STIs (sexually transmitted infections) are a group of diseases that are transmitted from person to person through sexual contact. They affect not only the genitals, but the entire body, and often lead to serious consequences.
STIs have been known to humanity since ancient times, but over time the number of cases of infection does not decrease, but rather increases. As “familiar” infections are overcome, new ones appear. Almost every person is at risk, regardless of gender and social status.
Modern medicine lists about 30 infections that can be classified as STIs. Most of them can be asymptomatic, and this makes them very dangerous for the health of various organs and systems.
Classification of STIs
Experts divide diseases acquired as a result of physical intimacy into “old” and “new.” The old ones are venereal, the new ones are called urogenital. The first include syphilis, gonorrhea, donovanosis, chancroid, lymphogranulomatosis. New ones are hepatitis, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, condylomas, trichomoniasis, genital herpes and others.
All these diseases are combined into classifications according to the type of infection, parasites and viruses that cause the disease.
Protozoans
This type includes trichomoniasis, which ranks first in terms of prevalence. The causative agent is Trichomonas vaginalis; every year WHO records this disease in 170 million people, that is, 10% of the world's population is infected.
Trichomoniasis is dangerous due to its consequences, complications leading to infertility, pathologies during pregnancy, etc. In men, the pathogen lives in the prostate gland, urethra, seminal vesicles, and in women in the vagina.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Foul-smelling and foamy discharge that is gray, white, yellow, greenish or clear.
- The discharge may contain blood.
- Irritation on the genitals.
- Burning and itching sensation.
- Swelling of the groin area.
- Painful and frequent urination.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
The presence of this disease significantly increases the risk of contracting HIV and other sexually transmitted infections.
Viral
This type includes a number of dangerous diseases: HPV, HIV, herpes, molluscum contagiosum, hepatitis.
HPV: human papillomavirus
It is one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. The causative agent is a group of certain viruses, of which there are currently more than 190 types. At least 13 of them provoke oncological processes. In particular, types 16 and 18 provoke the formation of cervical cancer.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse, between menstrual periods, irregular.
- Swelling of one of the legs.
- Fatigue, lack of appetite, rapid weight loss.
- Pain in the pelvis.
- Foul discharge.
In advanced cases, there may be: cancer of the vulva, oropharynx, anus, penis and vagina.
Papilloma viruses that do not have a high risk of developing cancer are accompanied by the formation of genital warts - warts.
HIV
In medicine - human immunodeficiency virus. It is one of the most dangerous and incurable diseases. The main symptom is the loss of the human body’s ability to fight diseases, infections, viruses, bacteria, etc. The final phase is AIDS. Manifested by the occurrence of oncological processes and rare infectious diseases.
Hepatitis
Inflammatory processes in the liver. They can be both rapid and quickly curable, and dangerous with serious consequences - fibrosis, cancer, cirrhosis, etc.
There are 5 types of viral hepatitis - A, B, C, D, E. All of them are severe and lead to death. Symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal area;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- sharp and dull pain in the abdomen;
- bloating;
- change in color of stool and urine;
- change in the color of the whites of the eyes and skin, etc.
Herpes
A common illness. Viruses “wedge” themselves into the genetic system of human cells and it is impossible to get rid of it. Once herpes enters the body, it is for the rest of your life. The virus is dangerous because it leads to weakened immunity, which is already the key to the occurrence of a number of serious diseases.
Interesting fact: research by specialists from the University of Manchester has proven that herpes is a virus that causes Alzheimer's syndrome. In approximately 70% of people suffering from vascular disease, DNA of the herpes virus was found in the brain cells. After its penetration, plaques form and the level of beta-amyloid increases.
Molluscum contagiosum
This pathology has 4 types: 1, 2, 3 and 4. The most common among people are 1 and 2, which are part of the poxvirus group. Symptoms: the formation of painful papules - round formations of beige (flesh) color with a dimple in the center. The diameter can reach 5 mm, the core is white, similar to the structure of wax.
Bacterial
Syphilis
A systemic, chronic disease that affects human skin, mucous membranes, organs, nervous and skeletal systems. The causative agent is Treponema pallidum. From the moment of infection to the manifestation of the disease - from 3 days to 3 weeks. Syphilis consists of 4 periods: incubation, primary secondary and tertiary.
Symptoms are the formation of a hard chancre, an ulcer surrounded by tissue swelling. There is pus inside the chancre.
It usually occurs near the vagina, on the lip, in the mouth, and in rare cases near the anus. In men, it can affect the scrotum or penis.
During the second phase, which occurs 2 and 3 months after infection, a rash forms on the hands, face, and entire body. All lymph nodes are enlarged and painful. Accompanied by rapid fatigue and general weakness. Some may experience hair loss and large warts growing in the anus and genitals.
The third phase - the process is irreversible, internal organs, bone, nervous, vascular, endocrine, and muscular systems are affected. During this phase, it is impossible to save a person. If it was possible, then the appearance was completely disfigured, and the health was completely destroyed.
Donovanosis
The second name is venereal inguinal granuloma. The causative agent is Donovan's body. The course is slow and progressive. Incubation - from 7 days to three months. It manifests itself in the formation of pea-sized nodules in the genitals, red in color with jagged edges. As it progresses, the ulcer grows in size and can lead to:
- damage to other areas of the body;
- narrowing of the anal passage;
- narrowing of the female vagina;
- urethra;
- changes in the genitals - the formation of elephantiasis.
Chancroid
The disease is more common in the countries of South and Central America and Africa. The causative agent is Chaemophilus ducray. Incubation – up to 7 days. Symptoms: a red spot forms in the affected area, with a bubble in the middle. It is formed on the preputial sac in men, and on the labia in women. Over time, it turns into a pustule, then into an abscess, accompanied by pain.
Chlamydia
A common disease that affects one hundred million people every year. And according to WHO, there are about one billion infected. The causative agent is Chlamydia trachomatis.
The incubation period ranges from a week to several months. Symptoms are almost invisible at first.
Chlamydia usually affects the genitals: cervix, vagina, appendages, tubes, endometrium, bladder and Bartholin's gland. As a result, an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane occurs, accompanied by:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent and impaired urination;
- painful urination;
- pain in the lower back;
- increased temperature and humidity in the genital area;
- unusual discharge;
- itching, burning.
The consequences of chlamydia can be infertility, the formation of adhesions, problems with the heart, eyes, skeletal system, arthritis, conjunctivitis. There is also a high risk of developing dangerous ailments - urethritis, narrowing of the urination channel, cystitis, inflammation of the liver capsule.
Chlamydia is most dangerous for pregnant women due to the development of complications, ectopic conception, termination of pregnancy, frozen fetus, etc.
Gonorrhea
The second name is gonorrhea, the causative agent is gonococcus, Neisseria gonorrhea. The mucous membranes of the genital and urinary areas are affected. The mucous membrane of the rectum, mouth, pharynx, and conjunctiva may also be affected.
Symptoms:
- yellow or white discharge from the penis, vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding during intermenstrual periods;
- pain and stinging when urinating.
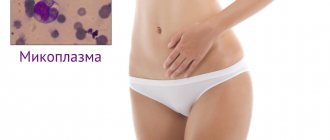
Mycoplasmosis (in women)
The causative agent is the bacterium Mycoplasma. In the first days after infection, it does not manifest itself in any way, then pain occurs during sexual intercourse, itching and burning during the flow of urine.
Dangerous consequences of mycoplasmosis can be:
- pyelonephritis;
- infertility;
- inflammation of the ovaries, testicles.
In pregnant women, it can cause miscarriage and premature birth.
Ureaplasmosis (in men)
The causative agent is ureaplasma, a bacterium that lives on the mucous membrane of the urinary canal and genital organs.
Symptoms:
- non-gonococcal urethritis;
- discharge;
- pain and stinging during sexual intercourse and urine leakage;
- inflammation of the testicles;
- infertility;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen.
Parasitic
This type includes pediculosis (pubic) and scabies.
Ftiriaz
Pediculosis pubis, the causative agents are insects that are relatives of common lice. Also called flat due to the flatness of the body. Once on the human pubic hair, the louse lays nits (eggs).
Symptoms:
- itching in the groin area;
- itching under the arms;
- formation of small blue dots;
- pustular rash.
In advanced stages, lice spread to the entire body - stomach, legs, arms, head, back, etc.
Scabies
The causative agent is the scabies mite. Incubation – from several hours to one and a half months.
The main symptom is severe itching, the intensity of which increases at night. Consequences – dermatitis, development of pustular pimples, boils, etc.
Fungal
This type includes candidiasis, popularly called thrush. The causative agent is the yeast fungus candida, which is part of the vaginal microflora. Its excessive reproduction after sexual intercourse leads to:
- discharge of yellow, white, transparent color;
- itching;
- burning when urinating;
- painful sensations.
An advanced stage can cause inflammation of the uterus, ovaries, vagina, penis, urinary canal, etc.
Risk of contracting STDs
The risk of contracting an STD can be significantly reduced by:
- remain faithful to a permanent partner;
- Get vaccinated against human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B before sexual activity;
- maintain personal hygiene - do not use someone else’s soap, towel, washcloth, underwear;
- use a condom during sexual intercourse;
- undergo an annual medical examination with your partner.
First signs of infections
The main indicator that an infection has occurred is a number of specific sensations and signs. These include:
- pain, cramping in the lower abdomen, pubic area, lower back;
- discharge - white, yellow, greenish, can be transparent;
- burning sensation;
- itching in organs;
- rash, redness, swelling of organs;
- frequent urination;
- formation of ulcers, pimples, pustules;
- stench from the vagina, the male organ;
- increased body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- Pain and discomfort during sex.
It is worth understanding that each of the listed pathologies does not go away without consequences if adequate treatment is not undertaken.
Thrush is a repeat offender.
Candidomycosis or thrush
stands apart from other representatives, although it traditionally refers to STIs. First of all, thrush is a manifestation of immunodeficiency, which occurs for various reasons: taking antibiotics, psychological stress, pregnancy, radiation, chronic inflammatory diseases and much more. Even virgins get thrush; a girl who has never been sexually active can get fungal colpitis. Why? It's simple: let's say a girl had a sore throat, she was actively treated with antibiotics, and as a result she got thrush. Candida albicants spores can be part of the normal vaginal flora, but clinical manifestations occur when the fungus becomes active. It is believed that the most frequently recurring thrush is a sign of the body’s immune dysfunction and its weakening. If thrush worsens more often than three times a year, this is an indication that the patient’s immunity is not all right. Of course, you can’t help but treat thrush, but first of all you need to pay attention to the body’s immune system.
Diagnostic methods
The danger of sexually transmitted diseases lies in their consequences and complications.
Transition to a more complex stage can cause serious health problems. To prevent this, after the first signs appear, you must consult a doctor and undergo a full examination to diagnose the disease.
List of tests for men
For the stronger sex, the following types of analyzes are provided:
- Bacterioscopy. Biomaterial from the urethra is examined, the collection occurs through the urination channel, and is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. The test result will be known in 3-5 days.
- Blood analysis. The study shows the level of leukocytes using a special formula. At the same time, the data is examined to establish a serological reaction to determine the pathogen.
- PCR to identify the type of pathogen. It is the most accurate research method and requires blood, urine or smear sampling.
- Spermogram - analysis helps to identify or exclude damage to a man’s reproductive functions and determine the activity of sperm.
- Enzyme immunoassay. The method detects the presence of specific antibodies, their quantity, as well as the approximate date of infection.
- Urine examination. The analysis shows the localization of the pathogen and how affected the urinary system is.
List of tests for women
The list of tests for investigating, identifying or excluding sexually transmitted infectious diseases in women is completely similar to the list for men. An important point in the study is proper preparation. To do this you need:
- A couple of days before the tests, refrain from sexual acts.
- Do not urinate 2 hours before the test.
- Commit a provocation - drink alcohol on the eve of the study, eat spicy, salty food.
- Submit your smear for research on the second or third day after the end of menstruation.
Herpes theater.
A distinctive feature of herpes is the talent for pretense. He often adds “false indications” to the main symptoms: general weakness, headache, muscle pain, fever - in general, everything that can lead to suspicion of a common cold. The herpes simplex virus is observed in almost the entire population of our planet and is transmitted only during an exacerbation period. By and large, herpes does not particularly threaten the health of an adult; it is dangerous for children, the elderly and pregnant women.
A little about the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases
Treatment involves taking immunostimulants, bactericidal, antiviral, antifungal agents, vitamin and mineral complexes. Modern medicine uses laser-magnetic, magnetoacoustic and physiotherapy. Due to the use of medications, therapy can take up to one week.
Therapy should be aimed at both partners to prevent recurrence of the disease:
- for bacterial infection, antibiotics are used;
- fungal disease is eliminated by the use of antifungal drugs;
- viral ones require taking antiviral medications, but it is impossible to completely get rid of them.
Doctors warn that after treatment, symptoms may persist for some time. This is how the human body reacts to therapy. If symptoms do not go away within 1-2 weeks, it makes sense to consult a specialist.
We must live in peace with viruses!
At the moment, all of the listed infections, except viral ones
. Unfortunately, science has not yet come up with antiviral antibiotics that could act on pathogens that have entered the cell; we just have to come to terms with them. Patients infected with viral infections can be advised to strengthen their immunity. Why? Yes, because since the virus cannot be “killed,” it means that the best we can achieve with these infections is to “drive the virus underground” so that it is not active.
Possible complications
The biggest problem associated with sexually transmitted diseases is the serious consequences and complications. It is worth noting that they pose a threat to both male and female health. These include:
- infertility;
- oncology;
- inflammation;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- damage to internal organs;
- pathology of newborns;
- skin pathology;
- hair loss;
- pathological changes in nails;
- problems in the bone structure;
- tooth loss;
- rotting of the muscle structure;
- brain inflammation;
- development of nervous and mental diseases.
We should not forget that advanced stages of a number of diseases often lead to death, or, to put it simply, to death.
Unpleasant neighborhood.
Living together between two people is not an easy matter; achieving peaceful coexistence is often not so easy, especially if the person has a complex character. However, what is not always within the control of humans is quite accessible to bacteria. And unlike a person, the more harmful the microbe, the easier it adapts, the faster it “moves in” and becomes an unpleasant tenant in the most critical areas of the living space of the human body. There are such “internal” tenants - diseases that well-mannered people prefer to tactfully keep silent about, and experts call them “genitourinary infections” and look reproachfully at patients. Many women, hearing about one of these “tenants,” experience real stress. And not in vain: communication with these “neighbors” does not bring any good. What kind of “neighbors” are these, where do they live, how do they behave and what are their threats? Let's try to figure it out.
Prevention methods
To avoid sexually transmitted diseases, doctors recommend a simple thing - to protect yourself. A simple rubber product sold in every pharmacy stall can protect a person and even save life. Condoms should be used by everyone, especially when changing sex partners frequently.
There is vaccination against a number of diseases - cervical cancer, vaccination against HPV, herpes and HIV, it is carried out in adolescence.
As for chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis, vaccines are just being developed.
Another method of prevention is circumcision, which reduces the risk of STIs during heterosexual contact.
Antibacterial drugs include Tenofovir gel, which is applied to the vaginal area to prevent infection with HIV and HSV.
Secondary prevention is also used - carrying out activities for young people and people who have been diagnosed with sexually transmitted infections.
Causes of STDs
The main route of infection for STDs
– sexual contact of any kind. Syphilis can be transmitted even by kissing (through saliva). Also, a child can become infected with various STDs from the mother during pregnancy and during childbirth. Syphilis, HIV and hepatitis are transmitted through blood and can be acquired through injection with a non-sterile syringe or blood transfusion. The household route of infection is unlikely, but still possible - with weakened immunity and prolonged household contact with the carrier of the disease.
It is quite common to become infected with several types of STDs at the same time.
The absence of symptoms does not mean that infection has not occurred. STDs can occur in a latent form, remaining dangerous both for the carrier of the infection and those who have sexual contact with him.
How long does it take for sexually transmitted diseases to appear?
It is impossible to say exactly how many days later sexually transmitted diseases make themselves felt.
Incubation times vary greatly for different pathologies.
In addition, infection of two different patients with the same disease leads to the appearance of symptoms at completely different times.
The duration of incubation is influenced by many factors:
- infectious dose;
- the patient’s gender, age, health status in general and reproductive organs in particular;
- the presence of other infections of the urogenital tract;
- taking antibacterial agents or drugs that affect the immune system;
- method of infection;
- the number and duration of sexual contacts with the source of infection;
- virulence of the microorganism.
Approximate incubation period values:
- herpes, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea – 1 week;
- chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, syphilis – 1 month;
- human papillomavirus infection – 3-6 months.
These are average and very approximate values.
Incubation in one individual patient can be several times longer or shorter.
Treatment
The course of treatment is selected for each patient individually. It depends on the pathogen that caused the pathological process. In addition to the main drugs, auxiliary agents are prescribed. They help strengthen the immune system and speed up recovery.
Incurable diseases are considered:
- HIV;
- HPV;
- herpes;
- hepatitis.
However, under the influence of medications, long-term remission of the disease can be achieved. They eliminate unpleasant symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.