Symptoms of neurodermatitis, treatment and causes Neurodermatitis (or atopic dermatitis, or diffuse neurodermatitis) is a chronic inflammatory disease - allergic dermatitis, affecting the skin of people with a predisposition in the genome, as well as a disorder of the immune status, nervous and endocrine systems, and the functionality of other organs.
The presence of congenital heart abnormalities, clubfoot, hernias, cataracts, etc. in patients also indicates a hereditary factor of atopic dermatosis. Neurodermatitis has a persistent chronic, often recurrent nature, differing in form depending on age, causes, symptoms, as well as the season of the year.
The leading role in the occurrence of neurodermatitis belongs to the nervous system. Synonym for atopic dermatitis. Nowadays the term “atopic neurodermatitis” is also used. The mechanism of development of the disease is neuroendocrine. The consequence of diathesis is transition to childhood eczema - pruritus - neurodermatitis.
Something like that?
In simple words, neurodermatitis is a chronic skin disease provoked by internal somatic factors.
The main “culprits” of the disease are pathologies of the nervous and endocrine systems. There is information that in neurodermatitis, as in atopic dermatitis, a hereditary factor is important, but so far there is no scientific evidence for this assumption.
Thus, a person with pathologies of the nervous system and hormonal disorders is in the “risk zone”, and in order for the clinical picture of the disease to develop, a single provoking factor, for example, stress, is sufficient. It is noteworthy that the role of stress can be not only a psychologically unpleasant situation for a person, but also an increased load on the body’s adaptive abilities, for example, during a sudden climate change.
Causes
Since the tendency to allergic reactions is often hereditary, patients with a similar diagnosis are also diagnosed with other allergic diseases, such as bronchial asthma, urticaria, hay fever, and allergic rhinitis.
In addition to hereditary predisposition, modern allergists point to several other causes of neurodermatitis. Let's list some of them:
- disturbances in the functioning of the body's endocrine system;
- nervous system disorders;
- depression or stress;
- eating foods that can cause allergies;
- various intoxications of the body, including infectious ones.
When neurodermatitis occurs, it is difficult to immediately identify the factor that caused the disease. After all, the allergen may be pollen from a plant, the hair of a pet, pillow filling, and so on. But, as mentioned above, the disease, in addition to allergic, also has a psycho-emotional origin. Therefore, the cause of sudden skin rashes may be depression, chronic fatigue syndrome or mental trauma.
What can cause exacerbation of neurodermatitis?
Exacerbations of neurodermatitis can occur under the influence of various substances to which the body has developed sensitization (hypersensitivity). A sensitized body produces special protective proteins - antibodies, the purpose of which is to neutralize foreign substances (antigens or allergens). However, in the process of binding antibodies to antigens (immune reaction), a cascade of reactions is launched, which causes severe allergic skin damage.
Allergens can be the most harmless substances in the surrounding world, which do not cause allergies in a person who does not have a hereditary predisposition to neurodermatitis.
Exacerbation of neurodermatitis can be caused by:
- allergenic factors – the allergens themselves;
- non-allergenic factors are substances of non-protein origin.
Allergenic factors for neurodermatitis include:
- house dust, namely the mites and fungi contained in it;
- animal hair, bird feathers, namely dandruff particles consisting of proteins;
- plant pollen;
- food products;
- medications;
- microorganisms (bacteria, fungi and viruses);
- aquatic crustaceans (daphnia) used as fish food.
Neurodermatitis can be aggravated by the following non-allergenic factors:
- Emotional stress. Dysfunction of the nervous system disrupts the regulation of allergic processes in the body.
- Intense physical activity. Sweat can cause or worsen skin irritation.
- Changes in weather conditions. Too cold weather increases dry skin, and too hot weather increases sweating.
- Tobacco smoke. Substances contained in tobacco stimulate allergic reactions.
- Food products. May contain plant allergens (pollen, which is part of honey) or substances that stimulate allergies (cheese contains a substance called histamine, which causes itching).
- Pollutants. Toxic chemicals in the air enhance the effects of allergens.
Classification
The division into types of this skin disease is determined by the degree of prevalence on the human skin. So, neurodermatitis comes in several types, namely:
- Limited, present only on some areas of the skin;
- Diffuse, the foci of manifestation of which are the neck, face, elbow joints, popliteal cavities, the most common neurodermatitis is on the hands;
- Hypertrophic with tumor-like manifestation in the groin area;
- Linear, in which itchy stripes appear at the bends of the limbs;
- Psoriasiform - neurodermatitis on the neck and head, in which compacted red lesions appear, covered with small scales;
- Follicular, in which pointed papules appear on hairy areas;
- Decalvating, manifesting itself on the hairy areas of the body with subsequent hair loss.
Each type of neurodermatitis brings significant discomfort to a person, so treatment is required without delay.
Definition
Diffuse neurodermatitis is characterized by extensive rashes and redness of the skin, causing severe itching and discomfort. Unlike localized neurodermatitis, diffuse one can appear on any part of the body and then spread over a large area. Read about localized neurodermatitis in this article.
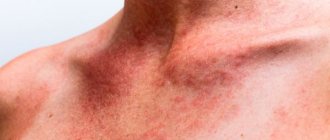
The first signs usually appear on the upper part of the body - on the neck, chest, and can be localized in the armpits or elbows. In adults, neurodermatitis spots are often found in the groin area and on the genitals. In the absence of adequate treatment, the affected areas quickly expand and can cover large areas of skin on the patient's body and face. Self-medication only leads to worsening of the condition and rapid progression of the disease.
The disease has a long course. It is usually encountered for the first time in childhood. During puberty, a new surge of the disease occurs. Then the condition may stabilize. But even one provoking factor is enough for neurodermatitis to worsen.
Sometimes neurodermatitis suddenly appears between the ages of 20 and 30. In this case, after the acute phase, the disease becomes chronic and develops in waves. An exacerbation can occur in women with the onset of menopause due to hormonal changes in the body. Cases of neurodermatitis in elderly people are far from isolated. In this case, the main symptom is not itching, but lichenification of the skin - individual areas become dense, rough, dry, with pronounced hyperpigmentation.
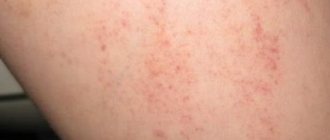
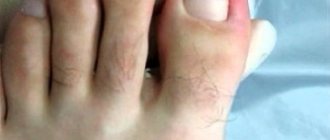
What does neurodermatitis look like?
If you look at photos of neurodermatitis, you will notice that pathological changes occur on the skin of patients. All rashes are accompanied by severe itching, which is why patients cannot stand it and begin to scratch the lesions, thereby causing themselves even greater harm and aggravating the course of the disease.
Symptoms of neurodermatitis
This is a multifaceted disease, during which there is an exacerbation of the symptoms of neurodermatitis in adults, and their remission. Different skin changes may occur at different stages of this chronic process.
The main symptoms of neurodermatitis are characterized by rash, itching, neurotic disorders, redness, and peeling. Moreover, the area of distribution of the disease can be varied depending on its specific variety.
The disease most often affects the flexor surfaces of the extremities (ulnar and popliteal fossae, forearms, wrists), face, buttocks, back of the neck, and scalp. Less common are changes to the palms and soles, thighs, back and abdomen. In general, processes are prone to migration, especially with a protracted course and long-term therapy. Thus, neurodermatitis in children, starting with lesions of the cheeks and scalp, neurodermatitis gradually affects the flexor surfaces of the arms and legs, and then can be diffuse.
It should be noted that the symptoms of neurodermatitis are most pronounced in the winter and in the evening, and in the summer, on the contrary, noticeable improvements are felt. Neurodermatitis on the hands brings the greatest discomfort, since moisture and frequent mechanical stress only worsen the disease.
Skin itching and scratching
Severe itching, intensifying when allergens enter the body (primarily food or drugs), upon contact with water or external environmental conditions (cold air or water, wind). Often provoked by contact allergens (local exposure to glue, creams, detergents). Night itching is characteristic. Scratching – linear excoriation (skin tearing). This is a direct consequence of itching.
Peeling and dryness
For neurodermatitis, it is typically small or large-lamellar. The scales are located in limited areas of often reddened and thickened skin. Excessive dryness of the skin causes easy trauma and disruption of the barrier function.
Cracks
Cracks are tears in the skin due to dryness. Most often they occur along the lines of elastic fibers. Cracks are very typical due to mechanical tension of the skin, especially against the background of unfavorable temperature conditions (cold air) or due to additional degreasing (frequent washing, aggressive detergents, chemical antiseptics). Typical cracks are in the corners of the mouth, in the corners of the eyelids, on the bends of the arms and legs, palms and fingers, and in the subgluteal folds.
Papules
Nodules or elevations of different sizes also occupy limited areas in the form of ill-defined foci. Sometimes, due to the allergic component, papules can be replaced by small pustules (vesicles with transparent contents), resulting from vacuolar degeneration of skin epithelial cells and detachment of the upper layers of the epidermis by intercellular edema.
Hyperpigmentation
These are areas of darkening of the skin along the periphery of the lesions and in places of frequent scratching. Also, with long-term therapy with GCS against the background of hypercortisolism, the skin of the knees, elbows, natural folds and the white line of the abdomen may darken.
Lichenification
These are thickening of the skin, coarsening of its pattern in areas of chronic inflammation and injury. Often have a geographical outline. They are very characteristic of a long-term course of neurodermatitis and persist during periods of remission. Typical features of the patient are thickening and roughening of the lower eyelid.
Getting wet
Occurs in areas of skin damage: in places of scratching or cracks. In this case, blood or lymph is released from the skin defects, which after some time dries out to form crusts.
Areas of depigmentation
Leukoderma is also a long-term symptom that persists beyond exacerbation and is associated with damage to areas of the skin containing pigment cells. As a rule, pigmentation is gradually restored if the skin area is not again subject to exacerbation of the disease.
Features of neurodermatitis in children
Neurodermatitis most often affects children with allergies. The disease develops not only due to allergies to food, wool or pollen. In some babies, a predisposing factor is congenital intolerance to certain substances. Children with an unstable psycho-emotional background and problems with the nervous system are also susceptible to the disease.
How neurodermatitis in children will be treated depends on the specific symptoms. The traditional variant of the pathology is one inflamed focus (a larger number of zones are observed less frequently).
In the acute period, an erythematous area is detected on the skin, which subsequently transforms into a bizarre papule with a diameter of up to 3 mm. Several papules merge into a single lesion of any shape. As the pathology progresses, weeping begins.
Important signs of neurodermatitis in children are:
- dry skin;
- white dermographism;
- the severity of the skin pattern (the lines are drawn most strongly on the palms).
The hyperpigmentation zone reaches several centimeters and smoothly transitions into normal tissue. At different ages of children, neurodermatitis behaves differently. In infants, a rash forms on the neck, face, extensor parts of the limbs and scalp. By the age of 3, the disease is usually cured.
After 2 years, inflammatory changes in the skin of children are observed in the elbow and popliteal cavities. The rash forms on the neck and on the joint surfaces - ankle or wrist. In adolescents, foci of neurodermatitis are localized on the flexor areas of the limbs, hands, lips and eyes.
Dermatologists are developing a treatment regimen for neurodermatitis for children from the following groups of drugs:
- sedatives;
- complexes with vitamins A, E, B;
- glucocorticosteroid ointments (Advantan, Afloderm, Elokom);
- antihistamines (Cetirizine, Loratadine);
- histamine receptor blockers (Cyproheptadine).
During the treatment of neurodermatitis, it is useful to feed the child with fermented milk products, fish, poultry, quail eggs, soybean oil, avocados, and multivitamin juices. It is forbidden to give sweets to the baby.
General symptoms of neurodermatitis and psychosomatics
Since the skin allergic process is not isolated from the entire body and is based not only on allergic, but also on vascular and nervous reactions, neurodermatitis will manifest itself in addition to skin symptoms by changes in general well-being, neurological status and even the psychological appearance of the patient.
Let's consider the symptoms of neurodermatitis in adults associated with psychosomatics:
- Sleep disorders. Most often associated with skin itching during periods of exacerbation. Insufficient night sleep prevents children from adapting normally to children's groups, complicates their learning during the daytime and also increases asthenia.
- Decreased immunity. It is developing in two directions. The initially low level of class A immunoglobulins, which protect the skin and mucous membranes, causes an easier occurrence of purulent skin infections (which is also facilitated by regular trauma and disruption of the barrier function). In addition, the skin is more easily affected by viral agents (molluscum contagiosum, warts, herpes). The general immune status worsens against the background of adrenal cortex deficiency (existing initially and aggravated by long-term glucocorticoid therapy). The outcome is frequent colds and infectious processes.
- Emotional lability. Manifested by instability of mood, increased irritability, outbursts of aggression against a background of frequent depressed mood. This is due to the predominance of sympathetic tone, as well as frequent skin itching, which neuroticizes patients. Less commonly (mainly in adolescents and adults), prolonged depression and desocialization are observed (more often against the background of long-term treatment with glucocorticoids and secondary adrenal insufficiency, as well as awareness of one’s defect in appearance, as well as in diffuse forms with a severe course and localization of pathological processes on the face and other open parts of the body ). In this regard, the palmar localization of the disease is considered the most unfavorable, since frequent exacerbations in these areas, weeping, and cracks disrupt normal self-care and also limit the work activity of patients.
- Asthenization. A general depressed state leads to difficulties in learning, work and everyday life. Fatigue and depression often narrow the circle of communication and interests of patients.
Often neurodermatitis is treated in a very truncated manner and attention is paid only to skin manifestations. For relief of which local treatment is directed. However, it is worth considering the process as a whole and paying attention to all stages of treatment.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of neurodermatitis is made by an allergist - immunologist or dermatologist. The disease is determined after examination by a doctor and undergoing a diagnostic examination, which consists of passing a series of tests. The main task of diagnosis is to identify provoking factors affecting the body.
Most often, the cause is contact with an allergen:
- animal hair;
- products;
- plants;
- household chemicals;
- etc.
A preliminary diagnosis is made based on the following indicators:
- symptoms of dermatitis with characteristic localization;
- dryness and redness of the skin;
- the presence of itching and marks from scratching;
- the presence of allergic diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- stressful condition.
Laboratory diagnostics includes blood tests to measure IgE levels. It is also required to take allergy tests, which reveal the body’s reaction to a specific allergen.
Complications
Long-term use of hormonal ointments for the treatment of neurodermatitis entails the occurrence of recurrent bacterial, viral and fungal infections. Folliculitis, furunculosis, impetigo, hidradenitis are the most common manifestations of infection with Staphylococcus aureus or white Staphylococcus. If a fungus gets on the affected areas of the skin, then neurodermatitis is complicated by candidal cheilitis.
Often, warty tumors form in the area of the disease, which are mainly localized on the sole, back of the hands and in the inguinal folds.
The most severe complication is Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis, provoked by the herpes simplex virus. Eczema is characterized by the appearance of pustules and vesicles on areas of the skin affected by neurodermatitis. The rashes are abundant, round in shape, protrude above the surface of the skin and have a small depression in the center. The elements are protected from healthy skin by a roll of inflamed epidermis.
Mechanisms of development of atopic dermatitis
AD is based on chronic allergic inflammation. The pathogenesis of AD is multifactorial with the leading role of immune disorders. The leading immunopathological mechanism for the development of AD is a change in the ratio of Th1/Th2 lymphocytes towards Th2 helper cells, which leads to a change in the cytokine profile and high production of specific IgE antibodies. The immune trigger for AD is the interaction of allergens with specific antibodies (reagins) on the surface of mast cells. Non-immune trigger factors enhance allergic inflammation by nonspecifically initiating the release of mediators of allergic inflammation (histamine, neuropeptides, cytokines), which have pro-inflammatory characteristics. An important role in maintaining chronic skin inflammation in AD is played by both fungal and coccal skin infections themselves, as well as allergic reactions to components of bacterial and fungal cells.
How to treat neurodermatitis?
Before you begin to treat the disease, you need to stop contact with the identified allergens. If the irritant cannot be identified, then all possible allergenic agents are excluded from the patient’s living environment, including food.
In addition to the use of medications, an adult patient should consider the following recommendations regarding the treatment of neurodermatitis:
- follow a strict diet;
- exclude contact with animals;
- do not come into contact with animal food, in particular fish food;
- Carry out regular thorough cleaning with moisture;
- remove carpets and clean anything that could be a habitat for dust mites;
- wear loose clothing so that it does not rub or injure the skin;
- avoid wearing items made of wool or synthetics;
- do not take baths and showers very often;
- try to avoid stress and overwork.
The primary goal of treating neurodermatitis in adults is to eliminate the inflammatory reaction of the skin and unbearable itching. Then it is necessary to achieve normalization of the nervous system and restoration of the skin structure. At the same time, the doctor prescribes therapy for concomitant diseases that aggravate the course of neurodermatitis (obesity, diabetes mellitus).
How to care for your skin?
Skin care for neurodermatitis in adults is a way to prolong remission (the period of absence of symptoms). In patients with neurodermatitis, the skin is markedly dry. An already weak protective barrier ceases to function under adverse environmental influences. Therefore, skin care is a way to restore the skin barrier function and prevent exacerbation of the disease.
For dry skin, the following rules must be observed:
- Wash your face with warm water several times a day. Warm water better moisturizes the skin, but too hot or cold water can irritate the skin, causing an exacerbation of neurodermatitis.
- Do not use too strong substances (chlorine, ammonia) to clean the bathroom. They can remain on the surface and get on the skin, causing irritation when taking a bath.
- The main therapeutic effect of taking water procedures is to moisturize the skin, so there is no need to rub it with washcloths (this contributes to the formation of microtraumas).
- It is necessary to use hypoallergenic products with a high pH for dry skin.
- It is not recommended to wipe yourself dry after taking a bath. For dry skin, rapid removal of moisture from the epidermis is disastrous.
The following are used as skin care products for neurodermatitis:
- Bepanten cream and ointment. Bepanten contains panthenol or provitamin B5, which promotes regeneration, moisturizing the skin and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Bepanten plus. In addition to panthenol, the drug contains the antiseptic chlorhexidine, which is active against skin bacteria.
- Emollient (synonym - emollient, emollient). These are non-cosmetic products that create a film on the surface of the skin, preventing moisture evaporation. Emollients are available in the form of creams, ointments, sprays, lotions, bath oils and soap substitutes. In addition to the ability to retain water in the skin, emollients eliminate itching and irritation, reduce flaking, soften cracks, protect the skin, and promote deeper absorption of other ointments and creams.
- Universal emollient cream. The cream contains shea butter, thermal water and cerasterol.
- Lipikar Balm. This balm restores the water-lipid mantle. Also available as a hypoallergenic bathing oil.
- Locobase. This is a rich cream (contains a lot of lipids) for very dry skin. Has a moisturizing and regenerating effect on the skin.
- Actovegin (methyluracil ointment). The cream promotes skin regeneration.
- Homeopathic ointment "Calendula". Like all homeopathic preparations, this ointment contains a small (disappearing) amount of active substance, but effectively moisturizes the skin and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Correction of major background disorders
It should include recommendations from a psychologist or psychoneurologist to help eliminate conditions for overwork, sleep disorders, psychoneurotic stress and stressful situations. In order to normalize the psycho-emotional state, drug treatment of neurodermatitis with the use of sedatives, antipsychotics, tranquilizers and antidepressants is also used.
General detoxification and hyposensitizing therapy is carried out through intravenous administration of solutions of sodium thiosulfate and gluconate or calcium chloride. Identified intestinal dysbiosis, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine, hepatobiliary and urinary systems require appropriate correction. In addition, foci of chronic infection in the body are subject to mandatory sanitation.
Drug treatment
It is necessary for a dermatologist to draw up a treatment plan for neurodermatitis, which includes the following drugs:
- Enterosorbents are substances in the form of a powder or gel, which, passing through the digestive tract, capture all harmful substances and toxins and are gently removed from the body. Activated carbon, Enterosgel, and Polyphepan can be used as medicine.
- Diuretics - diuretics cleanse the body well, provoking the renewal of lymphatic fluid, which “preserves” various toxins. Diuretics remove allergens from the body along with urine. Examples of diuretics include Veroshpiron, Hygroton, and Lespeflan.
- Antibiotics – if indicated, when it is revealed that the causative agent of the neurodermatitis process is a bacterial infection. The type of antibiotic is selected using blood cultures.
- Immunomodulators are drugs that help strengthen the immune system so that it can cope with pathologies. Immunomodulators are “Immunal”, “Kagocel”, “Likopid”.
Simultaneously with internal use, it is necessary to treat skin rashes with ointments.
For neurodermatitis, two types of ointments are used:
- keratoplasty (tar, zinc, sulfur);
- corticosteroids (“Sinalara”, “Hydrocortisone”, “Oxycort”).
Keratoplasty ointments act on the skin, softening it and exfoliating it. Thus, the layer of affected skin is quickly and non-traumatically removed, leaving healthy and smooth skin underneath. If the use of the drug was combined with the use of internal drugs, that is, the causes of the pathology were eliminated, such complex treatment gives a long-term therapeutic effect.
Corticosteroid ointments are a broad-spectrum dermatological agent. They eliminate inflammation, itching, swelling and stop the pathological proliferation of connective tissue.
Corticosteroid ointments have a more powerful effect, but at the same time they have a whole range of side effects, so their use should be under the supervision of the attending physician. Keratoplasty ointments can be used independently; they are sold in pharmacies without a prescription, but it is important to use them without violating the instructions.
And finally, physiotherapy procedures have a good effect on neurodermatitis:
- UV treatment;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser treatment;
- "Darsonval";
- baths with various healing compositions.
Treatment of neurodermatitis should have a complex effect: by simultaneously eliminating the root causes, improving the health of the body, using ointments and physiotherapy procedures, a cure or long-term stable remission can be achieved.
See also: a detailed review of ointments for neurodermatitis.
Treatment of neurodermatitis with folk remedies
Traditional medicine can help eliminate the symptoms of neurodermatitis, but is not able to have a significant therapeutic effect. For this reason, it is necessary to combine traditional and traditional medicine.
Treatment of the disease at home has many options for tinctures, ointments, decoctions, etc. These drugs should not be abused in order to prevent a side effect (increased allergic reaction).
- Propolis ointment. Vaseline is heated in a water bath until liquid. Then mix it with propolis in a ratio of 1:10 (most of it is propolis). The cooled ointment is rubbed into the inflamed skin once a day.
- Wax ointment. The product is prepared from beeswax, birch tar and goose fat. All products are taken in equal proportions. The wax, fat and tar are mixed and placed in a water bath (over very low heat) for two hours. Apply the ointment once throughout the day.
- Oak compress. Oak bark is crushed and mixed with birch leaves, coriander, nettle, mint, wormwood and flax seeds. Oak bark is added in the amount of 5 tsp, and all other components one at a time. Pour boiling water over the collection and leave for a day. The compress is applied for 1 hour daily.
The recipes described above can be used if the lesions are not scattered throughout the skin of the body. In cases where the rash is observed in different areas, it is recommended to take herbal baths.
- Crushed birch leaves, potato starch and walnut partitions. You will need a tablespoon of all components for one procedure.
- Sage (15 g), oak bark (50 g), horsetail (30 g), rowan berries (40 g) and mackerel leaves (40 g) are mixed and brewed for fifteen minutes with three liters of water. Then filter the tincture and add it to the bath.
- Yarrow, oregano, plantain and coltsfoot are mixed in equal parts, poured with hot water and after 30 minutes mixed into the bath. First, the herbal infusion is filtered.
Healing baths with the addition of herbs take no more than 30 minutes. After the procedure, the skin is thoroughly wiped to remove moisture and lubricated with olive oil or prepared ointment.
Therapy
Types and methods of treatment of infectious dermatitis
To determine treatment tactics, a dermatologist conducts a blood test for allergens and differential diagnosis of neurodermatitis with chronic eczema and lichen planus. In addition, the patient is prescribed an examination by doctors of various profiles to identify a chronic disease, which could become a “trigger factor” for the recurrence of dermatitis. It is possible to cure an exacerbation of neurodermatitis only with the help of complex therapy, which includes oral medications, ointments and creams, vitamin and mineral preparations, and traditional medicines. Patients may be prescribed physical therapy using hydrogen sulfide and radon baths, as well as ultraviolet irradiation.
During treatment, it is necessary to stabilize the rest regime, adhere to an antiallergic diet, and follow the recommendations of a gastroenterologist, neurologist or other specialist regarding the treatment of the underlying disease, if one has been identified.
Drug therapy
The following groups of drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets for neurodermatitis:
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, Zaditen, Diazolin, Tavegil). They eliminate redness and itching in the affected areas.
- Vitamins A, E, B3 and calcium compounds. Vitamin and mineral supplements improve the condition of the epidermis during illness and reduce peeling.
- If the body is intoxicated, the patient is recommended to take enterosorbents (Polysorb, Polyphepan, Enterosgel, activated carbon).
- Sedatives (valerian tincture, Novopassit). They reduce the patient’s anxiety and irritability caused by severe itching and poor condition of the skin. For diffuse dermatitis, tranquilizers are used that have a stronger sedative effect (Seduxen, Elenium).
- Antibiotics. Medicines in this group are prescribed in the presence of weeping crusts. Mainly used are agents effective against Staphylococcus aureus (Erythromycin, Amoxiclav, Mupirocin).
- If other groups of drugs are ineffective and the disease is severe, internal use of glucocorticoids (Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone) is recommended.
- Preparations for restoring the function of the gastrointestinal tract and adrenal glands, improving blood microcirculation (Curantil, Trental).
Main signs and methods of treatment of bacterial dermatitis
Various ointments and creams are applied externally to the affected skin . They can be hormonal and non-hormonal in nature.
- Hormonal agents (Prednisolone ointment, Triderm, Sinaflan) relieve inflammation and help quickly restore the skin. For limited neurodermatitis, injections into the affected parts of the hands may be recommended. Long-term (longer than 2 weeks) and frequent use of hormonal ointments can lead to stretch marks and atrophy of the skin.
- The effect of non-hormonal ointments is mainly to nourish the skin and reduce peeling (ichthyol ointment, Panthenol, Bepanten), a cooling effect (creams with menthol), drying weeping crusts (Zinc ointment), and relieving irritation (Dermatol cream).
- To prevent infection when scratching the affected areas, use antibacterial ointments that also contain glucocorticosteroids (Oxycort, Corticomycin).
You cannot treat neurodermatitis on your own: all drugs must be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, who selects the appropriate dosage based on the patient’s age, test results and the degree of skin damage.
Folk remedies
In addition to traditional medications, home recipes can also be used to treat exacerbations of atopic dermatitis:
- Herbal baths. To collect, take 1 part each of the herbs nettle, chamomile flowers, celandine, lavender and string, mix thoroughly. Pour 2 liters of boiling water into a glass of the collection and leave for 50-60 minutes. Strain the herbal infusion and add it to a lukewarm bath, take for 15-20 minutes. After the procedure, rinse the affected areas.
- Compresses with herbal tinctures. To prepare the infusion, take 10 g of oak bark, flaxseeds, mint, birch leaves and wormwood, put the herbal mixture in a thermos and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 10-12 hours, then strain and apply for compresses, which are applied daily for 1-2 hours.
- Aloe ointment. To prepare it, you need to take 100 g of aloe juice and lard, as well as 5-10 g of fir oil. Having melted the lard, you need to add aloe juice and oil to it, and then mix well and cool the ointment. You can store it in the refrigerator, lubricating the inflamed areas of the skin daily.
Diet
Proper nutrition for neurodermatitis in adults involves avoiding foods that contain large amounts of carbohydrates, salt, and the use of seasonings. During the acute period, it is forbidden to eat food containing allergens and harmful substances:
- meat and fish of fatty varieties;
- food with added artificial flavors and colors;
- seafood;
- citrus;
- eggs;
- chocolate;
- whole milk.
Drinking clean water will be a useful dietary habit - adults need to drink at least 2 liters of it per day. The diet for neurodermatitis should be based on certain products:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- low fat fermented milk products without additives;
- dietary varieties of boiled meat;
- porridge;
- low-fat broths;
- drinks: rosehip decoction, green tea, compote, mineral water.
Prevention
Prevention of neurodermatitis looks the same as prevention of any disease. Proper balanced nutrition, moderate physical activity, hardening and increasing immunity, avoiding stress. Dermatologists advise people prone to dermatological diseases to wear clothes made from natural materials that do not irritate the skin, so as not to provoke the development of the disease.
Also, during periods of remissions and exacerbations, you should not expose your skin to any irritants, for example, by doing peelings, scrubs, or using creams labeled “slimming” that contain substances that irritate the skin - pepper, cinnamon, menthol. And finally, it is important to protect sensitive skin from high and low temperatures.
Neurodermatitis: treatment with ointments, creams and medications Allergic urticaria: causes, symptoms and treatment at home Dermatitis: symptoms, photos, treatment and prevention Dyshidrotic eczema - what is it and how to treat it?
Preventive measures
The main preventive measure for a tendency to neurodermatitis is the elimination of factors that can provoke an exacerbation of the disease. Experts recommend paying special attention to your diet. Excessive consumption of allergenic foods can cause skin rashes even if you have good immunity.
Preventive measures for neurodermatitis are the following recommendations:
- exclusion from the diet of foods that can cause allergies (or minimal consumption);
- timely treatment of diseases of the endocrine system;
- avoiding excessive physical activity;
- elimination of malfunctions in the digestive system;
- eliminating the lack of vitamins in the body;
- maintaining immunity with special medications;
- prevention of nervous system diseases;
- adequate sleep and nutrition.