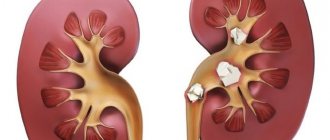
Kidney stones are otherwise called nephrolithiasis - this disease is characterized by small deposits of salts and minerals. They form inside the kidneys and can travel through the urinary tract.
Symptoms of the disease during attacks are unpleasant and are often accompanied by blood in the urine and pain in the abdomen and lower back. Over the course of their lifetime, about 5% of people in the world will experience kidney stones.
Why do kidney stones form?
The reasons for the formation of kidney stones are metabolic failures. Water-salt imbalance and disruptions in the chemical composition of the blood are especially dangerous. Metabolic disorders cause the development of many pathologies in the human body, including the development of urolithiasis. The salt content in the urine increases, which leads to the formation of crystals.
Various factors can contribute to metabolic failure, which will subsequently lead to the formation of stones, including:
- Regular consumption of water with high salt content. The harder the water a person drinks, the faster stones form in his kidneys. The incidence of urolithiasis is especially high in those areas where the hardness level of tap water is exceeded. Therefore, people living in such regions must use various methods to mitigate it. For this purpose, you can change filters; do not forget about traditional methods of water softening. This can significantly reduce the risk of kidney stones.
- Errors in nutrition. Eating sour, salty, spicy and fried foods in excess. Spicy, fried and fatty foods increase the acidity of urine, which leads to the formation of kidney stones. You should also not consume too much salt and drink large amounts of mineral water. If you exclude all harmful foods from your diet, you can minimize the risks of developing not only urolithiasis, but also many other diseases. Therefore, all doctors recommend sticking to proper nutrition.
- Lack of fluid in the body The urine will be more concentrated the less water a person drinks. Drinking enough fluid helps thin it out. In addition, the blood becomes less viscous. This will allow the body to quickly get rid of harmful substances and also prevent the formation of stones. A person needs to drink as much fluid as his body requires. The generally accepted norm is 2-3 liters of water per day. However, care must be taken that this does not negatively affect the functioning of other systems and organs. First of all, this concerns the heart. Therefore, you need to determine the volume of water you drink per day individually.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Physical inactivity is a problem in modern society. Many diseases develop from a lack of physical activity, because blood cannot circulate normally in the body, which means that all organs suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Bedridden patients are very susceptible to developing urolithiasis. A sedentary lifestyle is even more dangerous. Statistics show that physical inactivity increases the risk of death by 40%.
The less a person moves, the more his musculoskeletal system suffers, and the faster calcium is washed out of bone tissue. As a result, the level of calcium in the blood rises, and the body unsuccessfully tries to remove it through urine. As a result, stones begin to form in the kidneys.
To prevent the development of urolithiasis, you need to lead an active lifestyle, walk more, ride a bike, and stop using the elevator. It should be remembered that kidney stones form in people who move little.
- Climatic conditions. If a person lives in a hot climate, then he often suffers from dehydration, especially due to insufficient water consumption. The concentration of salts in the urine increases, which leads to the appearance of kidney stones. At risk are those people who lived in a temperate climate zone and then move to hot areas. The body does not have time to adapt, sweating increases, dehydration increases, etc.
- Disorders of the kidneys and urinary tract. Any injury to the kidneys leads to stagnation of urine in them. For the same reason, narrowing of the ureter, as well as the upper urinary tract, is dangerous. In addition, the risk of infection increases. Such violations must be identified and treated promptly.
- Chronic diseases of the digestive and genitourinary system. Urinary tract infections. Diseases of the urinary system such as pyelonephritis and cystitis are dangerous. Prostatitis and gastric ulcers often lead to the formation of kidney stones. However, almost any infection can provoke metabolic disorders, so any inflammatory process must be eliminated as quickly as possible. Leading a healthy lifestyle is the guarantee that most diseases will bypass a person. It is no secret that disruption of one system leads to disruption of the functioning of the body as a whole. This is exactly how a wide variety of diseases develop, step by step.
- Bone diseases, previous injuries. In terms of the formation of kidney stones, diseases such as osteomyelitis, osteoporosis and other diseases of the skeletal system are dangerous. Therefore, it is so important to maintain the health of the musculoskeletal system.
- Hereditary predisposition to the development of the disease If close relatives suffered from kidney stones, then the risk of developing this disease increases. However, it is possible and necessary to fight a hereditary predisposition to stone formation. A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition come to the rescue.
- Vitamin deficiency, vitamin excess. Kidney stones form when the level of vitamin C in the body is high. Deficiency of vitamin D and vitamin A is dangerous.
- Lack of ultraviolet radiation. If a person rarely spends time in the sun, then his risk of developing urolithiasis increases.
- Alcoholism, excessive use of diuretics. Taking diuretics causes the body to quickly lose fluid. This leads to an increase in urine concentration with subsequent stone formation. Therefore, it is so important not to deviate from the doctor’s recommendations and to follow the dosage and frequency of taking diuretics, if they have been prescribed. Self-medication with diuretics is unacceptable. Drinking alcohol also poses a risk of forming kidney stones. In general, alcohol abuse contributes to intoxication of the body.
- Taking certain medications. It is possible to form kidney stones while taking ascorbic acid, sulfonamides and other drugs that lead to a failure of metabolic processes.
Laboratory research methods
Among the laboratory methods for studying this pathology are: clinical urine analysis, bacteriological culture of urine for flora, study of the chemical composition of sand, if it is excreted in the urine, biochemical tests of urine and blood to identify metabolic imbalances in the body.
When considering the results of a general urine test, special attention is paid to the presence of red blood cells in it, which indicate hematuria, as well as leukocytes, which are a sign of an associated infection.
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
The main symptoms of kidney stones are as follows:
Kidney pain. The pain is localized in the lumbar region. They can also indicate not only urolithiasis, but also kidney infarction, organ tumor, etc.
An attack of renal colic is characterized by abdominal pain occurring on the left or right side. The pain radiates to the pubis or thigh area. Renal colic requires immediate assistance to a person.
Blood in the urine. The presence of blood in the urine (hematuria) is a serious symptom. It may indicate kidney stones, stones in the ureter, pyelonephritis, kidney tumors and other inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.
Blood in urine can often be detected independently. The fluid excreted by the body becomes similar to meat slop. Hematuria can develop after injury to the bladder or kidneys, or after excessive exercise.
Sometimes the urine may turn red after eating certain foods that contain the pigment. For example, after eating beets or pomegranates. This has nothing to do with hematuria.
Increase in body temperature. A sign such as an increase in body temperature does not in itself indicate kidney stones. However, if the temperature increases against the background of other symptoms of urolithiasis, then it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
The appearance of edema. When a person has kidney disease, swelling always appears. They are especially noticeable after waking up. Legs and arms swell, bags appear under the eyes. By the evening they subside, and by the morning they increase again. Despite this, people often do not notice or simply ignore this sign of kidney disease.
Increased blood pressure levels. Arterial hypertension is a reason to undergo examination of the entire urinary system. Very often, disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and adrenal glands lead to surges in blood pressure.
The appearance of pain during urination. Pain during urination may indicate the presence of kidney stones, cystitis and urethritis. In this case, you need to evaluate the color of the urine excreted. Normally it is transparent, with a yellowish tint. If the color of urine changes, this may be a sign of disease not only of the kidneys, but also of the liver, blood or biliary tract.
Change in the volume of urine excreted. The daily volume of urine excreted is reduced to 500 ml (oliguria). This symptom may indicate glomerulonephritis. In addition, oliguria is a sign that a person does not consume enough fluids or has increased sweating.
- The daily volume of urine is reduced to 50 ml (anuria). Such a symptom may indicate acute renal failure, intoxication of the body with poisons or narcotic substances, or renal colic. It is possible that anuria may occur if the ureter is blocked by a stone.
- The daily volume of urine increases to 10 liters (pollakiuria). This symptom indicates chronic kidney disease, the development of an irreversible process in organ tissues. Pollakiuria is also a symptom of diabetes mellitus.
Changes in the skin. Kidney disease may be indicated by changes in skin color. So, against the background of glomerulonephritis, the skin is dry, pale, with a yellowish tint. Multiple subcutaneous hemorrhages indicate kidney disease.
Deterioration in general health. A person gets tired faster, his appetite worsens, and weight loss occurs.
Types of stones
What are kidney stones? Solid elements are divided into three main types, depending on their chemical composition. Based on the state of the acid-base balance of urine, it may contain urates, oxalates and phosphates. In some cases, patients independently determine the pH of their urine using litmus paper: green means alkalization, red means increased acidity. But it is best to simply submit your urine for laboratory analysis. If a pH of more than 8 is found in the secretions, the alkaline indicator predominates, and if the result is less than 4.5, excessive oxidation is observed.
What causes kidney stones to form? This process is greatly influenced by a person’s diet. There are these types of stones:
- Oxalates - can occur due to increased acidity of urine excreted. The pathology is called oxalate nephrolithiasis and manifests itself due to a disorder in the metabolism of protein substances. Excessive consumption of smoked meats, sweets, meat and fish dishes, spices and alcohol leads to the development of this form of the disease. In this case, it is advised to remove oxidizing foods from the menu.
- Phosphates are elements formed in an environment with a high alkaline content. In medicine, such a disease is called phosphaturia. This type of illness often appears in patients who abuse lactic acid products and eat a lot of cereals and bread. For therapeutic purposes, the patient is recommended to exclude from his diet all foods that lead to alkalization of urine, and to increase the consumption of fish and meat.
- Urates - consist of mineral substances formed in an acidic environment. These compounds are not as aggressive as the previous ones. Drinking enough liquid will help get rid of them. It is recommended to drink purified, still water. Offal, fish and meat broth, and smoked dishes are excluded from the menu.
Important! Concretions with a homogeneous structure are not always formed in the human body. There are mixed types of stones that can be dangerous to the body. Coral formations are considered the most threatening - they grow in the pelvis of the kidneys, are distinguished by their irregular shape and long processes.
Signs of disease in other organs
Discomfort in the lower back can indicate many diseases. That's why it's so important to find out the cause of the pain.
- Acute appendicitis can manifest as pain in the lumbar region. In addition, a person’s body temperature rises and nausea and vomiting may occur. If such symptoms occur, you should seek immediate medical attention.
- Inflammation of the reproductive system. Lower back pain can occur due to inflammatory processes in the genital organs, and the urinary system has a very close relationship with the reproductive system.
- Diseases of organs located in the abdominal cavity can result in lumbar discomfort. To find out the nature of the pain, you need to consult a doctor for a more accurate diagnosis.
- Osteochondrosis of the spinal column very often leads to pain in the lumbar region. This also includes other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
What can happen if you have a kidney stone?
If a person has a kidney stone, then this condition requires treatment.
When no therapy is performed, the following complications may develop:
- In the place where the stone is located, a chronic inflammatory process will occur. This happens especially often after hypothermia, after suffering from acute respiratory viral infections, and against the background of a general decrease in immunity. As a result, diseases such as pyelonephritis, urethritis and cystitis appear.
- In the future, pyelonephritis can be complicated by paranephritis, and the formation of purulent abscesses in the kidney or carbuncle is possible. This threatens organ abscess, death of the renal papillae and sepsis. As a result, the person will need urgent surgical intervention, since such a condition poses a direct threat to life.
- It is possible to develop renal colic, which occurs when the ureter is blocked by a stone. In addition, blockage of the kidney by a stone makes it impossible for urine to flow out. This can lead to an increase in kidney size, hydronephrosis, and subsequently to the development of renal failure.
- Stones can grow. Sometimes they reach such sizes that they occupy the entire collecting system. This, in turn, provokes the appearance of constant mild pain in the lumbar region with the subsequent development of progressive renal failure.
- The presence of a kidney stone can trigger the development of nephrogenic hypertension, that is, the patient will have increased blood pressure, which cannot be controlled with conventional medications.
Can a kidney stone hurt?
A kidney stone can hurt. The pain is dull in nature; it can appear when the ureter or renal pelvis is blocked by a stone. If, against the background of pain, the urine becomes cloudy, a person’s body temperature rises and general health worsens, this will indicate an infection.
The pain is localized in the lumbar region and can radiate to the back, left or right side, or lower abdomen. Pain may be felt during emptying of the bladder. Sometimes the pain intensifies during shaking, for example, when traveling on public transport, or after physical activity.
Pain from kidney stones can be very minor or very intense (renal colic). Sometimes pain does not bother a person at all, and he does not even suspect that he has a kidney stone. The first attack of pain can immediately occur as renal colic.
Renal colic - what is it?
Renal colic is an acute attack of pain that occurs against the background of a sudden disruption of the outflow of urine. Most often, renal colic develops when a stone is strangulated in one of the sections of the ureter. The condition is accompanied by increased blood pressure and renal ischemia.
Renal colic is expressed in cramping pain in the lumbar region. They extend to the ureter and below. Urination also becomes extremely painful. At the same time, the person experiences nausea and may vomit. The patient is in an excited state. Renal colic requires immediate medical attention.
Causes of renal colic. When the ureter is blocked by a stone, the pressure in the renal pelvis increases sharply, and the pelvis stretches. Since there are many pain receptors in the wall of the pelvis, the pain is usually very severe. When the size of the stone is no more than 0.5–0.6 cm, the stone can pass out on its own in the urine. If the stone is large or the urinary tract is narrowed or for other reasons the stone remains in the urinary tract for a long time, preventing urine from leaving, the pressure in the renal pelvis remains high for a long time or constantly increases, and this can lead to dysfunction and even death of the kidney.
Can a kidney stone dissolve?
A kidney stone can dissolve, but this will require specific therapy in combination with diet. Only uric acid stones are reliably soluble with the help of litholytic therapy.
Oxalate and urate stones can be dissolved by drinking alkaline water. Sometimes small urate stones can be dissolved by switching to an increased drinking regime (ordinary water is suitable for this purpose).
Can kidney stones raise blood pressure?
Kidney stones can increase blood pressure. This condition is called secondary hypertension syndrome. Most often, the pressure increases when complications of urolithiasis occur, for example, chronic calculous pyelonephritis. In such patients, blood pressure is elevated in 12-64% of cases. Also, blood pressure always increases during an attack of renal colic.
Can kidney stones pass on their own?
Solid stones passing from the kidneys through the urethra are extremely rare. Most often they come out along with urine in the form of sand. In this case, the person will experience pain that intensifies when making sudden movements, possible increased frequency of urination, increased body temperature, and changes in the composition and color of urine.
If it is not a grain of sand, but a stone that comes out of the kidney, the patient will experience renal colic, with all the accompanying symptoms. When the stone is flattened and has an elongated shape, it can enter the ureter from the kidney and begin to move along it. However, the ureters have a curved shape, which is a natural obstacle to the movement of even a small stone, so they often get stuck in narrow places. Sometimes stones pass through the entire ureter, but linger at the outlet to the bladder, completely or partially blocking the flow of urine. Against the background of complete disruption of urine passage, surgical intervention is necessary.
Treatment of renal colic
It is believed that the pain associated with renal colic is the most severe of all possible, so pain control is the main task in relieving this complication of urolithiasis.
For renal colic, the best combination of effectiveness and safety is demonstrated by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Diclofenac, Ketorol, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, etc., which are prescribed for a period of 3 to 7 days (see list of injections for pain). Narcotic analgesics do not have any advantages over NSAIDs and are prescribed when the use of Diclofenac and its “relatives” is impossible, for example, due to allergies.
As an addition to NSAIDs, antispasmodics can be used: papaverine, no-spa, etc. (see medications for the treatment of kidneys).
If the kidney block cannot be eliminated with medication, surgical decompression of the urinary tract is performed, which can be of two types:
- Retrograde stenting. Using special equipment, a special catheter, a stent, is inserted through the ureter into the kidney. This stent is located at one end in the renal pelvis, and the other is lowered into the bladder, ensuring the outflow of urine.
- Percutaneous nephrostomy. Under ultrasound guidance, a puncture of the renal pelvis is performed through the skin of the back. A catheter is inserted into the pelvis through a puncture, draining urine out of it.
Percutaneous nephrostomy is much more traumatic, but much simpler, so stenting has not yet replaced it. Decompression is considered a temporary measure, followed by surgical removal of the stone.
Lithokinetic therapy
This is the expulsion of a kidney stone using medications. When to start treatment for urolithiasis is not an idle question. It is believed that urinary stones up to 6 mm, which do not give obvious symptoms, do not grow and do not cause complications - do not require treatment (see regular sex helps remove kidney stones (up to 6 mm)). Expulsion of such a calculus is a “double-edged sword.” You can remove it, or you can get even more sick. This stone will plug the kidney tightly and a small problem will grow into a huge one...
Lithokinetic therapy is considered justified if it is necessary to remove stone fragments from the kidney after its destruction by surgical methods.
Dissolving stones
Drug dissolution of uroliths in the kidneys, or chemolysis, is used to treat urate stones. To do this, you need to make your urine slightly alkaline. Using special citrate mixtures or sodium bicarbonate (soda), the urine pH is raised to 7.0 or higher, and maintained at this level for several weeks. The dose of the drug, including soda, is selected individually, and the effectiveness of treatment is monitored using special test strips.
External shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL)
The essence of the method is the non-contact destruction of stone by the force of an ultrasonic wave. It is considered the most effective and safe method of getting rid of stones; it allows you to eliminate uroliths up to 20 mm in size in 90% of cases.
Contraindications for ESWL
- Pregnancy
- Reduced blood clotting
- Active urinary tract infection
- Severe obesity
- Signs of urinary tract obstruction below the cleavage zone
Some features of the procedure:
- The ultrasonic wave affects not only the calculus, but also the skin, which can cause pain, sometimes quite severe, so ESWL requires adequate pain relief.
- During ESWL, the stone is broken into small fragments, which can cause renal colic.
- It is not always possible to destroy urolith from the first session; some patients may require 2 or more procedures.
Surgical Treatment Options
The choice of surgical treatment method for urolithiasis depends on the size and position of the stone, the condition of the urinary tract, the activity of the infection, the patient’s build, the doctor’s experience and many other factors.
- Endourethral technique - endoscopic equipment is inserted into the renal pelvis through the urethra or through a puncture in the skin. The device is brought to the stone, which is removed or destroyed in one of the following ways: mechanically, with a contact ultrasonic wave, or with a laser beam.
- Open surgery is the oldest, most reliable, but at the same time the most traumatic and therefore dangerous method. The stone is mechanically removed through an incision in the kidney or bladder. Used when it is impossible to use ESWL or endoscopic techniques: severe obesity, severe skeletal deformities, staghorn stone, etc.
What kind of examination do you need to undergo?
Diagnosis of kidney stones is a prerequisite that must be met before starting treatment. A qualitative examination allows you to select the optimal therapeutic measures for a particular patient. During diagnosis, it is very important to establish where the stones are located and what their size is.
So, to detect kidney stones you will need:
- Get an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. This method has its advantages. For example, during an X-ray examination, urate stones cannot be detected, but on an ultrasound they are clearly visible.
- X-ray examination can detect large stones - from 3 cm or more. Oxalate stones will be visible on the images. Urate stones are not visible to X-rays because they simply pass them through. X-ray examination of the kidneys is an auxiliary, not the main method of identifying stones.
- Taking laboratory tests allows you to identify metabolic disorders, as well as make a conclusion about the chemical composition of the stones. Based on blood and urine tests, one can suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Excretory radiocontrast urography of the kidneys allows you to determine the location of the stone and its exact coordinates. To conduct this type of study, a special substance is injected into a vein, which enters the kidneys and accumulates in them. After which the patient is examined using an x-ray method. The danger of this type of research is reduced to the occurrence of an allergic reaction to the administered drug.
- Kidney CT. Tomography is one of the most informative research methods, allowing you to provide maximum information about kidney stones.
Historical reference
Urolithiasis has existed as long as humanity itself has existed. Archaeologists find urine stones in the burials of prehistoric people, in the sarcophagi of Egyptian mummies, and in the tombs of the Middle Ages. “Master stone cutters” who extracted uroliths existed in ancient Egypt, “stone cutting” was practiced in ancient China and India. This procedure was carried out without anesthesia, and therefore required remarkable dexterity from the artisan (“stone cutters” were not considered doctors).
Many renowned medical minds have spent a lot of energy developing treatments for kidney stones. Even Hippocrates in the 4th century BC. e. described renal colic and methods of getting rid of it, and also mentioned stone cutting in his famous oath. Several treatises on this disease were written by Avicenna, who devoted a lot of time to developing the diagnosis and treatment of urolithiasis.
If you have kidney stones, what should you do?
Both surgical and conservative therapy are used to treat kidney stones. It is possible to determine the optimal method of getting rid of urolithiasis only together with a urologist. The patient's management tactics are determined based on his age, location of the stone, size of the stone, symptoms of the disease, anatomical and physical characteristics of the person. In addition, it is important to clarify whether the patient is developing renal failure.
Diet selection. The food that a patient with kidney stones takes should not contribute to the formation of new stones. In addition, a person must receive enough fluid so that the daily diuresis is at least 1.5 liters. Although the diet should be varied, the overall amount of food must be reduced.
Depending on the composition of the stones, the following recommendations can be given:
- If you have urate stones, you need to limit the intake of protein into the body, completely avoid drinking coffee, chocolate, spicy and fatty foods. Alcohol should not be consumed; meat, pates, and sausages are also excluded.
- If you have calcium oxalate stones, you need to limit the consumption of chocolate, milk, cheese, cottage cheese, nuts, strawberries, lettuce, sorrel, and spinach. You should not drink strong tea. All citrus fruits are prohibited.
- If a patient has calcium phosphate stones, then cottage cheese, cheese, berries, pumpkin, all green vegetables, potatoes and beans should not be eaten. Drinks that are prohibited include milk and alkaline mineral water.
Water shocks to flush the kidneys. If the ultrasound revealed microliths (small crystals) and not stones, then it is possible to flush the kidneys with water. To do this, a person will need to drink 0.5-1 liter of water or a decoction of dried fruits on an empty stomach. If there are no medical prohibitions, then this procedure can be repeated once a week. This method allows you to get rid of microliths and prevent the formation of stones.
Drug treatment. If the stones pass on their own, then patients are prescribed drugs from the group of terpenes. They have a sedative, antispasmodic and bacteriostatic effect.
The drug Uralit can be used to dissolve cystine stones. To get rid of oxalate stones - the drug Prolit. For phosphate stones, it is recommended to take the drug Prolit.
The most important factor influencing the course of urolithiasis is metabolic disorder, so it must be brought back to normal. To reduce uric acid levels, Allopurinol and Benzbromarone are taken. It is possible to supplement these drugs with citrate mixtures. Patients are also prescribed vitamins A and E, as powerful antioxidants that normalize the functioning of kidney cell membranes. The dose, frequency of administration and choice of a specific drug are selected individually for each patient.
If renal colic develops, the patient is advised to take antispasmodics (Drotaverine or Metamizole sodium), as well as thermal procedures (taking a bath, applying a heating pad). If antispasmodics are ineffective, and the attack of renal colic is prolonged, it is necessary to introduce a novocaine blockade of the spermatic cord or uterine ligament.
When inflammatory processes occur, antibiotics are indicated. It is important to understand that it will be impossible to completely get rid of pyelonephritis or other diseases caused by urolithiasis as long as the stone remains in the kidneys.
[Video] Dr. Berg - KIDNEY STONES: How to get rid of them?
More details about treatment methods:
- Modern methods of crushing kidney stones
- List of tablets that break up kidney stones
- Folk remedies (the most effective)
- Kidney tea - composition, reviews, indications and methods of use
- What can and cannot be done if you have kidney stones?
External lithotripsy method
The remote lithotripsy method allows you to crush stones from 4 mm to 1.5 cm in diameter. It is also used to get rid of small stones that are resistant to conservative therapy.
Remote lithotripsy can be used to treat patients at any age, as it is a non-contact treatment method. Contraindications to the procedure are:
- Pregnancy;
- Body weight more than 130 kg;
- Aortic aneurysm;
- Hemophilia;
- Acute myocardial infarction;
- Exacerbation of gastrointestinal and kidney diseases.
The procedure itself lasts about 40 minutes. The patient is placed on a special lithotripter table, then the device is aimed at the treatment area. Without touching the body, he begins to crush stones. At this time, a person may feel only a slight tingling sensation.
Abroad, external lithotripsy is performed on an outpatient basis. In Russia, it is customary to hospitalize a patient for up to 3 days. After the procedure, stones begin to leave the kidneys. The time for their removal depends on the condition of the human body, the age of the patient, and the chemical composition of the stone. Often the sand comes out almost painlessly. Within a day, the patient’s kidneys are completely cleansed. In other cases, stones may pass for more than a month, and the person will experience pain similar to cystitis.
1-2 days after lithotripsy, you need to visit a urologist. You must visit the doctor again after 30 days. At the same time, an ultrasound examination of the kidneys is performed. Most often, 1 or 2 procedures are enough to completely remove stones.
Types of stones
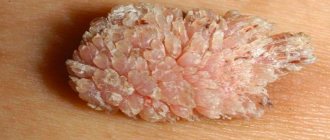
In the course of studies that are necessarily carried out after the removal of stones from the kidneys or their spontaneous passage, the following types of formations are identified:
- Cystine stones. Contains cystine amino acids. They have a soft structure, smooth edges and a white-yellow color.
- Phosphate stones. They consist of calcium salt, which is part of phosphoric acid. Such stones have a fragile consistency, gray-white color and are formed due to the alkaline composition of urine, which can occur as a result of infectious diseases.
- Oxalate stones. Formed from calcium salts, which are part of oxalic acid, they have a dense texture and uneven sharp edges.
- Protein stones. They consist of fibrin with an admixture of bacteria and salts, the consistency is soft, and the edges are smooth, usually small in size.
- Carbonate stones. Consisting of calcium salts that are part of carbonate acid, such formations are soft and white.
- Cholesterol stones. They occur extremely rarely with high cholesterol levels; they crumble easily and have a black tint.
- Urate stones. Formed by uric acid, they are dense and smooth.
Determining the type of stone makes it possible to understand the nature of its occurrence so that in the future it will be possible to adjust the diet, as well as cure concomitant diseases that could cause hard formations.
Surgery to remove kidney stones
Indications for surgery to remove kidney stones are:
- Hematuria.
- Severe pain syndrome.
- Frequent relapses of pyelonephritis.
- Hydronephrosis of the kidney.
Doctors, when choosing the type of surgical intervention, should follow the least traumatic path. If previously the only way to remove a stone was open surgery, which often led to the removal of the kidney itself, modern technologies make it possible to avoid this. Open surgery is performed only in the presence of large stones, with increasing renal failure, and when it is impossible to implement other treatment methods due to certain contraindications. Also, stones are removed using an open method when purulent pyelonephritis occurs.
Types of open kidney surgery:
- Pyelolithotomy. It is performed if there is a stone in the renal pelvis. Posterior, inferior and anterior pyelolithotomy is performed.
- If the stones are large, contact crushing will be required. We will use a method such as nephrolitholapaxy. In this case, the patient is given anesthesia (spinal or general), after which the skin over the kidney is pierced, with the help of bougies they expand its internal space and begin to crush the stone. Stones are crushed using ultrasound, pneumatic devices or lasers. The entire procedure is controlled by X-ray and ultrasound.
- Ureterolithotomy. This operation is performed if there is a stone in the ureter. In modern surgery, this method is used extremely rarely.
When deciding on the method of surgical treatment, it is very important to pay attention to such criteria as:
- Stone size;
- Its location in the urinary tract;
- Possibility of visualizing the stone using X-ray equipment (X-ray negative or X-ray positive stone).
As for the chemical composition of the stone, attention should be paid to it when choosing the most optimal diet for the patient. The set of permitted and prohibited products included in the patient’s menu will depend on this. In addition, the mineral composition of the stone allows you to decide on the choice of drugs that will promote its dissolution.
Diet
If the kidney hurts after a stone passes, a special nutritional system is prescribed, which is aimed at eliminating irritants that can make the urine more acidic or alkaline. During the diet, the following foods are completely prohibited:
- meat, fish, mushrooms, beans with urate stones;
- chocolate, cocoa, sorrel, beets, lettuce, spinach for oxalate stones;
- salt, carbonated drinks, alcohol, currants, cranberries, dairy products for phosphate stones.
At the end of the rehabilitation period, their use is permitted, however, in limited quantities.
Is relapse possible after kidney stones are removed?
Recurrence after removal of kidney stones is possible. Therefore, it is so important to adhere to medical recommendations after treatment. You should follow a diet and limit the consumption of fish and meat dishes. This must be done because meat and fish contain purines, they provoke the production of uric acid, which subsequently leads to the formation of stones.
Another important recommendation is to drink enough fluid. At a minimum, you need to drink 1.5 liters of water per day. This will dilute the urine and make it less concentrated. As a result, the creation of an unfavorable environment for starting the process of stone formation.
It is also possible to use phytotherapeutic drugs. They have a certain diuretic and antiseptic effect. In addition, patients who have undergone treatment for urolithiasis must undergo urine tests once every 3-6 months. An ultrasound of the entire urinary system is performed once every 6 months.
Urolithiasis often leads to various diseases of an inflammatory nature. During their exacerbation, kidney stones are not removed. First you need to carry out a BAC culture for microbial flora and eliminate inflammation.
Kidney inflammation is treated with antibiotics. Only after the inflammatory process has been eliminated will it be possible to proceed with surgical intervention. The exception is emergency operations, which are performed without prior treatment.
Urolithiasis in children
Unfortunately, recently children have been suffering from urolithiasis very often. The main reasons for this:
heredity; intrauterine development defects; consequences of past infectious and inflammatory diseases; poor nutrition.
The first signs of stone formation in a child’s body are dysfunction of the parathyroid glands or digestive system. If they are detected, it is necessary to examine the child for urolithiasis.