The organs of vision are often exposed to various injuries. One of the most common injuries to the visual system is an eye burn, which can occur under the influence of chemical, thermal or other factors. This ophthalmological problem is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms and can cause blindness. To avoid serious complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time and begin adequate treatment.
Causes
The main cause of eye burns is exposure to high temperatures or chemicals on the tissues of the visual organs. Burn injuries occur due to exposure to the skin and mucous membranes of the following substances:
- fire;
- steam fumes;
- hot liquids or objects;
- incendiary mixtures;
- acids;
- alkalis;
- poisonous plants;
- ultraviolet;
- infrared radiation.
Incorrect handling of aerosols, gas or pepper spray, paints and varnishes, and insecticides can also cause eye burns.
Most often, such injuries are industrial (for example, lime with calcium carbide).
Dangerous substances in our home
The most common burns occur due to exposure to alkali or various acids. Despite the fact that product labels always contain ingredients and instructions for use, consumers quite often ignore this, knowing in advance what’s what.
Therefore, the main chemicals that are found at home and can cause burns are:
| Common acids | Products |
| Sulfuric acid - its concentration in the product can vary from 8% to almost pure acid |
|
| Nitric acid |
|
| Hydrofluoric acid is a weak acid and in dilute form will not burn or cause pain on contact. |
|
| Hydrochloric acid – concentration ranges from 5-44% |
|
| Phosphoric acid |
|
| Basic alkalis | Products |
Sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide
|
|
| Sodium calcium hydrochloride |
|
| Ammonium |
|
| Phosphates |
|
As you might guess, the main causes of burns are inattention and violation of safety precautions.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eye burns may vary depending on the degree of damage to the visual apparatus. Most often, only the mucous membrane is damaged, but sometimes deeper ocular structures are also affected. When the retina is burned, blood circulation and material metabolism are disrupted, and as a result of tissue breakdown, intoxication begins. The appearance of such an injury in a mild form is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- hyperemia of the eyelids and skin around the eyes;
- redness of the cornea;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- soreness;
- burning, itching;
- increased sensitivity to light.
If the degree of damage to the organs of vision is high, then the symptomatic manifestations are more pronounced, and the following additional signs are observed:
- clouding of the cornea;
- inflammation of the eye vessels;
- violation of intraocular pressure;
- blepharospasm;
- tearfulness;
- severe discomfort;
- sensation of a foreign body under the eyelid.
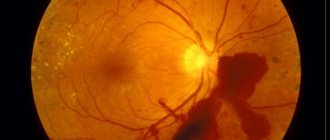
In the most severe cases (for example, when the retina is burned by a laser), a serious disruption of the structure of the ocular apparatus occurs: the sclera is exposed, and the conjunctival tissue begins to undergo necrotic changes, as a result of which an ulcerative formation is formed, which scars over time.
Electricity burn
A characteristic feature of this burn is:
- painless course
- clear separation of necrotic and healthy tissues,
- aseptic course.
Deep damage causes eyelid distortion and regurgitation, and can cause fundus hemorrhages retinal detachment . They also cause clouding of the cornea and lens, which can lead to cataracts. In the event of an electric shock (or lightning), cataracts (called electrical cataracts) can affect both eyes. Treatment is symptomatic. Due to the aseptic effect, there is no need to take an antibiotic.
Electric shock and lightning are associated with much more serious and life-threatening illnesses than damage to the eyeball. Actions at the scene of the accident are to move the victim to a safe place (in case of electric shock, first turn off the power!!!). Then assess his condition (in case of cardiac arrest, begin resuscitation!) and call an ambulance.
Classification
Taking into account the depth of tissue damage, 4 degrees of burn injuries to the organs of vision can be distinguished:
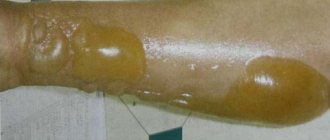
- First degree. There is a burn of the eyelid, which manifests itself in the form of hyperemia, swelling, and discomfort. Surface erosion forms, which after some time disappears without a trace.
- Second degree. The damage is more extensive. Immediately after a burn from the cream around the eyes, bubbles form on the surface of the eyelids, the cornea becomes cloudy and uneven, the conjunctiva swells and shallow tissue necrosis begins.
- Third degree. Necrosis of the conjunctiva spreads to nearby tissues, almost half of the eyeball is affected. The cornea becomes dry and acquires a gray-yellow tint. Cartilage and sclera begin to die, various pathological processes develop (cataracts, iridocyclitis).
- Fourth degree. There is deep necrosis, irreversible changes in the cornea and severe complications from the ophthalmology section.
Depending on the type of etiological factor, there are 3 types of eye burns. Let's consider them further.
Thermal
Thermal damage results from exposure of the eyeball to high temperatures. This injury is the least dangerous and most often occurs as a result of interaction of the eye shell with a burning cigarette, fire, boiling water or hot oil. Thermal damage can also result from improper handling of flammable items, particularly firecrackers and fireworks. In most cases, only the outer part of the visual apparatus, together with the adjacent skin, is affected.
Chemical
A burn to the mucous membrane of the eye with alkali is a more serious problem, since the chemical liquid penetrates deep into the structure, affecting most of the tissue.
Chemical burns to the retina are a more serious injury that occurs due to the interaction of the eye membrane with an acidic or alkaline substance. In most cases, corneal damage is caused by ethyl alcohol, ammonia or slaked lime. Damage to the eyes with acid is less dangerous, since a scab is formed, due to which only the upper tissues die, the substance does not penetrate into the deeper layers.
Read in a separate article: Eye burns from quartz and ultraviolet lamps: what to do
Radiation
Radiation burns of the eyes are less common than other types and are the result of exposure to ultraviolet or other radiation on the eye shell. Depending on the length of the radiation wave, the upper layers of the cornea or the retina along with the choroid may be affected. Most often, light burns of the eye occur as a result of non-compliance with safety regulations when working with welding or visiting a solarium. There are cases where the injury is caused by exposure to sunlight in the mountains (snow blindness), quartz or various laser equipment. Symptoms of radiation injury appear after some time.
If the visual organs are negatively affected by several agents simultaneously, a combined eye burn is diagnosed.
Degrees
There are several degrees of severity of eye burns:
- First. In mild cases, hyperemia of the skin of the conjunctiva and eyelid occurs. Symptoms disappear within a day.
- Second. In this case, the upper layer of skin around the eyelids is burned, the conjunctival tissue swells, and the first stage of epithelial necrosis appears. The cornea becomes cloudy and irregularities appear on it. After a while, burn blisters form around the eyelids.
- Third. The main symptom is pronounced necrosis of conjunctival tissue and cells of cartilage, eyelid, and sclera. The eyes become yellow, the cornea becomes cloudy and dries out. Cataracts subsequently develop.
- Fourth. A person develops deep necrosis of the sclera and conjunctiva. The cornea turns into a white plate.
First aid
Immediately after an incident involving a retinal burn occurs, the victim must be given first aid. In case of damage to the organs of vision by a chemical substance, the following actions must be taken:
- Rinse your eyes well with plenty of clean water or saline solution for half an hour.
- If the eye has been affected by acid, it should be washed with a solution of soda or potassium permanganate.
- When the eye membrane is exposed to alkali, it can be neutralized with acetic or boron solution.
- If there are foreign particles on the conjunctiva or cornea, they should be carefully removed.
- A sterile bandage is applied, after which the patient is sent to the hospital.
In case of a thermal burn of the eye, the first step is to rinse the eyes well with running water (the temperature should not exceed 18 degrees), then drip anti-inflammatory and analgesic eye drops, apply an antiseptic (Levomycetin), apply a bandage and send the victim to the hospital.
Diagnostics
A burn to the external tissues of the eye has a characteristic clinical picture ; additional diagnostic methods may be required only if the symptoms are mild (if the burn is first degree).
To detect damage to the cornea, a special liquid containing fluorochromes—substances that glow in ultraviolet light—is instilled into the patient’s eye. If there are cracks or ulcers on the surface of the cornea, then the pigment accumulates unevenly at the site of damage.
To assess the condition of the retina, the doctor examines the fundus of the eye. For this, you may need drugs that dilate the pupil (atropine, cyclomed, tropicamide, etc.). The visual function of the eye is also checked.
Medical treatment of burns
What to do if there is an injury to the visual organs? After emergency first aid has been provided, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist, who, based on the diagnostic results, will select the appropriate treatment. How to treat burns? For burn injury to the organs of vision, the following medications may be prescribed:
- antibacterial eye drops and ointments: Tetracycline, Levomycetin;
- regenerating eye gels: Dexpanthenol, Dialysate;
- anti-inflammatory drops: Dexamethasone, Dexapos;
- analgesics: Alcaine, Dicaine 0.3%;
- glucocorticosteroids: Maxitrol, Betamethasone;
- antihypertensive drugs: Dorzolamide.
Additionally, in stationary conditions, ocular instillations of cytoplegic drugs (Atropine) and various injections are performed. In addition to drug treatment for eye burns with oil, physiotherapy and eyelid massage are prescribed. In severe cases, surgery is performed.
Therapeutic measures
After hospitalization, the victim must be given a dose of antitetanus serum.
Medical care is provided in a hospital. Treatment tactics are determined by an ophthalmologist based on the type and severity of the damage. Medication courses are used. The administration of antitetanus serum to the victim is indicated. During the recovery period, physical therapy methods such as eyelid massage, electrophoresis with medications, thermal and ultrasound procedures will help. You can also use herbal remedies. In case of severe pathology with complications, surgical operations are indicated.
Timely and competently provided first aid and subsequent therapy allows you to avoid serious complications.
Traditional treatment drugs
Conservative therapy involves the use of medications to reduce pain and inflammation, prevent the appearance of adhesions, scars, bacterial infections, and accelerate regeneration. Topical ointments and eye drops, oral medications are used, and injections are made into the fold of the conjunctiva or under the lower eyelid. The following medications are used to treat eye burns:
The hormonal drug Betamethasone is administered to a patient with a severe burn.
- Anesthetics: “Novocaine”;
- "Dikain".
- "Ciprofloxacin";
- "Scopolamine."
- "Betamethasone."
- "Dorzolamide."
- eye gel "Korneregel".
Treatment with folk remedies
Grated potatoes make a good compress for damaged eyesight.
During the recovery period after injuries to the visual apparatus, you can use herbal remedies at home. Thermal burn of the cornea of the eye, which was caused by boiling water, can be cured with compresses of grated raw potatoes, linden decoction, infusion of chamomile, calendula, linseed oil and St. John's wort. After using such products, the burn goes away faster. Lotions using oak bark and peppermint are useful. To quickly heal a burn to the conjunctiva and eyelids, you can lubricate them with a mixture of beeswax, rosin, olive oil and baby cream boiled over a fire. Honey will help to avoid corneal clouding, but it can only be used after the acute period has ended.
Surgery
The decision on the need for surgical intervention is made by the attending physician. The surgical method is used if there is a severe and deep chemical burn, there is a threat of blindness, loss of the eyeball, or when it is not possible to remove the harmful agent from the eye. Various surgical techniques are used:
- removal of non-viable tissue;
- removal of the vitreous body;
- replacement of damaged structures of the ocular apparatus with donor ones;
- elimination of eyelid defects using plastic surgery;
- eyelash restoration;
- treatment of glaucoma and cataracts.
Possible complications
Untimely or incorrectly provided first aid for an eye burn can cause the following serious complications:
- atrophy of the eyeball;
- cataract;
- trichiasis of the century;
- thorn;
- glaucoma;
- uveitis;
- iridocyclitis;
- inflammation of the iris;
- closing the palpebral fissure.
First-degree eye burns usually resolve without any negative consequences. More severe injuries can provoke changes in the structure of the eyeball, scarring of the eyelids, and obstruction of the tear ducts. In advanced cases, vision loss is observed.
Prevention
Prevention of eye burns involves following safety rules when working with fire, chemicals and harmful radiation. It is also necessary to regularly visit an ophthalmologist and promptly treat existing pathologies. If an injury does occur, proper first aid must be provided.
Author of the article: Elena Nikolaevna Sedova, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Diagnostic measures
To assess the extent of the damage, the doctor examines the patient using eyelid lifters. If necessary, the following research methods may be prescribed:
- determination of visual acuity;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- biomicroscopy using special dyes.
Other studies may be carried out according to indications. Quite often, the doctor prescribes a general blood test to assess the functioning of the whole body.