There are many drugs that are used to normalize blood pressure. Physiotens is one of them. Next, you will learn how Physiotens works, how to use it correctly, what contraindications and side effects it has.
Hypertension is a pathology that is gaining more and more momentum every day. The reasons for this factor are different sources - these are stressful conditions, unhealthy diet, intense rhythm of life. This factor cannot be ignored. After all, hypertension can be life-threatening and cause death due to severe complications. In pharmacies you can find various pills to alleviate the patient’s condition. Physiotens tablets have an effective effect, reducing blood pressure to normal levels if you choose the right dosage for the patient. Next, we will study their instructions in detail.
Release form and composition
Physiotens is available in the form of film-coated tablets:
- dosage 0.2 mg: round, biconvex, pale pink, with “0.2” engraved on one side, white on the break (14 pieces in blisters, 1, 2 or 7 blisters in a cardboard package);
- dosage 0.3 mg: round, biconvex, pink, with “0.3” engraved on one side, white on the break (14 pieces in blisters, 1, 2 or 7 blisters in a cardboard package);
- dosage 0.4 mg: round, biconvex, brownish-pink, with “0.4” engraved on one side, white on the break (14 pieces in blisters, 1, 2 or 7 blisters in a cardboard package).
Composition of 1 tablet:
- active ingredient: moxonidine – 0.2; 0.3 or 0.4 mg;
- auxiliary components: povidone, magnesium stearate, lactose monohydrate, crospovidone;
- film shell: ethylcellulose, talc, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, macrogol, red iron oxide dye.
Analogs
Since both drugs are interchangeable, they have the same analogues. A change in medication may be unavoidable if the patient develops an allergy. The problem may also be the cost of the tablets. The price of Moxonidine and Physiotens differs significantly. If a domestic product can be purchased for 70-75 rubles, then an imported one will cost buyers 260-265 rubles.
Experts have compiled a list of the most effective medications that are suitable for replacing these tablets:
Tenzotran (160 rub.). The drug is based on moxonidine, available in tablet form, and has an antihypertensive effect.- Albarel (240 rubles). The main component is rilmenidine (1 mg in one pill). Inhibits the sympathomimetic activity of peripheral as well as cortical centers, reduces blood pressure.
- Clonidine (110-120 rub.). Manufacturers use clonidine as the active ingredient. Available in the form of tablets, eye drops and solution for injections. Helps increase cerebral vascular tone, improve blood flow in the kidneys and brain.
- Moxonitex (170-173 rubles). The active ingredient is moxonidine. The drug has an antihypertensive effect on the body.
All of the listed drugs have proven themselves well in the field of cardiology and neurology. However, before purchasing the medicine, you should consult a specialist.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Physiotens is a centrally acting antihypertensive drug. It selectively stimulates receptors that take part in the reflex and tonic regulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Due to stimulation of imidazoline receptors, peripheral sympathetic activity is reduced and blood pressure is reduced.
Moxonidine differs from other sympatholytic drugs for lowering blood pressure by its lower affinity for alpha2-adrenergic receptors, which reduces the likelihood of dry mouth and sedation.
As a result of taking Physiotens, systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure decrease. The antihypertensive effect of the drug has been confirmed by a number of studies (placebo-controlled, double-blind and randomized studies).
In patients with obesity, moderate arterial hypertension and insulin resistance, moxonidine improves the insulin sensitivity index by 21% (compared to placebo).
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, the drug is quickly and almost completely absorbed in the upper digestive tract. Bioavailability of moxonidine ~ 88%. The maximum concentration is reached after approximately 1 hour. When taken simultaneously with food, the pharmacokinetics of the drug does not change. Moxonidine is 7.2% bound to plasma proteins.
As a result of drug metabolism, dehydrogenated moxonidine (the main metabolite) is formed. Its pharmacodynamic activity is approximately 10% of that of moxonidine.
The half-life of moxonidine is 2.5 hours, and its metabolite is 5 hours. During the day, more than 90% of the drug is excreted by the kidneys (78% unchanged, 13% in the form of dehydrogenated moxonidine and about 8% in the form of other metabolites). Less than 1% of the dose taken is excreted through the intestines.
In patients with arterial hypertension, the pharmacokinetics of Physiotens do not change compared to healthy volunteers.
In elderly patients, pharmacokinetic parameters change slightly.
The drug is not recommended for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age (special studies of the pharmacokinetics of moxonidine in this group of patients have not been conducted).
The elimination of the drug depends on creatinine clearance. In patients with creatinine clearance in the range of 30–60 ml/min (moderate renal failure), the steady-state plasma concentrations and terminal half-life of moxonidine are approximately 2 and 1.5 times higher than those in patients with normal renal function (with creatinine clearance greater than 90 ml/min). In severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), steady-state plasma concentrations and terminal half-life are 3 times higher than in patients with normal renal function. When multiple doses of the drug are prescribed to patients with moderate to severe renal failure, a predictable accumulation of moxonidine occurs. When creatinine clearance is less than 10 ml/min (end-stage renal failure, the patient is on hemodialysis), steady-state plasma concentrations and terminal half-life are, respectively, 6 and 4 times higher than in patients with normal renal function. In all of these groups of patients, the maximum plasma concentration of the drug is 1.5–2 times higher than in patients without impaired renal function, therefore the dosage of Physiotenza should be selected on an individual basis. During hemodialysis, the excretion of moxonidine is insignificant.
How to take Physiotens correctly: under the tongue or with water?
When taking Physiotens, it is recommended to monitor your blood pressure and measure your pulse. To eliminate the manifestations of the disease, beta-adrenergic receptor blockers are taken along with Physiotens. If the patient needs to stop taking Physiotens, then first stop taking the blockers, and then the drug itself.
Rules for taking Phytosiotens
According to the instructions, the pills should be taken with water, but if a more effective effect of the tablets is required, then it is better to dissolve the tablet under the tongue. The active substances will penetrate the bloodstream, which significantly accelerates the normalization of blood pressure in patients. Use this method of taking the drug when a person’s blood pressure is too high.
IMPORTANT : Physiotens can be taken regardless of meal time. The required level of the main substance of the drug is achieved when only seven percent of moxonidine binds to plasma protein molecules. The highest level of the chemical component is recorded after 1.5-2 hours. The medicine comes out through the kidneys.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- severe bradycardia (resting heart rate less than 50 beats per minute);
- sick sinus syndrome;
- lactase deficiency, hereditary galactose intolerance, glucose/galactose malabsorption syndrome;
- children and adolescents up to 18 years of age;
- hypersensitivity to any component of the drug.
Relative (Physiotens is used with caution):
- severe renal failure;
- end-stage renal failure;
- hemodialysis;
- severe liver failure.
Directions for use and dosage
The tablets are taken orally, regardless of food. As a rule, the initial dose of the drug is 1 tablet of 0.2 mg once a day.
Maximum doses of Physiotens: single – 0.4 mg, daily – 0.6 mg in two doses.
For patients with moderate or severe renal failure, as well as for patients on hemodialysis, the drug is prescribed at an initial daily dose of 0.2 mg. If necessary and if the drug is well tolerated, the daily dose can be increased to 0.4 mg.
Overdose
In case of an overdose of the drug, the following symptoms may occur: dizziness, headache, dry mouth, drowsiness, fatigue, vomiting, marked decrease in blood pressure, bradycardia, pain in the epigastric region, sedation, asthenia. A transient increase in blood pressure, hyperglycemia and tachycardia may potentially occur.
There is no specific antidote. Symptomatic therapy is carried out: bradycardia - with atropine, critical level of hypotension - with dopamine, paradoxical hypotensive effects are stopped with alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists.
Several cases of Physiotens overdose have been reported, when doses up to 19.6 mg were used once (no fatal outcome was observed).
Possible adverse reactions of the body
If the specialist’s recommendations or individual intolerance are not followed, negative reactions of the body may occur. Side effects of Moxonidine include:
- Dizziness.
- Migraine.
- Asthenic condition.
- Vomiting or attacks of nausea.
- Rashes on the skin.
Side effects and interactions of Moxonidine with other drugs
Some patients experience a feeling of dry mouth and increased irritability.
Physiotens can provoke the manifestation of:
- dry mucous membranes;
- bradycardia;
- general weakness and decreased performance;
- allergic rashes.
If taken incorrectly, blood pressure can drop sharply and severely.
Adverse reactions that appear on days 3-4 are considered normal. If the condition does not worsen, the course of treatment can be continued. In cases where the symptoms are pronounced and intense, use should be stopped after consulting with your doctor.
An overdose of tablets increases the symptoms of adverse reactions. In such situations, it is necessary to perform gastric lavage on the patient and prescribe symptomatic treatment.
special instructions
When using Physiotens and beta-blockers simultaneously, and it is necessary to cancel the latter, beta-blockers should first be discontinued and only after a few days Physiotens is canceled.
During treatment, it is necessary to regularly monitor heart rate, blood pressure and electrocardiogram. Discontinuation of the drug should be carried out gradually.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
Special studies on the effect of Physiotens on the ability to drive vehicles and work with potentially dangerous mechanisms have not been conducted.
Considering the possible development of dizziness and drowsiness during drug therapy, it is recommended to exercise caution when performing work that requires increased concentration and high reaction speed.
Physiotens: reviews of patients who took these tablets
Tatyana, 34 years old:
After the New Year, my mother’s blood pressure rose to 190/100. We tried giving the Capoten tablet under the tongue, but there was no result. They called an ambulance, but there were no cars, they promised to arrive in an hour. We didn’t want to waste time, so we went to the pharmacy, where the pharmacist advised us to take Physiotens. After taking these pills, my mother immediately felt better, within an hour the headaches went away and her blood pressure returned to normal. They called an ambulance but refused the call.
Nona, 46 years old:
I have been using the drug for almost two years as prescribed by my doctor. There is a whole treatment regimen prescribed there. According to the prescription, it must be consumed strictly in the morning, thanks to this my blood pressure is normal. I experienced no side effects. I am under the supervision of my doctor and have a cardiogram every three months. When taking such drugs for a long time, you should definitely monitor your heart rate, blood pressure and heart function.
Alexandra, 39 years old:
Towards the evening I had a headache, I took my blood pressure, the readings were 155/100 and my pulse was higher than normal. My mother advised me to take Physiotens, the smallest dosage. She had just these pills in her medicine cabinet. I drank it, after half an hour the headache stopped hurting, and my blood pressure returned to normal. But I felt some panic and dizziness. I was scared. After which I decided to try to sleep. In the morning I woke up, there were no more side effects, I felt completely healthy. I still advise you to pay attention to the instructions for the drug, it indicated side effects, and Physiotrenz is still better to use in patients with the second or third degree of hypertension, and not with pressure values like mine. Moreover, I experience such pressure extremely rarely. Consult your doctors before using such serious means to avoid harming yourself.
On our website you can also read articles on the topic of cardiovascular health:
- Magnesium B6 – instructions for use;
- Blood pressure norms for women and men after 50;
- What are the normal heart rates for people by age?
- Bisoprolol is a drug used for chronic heart pathologies;
- How to measure blood pressure correctly?
Use during pregnancy and lactation
There are no data on the use of moxonidine in pregnant women. Animal studies have not revealed any direct or indirect negative effects on pregnancy, embryo formation, childbirth or postnatal development. During pregnancy, the drug is prescribed with caution and only after assessing the risk to the fetus/benefit ratio for the mother.
Since moxonidine passes into breast milk, women who are breastfeeding should interrupt or discontinue breastfeeding if use of the drug is necessary.
Drug interactions
When used simultaneously with calcium channel blockers, thiazide diuretics and other antihypertensive drugs, an additive effect is observed.
The combined use of Physiotens and tricyclic antidepressants is not recommended, as they may reduce the effectiveness of centrally acting antihypertensive drugs.
Moxonidine may enhance the sedative effects of benzodiazepines and also moderately improve cognitive function in patients receiving lorazepam.
Physiotens does not enter into pharmacokinetic interactions with digoxin, glibenclamide and hydrochlorothiazide. No pharmacodynamic interaction was observed when used together with moclobemide.
Physiotens or Moxonidine or Capoten: which is better, more effective?
It is impossible to say which drug is better for a particular patient. After all, people have different perceptions of different types of tablets. For some, Physiotens is not suitable at all, and for others, Capoten is not suitable. But if we judge the effectiveness of the drugs in general, then Physiotens and Moxonidine still have a better chance of success. The effect of using these drugs is stronger than that of Capoten. In addition to lowering blood pressure, the patient’s headache also stops hurting and his condition normalizes for a long time.
Capoten is a remedy that reduces blood pressure within 20-25 minutes, but its effectiveness lasts only six hours in a row. Therefore, hypertensive patients should always have Capoten in their first aid kit.
Kapoten - instructions for use
Capoten is suitable for patients with type 2 hypertension. It gently reduces the load on the heart and regulates the synthesis reaction in the adrenal glands. Moxidin and Physiotens are drugs with a similar active ingredient, so the tablets have the same effect.
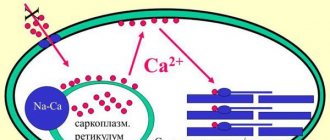
The principle of action of Moxonidine
IMPORTANT : You cannot use blood pressure medications haphazardly and uncontrollably. This threatens irreparable harm to the patient’s body and worsening the condition. And if you decide to use the pills without consulting a doctor, then read the instructions carefully, pay attention to the rules of administration and contraindications.
Price for Physiotens in pharmacies
Cost of the drug in pharmacies:
- film-coated tablets, dosage 0.2 mg (14 pieces per package) – from 279 rubles;
- film-coated tablets, dosage 0.4 mg (14 pieces per package) – from 426 rubles;
- film-coated tablets, dosage 0.2 mg (28 pieces per package) – from 478 rubles;
- film-coated tablets, dosage 0.4 mg (28 pieces per package) – from 691 rubles.
The price of Physiotens may vary slightly in different pharmacy chains.