The most dangerous for the patient and those around him are infectious diseases that occur in a latent form. The absence of obvious symptoms does not allow timely treatment to begin. At the same time, the disease progresses, and the patient is infectious to others. Of these diseases, the most common is tuberculosis. According to statistics, about a third of people, even in highly developed countries, are infected. Therefore, it is so important to carry out timely diagnosis of this disease. Along with the well-known Mantoux tests, diaskintest and fluorography, a clinical blood test is used to detect tuberculosis.
When is screening for pulmonary tuberculosis prescribed?
The modern Koch bacillus and its numerous strains, of which there are more than 74, are very different from the previously discovered mycobacterium. The ability of a virulent bacillus to penetrate healthy host cells and remain undetected in the human body, viability and resistance to acidic environments and disinfectants make the task very difficult for doctors and laboratory staff.
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis requires more and more new capabilities in order to conduct a full-fledged study. This also applies to people who are in a special risk group and have a predisposition to the occurrence of tuberculosis: HIV-infected patients or diagnosed with AIDS, with dependence on alcohol, drugs and nicotine products, with diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma and hereditary factors. Newborn children from an infected mother, minors and adolescents under 17 years of age, people of retirement and old age also need medical supervision.
There is another category of potential carriers of the disease - infected prisoners. But “prison” tuberculosis, the causative agents of which are mainly resistant new strains of the Koch virus, and its diagnosis with subsequent treatment can prevent the spread of the disease and the danger of infecting others after a person leaves prison.
PCR
PCR or polymerase chain reaction is the most accurate method of molecular genetic research that helps to identify various infections in the human body and determine which microorganism is the causative agent of the disease.
PCR research allows you to detect foreign DNA in the human body in any liquid taken from the body:
- blood;
- saliva;
- sputum;
- discharge from the reproductive system;
- flushing fluid from the bronchi;
- juice from the stomach.
Only a specialist can say exactly what fluid should be taken from the body in order to conduct an analysis and make an accurate diagnosis.
Preparing for analysis
Taking blood for testing for tuberculosis using the PCR technique is only the first stage.
In order for the analysis to give the most accurate diagnosis, it is important to prepare for it correctly:
- If sputum is taken for analysis, the oral cavity should be cleaned before collection. You need to do the toilet in the evening 12 hours before the fence and in the morning. Do not eat food during this entire period of time. In the evening, take a medicine that promotes better sputum discharge.
- If blood is taken for PCR testing, do not eat food 8 hours before collection. Take the test in the morning on an empty stomach. Smoking is not allowed in front of the fence. The fence is taken from a vein in the elbow. The blood is collected in a sterile tube, where an anticoagulant is also added to prevent the blood from clotting. Mix the two components carefully, without sudden movements.
- Urine for research is collected in the morning before breakfast. Before collecting fluid, you need to thoroughly toilet the genitals.
- Only a specialist in a hospital can collect bronchial swabs and cerebrospinal fluid.
Carrying out analysis
It is not difficult to test for tuberculosis in an adult using PCR, but it is important to follow the special requirements for the test. This is the only way to achieve accurate results that reveal a complete picture of the patient’s health.
The PCR method is the most accurate with which you can test for tuberculosis and more!
Not only the patient must follow all the rules for collecting material for analysis. Laboratory specialists must also follow certain rules. The material should be stored only in sterile containers and sent to the laboratory for further research.
And then the material is centrifuged in a special device, separating the cell sediment, which is then checked under a microscope. When the initial data has been studied, a special enzyme is added to the material - transcriptase, which carries out a chain reaction and forms enzymes of the genetic material for further research. Afterwards, the received data is decrypted by a specialist.
Decoding the results
The analysis period is no more than 7 hours. The patient receives an answer in his hands and there may be 2 options.
| Discovered | This means that the DNA of tuberculosis bacteria was detected in the material being tested. In this case, the possibility of infection is 98%. With this indicator, the doctor conducts an extended interpretation of the analysis, which will determine: the stage of the disease, the location of the lesion. If the test is positive, the patient is urgently sent to a tuberculosis clinic for treatment. |
| Not detected | This means that the causative agent of the disease has not been identified in the test material. |
How does pulmonary tuberculosis manifest?
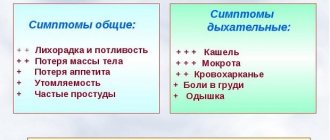
The danger posed by the latent form of tuberculosis is that early detection of the disease is not always possible due to the absence of pronounced symptoms. In other cases, the disease actively progresses. How to diagnose tuberculosis and what signs you should pay attention to:
- dry prolonged cough or with sputum production, wheezing;
- constant body temperature 37°C;
- pale complexion and tired appearance;
- decreased appetite and weight loss;
- shortness of breath and pain in the side;
- profuse sweating.
In women, the ways to determine pulmonary tuberculosis are menstrual irregularities and frequent headaches; from the urinary system, cystitis or bloody discharge in the urine is possible.
Possible consequences and side effects
As statistics show, the occurrence of complications and complex side effects after diaskintest is excluded. Depending on the body’s immunity, the result will be known after three days. The redness that appears lasts 5-7 days.
In most cases, vaccinated people do not have any symptoms. Statistics show that in 1% of patients, a test for tuberculosis can cause some consequences:
- increased body temperature;
- unstable blood pressure;
- physical fatigue;
- itching and lethargy;
- the appearance of a headache.
These side effects are not dangerous. This is the body's reaction to the test. The most common side effect of Diaskintest is fever.
The allergic process is one of the most dangerous consequences, since any vaccine is the introduction of a drug containing protein. That is, a foreign protein is introduced into the body.
Early diagnosis of tuberculosis in children and adolescents
Older people are able to objectively assess their health status and monitor it, and seek help from specialists. Minor children do not yet understand the full danger of infectious diseases, therefore, in preschool and educational institutions, measures are constantly being taken to prevent tuberculosis.
Clinical examination is the main primary type of examination. A pediatrician or phthisiatrician is obliged to listen to the complaints of a small patient and carefully read his medical record to determine congenital pathologies of the respiratory system and chronic diseases of the thyroid gland. An important role is played by the integrity and color of the skin, normal temperature - 36.6°C - 36.7°C and the absence of wheezing or shortness of breath when listening with a stethoscope.
If the general condition is assessed by the doctor as satisfactory, further methods for early diagnosis of tuberculosis in a child include mandatory Mantoux test and BCG vaccination once a year. Parents do not trust the composition of the vaccine and refuse to give their child tuberculin. In this case, they are obliged to provide as soon as possible the results of the tuberculosis test, which was done instead of Mantoux.
Contraindications
The list of contraindications for Diaskintest is very short. You should not do Diaskintest if you have a runny nose or cough. The presence of an infectious disease cancels the test.
Firstly, the result will not be correct. Secondly, testing for tuberculosis can complicate the course of the disease. After recovery, it is better to wait a while. The optimal period is a month after illness. Main contraindications:
- infectious diseases;
- chronic diseases;
- various skin diseases;
- severe allergic reactions;
- epilepsy;
- recent vaccination.
It is advisable to carry out Diaskintest a month after other vaccines, as it does not combine well with other drugs.
Detection of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults
Frequent colds or exacerbations of chronic diseases, infections and inflammatory processes that are provoked by hypothermia, heavy physical work or low immunity can cause tuberculosis in the older generation. The Mantoux test is an underpowered test for adults. Vaccination is used after treatment of tuberculosis infection or in the presence of pronounced signs of the disease. There are diagnostic examination methods for recognizing tuberculosis in adults.
Most often, during an annual medical examination, doctors prescribe fluorography or x-ray of the lungs. An overview method of chest imaging gives an idea of the state of the respiratory organs in the form of a black and white image, on the basis of which a focus of tuberculosis can be detected. Suspicion by a radiologist or detected pathologies of the respiratory system will require additional examination.
Tuberculin diagnostics
In order to prevent the spread of the disease among the younger generation, a subcutaneous injection or Mantoux test is used, which is carried out every year. The child receives the substance tuberculin or a strain of the tuberculosis pathogen created in artificial laboratory conditions. The weakened mycobacterium should cause a reaction from the immune system at the injection site. Evaluate the result of the Mantoux test after 72 hours:
- negative - up to 1 mm
- doubtful - 2-5 mm;
- positive - more than 6 mm;
- weakly positive - 5-9 mm;
- average intensity level - 10-14 mm;
- pronounced - up to 16 mm;
- hyperergic. In children and adolescents - more than 17 mm, in adults - more than 21 mm.
In addition, there are also false indicators. Previous data is also taken into account. Even a negative result does not guarantee the absence of Koch's bacillus in the body. But even with such shortcomings, the Mantoux test is the most common prevention and diagnosis of tuberculosis in children and adolescents in the early stages. Vaccination is unacceptable for allergies and bronchial asthma, inflammation and diseases of the digestive system, and diabetes.
Features of the disease
Spinal tuberculosis, or tuberculous spondylitis, is caused by mycobacteria that spread through the lymphatic and blood vessels. Most often, the lesion is localized in the center of the vertebra; in some cases, it can be located in the arches, spinous and articular processes. As the disease develops, multiple granulomas form in the affected area, which leads to the destruction of bone tissue and the formation of an abscess. Along with the vertebral body, the intervertebral disc is also damaged, as a result of which its height decreases, shock-absorbing properties decrease, and the mobility of the spine is impaired.
The thoracic region is most susceptible to tuberculosis - about 60% of all cases of the disease, 30% are in the lumbar region, 10% are equally affected by the cervical vertebrae and sacrum. If the body's immune defense is strong enough, the granulosa tissue gradually degenerates, a scar forms at the site of the lesion, and the development of the disease completely stops. Sometimes even complete restoration of the bone structure occurs. In the presence of unfavorable conditions against the background of weakened immunity, tuberculosis quickly progresses, the abscess spreads to soft tissues, and necrosis develops. When several segments are involved in the process at once, spinal deformation occurs, manifested mainly by kyphosis.
What are the dangers of spinal tuberculosis? In addition to orthopedic disorders, expressed in curvature of the spinal column and instability of the vertebrae, the disease provokes many other complications:
- allergic reactions due to damage to toxins;
- protein metabolism disorder;
- radicular syndrome;
- secondary immunodeficiency;
- myelopathy;
- fistula formation;
- disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs;
- paresis of varying severity.
Tests for tuberculosis
Traditional methods of prevention and early detection of tuberculosis can be replaced with the help of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent blood test, which is often used instead of the Mantoux test. The principle of this study is the immune response of the body, antibodies to the IgG and IgM antigens of the pathogen, mycobacteria. During the analysis process, protective cells containing a staining substance are placed in a medium containing suspected M. Tuberculosis bacilli, which interact with the source of infection and transfer part of the enzyme to the virus.
"Diaskintest". A trial attempt to replace an existing tuberculin test. The main active ingredient is not a weakened strain of mycobacterium of the human and bovine type, as in tuberculin, but a protein with an antigen of the causative agent of tuberculosis, unique to humans. Diaskintext limits the number of false positives and detects only the active virus. At the beginning of the disease it gives negative results.
PCR diagnostic method. For laboratory testing, it is better to use sputum. When exposed to high temperature, foreign DNA is released. In order to identify mycobacteria or their strains, the sample is compared with those already obtained previously. Diagnosed tuberculosis can be obtained within 5 hours after the delivery of the starting material. The procedure is often used for children with contraindications for tuberculin diagnostics or to confirm the diagnosis.
X-ray examination
It is prescribed during an annual medical examination for representatives of the older generation. Children are not allowed to undergo the procedure due to the high dose of radiation for the immune system that is not yet strong enough. Radiation diagnostics is intended for screening chest organs, searching for foci of tuberculosis and preventing other pathologies.
X-ray and fluorography of the chest organs. Using a special screen, X-rays pass through the body of the person being examined, the shadow image is processed and transferred to film. Development takes a few minutes. Digital fluorography displays a finished image on the monitor, which is printed in black and white on a printer or saved electronically. The fluorography image shows focal, infiltrative and chronic advanced tuberculosis in the form of lesions.
Computed and magnetic resonance imaging of the lungs. Methods of a more informative nature for the accurate detection of tuberculosis, which make it possible to accurately determine the size of lesions and fluid accumulations, pathologies. The sensitivity is 100 times higher than fluorography and x-rays.
General blood test for tuberculosis
Studying the composition and quantitative indicators of liquid connective tissue, which, one way or another, encounters the M. Tuberculosis bacillus, is important for early diagnosis of the disease. With tuberculosis, the patient experiences moderate anemia, the hemoglobin level in men is below 130, in women less than 120. During the period of exacerbation of the pulmonary form, the granularity of leukocytes changes and their number increases from 20% to 50%, the number of eosinophils, young immune cells, decreases.
But the main indicator of tuberculosis activity is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate or ESR. This test shows the ability of red blood cells, whose density is greater than plasma, to settle under the influence of gravity. In a healthy body, the norm for women should not exceed 15 mm/hour, for men - 10 mm/hour. An increase in ESR from 20 mm/h to 80 mm/h indicates a large amount of immunoglobulins and a low level of albumin in the blood, which means the activation of the body's defenses under the influence of foreign cells.
A leukogram is often used, which is based on changes in the protein composition of the blood during an acute inflammatory process. The indicators of leukocytes such as neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes and lymphocytes are taken into account. Examination for pulmonary tuberculosis distinguishes three phases of damage to the body’s immune system:
- neutrophilic. Active defensive reaction. The number of neutrophils increases, the level of monocytes and lymphocytes decreases, eosinophils are absent;
- monocytic. Trying to overcome tuberculosis infection. The number of neutrophils is low, single eosinophils are visible, lymphocytes increase;
- recovery. Observed after the patient has recovered. The number of lymphocytes and eosinophils is increased, but their levels return to normal.
In comparison with ELISA and PCR tests, the tuberculosis pathogen itself will not be detected, but changes in blood composition will be enough to suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and continue the examination aimed at finding the source.
Method for detecting acid-fast mycobacteria
A feature of the cell wall of the tuberculosis bacillus is the lack of reaction to chlorine-containing agents and acidic environments. Therefore, diagnostic measures in laboratory conditions are often impossible to perform. Microscopic methods of examining a smear in such cases are replaced by bacterioscopy or staining of sputum.
Microscopy of a smear or material containing AFB is carried out using the Gram method and a staining method known as the Ziehl-Neelsen method. The Koch virus is first exposed to the red substance carbol fuchsin, which penetrates the cell membrane, and then is treated on top with a solution of methylene blue. A positive result of the presence of a tuberculosis bacillus will be the presence of red mycobacteria in a smear on a blue background. In modern medicine, auramine-rhodamine is more often used. After exposure to the ultraviolet spectrum, the bacilli acquire a yellow tint.
Fluorescence microscopy
An optical method for studying tuberculosis pathogens, which are stained with fluorochromes and, as a result, begin to glow under ultraviolet light. For this examination, special devices are used, which consist of an ultraviolet-producing element and a filter system.
Many microbes do not have their own luminescence, so there are various methods for staining them to study using a special device. One of the methods is fluorochrome plating, i.e. staining with intensely diluted fluorochromes. This technique is used for bacterioscopic examination of tuberculosis pathogens.
In the reaction to antibodies, which are labeled with fluorochromes, antigens of microorganisms are detected.
Bacteriological study of bronchial lavage waters
It is used as an additional method of collecting sputum and a method for identifying the causative agent of tuberculosis in it, when the patient is unable to collect the material on his own or the amount of secretions is not enough to conduct an examination. It is prohibited to prescribe to people of retirement age, with diseases of the cardiovascular system and bronchial asthma, and to children under 15 years of age.
The procedure involves local anesthesia of the respiratory tract and the introduction of a heated saline solution into the larynx using a special syringe to increase the level of secretion. After the manipulations, the patient’s sputum is intensively secreted naturally and collected by medical workers in a test tube for subsequent sowing and cultivation of mycobacteria.
Patient examination
Specialists know how to identify tuberculosis during examination.
Detection of tuberculosis is based on the following deviations from the norm:
- change in skin color;
- problems with metabolism, which is expressed by weight loss, general weakness of the body, decreased immunity;
- enlargement of lymph nodes - the appearance of compactions, pathological changes in the structure.
In addition, patients with tuberculosis experience abnormal movement of the lungs when inhaling, which is also determined during examination.
Needle biopsy of the lung
To determine the pathological process occurring in the lungs and obtain an initial sample, invasive diagnostics of tuberculosis in adults is prescribed. It is aimed at studying the causes of coughing up blood, internal pulmonary bleeding, obvious respiratory failure, taking material from the mucous membranes, bronchial secretions or sputum, and obtaining a sample of the affected area.
A prerequisite for puncture biopsy is clear control over the actions performed through an ultrasound machine or using X-rays. The essence of the procedure consists of local anesthesia of the chest area and insertion of a Silverman needle to capture and separate a fragment of lung tissue. After a biopsy, the degree and form of damage to the respiratory system is determined. In advanced cases, they resort to open surgery under general anesthesia.
Bronchoscopy
To study and assess the extent of damage to the pulmonary system, including the trachea, bronchi and mucous membranes, in medical practice they are increasingly giving preference to endoscopic diagnosis of tuberculosis. Indications for the procedure include a prolonged cough that has been observed in a person for more than 1 month, sputum with blood, and previously identified pathologies in the lungs.
During the examination, local anesthesia and muscle relaxants are necessary to ensure free passage of the flexible tube with the light-conducting device into the airway. Taking mucosal material or secretions from the trachea and bronchi helps to study the cytological composition of sputum for the presence of foreign cells of the tuberculosis bacillus.