Many people do not know what arterial hypotension (AHT, arterial hypotension) is. Hypotension is a condition in which blood pressure drops below 90/60 mm Hg. Art. However, these indicators may vary depending on individual characteristics.
A person who has no idea what hypotension is and why it develops may experience signs of impaired blood supply to internal vital organs. And this, in turn, is already accompanied by migraines, darkening of the eyes, dizziness, and weakness. A patient suffering from hypotension notes the appearance of photophobia (excessive sensitivity to light) and intolerance to loud sounds.
Classification
There are acute and chronic forms. Acute arterial hypotension is expressed by a sharp decrease in blood pressure and vascular tone.
The chronic form of the disease is divided into physiological and pathological hypotension:
- Physiological AGT is caused by a decrease in pressure, but does not pose a threat to human life, and also does not lead to a decrease in his performance. Despite the fact that physiological arterial hypotension is a condition in which low blood pressure is observed, it can be a variant of the norm (normal hypotension).
Physiological AHT does not require treatment, but develops as a result of playing sports or living in high mountains, the tropics, and the Arctic. In this regard, sports and adaptive (compensatory) chronic arterial hypotension are distinguished.
- AHT is called pathological if it disrupts the normal functioning of a person. It is divided into primary (idiopathic, essential) and secondary (symptomatic) arterial hypotension.
There are also drug-induced, orthostatic and hypotension, the causes of which are unknown (unexplained etiology).
Can hypertension turn into hypotension?
Patients often wonder whether hypertension can turn into hypotension. Cardiologists say that hypertension cannot by itself transform into hypotension. However, this does not exclude the possibility that high pressure may drop sharply to low values.
For example, this often happens when there is a problem with the heart, in particular after an acute myocardial infarction or stroke. This is a very dangerous condition that requires immediate and competent medical action.
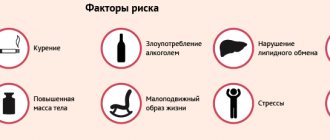
Causes of low blood pressure
- Development of acute AHT
The causes of hypotension are varied. The main causes of severe arterial hypotension are:
- Blood loss;
- Malfunctions of the heart (decreased myocardial contractility - myocardial infarction, acute myocarditis, etc.);
- Lack of water and electrolytes due to diarrhea and vomiting;
- Injuries;
- Poisoning;
- Anaphylactic shock;
- Prolonged stress.
- Development of chronic AHT
Primary hypotension is an independent disease. It develops as a result of neurosis-like conditions accompanied by a violation of the vasomotor center of the brain.
Secondary AHT is a consequence of other diseases, including:
- Anemia;
- Hypothyroidism (a condition in which there is a long-term lack of thyroid hormones);
- Cardiomyopathy (heart damage);
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle);
- Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat);
- Diabetic neuropathy (impairments in the functioning of the nervous system due to damage to small blood vessels due to diabetes);
- Osteochondrosis (damage to the intervertebral discs) of the cervical spine;
- Tumors (pathological formation);
- Infectious diseases;
- Hormonal disorders (decreased functions of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, etc.);
- Heart failure.
- The causes of secondary hypotension can also be the body’s adaptation to various environmental factors, namely:
- Air humidity;
- Climate change;
- Weather changes;
- Exposure to radiation;
- Exposure to electromagnetic fields.
Secondary arterial hypotension can appear due to fasting, as well as with hypovitaminosis (i.e., deficiency) of vitamins E, C, B, pantothenic acid B5.
Chronic sports hypotension develops due to prolonged heavy physical activity. The body, getting used (adapting) to them, begins to “work” in a saving mode. The heart rate (heart rate) decreases and, as a result, hypotension develops.
Among the reasons for the development of arterial hypotension are also poor compressibility and dilatability of blood vessels. Normally, these reactions should occur quickly. In hypotensive patients, they occur slowly and, as a result, both the brain and organs suffer from a lack of oxygen (hypoxia).
If the following medications are taken incorrectly, drug-induced hypotension may develop:
- Nitroglycerine;
- Diuretics;
- ACE inhibitors;
- Beta blockers;
- Alpha blockers;
- Angiotensin receptor blockers;
- Some antidepressants.
Important! Before using any drugs on this list, consult your doctor.
Forecast
If low blood pressure is caused by brain tumors or a severe stage of heart failure, a rare rhythm, serious injuries (car accidents), bleeding, then the prognosis is determined by the success of treatment of the underlying pathology.
In general, the prognosis is favorable; in all patients, in the absence of serious concomitant diseases, it is necessary to eliminate the manifestations of the disease that cause inconvenience in life. All these patients lead a normal and active lifestyle. If symptoms of hypotension are diagnosed in children or adolescents, then there is a high probability of normalization of blood pressure numbers after 25 years (more than 70% of cases).
Symptoms
- Signs of acute hypotension
Acute hypotension is caused by oxygen starvation, due to which signs of hypotension develop such as:
- Dizziness;
- Short-term visual disturbances;
- Pale skin;
- Loss of consciousness;
- General weakness;
- Fatigue.
It is necessary to know what to do in case of hypotension, since acute hypertension often ends in death for the victim. To provide first aid to the victim, you need to perform the following steps:
- Call emergency medical assistance.
- If there is bleeding, stop it.
- Provide access to fresh air.
- Unfasten clothing that is constricting the chest (if the patient is wearing one).
- If the hypotensive person is conscious, then give him special drops (Eleutherococcus extract).
- Signs of chronic hypotension
Symptoms of primary AHT are caused by cerebral hypoxia:
- Loss of strength, weakness, sleep disturbances;
- Irritability;
- Frequent dull, pulsating, bursting headaches, localized mainly in the temporo-frontal, temporo-parietal region;
- During exercise, the heartbeat increases or shortness of breath appears;
- Difficulty waking up in the morning;
- Increased sweating;
- Nausea, dizziness.
With secondary hypotension, the symptoms of the disease that caused the hypotension are expressed. In addition to them, the above-described symptoms of hypotension can be observed in hypotensive patients.
Symptoms such as:
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Problems with potency.
A hypotensive patient experiences drowsiness during the day and wakefulness at night. Therefore, he needs more time to sleep - 8-12 hours. Despite the long period of sleep, he most often feels sleep-deprived, and when he wakes up, he sometimes feels a headache.
In most cases, a person does not notice the course of physiological hypotension (asymptomatic course). The patient becomes ill with orthostatic hypotension (presyncope), as well as when he changes the position of the body in space (from horizontal to vertical).
Why is hypotension dangerous?
Primary hypotension usually has a favorable prognosis. But over time, when it passes, it is often replaced by arterial hypertension. At the same time, people tolerate even a slight increase in blood pressure very poorly.
Progressive hypotension should cause concern, as it threatens the development of the following complications:
- The risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies increases;
- As a result of hypotension, vascular tone is constantly reduced, which leads to a slowdown in blood flow, which means the body experiences oxygen starvation. The brain and internal organs are primarily affected;
- Severe hypotension is dangerous due to fainting. If a person loses consciousness, he or she may suffer serious bruises and injuries;
- In old age, hypotension can cause ischemic stroke;
- Scientists believe that frequent surges in blood pressure increase the risk of developing senile dementia.
Treatment
People live with hypotension for a long time, without paying enough attention to this problem, because they do not think about how hypotension is dangerous. In addition to hypoxia, it can cause the development of cerebral ischemia and stroke. For people who have cardiovascular diseases, hypotension can be fatal.
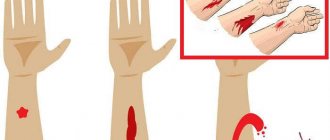
Also, death is possible due to acute hypotension, which is caused by bleeding. Before the ambulance arrives, he must be stopped immediately. There are external and internal bleeding. External bleeding can be arterial (light blood), venous (dark blood), capillary (light blood). The danger in this case is represented by the first two types.
To stop arterial bleeding, you need to apply a tourniquet. It is wound above the injured area (upper third of the shoulder, lower third of the thigh). The tourniquet is applied for no more than 40 minutes, be sure to record the time it is applied. In order to stop venous and capillary bleeding, apply a tight bandage to the bleeding site.
First aid for internal bleeding involves applying cold to the suspected affected area. It is imperative to give the patient a special position, namely:
- Semi-seated, with a bolster located under the knees - bleeding is expected in the chest area (breathing disorders, coughing up blood, cyanosis of the skin are noted);
- Recumbent - bleeding in the abdominal cavity is expected (vomiting with blood, pallor is observed).
The consequences of hypotension for pregnant women are very serious, because not only the vital organs of the mother, but also the fetus itself lacks oxygen. In order to avoid this, you need to contact the appropriate doctor, who will tell you how to treat hypotension and prevent its occurrence. Treatment of hypotension can be medicinal or non-medicinal.
Non-drug treatment for hypotension
With a non-drug method of treating arterial hypotension, it is necessary, first of all, to normalize the daily routine and nutrition. Create a favorable atmosphere in the family and place of work of the hypotensive patient, while eliminating stress. They use massage of the collar area, exercise therapy (physical therapy), and physiotherapeutic procedures. Excessive stress and extreme rest are completely excluded. The following water procedures aimed at increasing the tone (elasticity) of blood vessels are indicated:
- Contrast shower (alternating cold and hot water);
- Fan shower (the stream of water is dispersed, a more gentle shower than Charcot's shower);
- Cool sea baths;
- Charcot shower (looks like an active massage with a jet of water);
- Reflexology (acupuncture) is used.
Drug treatment for hypotension
The fight against acute hypotension, which is caused by fluid loss, is carried out by a doctor by catheterizing the central veins followed by the administration of dextrose, crystalloid and polyionic solutions. If the patient's condition has not improved, then he uses sympathomimetics with air-oxygen inhalation.
If the non-drug method of chronic hypotension is ineffective, then drug treatment of arterial hypotension is prescribed. It includes:
- Plant adaptogens;
- Nootropic drugs;
- Anticholinergics;
- Adrenergic agents;
- Tranquilizers.
The infusion of Chinese lemongrass, ginseng, and eleutherococcus extract has a therapeutic effect. They have a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, reduce mental and physical fatigue, and increase blood pressure.
Nootropic drugs include Piracetam, Pantogam, Phenotropil, etc. Nootropic drugs increase the resistance of the central nervous system to hypoxia, negative toxic effects, and also affect higher brain functions. Sometimes when taking them, it is possible to increase feelings of anxiety and cause headaches.
Bellataminal is classified as an anticholinergic drug. It inhibits the excitability of the central and peripheral cholinergic systems.
Adrenergic agonists are used if there are orthostatic disorders or loss of consciousness is observed. They have a stimulating effect on peripheral adrenergic receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Tranquilizers are prescribed for neurotic symptoms, emotional tension, and hypochondriacal syndrome. Preference is given to tranquilizers that have an activating property (Tofisopam, Trioxazine, etc.). They improve mood and do not cause drowsiness. The doctor may also prescribe medications that improve cerebral hemodynamics. They have a positive effect on brain activity and improve the deformation of white blood cells (erythrocytes).
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies for hypotension is very effective. There are many herbal preparations that increase vascular tone and thereby improve the well-being of hypotensive patients. Such plants include:
- Ginseng;
- Echinacea;
- Chinese lemongrass;
- Eleutherococcus;
- Rhodiola rosea.
It is worth taking these herbal preparations in the absence of contraindications according to the usual regimens indicated on the package.
It is believed that freshly brewed coffee can help prevent low blood pressure. Indeed, the invigorating effect of caffeine has been proven. But, firstly, it is contained much more in green tea, and secondly, caffeine becomes addictive quite quickly, therefore, the therapeutic effect will disappear.
With a general decrease in tone and the so-called blues, St. John's wort can have a slight antidepressant effect, sufficient to treat hypotension.
Non-specific techniques
It happens that the pressure drops quite sharply, and you feel an approaching fainting. To avoid injury, you should:
- Sit on the floor or lie on the bed
- Legs should be raised and head slightly lowered
- Next, rub your earlobes vigorously until they turn red.
- If the condition improves, you can lie down so that your head hangs down slightly
- After an attack, you should eat or drink sweet tea
Every person suffering from hypotension must understand that only a comprehensive, consistent, individually tailored approach to the treatment of the disease with its multiple organ symptoms will control the course of hypotension, stop its progression and improve the quality of life!
Author:
Sabuk Tatyana Leonidovna hygienist, epidemiologist
What are we eating?
A hypotensive person's morning begins with coffee. And rightly so - caffeine is a great tonic. What to eat? Not cottage cheese or porridge, but a sandwich with butter and cheese - this is the perfect balance of fat and salt, which increase blood pressure. Moreover, it is better to choose hard varieties of cheese: they contain substances similar to serotonin. Nuts and fruits are perfect for office snacks - the vitamin C they contain helps blood vessels work better.
For lunch, be sure to have a meat or fish dish; they contain the proteins you need. Hypotonic people may not limit themselves to spicy foods and spices, which constrict blood vessels and increase blood pressure.
Products containing potassium are very useful - dried apricots, beans, seaweed, prunes, raisins, peas, potatoes and others. Potassium helps prevent vascular spasms and keeps blood pressure at the same level. During the day, drink strong sweet tea with lemon or a slice of dark chocolate. In the evening, do not forget about dairy products. Try to eat little but often - do not overload your body with a large amount of food eaten at one time. This lowers blood pressure.
Diagnostics
A set of diagnostic measures is aimed not only at making the correct diagnosis, but also at establishing the causes of arterial hypotension and determining the type of its course.
Primary diagnostic procedures are carried out by a cardiologist and involve:
- studying the medical history of not only the patient, but also his closest relatives - to determine the occurrence of symptomatic hypotension or its development against the background of a genetic predisposition;
- collection and analysis of a person’s life history - will indicate the course of physiological and primary hypotension, as well as changes in tonometer values caused by orthostasis;
- conducting a thorough physical examination of the patient - this includes measuring blood tone three times with an interval of 5 minutes. In addition, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring and listening to the patient using a phonendoscope will also be required;
- a detailed survey of the patient - for the doctor to draw up a complete symptomatic picture, which will indicate the severity of the disease, as well as the possible pathological root cause of low blood pressure.
Laboratory studies are based on the following procedures:
- general clinical blood test;
- orthostatic test;
- blood biochemistry;
- general urine analysis.
Instrumental diagnostics involves the following:
- Ultrasound of the heart and abdominal cavity;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels;
- ECG both at rest and with stress tests;
- EchoCG;
- electroencephalography;
- cardiointervalography.
If, after performing the above diagnostic measures, the clinician was unable to determine the predisposing factor, the patient may be referred for additional examination to:
- pediatrician;
- obstetrician-gynecologist;
- ophthalmologist;
- endocrinologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- neurologist.
First aid
With the development of a hypotensive crisis and fainting, it is important:
- Place the person in the feet-over-head position. If this happens in transport and there is nowhere to put it, you can lower your head down below your knees.
- Unbutton your clothes and, if possible, provide access to fresh air.
- If the person is conscious, calm him down and give him water to drink.
- You can rub your ears and massage the collar area and fingertips (the endings of many of the body’s energy channels are located here).
- In case of prolonged fainting, call an ambulance.
Development mechanism
The pathogenesis of arterial hypotension, regardless of the causes of the disease, is always associated with one of the following factors:
- Decrease in circulating blood volume. Occurs with internal/external bleeding.
- Decrease in cardiac output and stroke. Diagnosed with diseases of the cardiovascular system, for example, with atherosclerotic and myocardial cardiosclerosis.
- Decreased venous blood flow to the heart. Develops with an overdose of ß-blockers, heart attack (myocardial dysfunction), severe forms of arrhythmia.
- Reduced resistance and tone of peripheral vessels. It is a consequence of collapse of an infectious or toxic nature, anaphylactic shock.
Raise the tone
Many hypotensive people experience attacks of weakness and drowsiness in the middle of the day. In this situation, a simple exercise helps restore tone. Sit on a chair with your legs apart and your arms crossed behind your head. Take a deep breath and slowly bend towards your knees. Straighten up and exhale sharply. Repeat the exercise three times.
The best medicine for hypotension is sleep. Moreover, you need to sleep at least 9–11 hours a day!
If possible, try to take a walk outside for at least half an hour before going to bed. Don't sit too long in front of the computer or TV. To fall asleep faster, it is useful to do this procedure at night. Fill the bathtub with cool water to cover your ankles and walk in the water for a few minutes. Then rub your feet with a towel until they are warm, put on wool socks and go to bed.
A simple breathing exercise that needs to be performed 5-7 times without getting out of bed will help you get an extra boost of energy early in the morning. Lying on your back, inhale deeply, inflating your stomach, then exhale slowly - your stomach smoothly lowers and presses inward. This type of breathing improves blood flow and raises the tone of the nervous system.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0.01 | 3.1 | 6.3 | 13 | 20.8 | 26.7 | 0 | 0.01 | 6.5 | 12.4 | 18 | 23.6 | 32.9 |
When to take medications
Drug correction is carried out if it is not possible to stabilize the patient’s condition with the help of a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and elimination of mental stress.
Medicines that increase blood pressure should be taken for conditions such as:
- orthostatic hypotension (OH);
- decrease in blood pressure: systolic by 20 mm Hg. Art. and diastolic by 10 mm Hg. st;
- shock;
- collapse.
People at risk should take medications for OH:
- elderly patients;
- patients with diabetes mellitus.
Sometimes a person suffering from primary hypotension does not know what to drink for hypotension. The patient must remember the clinical symptoms and tell the doctor about them, who will establish the main diagnosis.
General contraindications
Tablets that increase blood pressure are not prescribed to people suffering from diseases such as:
- pheochromocytoma;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- prostatitis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- obstruction of the urinary tract;
- arrhythmia;
- pregnancy;
- renal failure.
The list of contraindications is supplemented by such conditions as:
- TBI;
- concussion or bruise of the brain;
- abdominal pain;
- eclampsia;
- acute cerebrovascular accident;
- epileptic seizure.
What a patient needs to drink when their blood pressure drops is easy to find out at a doctor’s appointment, taking into account concomitant diseases. Vasodilator drugs for the brain, for example, Piracetam in large doses, cause agitation, dizziness, and worsen the patient’s condition. Cinnarizine promotes drowsiness and decreased response to external stimuli.
If the patient has developed a chronic form of hypotension, before taking the pills it is necessary to exclude the presence of symptoms of hidden blood loss, neurological or mental diseases. It is dangerous to take medications on your own without knowing the cause of the disease.