Uterine bleeding is the discharge of blood from the vagina, characterized by abundance and duration. This pathological condition poses a danger to the life and health of a woman and is a sign of serious diseases of the reproductive system.
To save the patient, it is important to immediately provide her with first aid and find out the cause of the bleeding.
Natural bleeding from the vagina is called menstruation. Menstrual bleeding is characterized by cyclicity and repeats at regular intervals. The period between menstruation usually lasts 25–30 days.
Blood from the vagina should not be released for more than 8 days, otherwise we can talk about pathology. Menstrual irregularities are a reason to immediately consult a gynecologist. The doctor will find out the cause of the pathological phenomenon and help get rid of the disease at an early stage, before complications arise.
Mechanism of development of uterine bleeding
The source of blood secretion is the endometrium - the internal mucous lining, which is shed with each menstruation.
After the endometrium is rejected, the spiral arteries become exposed and bleed. Normally, this process stops quickly. If the hormonal balance is disturbed, then treatment with hormonal drugs will be required to stop the bleeding.
At what age can bleeding begin?
Blood from the uterus most often appears between the ages of 18 and 45, but there is a risk of the disease occurring in adolescence and even during the neonatal period.
In newborns, the phenomenon is temporary and not associated with disease. In adolescents, bleeding from the vagina indicates the need for a comprehensive examination.
Diagnostics
Photo: i1.wp.com
Initially, the nature of the disturbing complaints is established, then the date of menarche and last menstruation is specified. It is especially important to clarify the time of onset of bleeding, as well as possible factors preceding it. After the interview, the doctor begins a gynecological examination, which includes examination of the external genitalia and the vestibule of the vagina, examination using a gynecological speculum, vaginal examination (manual, bimanual) and, if necessary, rectal examination.
Next, using laboratory diagnostics, the level of hemoglobin in the blood serum is assessed and the indicators responsible for blood clotting are determined. In addition, if necessary, the level of the following hormones is determined: estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, LH (luteinizing hormone), FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), cortisol, T3 (triiodothyronine), T4 (thyroxine), TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone).
Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, pelvic ultrasound is performed first. Using a standard ultrasound examination, the structures of the uterus, ovaries, retrouterine space and bladder are assessed. An increase in ovarian volume during the intermenstrual period indicates the possibility of juvenile uterine bleeding. In addition, periodic ultrasound examination of the ovaries allows you to monitor the growth of the follicle, thereby monitoring the ovulation process. In rare cases, the cause of uterine bleeding may be a hormonally active ovarian formation, which is also detected using this study.
If there are certain indications, hysteroscopy is performed - a minimally invasive method of examining the uterine cavity using a special optical device (hysteroscope). In addition, separate diagnostic curettage can be performed. During this procedure, the functional (superficial) layer of the uterine mucosa is removed, after which a histological examination of the resulting material is carried out.
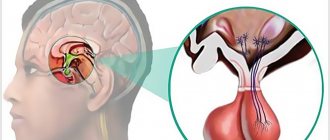
To assess the state of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, which performs a regulatory function, the following studies may be prescribed:
- radiography of the skull with a projection of the sella turcica;
- echoencephalography is an ultrasound diagnostic method that allows you to assess the state of brain structures, as well as indirectly judge the state of cerebral vessels;
- EEG (electroencephalography) is a research method that allows one to study the functioning of the brain by recording electrical impulses emanating from its individual zones and areas;
- CT (computed tomography) of the brain is an x-ray diagnostic method that uses a series of layer-by-layer x-rays in different planes. This technology makes it possible to study the organ under study in more detail;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain is a non-invasive research method based on measuring electromagnetic fields emanating from the organ under study.
If necessary, an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands is prescribed.
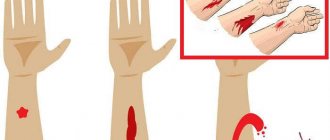
Symptoms of uterine bleeding
Signs of blood loss are:
- cardiopalmus;
- weak pulse filling;
- hypotension;
- decreased ability to work, weakness;
- pale skin;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- confusion, fainting.
How to distinguish from menstruation
- Clots appear in the discharge.
- Discharge increases at night.
- More than 5 pads are used per day.
- Menstruation lengthens.
- Blood appears after sexual intercourse.
- There is pain in the lower abdomen, an unpleasant odor, and an increase in body temperature.
Prevention
- Activities that strengthen the body: proper work and rest schedule, proper nutrition, absence of stress and negative emotions.
- Using 1-2 monthly anti-inflammatory drugs for the first time.
- For the first time , use drugs that stop bleeding for 1-2 months.
- Hormonal therapy. The approximate duration of therapy is from 3 months to six months. The weak effectiveness of such treatment indicates an incorrectly diagnosed cause of bleeding or incorrect selection of the drug or its dosage, susceptibility, or early cessation of therapy.
- Vitamin complex: vitamin C 1 g. per day starting from the 16th day of the cycle, for 10 days; folic acid 1 tablet. per day from the 5th day of the cycle for 10 days; tocopherol acetate for 2 months, multivitamin and mineral products that contain iron and zinc.
- Medicines that calm and stabilize the nervous system.
- Physical education, fitness, swimming, jogging, yoga, and dancing have quite a beneficial
Treatment methods
Uterine bleeding in life-threatening situations is stopped by taking the hormonal drugs Rigevidon, Marvelon, Mercilon.
To stop the bleeding, a therapeutic and diagnostic curettage is performed, during which a tissue sample is taken.
Drug therapy
Treatment to prevent blood loss is prescribed by a gynecologist, mainly:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- iron supplements for low hemoglobin;
- medications that increase blood clotting;
- means for contracting the uterus.
Infusion methods
Infusion therapy is aimed at restoring the volume of circulating blood.
In case of extensive blood loss, the following is transfused:
- red blood cell mass;
- whole blood;
- fresh frozen plasma.
Surgical methods of treatment
If the effectiveness of drug and infusion treatment is low, surgery is performed to cleanse purulent foci and eliminate endometrial remnants.
Depending on the intensity of bleeding, they resort to:
- hysteroscopic ablation of the endometrium;
- diagnostic curettage;
- removal of the uterus.
Traditional recipes for stopping bleeding
Traditional methods of treatment are used as additional methods of combating the disease.
They take infusions of nettle, water pepper, yarrow, viburnum bark, horsetail, knotweed, shepherd's purse, and hogweed.
Drug therapy
Treatment of diseases that cause bleeding from the uterus is carried out in a hospital setting. Additionally, the doctor prescribes medications to the patient to help stop the bleeding.
Hemostatic medications are taken only on the recommendation of a medical specialist; taking medications at your own discretion is strictly prohibited.
Below is a list of medications most commonly used to stop bleeding.
- Etamzilat . This drug stimulates the synthesis of thromboplastin and changes the permeability of blood vessels. Blood clotting increases, resulting in decreased bleeding. The medication is intended for intramuscular injection.
- Oxytocin . A hormonal drug often used during childbirth to improve uterine contractility. As a result of contraction of the uterine muscles, bleeding stops. The drug oxytocin is prescribed for intravenous administration with the addition of glucose and has a large list of contraindications.
- Aminocaproic acid . This medicinal substance prevents blood clots from dissolving under the influence of certain factors, thereby reducing bleeding. The medicine is either taken orally or administered intravenously. Treatment of uterine bleeding with aminocaproic acid is carried out under close medical supervision.
- Vikasol . The drug is based on vitamin K. With a deficiency of this vitamin in the body, blood clotting worsens. The medication is prescribed to patients who have a tendency to uterine bleeding. However, vitamin K begins to act only 10–12 hours after entering the body, so it is not advisable to use the drug to stop bleeding in emergency cases.
- Calcium gluconate . The drug is prescribed for calcium deficiency in the body. Deficiency increases the permeability of vascular walls and impairs blood clotting. This medicine is also not suitable for use in emergency cases, but is used to strengthen blood vessels in patients prone to bleeding.
First aid for uterine bleeding
If there is bleeding, call an ambulance. The patient should be reassured, air access should be provided, and sweet tea should be offered. To stop the bleeding, you can lie on your stomach. In this position the condition improves slightly.
What not to do
- take warm baths;
- warm up the genital area;
- use a syringe;
- take any medications without a doctor's prescription.
What to do
- put the patient to bed with her legs elevated;
- a cold compress is placed on the stomach;
- Give rosehip infusion.
It is allowed to take Etamzilate or Dicinone tablets at home.
Recommendations
- If you are pregnant, you must register for pregnancy at the antenatal clinic.
- Systematically, at least once a year, undergo a medical examination - check the level of hormones, the condition of the organs of the reproductive system, and take all necessary tests.
- Do not delay treatment of chronic infections or diseases of the reproductive and reproductive systems.
- Keep a close eye on your menstrual cycle.
- Do not take hormonal medications without consulting a specialist (this also includes contraceptives).
- Maintain intimate hygiene.
- Protect yourself from sexually transmitted diseases.
- Watch your weight.
- Avoid overexertion, stress and overwork.
- Plan your pregnancy to avoid abortion.
- Boost your immunity, strengthen yourself, play sports.
Complications
As a complication of dysfunctional uterine bleeding in adolescence, acute blood loss syndrome . But if such a complication occurs in physically healthy girls, then we are not talking about a fatal outcome. In addition, with bleeding, anemic syndrome , the occurrence of which is associated with the intensity and duration of bleeding. Cases of death due to bleeding during puberty are usually associated with the presence of acute multiple organ disorders resulting from severe anemia, as well as the occurrence of irreversible systemic disorders. They develop as a consequence of chronic iron deficiency in girls who suffer from intense uterine bleeding for a long period.
If there is no proper treatment, then dysfunction of the ovaries can subsequently lead to infertility in a woman (so-called endocrine infertility ).
Kinds
According to the nature of the manifestation and the factors of occurrence, uterine bleeding is usually divided into several types:
- dysfunctional;
- atonic;
- hypotonic;
- acyclic;
- breakthrough;
- anovulatory;
- discirculatory.
Dysfunctional
In healthy women, blood flows from the vagina only in the form of menstruation. At this time, the non-viable egg and the endometrial layer that has been rejected are removed from the uterus. If there is a failure in the body’s production of hormones, then there is a risk of follicular atresia. This phenomenon is a condition in which the maturation of the egg does not occur.
Features of the condition are as follows:
- The follicle grows to the desired size, but its rupture is blocked. This provokes a whole series of deviations.
- The formation of the corpus luteum does not occur.
- The amount of progesterone remains at the same level.
- Due to a lack of the hormone progesterone, the menstrual cycle cannot complete.
- During this period, the endometrium grows greatly.
All of the above phenomena lead to the fact that the woman’s uterus begins to bleed heavily.
There are several explanations for this pathology:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands.
- Disturbances in the activity of the pituitary gland.
- Endometriosis, benign and malignant tumors, polyps in the uterus.
- Increased production of thyroid-stimulating hormones, the production of which is responsible for the thyroid gland.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Uncontrolled use of anti-inflammatory medications and incorrect selection of hormonal drugs.
The dysfunctional type is usually divided into several subtypes. According to age criteria, there are 3 categories:
- juvenile (11-18 years old);
- reproductive (from 18 to menopause);
- menopausal.
Atonic
You need to understand what atony is. This is a medical term that refers to the complete absence of contractile function and tone of the uterus. The bleeding that occurs with this pathology is called atonic.
Bleeding from the vagina against the background of atony occurs relatively rarely. Doctors have still not been able to accurately determine the impetus for the appearance of atony. Doctors believe that in some cases the lack of contractions is a congenital pathology. In addition, atony can develop due to uterine hypotension.
The impetus for the occurrence of such pathology is:
- prolonged or rapid labor, as well as any depletion of the central nervous system;
- disruptions in the biochemical processes of the uterine muscles (this may be a reduction in the enzyme hexokinase, ATP, reduced hysterominase activity);
- the appearance of factors affecting the contractile activity of the uterus.
Hypotonic
Hypotonic vaginal bleeding occurs due to low contractile activity of the uterus (hypotonia). This pathology is observed in the early postpartum period and occurs based on the same factors as atonic bleeding. The division of the disease into atony and hypotension is theoretical in nature, since diagnosis and therapeutic measures in these cases are similar.
The development of this syndrome leads to heavy bleeding, which often provokes mortality in women. According to statistics, the incidence of hypotension and atony in the early postpartum period is 2-2.5% of the total number of births.
Despite the serious consequences, bleeding from uterine hypotension is reversible. With timely detection and proper treatment, the mother's condition improves.
Important information: Why does it bleed heavily during early pregnancy without pain and can the fetus survive after bleeding with blood clots?
In the late postpartum period, the risk of such a pathology tends to zero, and the occurrence of excessive bleeding is associated with purulent-septic complications.
Acyclic
Acyclic vaginal bleeding is heavy bleeding that occurs in the middle of the cycle or a few days before menstruation. In medicine, this pathology is called metrorrhagia. It is impossible to track the frequency and amount of bleeding - they can be scanty, spotting or abundant.
The appearance of such symptoms in a woman always indicates pathological changes in the body, including:
- increased or decreased production of hormones;
- inflammation of the reproductive system;
- mechanical injuries;
- endometriosis (growth of the inner layer of the uterus);
- benign or malignant tumors;
- cervical erosion;
- lack of vitamins, strict diets, monotonous diet;
- frequent stress.
If the uterus bleeds between menstruation or during a delay, independent actions can lead to complications. If symptoms are detected, medical attention is necessary.
Breakthrough
Breakthrough vaginal bleeding occurs from the use of hormonal contraceptives. Most often they develop at the very beginning of taking oral contraceptives and are not abundant. Such bleeding indicates the body’s adaptation to new conditions. In such cases, doctors may recommend temporarily increasing the dosage.
If such measures do not bring results and the woman is bleeding (but not menstruating), she should consult a doctor as soon as possible, as this is a sign of problems with the uterus or ovaries.
Anovulatory
Anovulatory bleeding is one of the types of dysfunctional pathologies. Such bleeding is characterized by acyclicity and occurs between menstruation. The frequency of their occurrence may vary, with breaks lasting from 2 to 6 months. Their duration most often does not exceed 10 days.
Most patients with this diagnosis are young girls in the period of formation of the reproductive system and women 45-55 years old. Uterine bleeding with excessive discharge requires medical attention.
Discirculatory
Dyscirculators are those blood discharges that develop against the background of ovarian dysfunction. In some cases, the trigger may be severe stress, severe viral infection and other negative factors. At the same time, bleeding from the uterus is not profuse. Most often, women complain of similar symptoms after a prolonged absence of menstruation.
Folk remedies
Many women are interested in what to do if there is heavy bleeding and whether this problem can be eliminated using folk remedies. Such methods can only be used after a comprehensive diagnosis and permission from the treating doctor. Self-medication is very dangerous, as it can lead to aggravation of the problem and complications.
If the causes of heavy discharge are stress and overwork, as well as a lack of nutrients, you need to brew 2 tbsp with boiling water. l. nettles, leave to stand for 10 minutes. Filter and drink in 2 doses on an empty stomach. Instead of nettle, you can use shepherd's purse grass. An infusion from it is prepared in a similar way.
Mix chopped raspberry and mint leaves in equal proportions. Brew as tea and drink 3 days before the onset of menstruation and until its end every day. A decoction of corn silk will help stop bleeding. You need to drink it throughout the day.
An alcohol solution prepared with water pepper significantly reduces the intensity and duration of discharge. You can buy it at the pharmacy. Drink as prescribed by the doctor for heavy bleeding during menstruation, as well as after surgery. The course of therapy is selected strictly individually.
If the bleeding is very severe, then bird knotweed can be used. Take 12 g of the plant, add 1 tbsp. boiling water When the product is well infused, you need to drink it 1 tbsp. l. three times a day. This infusion has pronounced analgesic and hemostatic properties. It is good for heavy uterine or menstrual bleeding.
Take 1 tbsp. l. lilacs and pour 500 ml of water. Then simmer for 15 minutes covered. Then cool the product a little and filter. Drink daily in the morning 20 minutes before eating. The dosage of the healing decoction is 100 g.
The herbal mixture gives good results. To do this, you will need 5 parts of cinquefoil, 3 parts of centaury and 1 part each of horsetail and knotweed. Mix everything thoroughly, 1 tbsp. l. collection pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and let it brew for at least 1 hour. Filter and drink the product in small sips throughout the day. The course of therapy lasts 10 days. This healing remedy not only normalizes the volume of discharge, but also helps eliminate severe pain.
Viburnum bark can be used for therapy. This will require 4 tsp. vegetable raw materials. First you need to grind it well. Then pour 1 tbsp. water and boil for 30 minutes. While the liquid is hot, it must be filtered and boiled water added to the original volume. Drink 1 tbsp. l. three times a day before eating. This remedy is used for uterine bleeding and hemorrhoidal hemorrhages. It helps not only to normalize the amount of discharge, but also to reduce the severity of pain.
For heavy and painful periods, barberry can be used. Take 1 tbsp. l. leaves of this plant, pour into a glass container, add ½ tbsp. 70% alcohol. Place the container in a dark place for 7 days, filter. Drink 30 drops twice a day. It is worth considering that this remedy has a choleretic effect.
Based on oak bark, you can prepare a decoction using water or wine. It is recommended to use it for insertion into the vagina. On the first day, use 1 tbsp. l. solution, from 2 to 5 days, 2 tbsp. l. Then apply 1 tbsp again. l. liquids.
These remedies are considered quite effective, but it is necessary to take into account the existing contraindications.
Other means
In order to subsequently prevent heavy bleeding during menstruation, you need to completely reconsider your lifestyle during treatment. It is important to completely eliminate alcohol and reduce the consumption of strong tea and coffee. You need to give up active sports during your period and not lift weights.
Increased bleeding can be provoked by taking a hot bath, visiting a sauna, bathhouse, and performing any other procedures involving thermal effects. That is why it is better to refuse them.
In very difficult situations, hemostatic drugs may be completely powerless. The only treatment method in this case will be mechanical removal of endometrial remnants from the uterine cavity. With very intense blood loss, a transfusion of blood or its components may be required.
Only the attending doctor should choose a treatment method after conducting a number of diagnostic procedures. Self-medication can only worsen a woman’s condition and pose a real threat to her life.
Causes
Uterine bleeding of the juvenile period occurs in 20% of cases among all pathologies in the field of gynecology. The causes of such a deviation can be anything: mental or physical trauma, overwork, stress, poor living conditions, the problem of dysfunction of the adrenal cortex (or thyroid gland), hypovitaminosis, and more. Childhood infections (measles, chickenpox, whooping cough, rubella) can also cause bleeding to occur soon after. Moreover, chronic tonsillitis or a history of acute respiratory infections can cause juvenile bleeding.
Carrying out the operation
Answering the question of how to stop heavy bleeding during menstruation, it must be said that in some cases surgery may be required. Among the main indications for intervention it should be noted:
- heavy bleeding with recurrent occurrence;
- physiological disorders and damage to genital tissue;
- lack of results after drug therapy;
- pronounced signs of anemia.
In case of severe bleeding, hysteroscopy may be prescribed as a diagnosis. It allows you to identify uterine pathologies and then eliminate them. If heavy menstruation occurs due to fibroids or polyps, then they are removed. Women over 40 can have their uterus completely removed.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist with ultrasound examination (primary) | 4 200 |
| Taking gynecological smears | 700 |
| Hysteroscopy (diagnostic, therapeutic) | 47 500 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
How it manifests itself
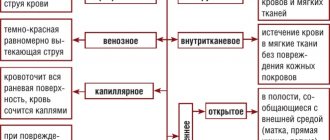
First of all, it is necessary to identify the difference between physiological and pathological bleeding.
Physiological include menstrual discharge, postpartum and those that accompany mechanical effects on the uterus (cauterization of erosion, abortion). Such bleeding will completely disappear on its own over time.
The following conditions are called signs of pathological uterine bleeding:
- bloody discharge from the genital tract when the next menstruation is delayed or during the intermenstrual period;
- after abortion and childbirth, copious bleeding does not stop and is accompanied by other signs (high fever, weakness, pain);
- discharge with blood during the postmenopausal period (most often it is scanty and spotting);
- a sharp change in the nature of menstruation (they become excessively heavy or prolonged);
- low blood pressure.
In the list of the main symptoms of uterine bleeding, patients name:
- severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- attacks of nausea (often they end in vomiting);
- pale skin;
- weak rapid pulse;
- fainting.
Each of these conditions occurs with heavy internal bleeding. If the discharge is insignificant and spotting, then the woman often feels only weakness and increased fatigue.
Causes
In the premenopausal period, uterine bleeding occurs in 16% of cases. It is known that as a woman ages, the amount of gonadotropins secreted by the pituitary gland decreases. The release of these substances becomes irregular from year to year. The latter causes disruption of the ovarian cycle, which implies disruption of ovulation, development of the corpus luteum and folliculogenesis. Progesterone deficiency usually leads to hyperplastic growth of the endometrium or the development of hyperestrogenism. In most cases, menopausal uterine bleeding occurs in parallel with menopausal syndrome.
DMC of the reproductive period
Hysteroscopy (diagnostic, therapeutic)
- Cost: 47,500 rub.
- Duration: 20 to 60 minutes
- Hospitalization: 1 day in hospital
More details
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding in the reproductive period occurs more often after termination of pregnancy, unsuccessful childbirth, against the background of stress, infectious processes in the reproductive tract, against the background of endocrine diseases, polycystic ovaries, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Treatment of DUB
The selection of a treatment strategy is carried out after scraping and histological examination. Hormonal and non-hormonal hemostasis is performed if relapses occur frequently. Experts prescribe hormonal drugs based on tests to even out the menstrual cycle and avoid relapse. Complex therapy involves normalizing the functioning of the central nervous system, replenishing the lack of nutrients, and relieving exacerbations of chronic diseases. If anemia is observed, then drugs with a high iron content are prescribed.
Treatment also includes 2 stages: stopping bleeding (hemostasis - surgical or hormonal) and preventing recurrent bleeding.
Surgical hemostasis in this age group is of significant importance, since it is carried out under the control of hysteroscopy, and makes it possible to exclude or clarify the presence of intrauterine pathology (fibroids, polyp, adenomyosis); subsequent histological examination allows one to assess the degree of endometrial hyperplasia and exclude the presence of adenocarcinoma.
The choice of surgical methods, drugs and routes of drug administration for the treatment of bleeding in this age group always takes into account the need to fulfill the woman’s reproductive goals.
Diagnosis of DMC
To check the state of health, an MRI or ultrasound is prescribed to exclude neoplasms and severe injuries in the reproductive system. Additionally, a comprehensive check of the blood condition and consultation with a hematologist are carried out. You will definitely need to take hormonal tests to determine malfunctions of the reproductive system and thyroid gland.
Caused by spontaneous miscarriage
Spontaneous abortion is the spontaneous termination of pregnancy (miscarriage) before 20 weeks. After 20 weeks of gestation, spontaneous abortion is called preterm labor. Spontaneous abortion occurs in approximately 20% of pregnancies.
Spontaneous abortion can be caused by various factors:
- Bacterial or viral infection of the fetus.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Habitual miscarriage.
- Gynecological diseases.
- Injuries.
- Chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus.
Symptoms of spontaneous abortion include the following:
- Intense bleeding.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Abdominal pain.
When choosing therapy for spontaneous abortion, a correct clinical assessment of the woman’s condition is important. For this purpose, an ultrasound examination is performed. Since the doctor needs to know at what stage the spontaneous abortion is and whether it is possible to continue the pregnancy.
If spontaneous abortion is accompanied by the development of massive bleeding, then in this case the following drugs are prescribed:
- Tranexan (tranexamic acid). On the first day, the drug is administered intravenously at a rate of up to 1 thousand mg of the drug per day. And then a gradual transition to the tablet form of the drug is carried out. After the transition, the dosage of the drug is 750 mg per day.
- Antispasmodic drugs (to relax the muscle fibers of the uterus). For this purpose, No-shpa is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. Then there is a transition to tablet drugs.
If the pregnancy cannot be maintained, the remaining fetal egg is aspirated using a vacuum or in the form of a minor gynecological operation.