that, in case of therapeutic inaction, can cause complications (anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema). These conditions can lead to the death of the patient if an ambulance is not called in time. Therefore, it is better to prevent their occurrence. If there are any signs of dermatitis, appropriate measures should be taken.
Reasons for appearance
The main factors that can trigger the appearance of one or another form of dermatitis have already been listed. All inflammation and irritation of skin diseases are the result of remote or provoked causes.
- Remote ones include genetic predisposition or acquired individual predisposition. The latter occurs, for example, due to allergies or a previous infectious disease.
Related causes that trigger the development of dermatitis are various conditions to which the body reacts with skin irritation. These include stress, contact with chemicals, reaction to climate, and hormonal changes in the body.
Regardless of what resulted from the onset of the disease, remember: dermatitis must be treated immediately before it becomes protracted and chronic.